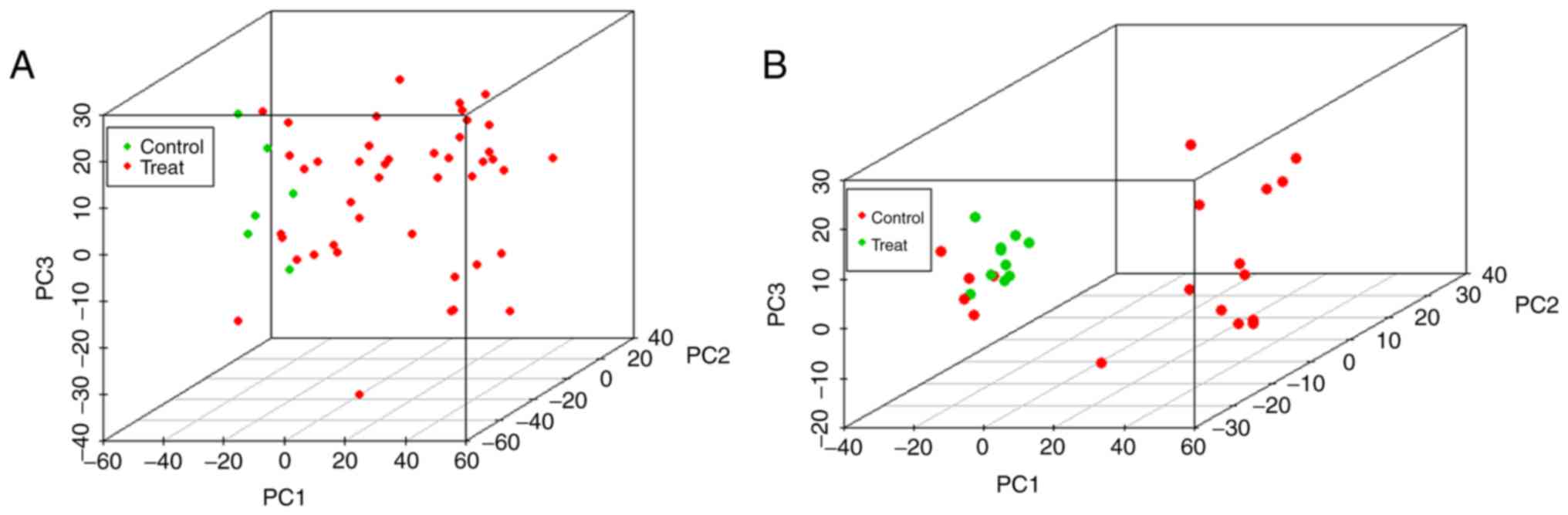
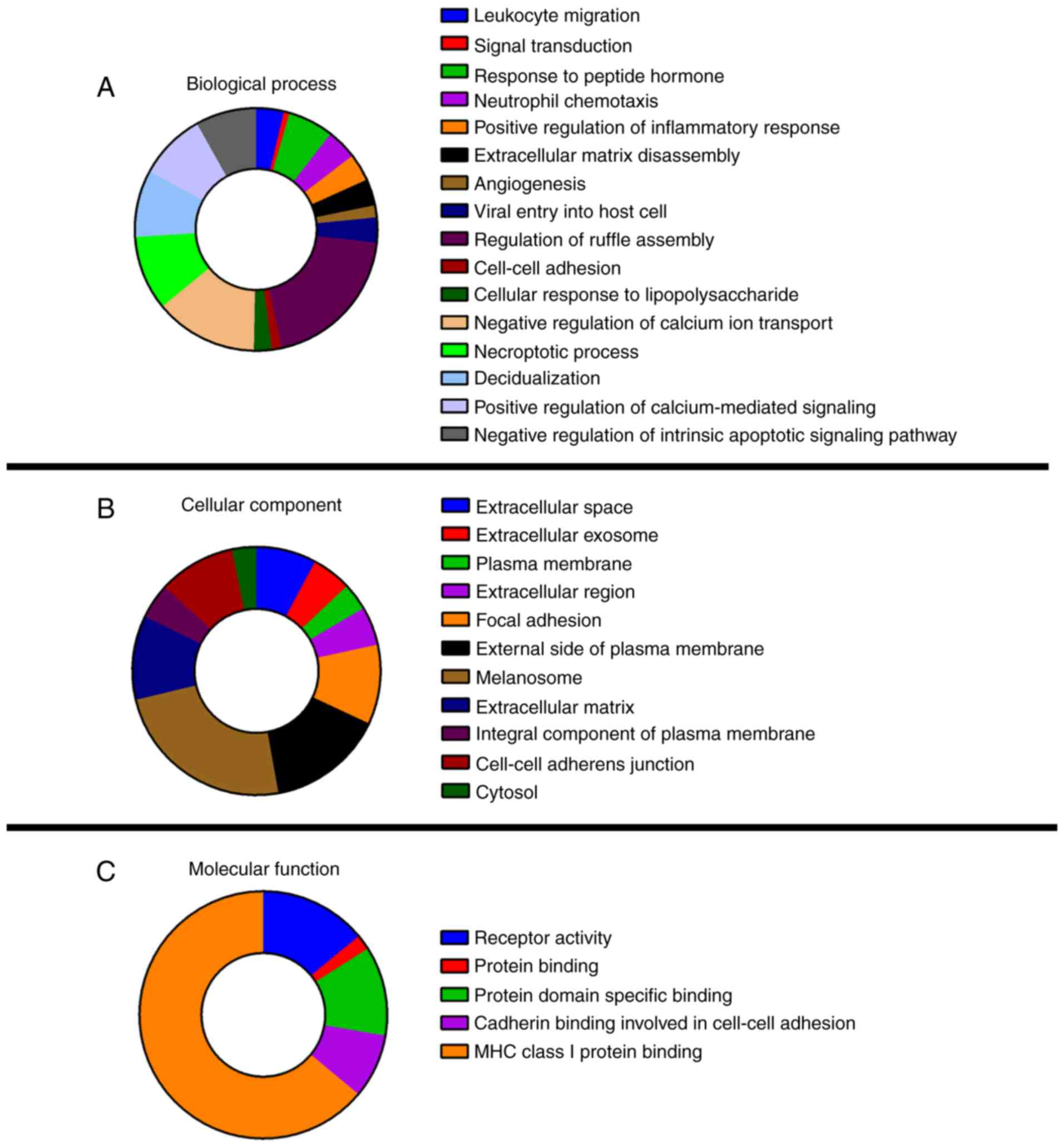
|
1
|
Dickson RP, Erb-Downward JR and Huffnagle
GB: The role of the bacterial microbiome in lung disease. Expert
Rev Respir Med. 7:245–257. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Marik PE: Aspiration pneumonitis and
aspiration pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 344:665–671. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Levy SB and Marshall B: Antibacterial
resistance worldwide: Causes, challenges and responses. Nat Med. 10
Suppl 12:S122–S129. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jones RN: Microbial etiologies of
hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated
bacterial pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 51 Suppl 1:S81–S87. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fagon J, Patrick H, Haas DW, Torres A,
Gibert C, Cheadle WG, Falcone RE, Anholm JD, Paganin F, Fabian TC
and Lilienthal F: Treatment of gram-positive nosocomial pneumonia:
Prospective randomized comparison of quinupristin/dalfopristin
versus vancomycin. Nosocomial Pneumonia Group. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 161:753–762. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Testa A, Giannuzzi R, Daini S, Bernardini
L, Petrongolo L and Gentiloni Silveri N: Psychiatric emergencies
(part III): Psychiatric symptoms resulting from organic diseases.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 17 Suppl 1:S86–S99. 2013.
|
|
7
|
Kirby WM: Treatment of bacterial
pneumonia. AMA Arch Intern Med. 96:809–817. 1955. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Burwen DR, Banerjee SN and Gaynes RP:
Ceftazidime resistance among selected nosocomial gram-negative
bacilli in the United States. National nosocomial infections
surveillance system. J Infect Dis. 170:1622–1625. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
El Moujaber G, Osman M, Rafei R, Dabboussi
F and Hamze M: Molecular mechanisms and epidemiology of resistance
in Streptococcus pneumoniae in the middle east region. J Med
Microbiol. 66:847–858. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lee HY, Wu TL, Su LH, Li HC, Janapatla RP,
Chen CL and Chiu CH: Invasive pneumococcal disease caused by
ceftriaxone-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in Taiwan. J
Microbiol Immunol Infect. Jun–26;2017.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yusef D, Shalakhti T, Awad S, Algharaibeh
H and Khasawneh W: Clinical characteristics and epidemiology of
sepsis in the neonatal intensive care unit in the era of multi-drug
resistant organisms: A retrospective review. Pediatr Neonatol. Jun
9–2017.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
12
|
Karlowsky JA, Thornsberry C, Jones ME,
Evangelista AT, Critchley IA and Sahm DF: TRUST Surveillance
Program: Factors associated with relative rates of antimicrobial
resistance among Streptococcus pneumoniae in the United
States: Results from the TRUST surveillance program (1998–2002).
Clin Infect Dis. 36:963–970. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kajikawa O, Frevert CW, Lin SM, Goodman
RB, Mongovin SM, Wong V, Ballman K, Daubeuf B, Elson G and Martin
TR: Gene expression of Toll-like receptor-2, Toll-like receptor-4,
and MD2 is differentially regulated in rabbits with Escherichia
coli pneumonia. Gene. 344:193–202. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ramilo O, Allman W, Chung W, Mejias A,
Ardura M, Glaser C, Wittkowski KM, Piqueras B, Banchereau J,
Palucka AK and Chaussabel D: Gene expression patterns in blood
leukocytes discriminate patients with acute infections. Blood.
109:2066–2077. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Levy H, Wang X, Kaldunski M, Jia S, Kramer
J, Pavletich SJ, Reske M, Gessel T, Yassai M, Quasney MW, et al:
Transcriptional signatures as a disease-specific and predictive
inflammatory biomarker for type 1 diabetes. Genes Immun.
13:593–604. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Heber S and Sick B: Quality assessment of
Affymetrix GeneChip data. OMICS. 10:358–68. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu C, Irizarry R and Gentry J: gcrma:
Background adjustment using sequence information. 2005.
|
|
18
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wickham H: ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for
Data Analysis. Springer-Verlag; New York: 2009, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen H and Boutros PC: VennDiagram: A
package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler
diagrams in R. BMC Bioinformatics. 12:352011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kolde R: pheatmap. In: Pretty Heatmaps. R
package version 1.0.2, 2015. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/pheatmap/pheatmap.pdfJune
12–2016
|
|
22
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Alishahi K, Ehyaei AR and Shojaie A: A
generalized benjamini-hochberg procedure for multivariate
hypothesis testing. Methodology. 33:2016.
|
|
24
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:(Database issue). D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mandourah Y, Al-Radi A, Ocheltree AH,
Ocheltree SR and Fowler RA: Clinical and temporal patterns of
severe pneumonia causing critical illness during Hajj. BMC Infect
Dis. 12:1172012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cilloniz C, Martin-Loeches I, Garcia-Vidal
C, San Jose A and Torres A: Microbial etiology of pneumonia:
Epidemiology, diagnosis and resistance patterns. Int J Mol Sci.
17:E21202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Osiyemi O and Dickinson G: Gram-positive
pneumonia. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2:207–214. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Scannapieco FA: Role of oral bacteria in
respiratory infection. J Periodontol. 70:793–802. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Garibaldi RA: Epidemiology of
community-acquired respiratory tract infections in adults:
Incidence, etiology and impact. Am J Med. 78:32–37. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guan E, Wang J, Roderiquez G and Norcross
MA: Natural truncation of the chemokine MIP-1 beta/CCL4 affects
receptor specificity but not anti-HIV-1 activity. J Biol Chem.
277:32348–32352. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Luther SA and Cyster JG: Chemokines as
regulators of T cell differentiation. Nat Immunol. 2:102–107. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guan E, Wang J and Norcross MA:
Identification of human macrophage inflammatory proteins 1alpha and
1beta as a native secreted heterodimer. J Biol Chem.
276:12404–12409. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Carlson M, Nakamura Y, Payson R, O'Connell
P, Leppert M, Lathrop GM, Lalouel JM and White R: Isolation and
mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence (pMCT108.2) on chromosome 18
[D18S24]. Nucleic Acids Res. 16:41881988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Katz FE, Parkar M, Stanley K, Murray LJ,
Clark EA and Greaves MF: Chromosome mapping of cell membrane
antigens expressed on activated B cells. Eur J Immunol. 15:103–106.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Murdoch C, Read RC, Zhang Q and Finn A:
Choline-binding protein A of Streptococcus pneumoniae
elicits chemokine production and expression of intercellular
adhesion molecule 1 (CD54) by human alveolar epithelial cells. J
Infect Dis. 186:1253–1260. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shapiro S, Miller A, Lahat N, Sobel E and
Lerner A: Expression of matrix metalloproteinases, sICAM-1 and IL-8
in CSF from children with meningitis. J Neurol Sci. 206:43–48.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Brew K and Nagase H: The tissue inhibitors
of metalloproteinases (TIMPs): An ancient family with structural
and functional diversity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1803:55–71. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ylisirniö S, Höyhtyä M and
Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T: Serum matrix metalloproteinases-2, −9 and
tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases-1, −2 in lung cancer-TIMP-1
as a prognostic marker. Anticancer Res. 20:1311–1316.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fong KM, Kida Y, Zimmerman PV and Smith
PJ: TIMP1 and adverse prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 2:1369–1372. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wu ZS, Wu Q, Yang JH, Wang HQ, Ding XD,
Yang F and Xu XC: Prognostic significance of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 serum
and tissue expression in breast cancer. Int J Cancer.
122:2050–2056. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jiang Z, Sui T and Wang B: Relationships
between MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 levels and their
pathogenesis in patients with lupus nephritis. Rheumatol Int.
30:1219–1226. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim H, Oda T, López-Guisa J, Wing D,
Edwards DR, Soloway PD and Eddy AA: TIMP-1 deficiency does not
attenuate interstitial fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 12:736–748. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kakugawa T, Mukae H, Saito M, Ishii K,
Ishimoto H, Sakamoto N, Takazono T, Fukuda Y, Ooe N and Kohno S:
Rapidly progressive interstitial pneumonia associated with
clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis successfully treated with
polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column hemoperfusion. Intern Med.
47:785–790. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Vissers M, Hartman Y, Groh L, de Jong DJ,
de Jonge MI and Ferwerda G: Recognition of Streptococcus
pneumoniae and muramyl dipeptide by NOD2 results in potent
induction of MMP-9, which can be controlled by lipopolysaccharide
stimulation. Infect Immun. 82:4952–4958. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chan SJ, San Segundo B, McCormick MB and
Steiner DF: Nucleotide and predicted amino acid sequences of cloned
human and mouse preprocathepsin B cDNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
83:7721–7725. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cao L, Taggart RT, Berquin IM, Moin K,
Fong D and Sloane BF: Human gastric adenocarcinoma cathepsin B:
Isolation and sequencing of full-length cDNAs and polymorphisms of
the gene. Gene. 139:163–169. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Foghsgaard L, Lademann U, Wissing D,
Poulsen B and Jaattela M: Cathepsin B mediates tumor necrosis
factor-induced arachidonic acid release in tumor cells. J Biol
Chem. 277:39499–39506. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Borgfeldt C, Bendahl PO, Gustavsson B,
Långström E, Fernö M, Willén R, Grenman S and Casslén B: High tumor
tissue concentration of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor is
associated with good prognosis in patients with ovarian cancer. Int
J Cancer. 107:658–665. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chavakis T, Kanse SM, May AE and Preissner
KT: Haemostatic factors occupy new territory: The role of the
urokinase receptor system and kininogen in inflammation. Biochem
Soc Trans. 30:168–173. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|