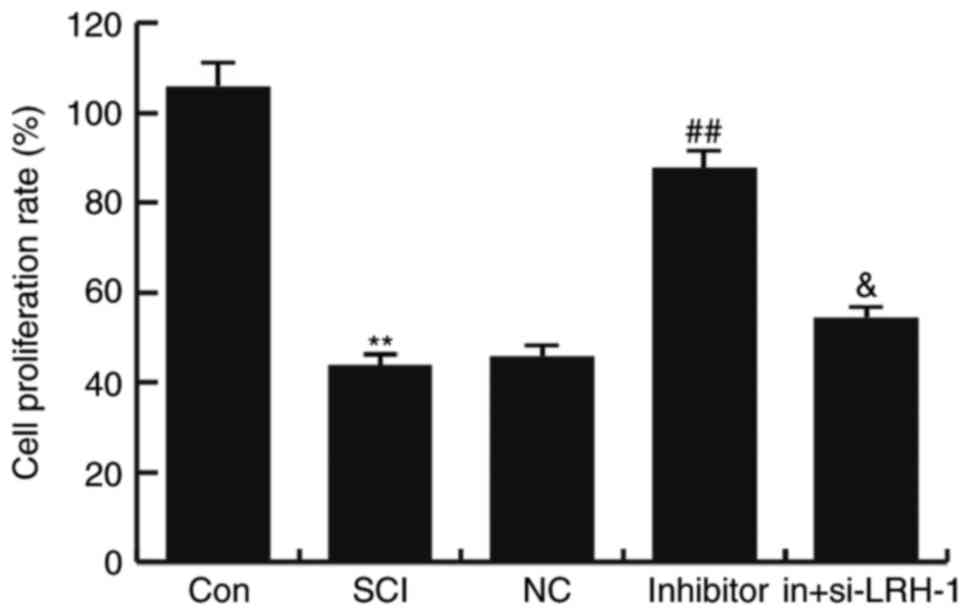
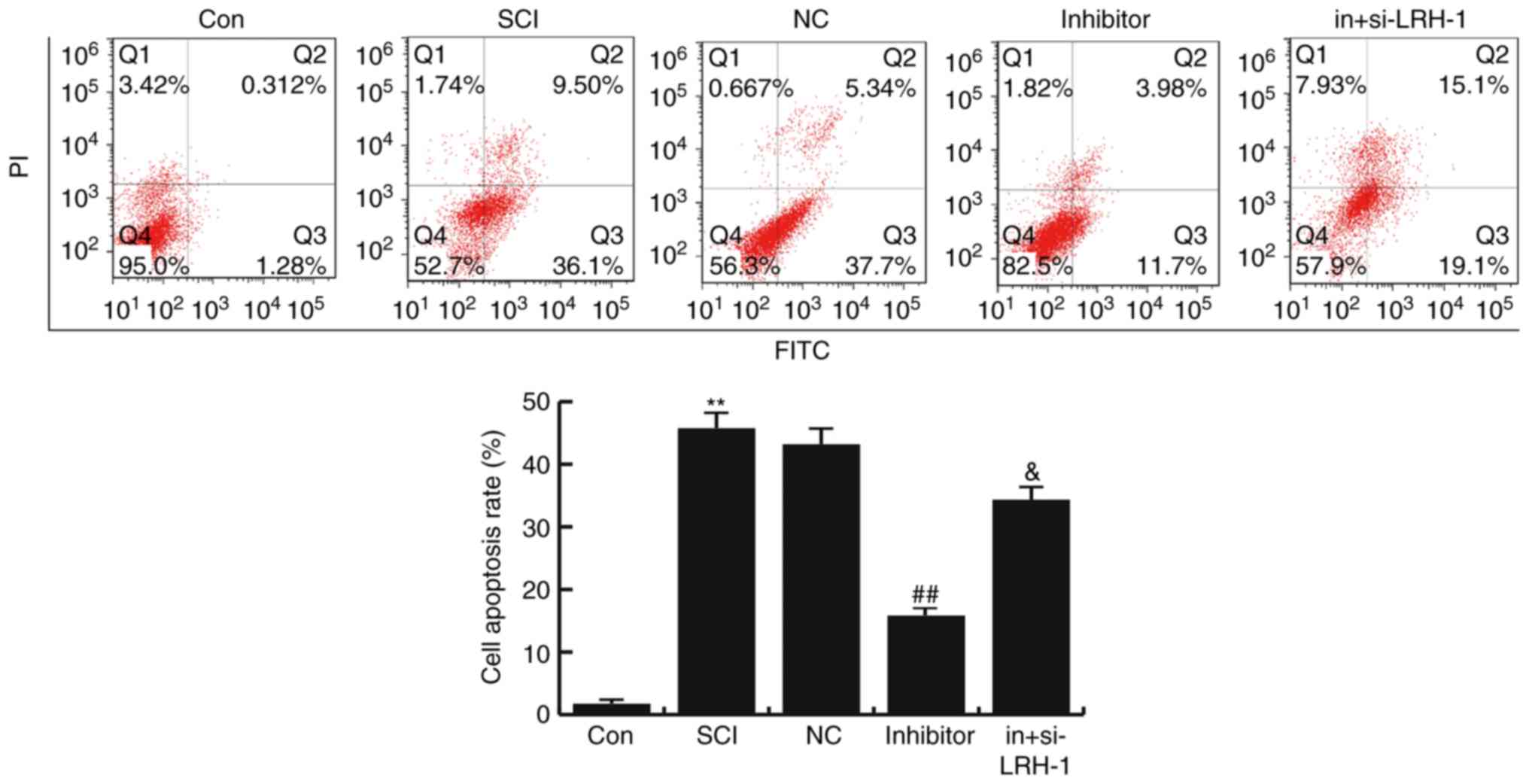
|
1
|
Hulsebosch CE: Recent advances in
pathophysiology and treatment of spinal cord injury. Adv Physiol
Educ. 26:238–255. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dumont RJ, Okonkwo DO, Verma S, Hurlbert
RJ, Boulos PT, Ellegala DB and Dumont AS: Acute spinal cord injury,
part I: Pathophysiologic mechanisms. Clin Neuropharmacol.
24:254–264. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bareyre FM and Schwab ME: Inflammation,
degeneration and regeneration in the injured spinal cord: Insights
from DNA microarrays. Trends Neurosci. 26:555–563. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
W.H.O., . Spinal Cord Injury Fact Sheet N
384. 2013.
|
|
5
|
Ozdemir M, Attar A and Kuzu I:
Regenerative treatment in spinal cord injury. Curr Stem Cell Res
Ther. 7:364–369. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pereira JE, Costa LM, Cabrita AM, Couto
PA, Filipe VM, Magalhães LG, Fornaro M, Di Scipio F, Geuna S,
Maurício AC and Varejão AS: Methylprednisolone fails to improve
functional and histological outcome following spinal cord injury in
rats. Exp Neurol. 220:71–81. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI and
Diederichs S: Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways
and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol. 11:228–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang W, Kwon EJ and Tsai LH: MicroRNAs in
learning, memory, and neurological diseases. Learn Mem. 19:359–368.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rao P, Benito E and Fischer A: MicroRNAs
as biomarkers for CNS disease. Front Mol Neurosci. 6:392013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dong J, Lu M, He X, Xu J, Qin J, Cheng Z,
Liang B, Wang D and Li H: Identifying the role of microRNAs in
spinal cord injury. Neurol Sci. 35:1663–1671. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ning B, Gao L, Liu RH, Liu Y, Zhang NS and
Chen ZY: microRNAs in spinal cord injury: Potential roles and
therapeutic implications. Int J Biol Sci. 10:997–1006. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nieto-Diaz M, Esteban FJ, Reigada D,
Muñoz-Galdeano T, Yunta M, Caballero-López M, Navarro-Ruiz R, Del
Águila A and Maza RM: microRNA dysregulation in spinal cord injury:
Causes, consequences and therapeutics. Front Cell Neurosci.
8:532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Q, Zhu L, Jiang Y, Xu J, Wang F and
He Z: miR-219-5p suppresses the proliferation and invasion of
colorectal cancer cells by targeting calcyphosin. Oncol Lett.
13:1319–1324. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li C, Dong J, Han Z and Zhang K:
MicroRNA-219-5p represses the proliferation, migration and invasion
of gastric cancer cells by targeting the LRH-1/Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway. Oncol Res. 25:617–627. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang C, Cai Z, Huang M, Mao C, Zhang Q,
Lin Y, Zhang X, Tang B, Chen Y, Wang X, et al: miR-219-5p modulates
cell growth of papillary thyroid carcinoma by targeting estrogen
receptor α. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 100:E204–E213. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang N, Lin J, Ruan J, Su N, Qing R, Liu
F, He B, Lv C, Zheng D and Luo R: MiR-219-5p inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by targeting
glypican-3. FEBS Lett. 586:884–891. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hachisuka S, Kamei N, Ujigo S, Miyaki S,
Yasunaga Y and Ochi M: Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for
evaluating the severity of acute spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord.
52:596–600. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jee MK, Jung JS, Choi JI, Jang JA, Kang
KS, Im YB and Kang SK: MicroRNA 486 is a potentially novel target
for the treatment of spinal cord injury. Brain. 135:1237–1252.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jaworski J and Sheng M: The growing role
of mTOR in neuronal development and plasticity. Mol Neurobiol.
34:205–219. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Z, Zhou L, Zheng X, Chen G, Pan R, Li
J and Liu W: Autophagy protects against PI3K/Akt/mTOR-mediated
apoptosis of spinal cord neuronsafter mechanical injury. Neurosci
Lett. 656:158–164. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhai G, Song J, Shu T, Yan J, Jin X, He J
and Yin Z: LRH-1senses signaling from phosphatidylcholine to
regulate the expansion growth of digestive organs via synergy with
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in zebrafish. J Genet Genomics. 20:307–317.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kramer HB, Lai CF, Patel H, Periyasamy M,
Lin ML, Feller SM, Fuller-Pace FV, Meek DW, Ali S and Buluwela L:
LRH-1 drives colon cancer cell growth by repressing the expression
of the CDKN1A gene in a p53-dependent manner. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:582–594. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Harkema SJ: Neural plasticity after human
spinal cord injury: Application of locomotor training to the
rehabilitation of walking. Neuroscientist. 7:455–468. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Martirosyan NL, Carotenuto A, Patel AA,
Kalani MY, Yagmurlu K, Lemole GM Jr, Preul MC and Theodore N: The
role of microRNA markers in the diagnosis, treatment and outcome
prediction of spinal cord injury. Front Surg. 3:562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu D, Huang Y, Jia C, Li Y, Liang F and
Fu Q: Administration of antagomir-223 inhibits apoptosis, promotes
angiogenesis andfunctional recovery in rats with spinal cord
injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 35:483–491. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang Z, Xu J, Zhu R and Liu L:
Down-regulation of miRNA-128 contributes to neuropathic pain
following spinal cord injury via activation of P38. Med Sci Monit.
23:405–411. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou HJ, Wang LQ, Xu QS, Fan ZX, Zhu Y,
Jiang H, Zheng XJ, Ma YH and Zhan RY: Downregulation of miR-199b
promotes the acute spinal cord injury through IKKβ-NF-κB signaling
pathway activating microglial cells. Exp Cell Res. 349:60–67. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tao B and Shi K: Decreased miR-195
expression protects rats from spinal cord injury primarily by
targeting HIF-1α. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 46:49–53. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Boon H, Sjögren RJ, Massart J, Egan B,
Kostovski E, Iversen PO, Hjeltnes N, Chibalin AV, Widegren U and
Zierath JR: MicroRNA-208b progressively declines after spinal cord
injury in humans and is inversely related to myostatin expression.
Physiol Rep. 3:pii e126222015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang T, Yuan W, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Wang Z,
Chen X, Feng S, Xiu Y and Li W: miR-142-3p is a potential
therapeutic target for sensory function recovery of spinal cord
injury. Med Sci Monit. 21:2553–2556. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rao SA, Arimappamagan A, Pandey P, Santosh
V, Hegde AS, Chandramouli BA and Somasundaram K: miR-219-5p
inhibits receptor tyrosine kinase pathway by targeting EGFR in
glioblastoma. PLoS One. 8:e631642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cheng J, Deng R, Zhang P, Wu C, Wu K, Shi
L, Liu X, Bai J, Deng M, Shuai X, et al: miR-219-5p plays a tumor
suppressive role in colon cancer by targeting oncogene Sall4. Oncol
Rep. 34:1923–1932. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nadolny C and Dong X: Liver receptor
homolog-1 (LRH-1): A potential therapeutic target for cancer.
Cancer Biol Ther. 16:997–1004. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Botrugno OA, Fayard E, Annicotte JS, Haby
C, Brennan T, Wendling O, Tanaka T, Kodama T, Thomas W, Auwerx J
and Schoonjans K: Synergy between LRH-1 and beta-catenin induces G1
cyclin-mediated cell proliferation. Mol Cell. 15:499–509. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|