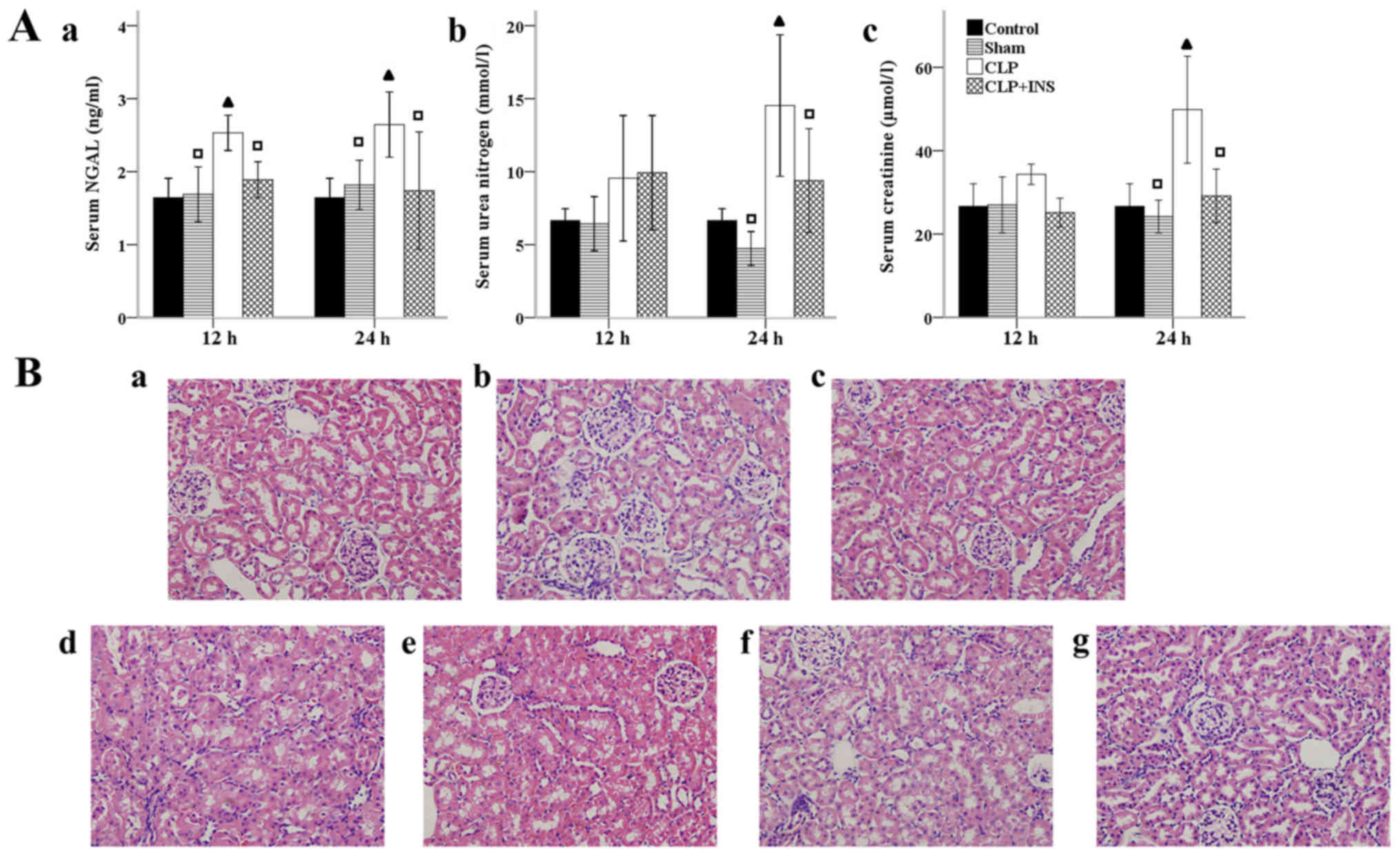
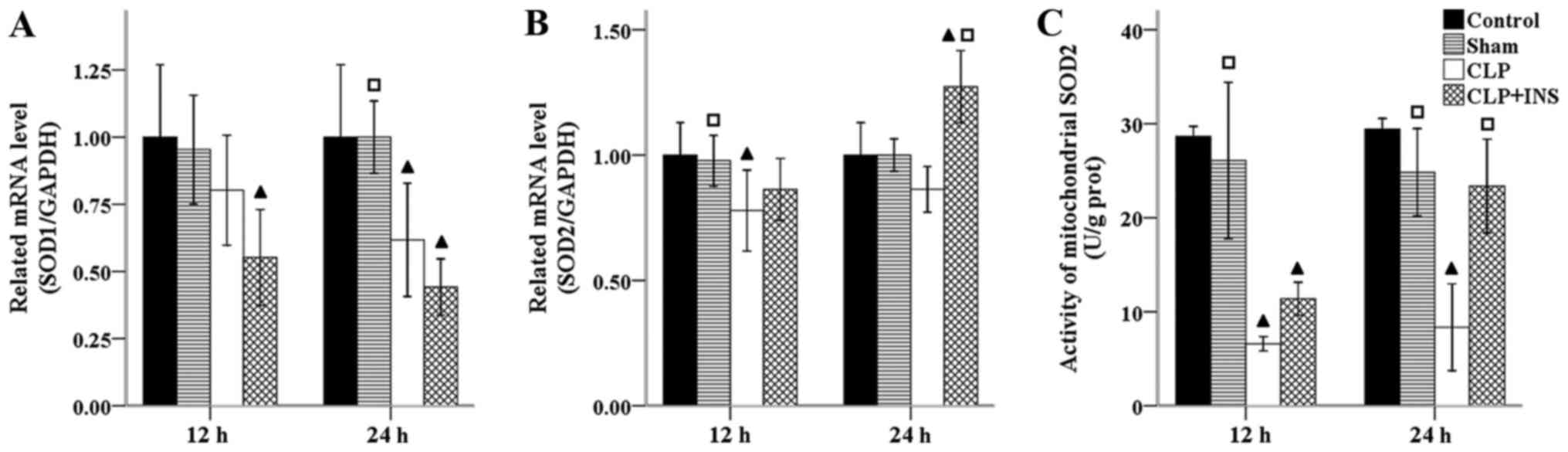
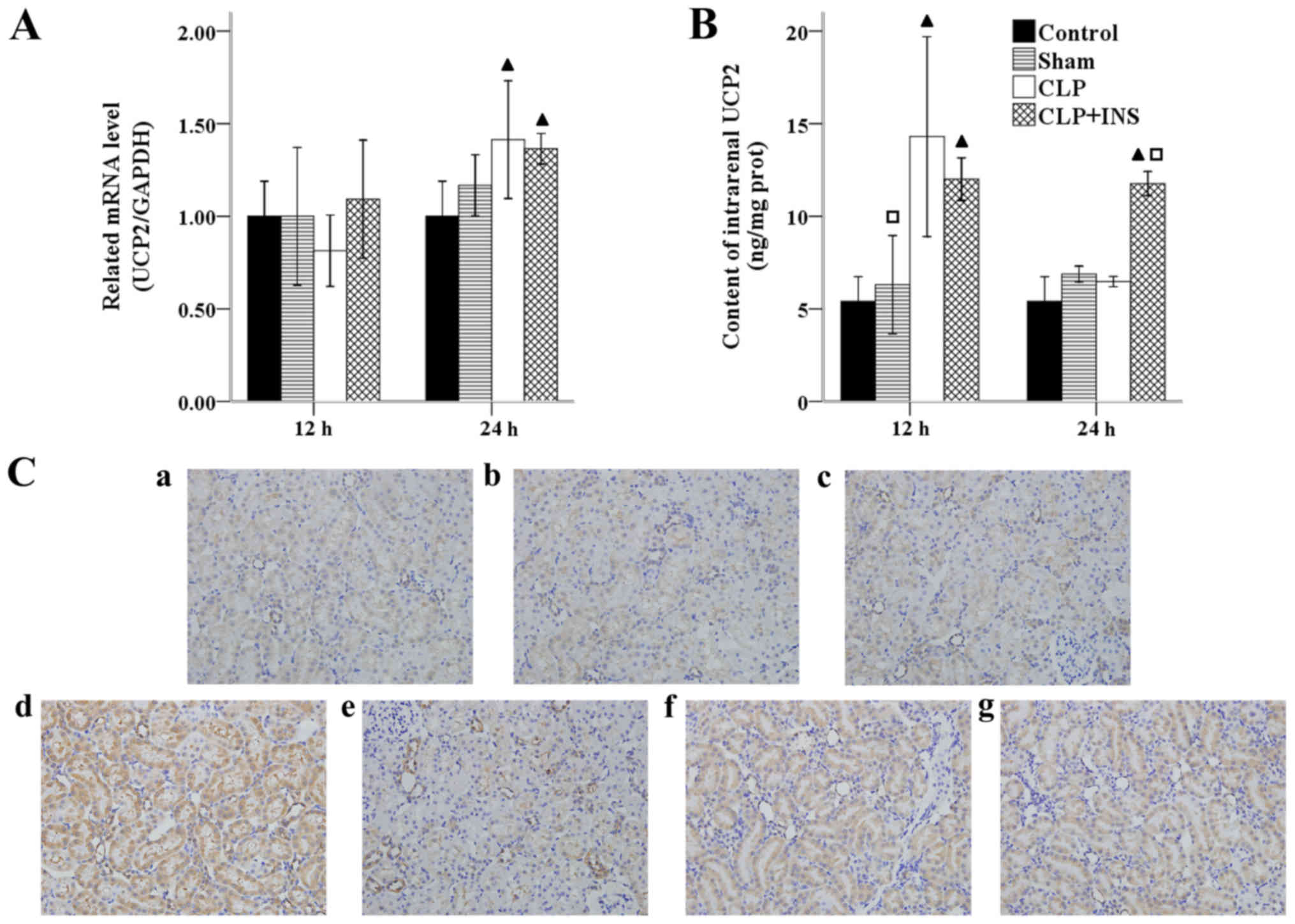
|
1
|
Abraham E: New definitions for sepsis and
septic shock: Continuing evolution but with much still to be done.
JAMA. 315:757–759. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bagshaw SM, George C and Bellomo R; ANZICS
Database Management Committee, : Early acute kidney injury and
sepsis: A multicentre evaluation. Crit Care. 12:R472008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schrier RW and Wang W: Acute renal failure
and sepsis. N Engl J Med. 351:159–169. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Galley HF: Bench-to-bedside review:
Targeting antioxidants to mitochondria in sepsis. Crit Care.
14:2302010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang RL, Wang XT, Liu DW and Liu SB:
Energy and oxygen metabolism disorder during septic acute kidney
injury. Kidney Blood Press Res. 39:240–251. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pathak E, Macmillan-Crow LA and Mayeux PR:
Role of mitochondrial oxidants in an in vitro model of
sepsis-induced renal injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 340:192–201.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee SY, Lee YS, Choi HM, Ko YS, Lee HY, Jo
SK, Cho WY and Kim HK: Distinct pathophysiologic mechanisms of
septic acute kidney injury: Role of immune suppression and renal
tubular cell apoptosis in murine model of septic acute kidney
injury. Crit Care Med. 40:2997–3006. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Quoilin C, Mouithys-Mickalad A, Lècart S,
Fontaine-Aupart MP and Hoebeke M: Evidence of oxidative stress and
mitochondrial respiratory chain dysfunction in an in vitro model of
sepsis-induced kidney injury. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1837:1790–1800.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Patil NK, Parajuli N, MacMillan-Crow LA
and Mayeux PR: Inactivation of renal mitochondrial respiratory
complexes and manganese superoxide dismutase during sepsis:
Mitochondria-targeted antioxidant mitigates injury. Am J Physiol
Renal Physiol. 306:F734–F743. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Parikh SM, Yang Y, He L, Tang C, Zhan M
and Dong Z: Mitochondrial function and disturbances in the septic
kidney. Semin Nephrol. 35:108–119. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kastl L, Sauer SW, Ruppert T, Beissbarth
T, Becker MS, Suss D, Krammer PH and Gülow K: TNF-α mediates
mitochondrial uncoupling and enhances ROS-dependent cell migration
via NF-κB activation in liver cells. FEBS Lett. 588:175–183. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mesotten D, Swinnen JV, Vanderhoydonc F,
Wouters PJ and Van den Berghe G: Contribution of circulating lipids
to the improved outcome of critical illness by glycemic control
with intensive insulin therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
89:219–226. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Heuer JG, Sharma GR, Zhang T, Ding C,
Bailey DL, Stephens EJ, Holmes KC, Grubbs RL, Fynboe KA, Chen YF
and Jakubowski JA: Effects of hyperglycemia and insulin therapy on
outcome in a hyperglycemic septic model of critical illness. J
Trauma. 60:865–872. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zeng QY, Zhang CM and Qian XH: Protective
effects of continue insulin infusion on liver mitochondrion in the
early stage of septic rats. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi.
25:525–528. 2009.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mailloux RJ and Harper ME: Uncoupling
proteins and the control of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species
production. Free Radic Biol Med. 51:1106–1115. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mccreath G, Scullion MM, Lowes DA, Webster
NR and Galley HF: Pharmacological activation of endogenous
protective pathways against oxidative stress under conditions of
sepsis. Br J Anaesth. 116:131–139. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rittirsch D, Huber-Lang MS, Flierl MA and
Ward PA: Immunodesign of experimental sepsis by cecal ligation and
puncture. Nat Protoc. 4:31–36. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gomez H, Ince C, De Backer D, Pickkers P,
Payen D, Hotchkiss J and Kellum JA: A unified theory of
sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: Inflammation, microcirculatory
dysfunction, bioenergetics and the tubular cell adaptation to
injury. Shock. 41:3–11. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Raimundo N: Mitochondrial pathology:
Stress signals from the energy factory. Trends Mol Med. 20:282–292.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dandona P, Ghanim H, Bandyopadhyay A,
Korzeniewski K, Ling Sia C, Dhindsa S and Chaudhuri A: Insulin
suppresses endotoxin-induced oxidative, nitrosative, and
inflammatory stress in humans. Diabetes Care. 33:2416–2423. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen Q, Yu W, Shi J, Shen J, Gao T, Zhang
J, Xi F, Li J and Li N: Insulin alleviates the inflammatory
response and oxidative stress injury in cerebral tissues in septic
rats. J Inflamm (Lond). 11:182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dandona P, Aljada A, Mohanty P, Ghanim H,
Hamouda W, Assian E and Ahmad S: Insulin inhibits intranuclear
nuclear factor kappaB and stimulates IkappaB in mononuclear cells
in obese subjects: Evidence for an anti-inflammatory effect? J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 86:3257–3265. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yoneyama S, Terashima H, Yamaguchi R,
Tadano S and Ohkohchi N: The manner of the inflammation-boosting
effect caused by acute hyperglycemia secondary to overfeeding and
the effects of insulin therapy in a rat model of sepsis. J Surg
Res. 185:380–387. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Efrati S, Berman S, Hamad RA, Siman-Tov Y,
Chanimov M and Weissgarten J: Hyperglycaemia emerging during
general anaesthesia induces rat acute kidney injury via impaired
microcirculation, augmented apoptosis and inhibited cell
proliferation. Nephrology (Carlton). 17:111–122. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Verbruggen SC, Joosten KF, Castillo L and
van Goudoever JB: Insulin therapy in the pediatric intensive care
unit. Clin Nutr. 26:677–690. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wiryana M: The role of intensive insulin
therapy in increasing superoxide dismutase (SOD) and normalizing
hyperglycemia in critically ill patients. Acta Med Indones.
41:59–65. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Galley HF: Oxidative stress and
mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis. Br J Anaesth. 107:57–64. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Maitra SR, Wojnar MM and Lang CH:
Alterations in tissue glucose uptake during the hyperglycemic and
hypoglycemic phases of sepsis. Shock. 13:379–385. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zheng G, Lyu J, Liu S, Huang J, Liu C,
Xiang D, Xie M and Zeng Q: Silencing of uncoupling protein 2 by
small interfering RNA aggravates mitochondrial dysfunction in
cardiomyocytes under septic conditions. Int J Mol Med.
35:1525–1536. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cao T, Dong Y, Tang R, Chen J, Zhang CY
and Zen K: Mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2 protects splenocytes
from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis during pathogen activation.
Cell Immunol. 286:39–44. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Leffler M, Hrach T, Stuerzl M, Horch RE,
Herndon DN and Jeschke MG: Insulin attenuates apoptosis and exerts
anti-inflammatory effects in endotoxemic human macrophages. J Surg
Res. 143:398–406. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vanhorebeek I, De Vos R, Mesotten D,
Wouters PJ, De Wolf-Peeters C and Van den Berghe G: Protection of
hepatocyte mitochondrial ultrastructure and function by strict
blood glucose control with insulin in critically ill patients.
Lancet. 365:53–59. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu HY, Han J, Cao SY, Hong T, Zhuo D, Shi
J, Liu Z and Cao W: Hepatic autophagy is suppressed in the presence
of insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia: Inhibition of
FoxO1-dependent expression of key autophagy genes by insulin. J
Biol Chem. 284:31484–31492. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Choi AM, Ryter SW and Levine B: Autophagy
in human health and disease. N Engl J Med. 368:651–662. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Giardina TM, Steer JH, Lo SZ and Joyce DA:
Uncoupling protein-2 accumulates rapidly in the inner mitochondrial
membrane during mitochondrial reactive oxygen stress in
macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1777:118–129. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|