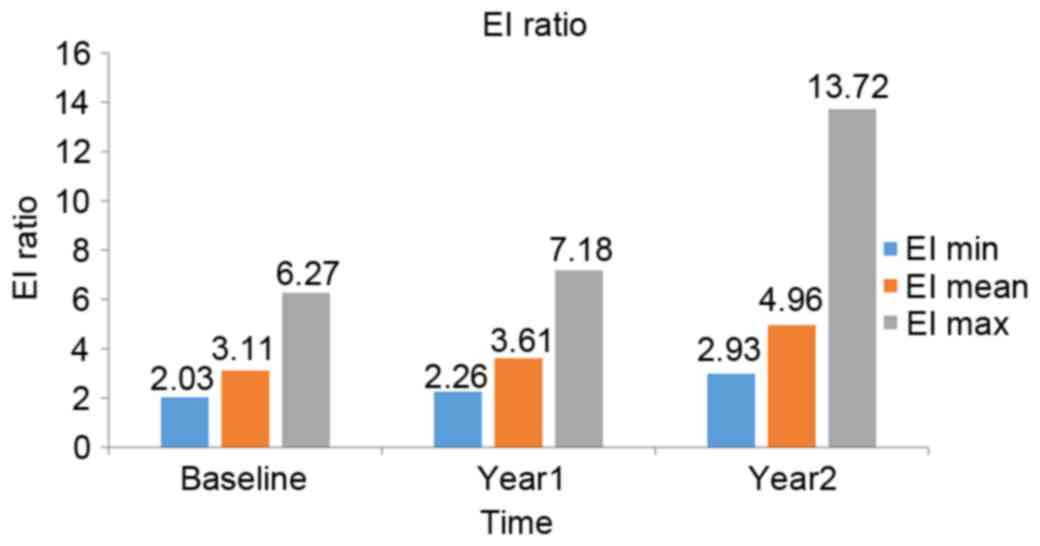
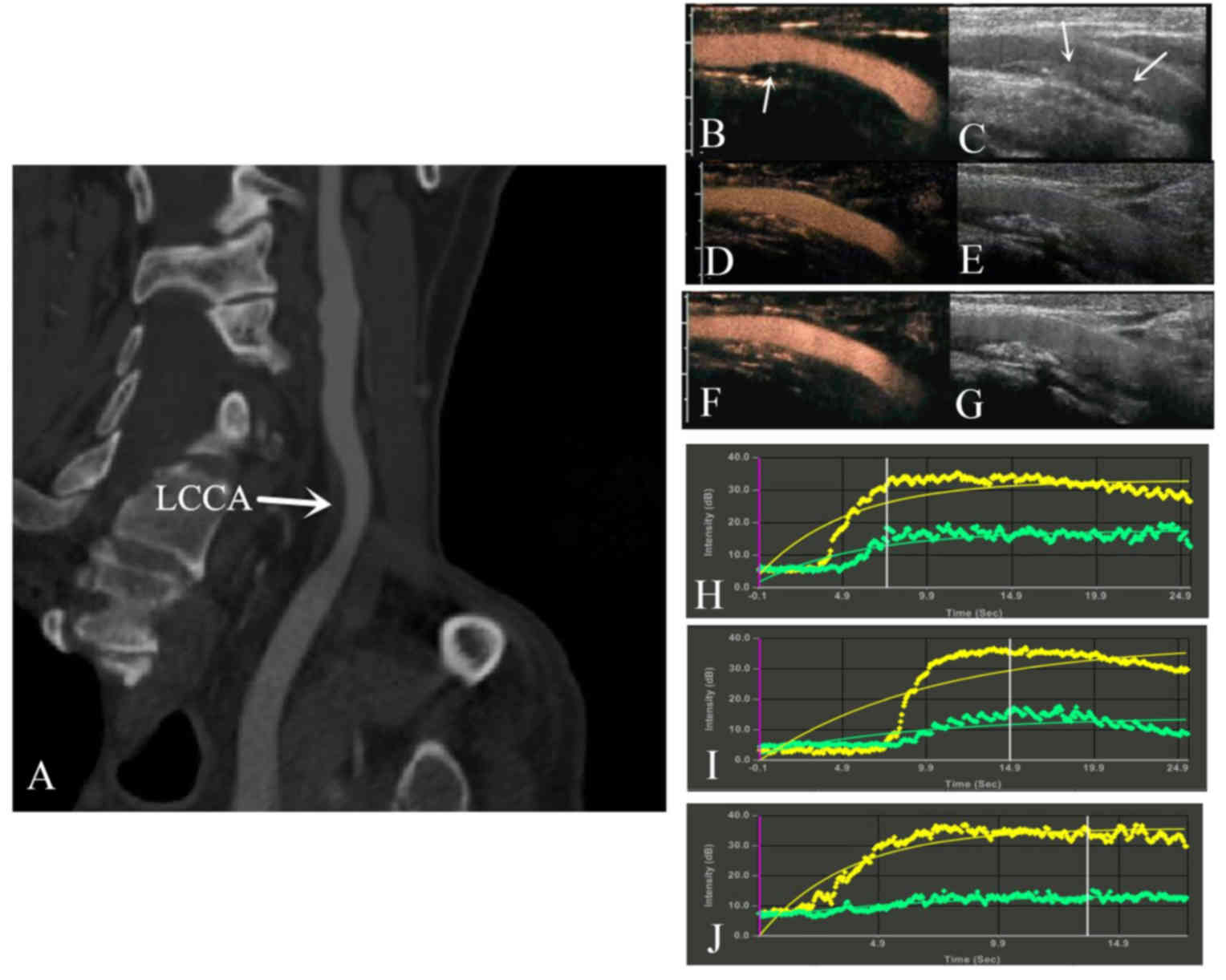
|
1
|
McCarthy MJ, Loftus IM, Thompson MM, Jones
L, London NJ, Bell PR, Naylor AR and Brindle NP: Angiogenesis and
the atherosclerotic carotid plaque: An association between
symptomatology and plaque morphology. J Vasc Surg. 30:261–268.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Finn AV, Nakano M, Narula J, Kolodgie FD
and Virmani R: Concept of vulnerable/unstable plaque. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 30:1282–1292. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Michel JB, Delbosc S, Ho-Tin-Noé B,
Leseche G, Nicoletti A, Meilhac O and Martin-Ventura JL: From
intraplaque haemorrhages to plaque vulnerability: Biological
consequences of intraplaque haemorrhages. J Cardiovasc Med
(Hagerstown). 13:628–634. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Finn AV,
Gold HK, Tulenko TN, Wrenn SP and Narula J: Atherosclerotic plaque
progression and vulnerability to rupture: Angiogenesis as a source
of intraplaque hemorrhage. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
25:2054–2061. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Di Stefano R, Felice F and Balbarini A:
Angiogenesis as risk factor for plaque vulnerability. Curr Pharm
Des. 15:1095–1196. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sluimer JC and Daemen MJ: Novel concepts
in atherogenesis: Angiogenesis and hypoxia in atherosclerosis. J
Pathol. 218:7–29. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dunmore BJ, McCarthy MJ, Naylor AR and
Brindle NP: Carotid plaque instability and ischemic symptoms are
linked to immaturity of microvessels within plaques. J Vasc Surg.
45:155–159. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kodama T, Narula N, Agozzino M and
Arbustini E: Pathology of plaque haemorrhage and neovascularization
of coronary artery. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 13:620–627.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen S, Guo L, Chen B, Sun L and Cui M:
Association of serum angiopoietin-1, angiopoietin-2 and
angiopoietin-2 to angiopoietin-1 ratio with heart failure in
patients with acute myocardial infarction. Exp Ther Med. 5:937–941.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Warburton L and Gillard J: Functional
imaging of carotid atheromatous plaques. J Neuroimaging.
16:293–301. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Laufer EM, Winkens HM, Corsten MF,
Reutelingsperger CP, Narula J and Hofstra L: PET and SPECT imaging
of apoptosis in vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques with
radiolabeled Annexin A5. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 53:26–34.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Grønholdt ML, Nordestgaard BG, Schroeder
TV, Vorstrup S and Sillesen H: Ultrasonic echolucent carotid
plaques predict future strokes. Circulation. 104:68–73. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Giannoni Fabrizia M, Vicenzini E, Monaco C
and Cao P: Contrast enhanced ultrasonography and carotid plaque
imaging: From the hemodynamic evaluation to the detection of
neoangiogenesis-The new approach to the identification of the
unstable plaque: From morphology to pathophysiologyUltrasound
Imaging. Tanabe M: InTech; pp. 171–188. 2011
|
|
14
|
Faggioli GL, Pini R, Mauro R, Pasquinelli
G, Fittipaldi S, Freyrie A, Serra C and Stella A: Identification of
carotid ‘vulnerable plaque’ by contrast-enhanced ultrasonography:
Correlation with plaque histology, symptoms and cerebral computed
tomography. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 41:238–248. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Feinstein SB: The powerful microbubble:
From bench to bedside, from intravascular indicator to therapeutic
delivery system, and beyond. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
287:H450–H457. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Feinstein SB: Contrast ultrasound imaging
of the carotid artery vasa vasorum and atherosclerotic plaque
neovascularization. J Am Coll Cardiol. 48:236–243. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Staub D, Patel MB, Tibrewala A, Ludden D,
Johnson M, Espinosa P, Coll B, Jaeger KA and Feinstein SB: Vasa
vasorum and plaque neovascularization on contrast-enhanced carotid
ultrasound imaging correlates with cardiovascular disease and past
cardiovascular events. Stroke. 41:41–47. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Della-Morte D, Moussa I, Elkind MS, Sacco
RL and Rundek T: The short-term effect of atorvastatin on carotid
plaque morphology assessed by computer-assisted gray-scale
densitometry: A pilot study. Neurol Res. 33:991–994. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Touboul PJ, Hennerici MG, Meairs S, Adams
H, Amarenco P, Desvarieux M, Ebrahim S, Fatar M, Hernandez
Hernandez R, Kownator S, et al: Mannheim intima-media thickness
consensus. Cerebrovasc Dis. 18:346–349. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Touboul PJ, Hennerici MG, Meairs S, Adams
H, Amarenco P, Bornstein N, Csiba L, Desvarieux M, Ebrahim S,
Hernandez Hernandez R, et al: Mannheim carotid intima-media
thickness and plaque consensus (2004-2006-2011). An update on
behalf of the advisory board of the 3rd, 4th and 5th watching the
risk symposia, at the 13th, 15th and 20th European Stroke
Conferences, Mannheim, Germany, 2004, Brussels, Belgium, 2006, and
Hamburg, Germany, 2011. Cerebrovasc Dis. 34:290–296. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J,
Shan Z, Liu J, Tian H, Ji Q, et al: Prevalence of diabetes among
men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 362:1090–1101. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kern R, Szabo K, Hennerici M and Meairs S:
Characterization of carotid artery plaques using real-time compound
B-mode ultrasound. Stroke. 35:870–875. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ferrara KW, Merritt CR, Burns PN, Foster
FS, Mattrey RF and Wickline SA: Evaluation of tumor angiogenesis
with US: Imaging, Doppler, and contrast agents. Acad Radiol.
7:824–839. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Staub D, Partovi S, Schinkel AF, Coll B,
Uthoff H, Aschwanden M, Jaeger KA and Feinstein SB: Correlation of
carotid artery atherosclerotic lesion echogenicity and severity at
standard US with intraplaque neovascularization detected at
contrast-enhanced US. Radiology. 258:618–626. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kadoglou NP, Sailer N, Moumtzouoglou A,
Kapelouzou A, Gerasimidis T and Liapis CD: Aggressive
lipid-lowering is more effective than moderate lipid-lowering
treatment in carotid plaque stabilization. J Vasc Surg. 51:114–21.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gupta M, Martineau P, Tran T, Després JP,
Gaw A, de Teresa E, Farsang C, Gensini GF, Leiter LA, Blanco-Colio
LM, et al: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and high-sensitivity
C-reactive protein lowering with atorvastatin in patients of South
Asian compared with European origin: Insights from the achieve
cholesterol targets fast with atorvastatin stratified titration
(ACTFAST) study. J Clin Pharmacol. 52:850–858. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Colhoun HM, Betteridge DJ, Durrington PN,
Hitman GA, Neil HA, Livingstone SJ, Thomason MJ, Mackness MI,
Charlton-Menys V and Fuller JH: CARDS investigators: Primary
prevention of cardiovascular disease with atorvastatin in type 2
diabetes in the collaborative atorvastatin diabetes study (CARDS):
Multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet.
364:685–696. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Min L, Shao S, Wu X, Cong L, Liu P, Zhao H
and Luo Y: Anti-inflammatory and anti-thrombogenic effects of
atorvastatin in acute ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res.
8:2144–2154. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao SP, Yu BL, Peng DQ and Huo Y: The
effect of moderate-dose versus double-dose statins on patients with
acute coronary syndrome in China: Results of the CHILLAS trial.
Atherosclerosis. 233:707–712. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jia W and Zhou L: Effect of 20 mg/day
atorvastatin: Recurrent stroke survey in Chinese ischemic stroke
patients with prior intracranial hemorrhage. J Clin Neurol.
9:139–143. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee E, Ryan S, Birmingham B, Zalikowski J,
March R, Ambrose H, Moore R, Lee C, Chen Y and Schneck D:
Rosuvastatin pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenetics in white and
Asian subjects residing in the same environment. Clin Pharmacol
Ther. 78:330–341. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao SP, Yu BL, Peng DQ and Huo Y: The
effect of moderate-dose versus double-dose statins on patients with
acute coronary syndrome in China: Results of the CHILLAS trial.
Atherosclerosis. 233:707–712. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu PY, Lin LY, Lin HJ, Hsia CH, Hung YR,
Yeh HI, Wu TC, Chen JY, Chien KL and Chen JW: Pitavastatin and
atorvastatin double-blind randomized comparative study among
high-risk patients, including those with type 2 diabetes mellitus,
in Taiwan (PAPAGO-T Study). PLoS One. 8:e762982013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Desai MY and Schoenhagen P: Emergence of
targeted molecular imaging in atherosclerotic cardiovascular
disease. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 7:197–203. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shah F, Balan P, Weinberg M, Reddy V,
Neems R, Feinstein M, Dainauskas J, Meyer P, Goldin M and Feinstein
SB: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of atherosclerotic carotid
plaque neovascularization: A new surrogate marker of
atherosclerosis? Vasc Med. 12:291–297. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hong LF, Yan XN, Fan Y, Wu Q, Luo SH, Yang
B and Li JJ: Is the ratio of apoB/apoA-1 the best predictor for the
severity of coronary artery lesions in Chinese diabetics with
stable angina pectoris? An assessment based on Gensini scores. J
Geriatr Cardiol. 12:402–409. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang Q, Li C, Han H, Dai W, Shi J, Wang Y
and Wang W: Spatio-temporal quantification of carotid plaque
neovascularization on contrast enhanced ultrasound: Correlation
with visual grading and histopathology. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg.
50:289–296. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hoogi A, Adam D, Hoffman A, Kerner H,
Reisner S and Gaitini D: Carotid plaque vulnerability:
Quantification of neovascularization on contrast-enhanced
ultrasound with histopathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol.
196:431–436. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Coli S, Magnoni M, Sangiorgi G,
Marrocco-Trischitta MM, Melisurgo G, Mauriello A, Spagnoli L,
Chiesa R, Cianflone D and Maseri A: Contrast enhanced ultrasound
imaging of intraplaque neovascularization in carotid arteries:
Correlation with histology and plaque echogenicity. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 52:223–230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Coll B, Nambi V and Feinstein SB: New
advances in noninvasive imaging of the carotid artery: CIMT,
contrast-enhanced ultrasound, and vasa vasorum. Curr Cardiol.
12:497–502. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kolodgie FD, Narula J, Yuan C, Burke AP,
Finn AV and Virmani R: Elimination of neoangiogenesis for plaque
stabilization: Is there a role for local drug therapy? J Am Coll
Cardiol. 49:2093–2101. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jain RK, Finn AV, Kolodgie FD, Gold HK and
Virmani R: Antiangiogenic therapy for normalization of
atherosclerotic plaque vasculature: A potential strategy for plaque
stabilization. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 4:491–502. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Doyle B and Caplice N: Plaque
neovascularization and antiangiogenic therapy for atherosclerosis.
J Am Coll Cardiol. 49:2073–2080. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|