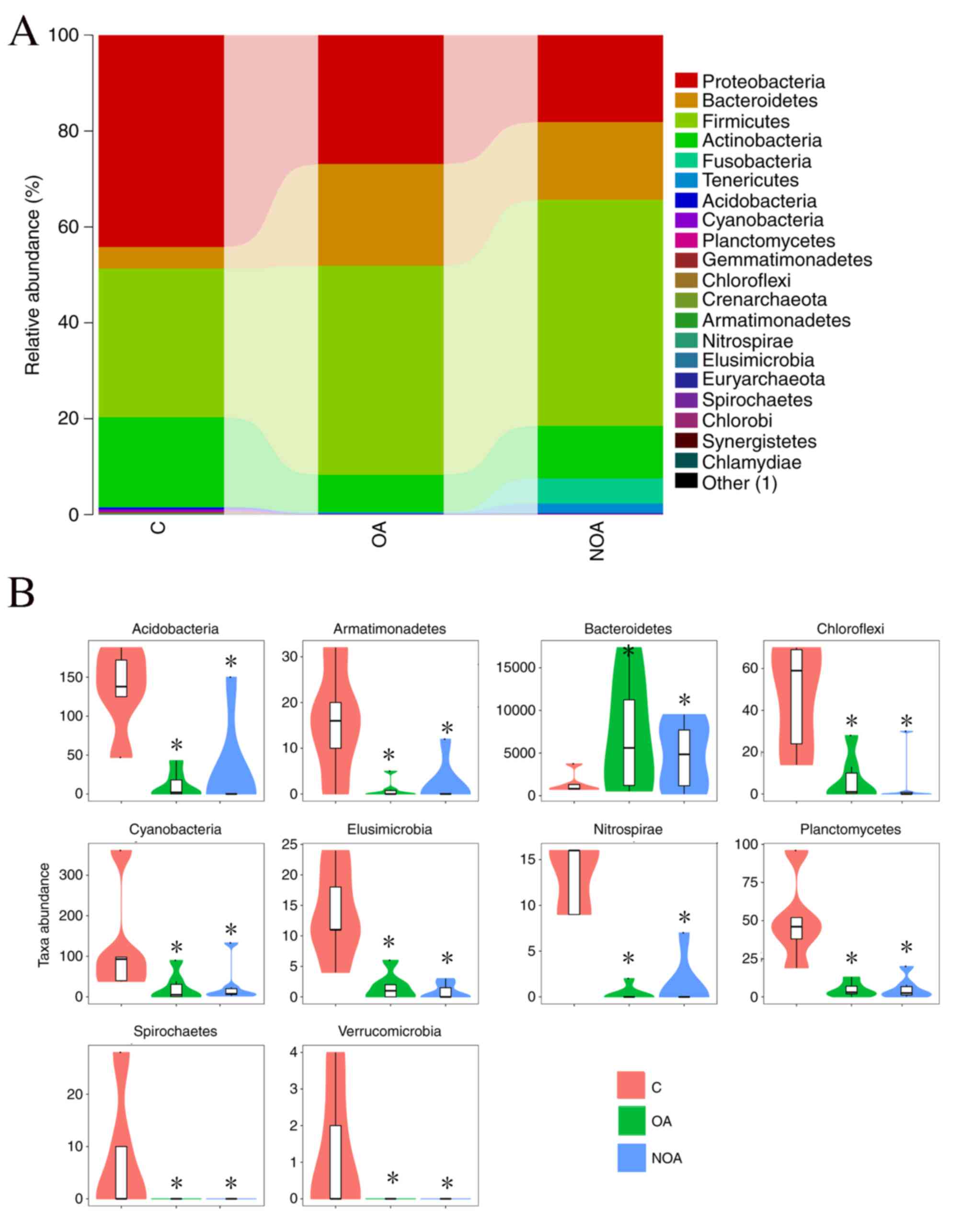
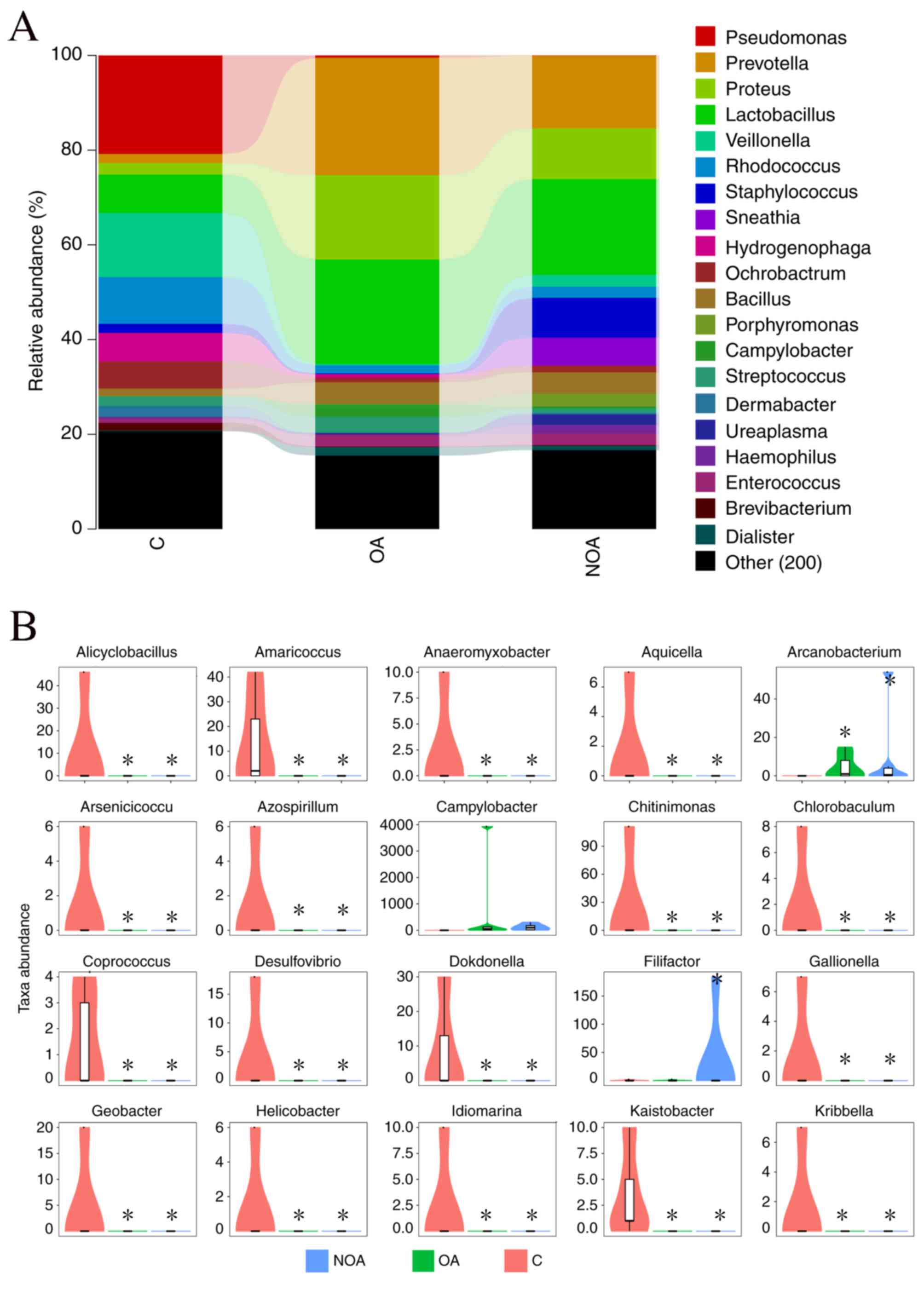
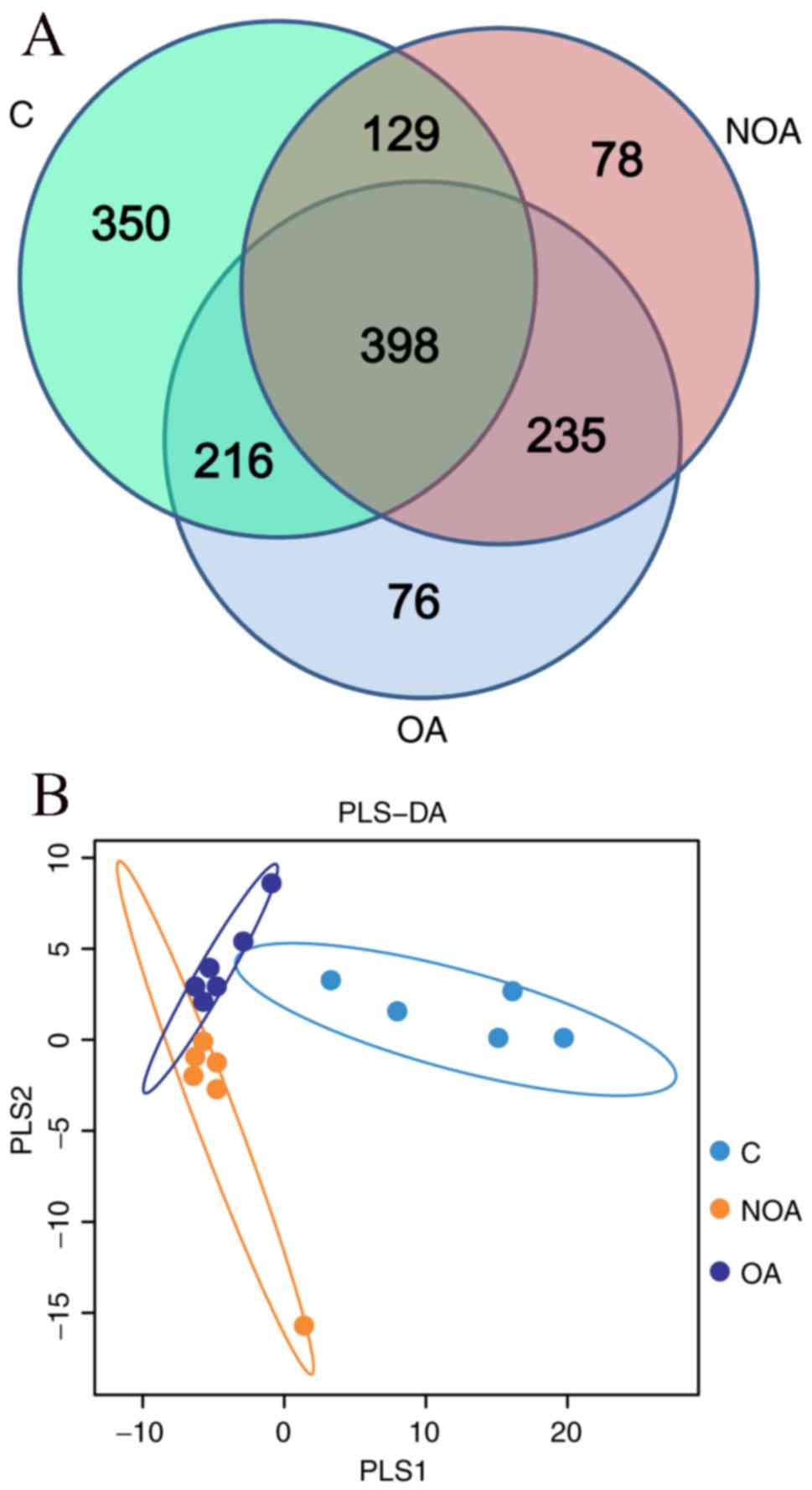
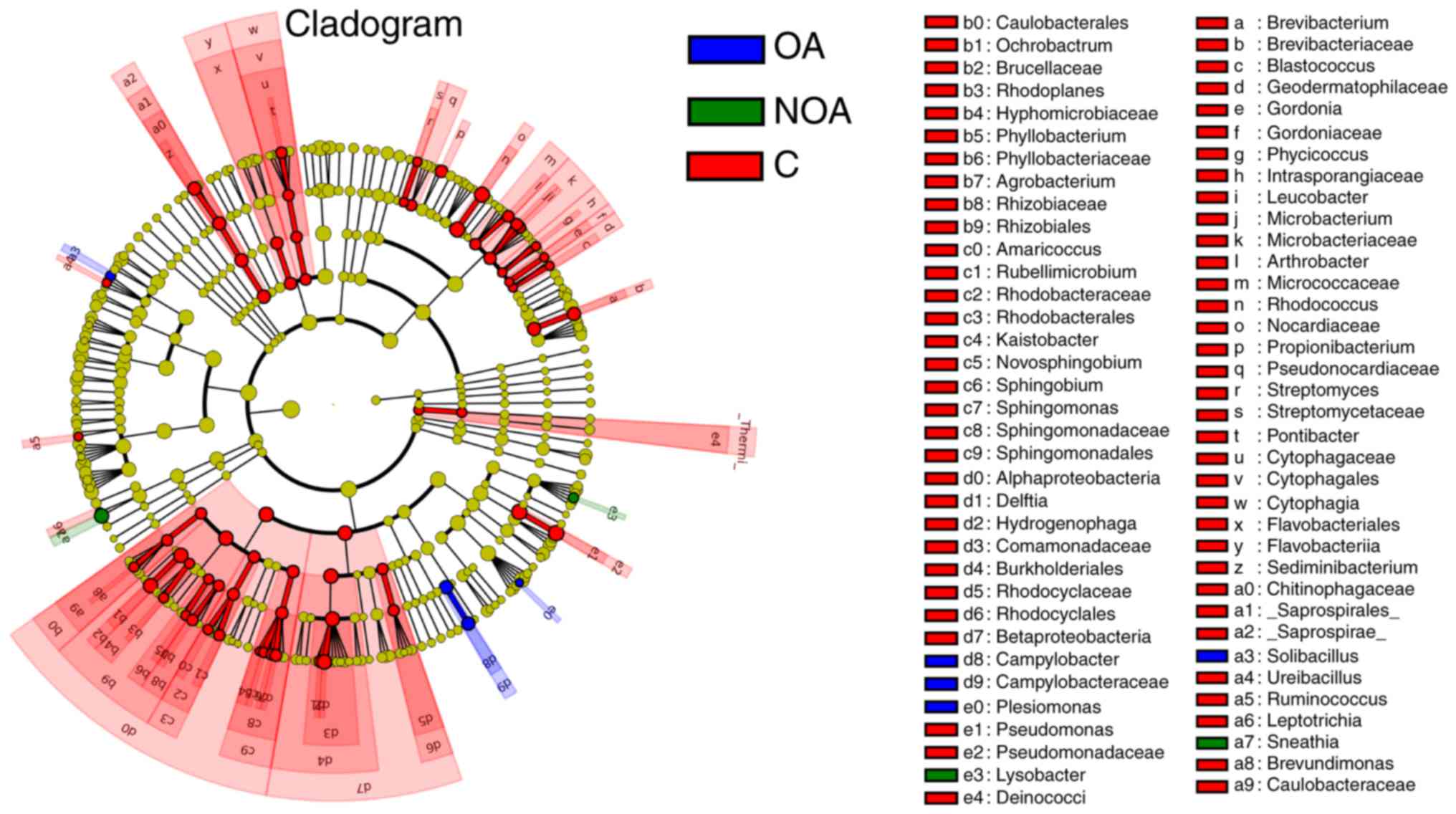
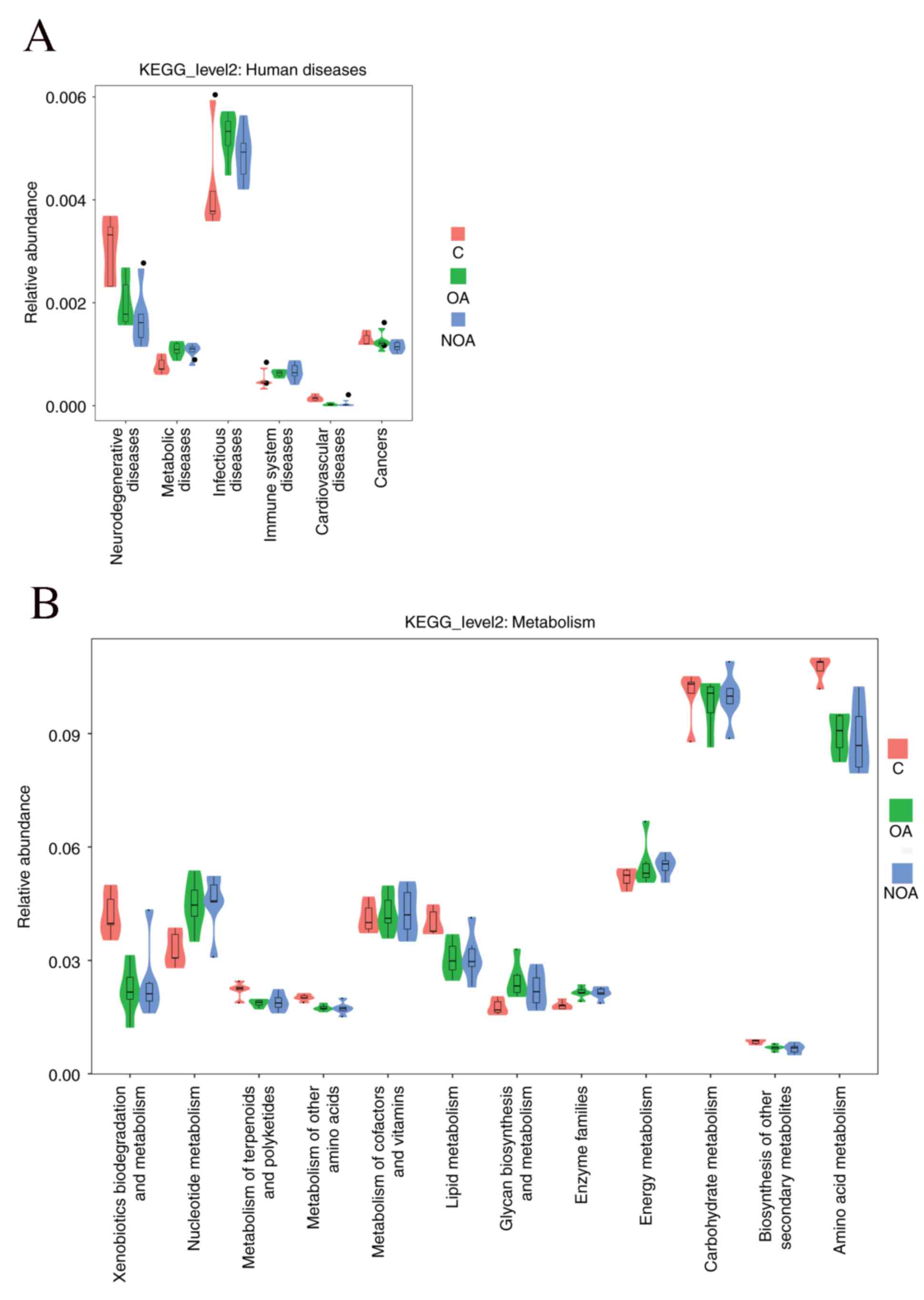
|
1
|
Luo T, Zou QX, He YQ, Wang HF, Wang T, Liu
M, Chen Y and Wang B: Matrine compromises mouse sperm functions by
a [Ca(2+)]i-related mechanism. Reprod Toxicol. 60:69–75. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
He Y, Zou Q, Li B, Chen H, Du X, Weng S,
Luo T and Zeng X: Ketamine inhibits human sperm function by
Ca(2+)-related mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 478:501–506.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
He Y, Zou Q, Chen H, Weng S, Luo T and
Zeng X: Lead inhibits human sperm functions by reducing the levels
of intracellular calcium, cAMP and tyrosine phosphorylation. Tohoku
J Exp Med. 238:295–303. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hooper LV, Littman DR and Macpherson AJ:
Interactions between the microbiota and the immune system. Science.
336:1268–1273. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nelson MH, Diven MA, Huff LW and Paulos
CM: Harnessing the microbiome to enhance cancer immunotherapy. J
Immunol Res. 2015:3687362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nakatsuji T, Chen TH, Narala S, Chun KA,
Two AM, Yun T, Shafiq F, Kotol PF, Bouslimani A, Melnik AV, et al:
Antimicrobials from human skin commensal bacteria protect against
Staphylococcus aureus and are deficient in atopic dermatitis. Sci
Transl Med. 9:pii: eaah46802017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
De Croo I, Van der Elst J, Everaert K, De
Sutter P and Dhont M: Fertilization, pregnancy and embryo
implantation rates after ICSI in cases of obstructive and
non-obstructive azoospermia. Hum Reprod. 15:1383–1388. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Franasiak JM and Scott RT Jr: Reproductive
tract microbiome in assisted reproductive technologies. Fertil
Steril. 104:1364–1371. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Javurek AB, Spollen WG, Ali AM, Johnson
SA, Lubahn DB, Bivens NJ, Bromert KH, Ellersieck MR, Givan SA and
Rosenfeld CS: Discovery of a novel seminal fluid microbiome and
influence of estrogen receptor alpha genetic status. Sci Rep.
6:230272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tuddenham S and Ghanem KG: A microbiome
variable in the HIV-prevention equation. Science. 356:907–908.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
De Francesco MA, Negrini R, Ravizzola G,
Galli P and Manca N: Bacterial species present in the lower male
genital tract: A five-year retrospective study. Eur J Contracept
Reprod Health Care. 16:47–53. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Younes JA, Lievens E, Hummelen R, van der
Westen R, Reid G and Petrova MI: Women and their microbes: The
unexpected friendship. Trends Microbiol. 26:16–32. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Weng SL, Chiu CM, Lin FM, Huang WC, Liang
C, Yang T, Yang TL, Liu CY, Wu WY, Chang YA, et al: Bacterial
communities in semen from men of infertile couples: Metagenomic
sequencing reveals relationships of seminal microbiota to semen
quality. PLoS One. 9:e1101522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu X, Wu X, Qiu L, Wang D, Gan M, Chen X,
Wei H and Xu F: Analysis of the intestinal microbial community
structure of healthy and long-living elderly residents in Gaotian
village of liuyang city. Appl Microbiol Biot. 99:9085–9095. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sivan A, Corrales L, Hubert N, Williams
JB, Aquino-Michaels K, Earley ZM, Benyamin FW, Lei YM, Jabri B,
Alegre ML, et al: Commensal Bifidobacterium promotes antitumor
immunity and facilitates anti-PD-L1 efficacy. Science.
350:1084–1089. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhernakova A, Kurilshikov A, Bonder MJ,
Tigchelaar EF, Schirmer M, Vatanen T, Mujagic Z, Vila AV, Falony G,
Vieira-Silva S, et al: Population-based metagenomics analysis
reveals markers for gut microbiome composition and diversity.
Science. 352:565–569. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Derrien M and van Hylckama Vlieg JE: Fate,
activity and impact of ingested bacteria within the human gut
microbiota. Trends Microbiol. 1–366. 2015.
|
|
18
|
Xin F, Xin W, Yang S, Meng F, Wang X, Wei
H and Chen T: Evaluation of the microbial diversity in amyotrophic
lateral sclerosis using high-throughput sequencing. Front
Microbiol. 7:14792016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cui M, Xiao H, Li Y, Zhou L, Zhao S, Luo
D, Zheng Q, Dong J, Zhao Y, Zhang X, et al: Faecal microbiota
transplantation protects against radiation-induced toxicity. EMBO
Mol Med. 4:448–461. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen T, Wu Q, Zhou H, Deng K, Wang X, Meng
F, Yang S, Wang X, Shah NP and Wei H: Assessment of commercial
probiotic products in China for labelling accuracy and probiotic
characterisation of selected isolates. Int J Dairy Technol.
70:119–126. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xu J, Lian F, Zhao L, Zhao Y, Chen X,
Zhang X, Guo Y, Zhang C, Zhou Q, Xue Z, et al: Structural
modulation of gut microbiota during alleviation of type 2 diabetes
with a Chinese herbal formula. Isme J. 9:552–562. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bolger A, Lohse M and Usadel B:
Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data.
Bioinformatics. 30:2114–2120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Edgar R: UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU
sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods. 10:996–998.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Steege HT: Measuring biological diversity.
Environ Ecol Stat. 1:95–103. 2004.
|
|
25
|
Cole JR, Wang Q, Fish JA, Chai B,
McGarrell DM, Sun Y, Brown CT, Porras-Alfaro A, Kuske CR and Tiedje
JM: Ribosomal database project: Data and tools for high throughput
rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 42(Database Issue): D633–D642.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J,
Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich
JK, Gordon JI, et al: QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput
community sequencing data. Nat Methods. 7:3352010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Javurek AB, Spollen WG, Johnson SA, Bivens
NJ, Bromert KH, Givan SA and Rosenfeld CS: Consumption of a
high-fat diet alters the seminal fluid and gut microbiomes in male
mice. Reprod Fert Devel. 29:1602–1612. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Langille MG, Zaneveld J, Caporaso JG,
McDonald D, Knights D, Reyes JA, Clemente JC, Burkepile DE, Vega
Thurber RL, Knight R, et al: Predictive functional profiling of
microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat
Biotechnol. 31:814–821. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wolf M, Müller T, Dandekar T and Pollack
JD: Phylogeny of Firmicutes with special reference to Mycoplasma
(Mollicutes) as inferred from phosphoglycerate kinase amino acid
sequence data. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 54:871–875. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Donders GG, Bosmans E, Dekeersmaeckerb A,
Vereecken A, Van Bulck B and Spitz B: Pathogenesis of abnormal
vaginal bacterial flora. Am J Obstet Gyneco. 182:872–878. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kovachev SM: Obstetric and gynecological
diseases and complications resulting from vaginal. dysbacteriosis.
68:1–184. 2014.
|
|
32
|
Bae HS, Im WT and Lee ST: Lysobacter
concretionis sp. nov., isolated from anaerobic granules in an
upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol.
55:1155–1161. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|