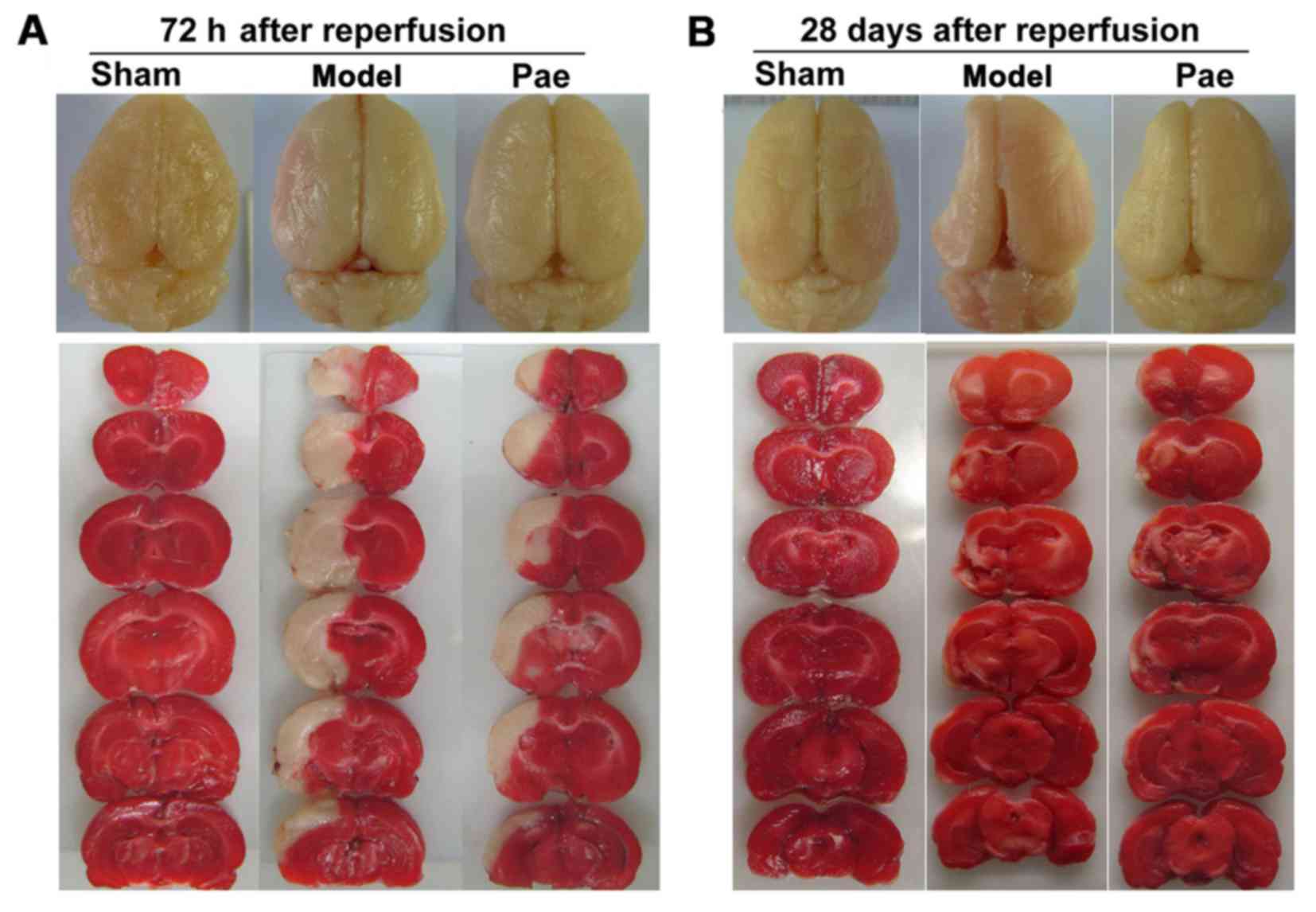
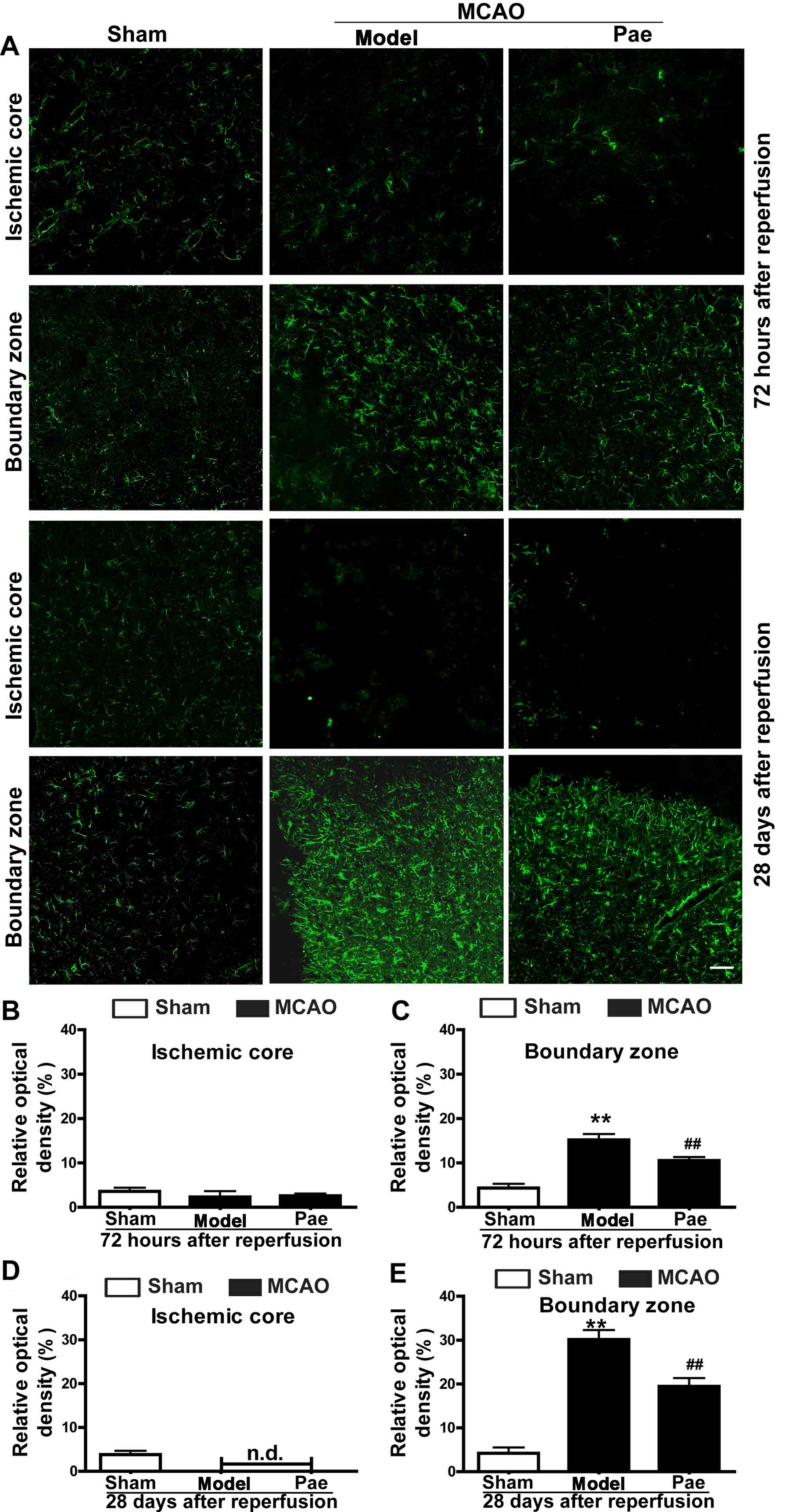
|
1
|
Hankey GJ: Stroke. Lancet. 389:641–654.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP Jr, Bruno A,
Connors JJ, Demaerschalk BM, Khatri P, McMullan PW Jr, Qureshi AI,
Rosenfield K, et al: Guidelines for the early management of
patients with acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare
professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke
Association. Stroke. 44:870–947. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li L and Stary CM: Targeting glial
mitochondrial function for protection from cerebral ischemia:
Relevance, mechanisms, and the role of MicroRNAs. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2016:60323062016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, Brozman M,
Dávalos A, Guidetti D, Larrue V, Lees KR, Medeghri Z, Machnig T, et
al: Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 h after acute ischemic
stroke. N Engl J Med. 359:1317–1329. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shichita T, Ago T, Kamouchi M, Kitazono T,
Yoshimura A and Ooboshi H: Novel therapeutic strategies targeting
innate immune responses and early inflammation after stroke. J
Neurochem. 123 Suppl 2:S29–S38. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Fagan SC, Hess DC, Hohnadel EJ, Pollock DM
and Ergul A: Targets for vascular protection after acute ischemic
stroke. Stroke. 35:2220–2225. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Burda JE and Sofroniew MV: Reactive
gliosis and the multicellular response to CNS damage and disease.
Neuron. 81:229–248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hanisch UK and Kettenmann H: Microglia:
Active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and
pathologic brain. Nat Neurosci. 10:1387–1394. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao B, Zhao CZ, Zhang XY, Huang XQ, Shi
WZ, Fang SH, Lu YB, Zhang WP, Xia Q and Wei EQ: The new P2Y-like
receptor G protein-coupled receptor 17 mediates acute neuronal
injury and late microgliosis after focal cerebral ischemia in rats.
Neuroscience. 202:42–57. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Choudhury GR and Ding S: Reactive
astrocytes and therapeutic potential in focal ischemic stroke.
Neurobiol Dis. 85:234–244. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Z and Chopp M: Astrocytes, therapeutic
targets for neuroprotection and neurorestoration in ischemic
stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 144:103–120. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim JY, Kim N and Yenari MA: Mechanisms
and potential therapeutic applications of microglial activation
after brain injury. CNS Neurosci Ther. 21:309–319. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jin X and Yamashita T: Microglia in
central nervous system repair after injury. J Biochem. 159:491–496.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bu Y, Lee K, Jung HS and Moon SK:
Therapeutic effects of traditional herbal medicine on cerebral
ischemia: A perspective of vascular protection. Chin J Integr Med.
19:804–814. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ding Y, Li Q, Xu Y, Chen Y, Deng Y, Zhi F
and Qian K: Attenuating oxidative stress by paeonol protected
against Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. PLoS One.
11:e01543752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu YR, Chen JJ and Dai M: Paeonol
protects rat vascular endothelial cells from ox-LDL-induced injury
in vitro via downregulating microRNA-21 expression and TNF-α
release. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:483–488. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li M, Tan SY and Wang XF: Paeonol exerts
an anticancer effect on human colorectal cancer cells through
inhibition of PGE, synthesis and COX-2 expression. Oncol Rep.
32:2845–2853. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu J, Feng L, Ma D, Zhang M, Gu J, Wang
S, Fu Q, Song Y, Lan Z, Qu R and Ma S: Neuroprotective effect of
paeonol on cognition deficits of diabetic encephalopathy in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Neurosci Lett. 549:63–68.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liao WY, Tsai TH, Ho TY, Lin YW, Cheng CY
and Hsieh CL: Neuroprotective effect of paeonol mediates
anti-inflammation via suppressing Toll-like receptor 2 and
Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathways in cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2016:37046472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao Y, Fu B, Zhang X, Zhao T, Chen L,
Zhang J and Wang X: Paeonol pretreatment attenuates cerebral
ischemic injury via upregulating expression of pAkt, Nrf2, HO-1 and
ameliorating BBB permeability in mice. Brain Res Bull. 109:61–67.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shi X, Chen YH, Liu H and Qu HD:
Therapeutic effects of paeonol on
methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine/probenecid-induced
Parkinson's disease in mice. Mol Med Rep. 14:2397–2404. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou A, Wu H, Pan J, Wang X, Li J, Wu Z
and Hui A: Synthesis and evaluation of paeonol derivatives as
potential multifunctional agents for the treatment of Alzheimer's
disease. Molecules. 20:1304–1318. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shi QJ, Wang H, Liu ZX, Fang SH, Song XM,
Lu YB, Zhang WP, Sa XY, Ying HZ and Wei EQ: HAMI 3379, a CysLT2R
antagonist, dose- and time-dependently attenuates brain injury and
inhibits microglial inflammation after focal cerebral ischemia in
rats. Neuroscience. 291:53–69. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yano T, Anraku S, Nakayama R and Ushijima
K: Neuroprotective effect of urinary trypsin inhibitor against
focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Anesthesiology.
98:465–473. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Graham SM, McCullough LD and Murphy SJ:
Animal models of ischemic stroke: Balancing experimental aims and
animal care. Comp Med. 54:486–496. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rewell SS, Churilov L, Sidon TK, Aleksoska
E, Cox SF, Macleod MR and Howells DW: Evolution of ischemic damage
and behavioural deficit over 6 months after MCAo in the rat:
Selecting the optimal outcomes and statistical power for
multi-centre preclinical trials. PLoS One. 12:e01716882017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yonemori F, Yamaguchi T, Yamada H and
Tamura A: Evaluation of a motor deficit after chronic focal
cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 18:1099–1106.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lu LQ, Lou Q, Guo HG, Zhou WW, Ying HZ,
Wei EQ and Shi QJ: Neuroprotective effect of HAMI 3379, a CysLT2R
receptor antagonist, on chronic brain injury after focal cerebral
ischemia in rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 10:4123–4136. 2017.
|
|
30
|
Shen LH, Li Y, Chen J, Cui Y, Zhang C,
Kapke A, Lu M, Savant-Bhonsale S and Chopp M: One-year follow-up
after bone marrow stromal cell treatment in middle-aged female rats
with stroke. Stroke. 38:2150–2156. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Garbuzova-Davis S, Haller E, Tajiri N,
Thomson A, Barretta J, Williams SN, Haim ED, Qin H, Frisina-Deyo A,
Abraham JV, et al: Blood-spinal cord barrier alterations in
subacute and chronic Stages of a rat model of focal cerebral
ischemia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 75:673–688. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ma Y, Wang J, Wang Y and Yang GY: The
biphasic function of microglia in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol.
157:247–272. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu L, He D and Bai Y: Microglia-mediated
inflammation and neurodegenerative disease. Mol Neurobiol.
53:6709–6715. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Benarroch EE: Microglia: Multiple roles in
surveillance, circuit shaping, and response to injury. Neurology.
81:1079–1088. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee Y, Lee SR, Choi SS, Yeo HG, Chang KT
and Lee HJ: Therapeutically targeting neuroinflammation and
microglia after acute ischemic stroke. Biomed Res Int.
2014:2972412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kawabori M and Yenari MA: The role of the
microglia in acute CNS injury. Metab Brain Dis. 30:381–392. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nam KN, Woo BC, Moon SK, Park SU, Park JY,
Hwang JW, Bae HS, Ko CN and Lee EH: Paeonol attenuates
inflammation-mediated neurotoxicity and microglial activation.
Neural Regen Res. 8:1637–1643. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Himaya SW, Ryu B, Qian ZJ and Kim SK:
Paeonol from Hippocampus kuda Bleeler suppressed the
neuro-inflammatory responses in vitro via NF-kB and MAPK signaling
pathways. Toxicol In Vitro. 26:878–887. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|