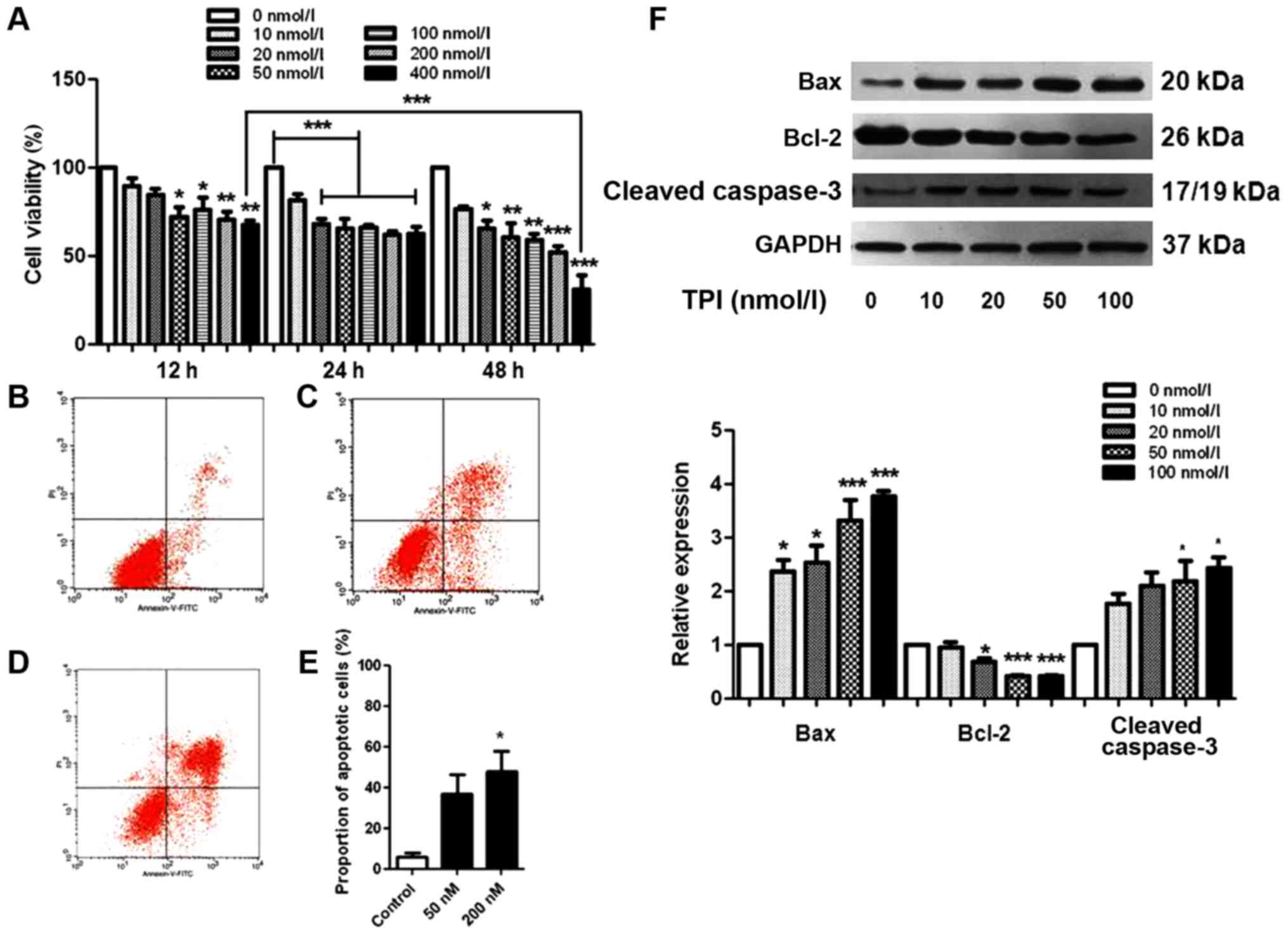
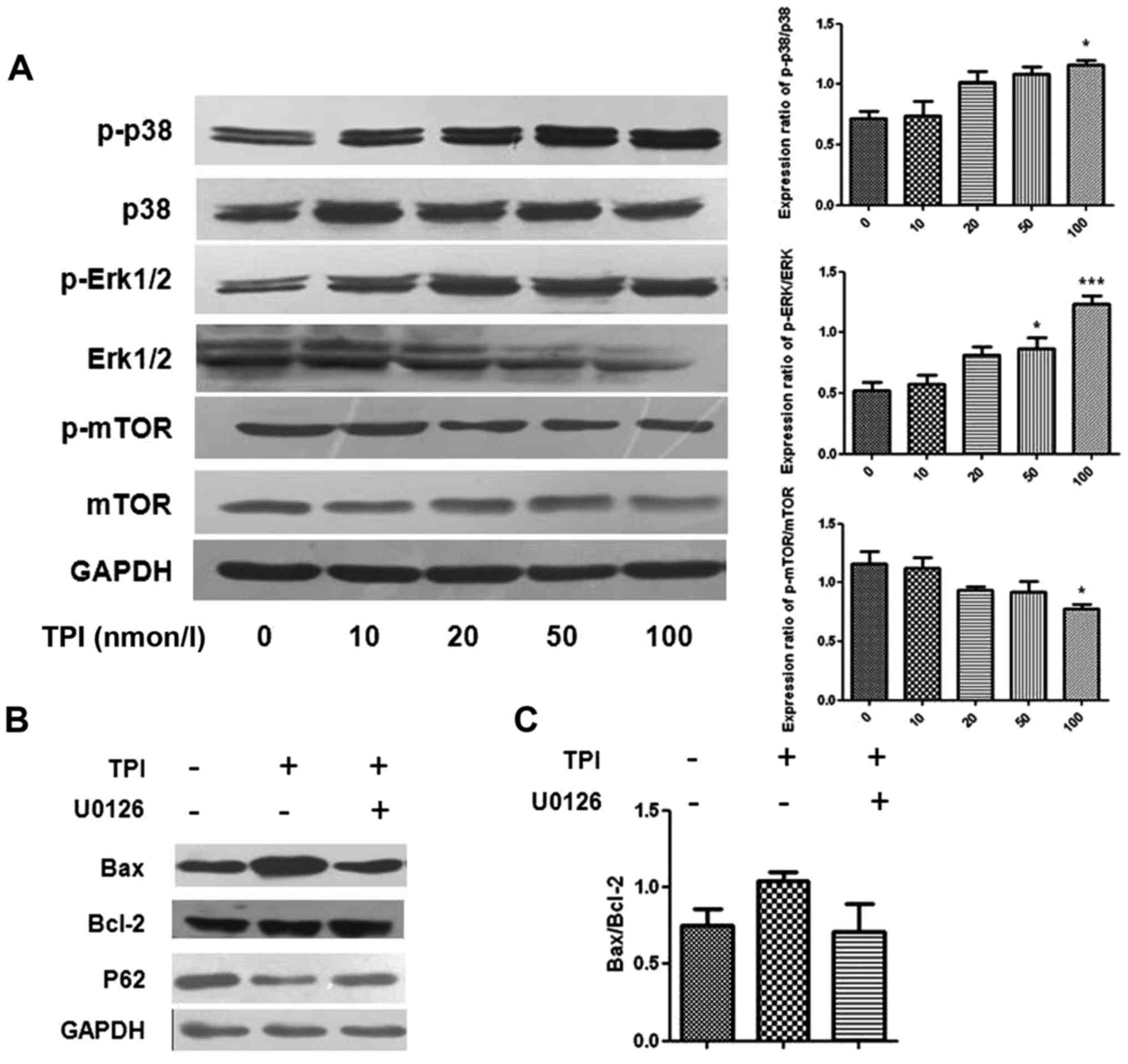
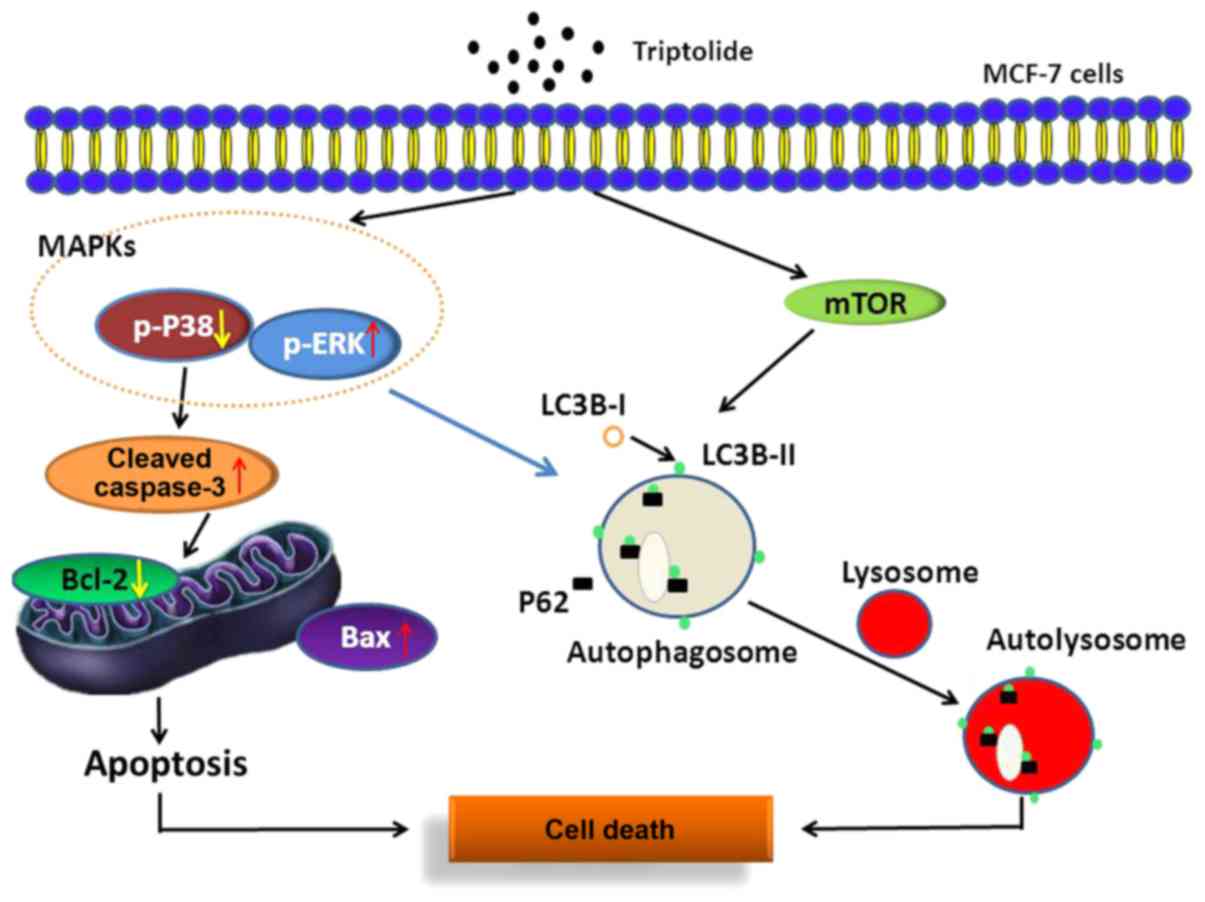
|
1
|
Cedolini C, Bertozzi S, Londero AP,
Bernardi S, Seriau L, Concina S, Cattin F and Risaliti A: Type of
breast cancer diagnosis, screening, and survival. Clin Breast
Cancer. 14:235–240. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de la Mare JA, Contu L, Hunter MC, Moyo B,
Sterrenberg JN, Dhanani KC, Mutsvunguma LZ and Edkins AL: Breast
cancer: Current developments in molecular approaches to diagnosis
and treatment. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 9:153–175. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Robijns J, Censabella S, Bulens P, Maes A
and Mebis J: The use of low-level light therapy in supportive care
for patients with breast cancer: Review of the literature. Lasers
Med Sci. 32:229–242. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ikeda H, Taira N, Nogami T, Shien K, Okada
M, Shien T, Doihara H and Miyoshi S: Combination treatment with
fulvestrant and various cytotoxic agents (doxorubicin, paclitaxel,
docetaxel, vinorelbine and 5-fluorouracil) has a synergistic effect
in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancer Sci.
102:2038–2042. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zheng RR, Hu W, Sui CG, Ma N and Jiang YH:
Effects of doxorubicin and gemcitabine on the induction of
apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 32:2719–2725. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tacar O, Sriamornsak P and Dass CR:
Doxorubicin: An update on anticancer molecular action, toxicity and
novel drug delivery systems. J Pharm Pharmacol. 65:157–170. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li XJ, Jiang ZZ and Zhang LY: Triptolide:
Progress on research in pharmacodynamics and toxicology. J
Ethnopharmacol. 155:67–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Reno TA, Kim JY and Raz DJ: Triptolide
inhibits lung cancer cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Ann
Thorac Surg. 100:1817–1825. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen Z, Sangwan V, Banerjee S, Chugh R,
Dudeja V, Vickers SM and Saluja AK: Triptolide sensitizes
pancreatic cancer cells to TRAIL-induced activation of the death
receptor pathway. Cancer Lett. 348:156–166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu Y, Xiao E, Yuan L and Li G: Triptolide
synergistically enhances antitumor activity of oxaliplatin in colon
carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. DNA Cell Biol. 33:418–425. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grossi V, Peserico A, Tezil T and Simone
C: p38α MAPK pathway: A key factor in colorectal cancer therapy and
chemoresistance. World J Gastroenterol. 20:9744–9758. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou HF, Liu XY, Niu DB, Li FQ, He QH and
Wang XM: Triptolide protects dopaminergic neurons from
inflammation-mediated damage induced by lipopolysaccharide
intranigral injection. Neurobiol Dis. 18:441–449. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang Y, Wang J, Cheng J and Wang L:
Antiestrogenic activity of triptolide in human breast cancer cells
MCF-7 and immature female mouse. Drug Dev Res. 78:164–169. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu J, Jiang Z, Xiao J, Zhang Y, Lin S,
Duan W, Yao J, Liu C, Huang X, Wang T, et al: Effects of triptolide
from Tripterygium wilfordii on ERalpha and p53 expression in two
human breast cancer cell lines. Phytomedicine. 16:1006–1013. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng X, Shi W, Zhao C, Zhang D, Liang P,
Wang G and Lu L: Triptolide sensitizes human breast cancer cells to
tumor necrosis factor-α-induced apoptosis by inhibiting activation
of the nuclear factor-κB pathway. Mol Med Rep. 13:3257–3264. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tan BJ and Chiu GN: Role of oxidative
stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress and ERK activation in
triptolide-induced apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 42:1605–1612. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lewinska A, Adamczyk-Grochala J,
Kwasniewicz E, Deregowska A and Wnuk M: Diosmin-induced senescence,
apoptosis and autophagy in breast cancer cells of different p53
status and ERK activity. Toxicol Lett. 265:117–130. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu M, Chen J, Huang Y, Ke J, Li L, Huang
D and Wu W: Triptolide alleviates isoprenaline-induced cardiac
remodeling in rats via TGF-β1/Smad3 and p38 MAPK signaling pathway.
Pharmazie. 70:244–250. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meng G, Wang W, Chai K, Yang S, Li F and
Jiang K: Combination treatment with triptolide and
hydroxycamptothecin synergistically enhances apoptosis in A549 lung
adenocarcinoma cells through PP2A-regulated ERK, p38 MAPKs and Akt
signaling pathways. Int J Oncol. 46:1007–1017. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Parzych KR and Klionsky DJ: An overview of
autophagy: Morphology, mechanism, and regulation. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 20:460–473. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Porter AG and Jänicke RU: Emerging roles
of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang Q, Liu X, Cao C, Lei J, Han D, Chen
G, Yu J, Chen L, Lv D and Li Z: Apelin-13 induces autophagy in
hepatoma HepG2 cells through ERK1/2 signaling pathway-dependent
upregulation of Beclin1. Oncol Lett. 11:1051–1056. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Koleini N and Kardami E: Autophagy and
mitophagy in the context of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.
Oncotarget. 8:46663–46680. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao F, Huang W, Zhang Z, Mao L, Han Y,
Yan J and Lei M: Triptolide induces protective autophagy through
activation of the CaMKKβ-AMPK signaling pathway in prostate cancer
cells. Oncotarget. 7:5366–5382. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li H, Pan GF, Jiang ZZ, Yang J, Sun LX and
Zhang LY: Triptolide inhibits human breast cancer MCF-7 cell growth
via downregulation of the ERα-mediated signaling pathway. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 36:606–613. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang N, Dong XP, Zhang SL, You QY, Jiang
XT and Zhao XG: Triptolide reverses the Taxol resistance of lung
adenocarcinoma by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway and the
expression of NF-κB-regulated drug-resistant genes. Mol Med Rep.
13:153–159. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kang DW, Lee JY, Oh DH, Park SY, Woo TM,
Kim MK, Park MH, Jang YH and Min do S: Triptolide-induced
suppression of phospholipase D expression inhibits proliferation of
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Exp Mol Med. 41:678–685. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim YC and Guan KL: mTOR: A pharmacologic
target for autophagy regulation. J Clin Invest. 125:25–32. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Meijer AJ, Lorin S, Blommaart EF and
Codogno P: Regulation of autophagy by amino acids and
MTOR-dependent signal transduction. Amino Acids. 47:2037–2063.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shen P, Chen M, He M, Chen L, Song Y, Xiao
P, Wan X, Dai F, Pan T and Wang Q: Inhibition of ERα/ERK/P62
cascades induces ‘autophagic switch’ in the estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancer cells exposed to gemcitabine.
Oncotarget. 7:48501–48516. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yue X, Zhao P, Wu K, Huang J, Zhang W, Wu
Y, Liang X and He X: GRIM-19 inhibition induced autophagy through
activation of ERK and HIF-1α not STAT3 in Hela cells. Tumour Biol.
37:9789–9796. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Innajak S, Mahabusrakum W and
Watanapokasin R: Goniothalamin induces apoptosis associated with
autophagy activation through MAPK signaling in SK-BR-3 cells. Oncol
Rep. 35:2851–2858. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|