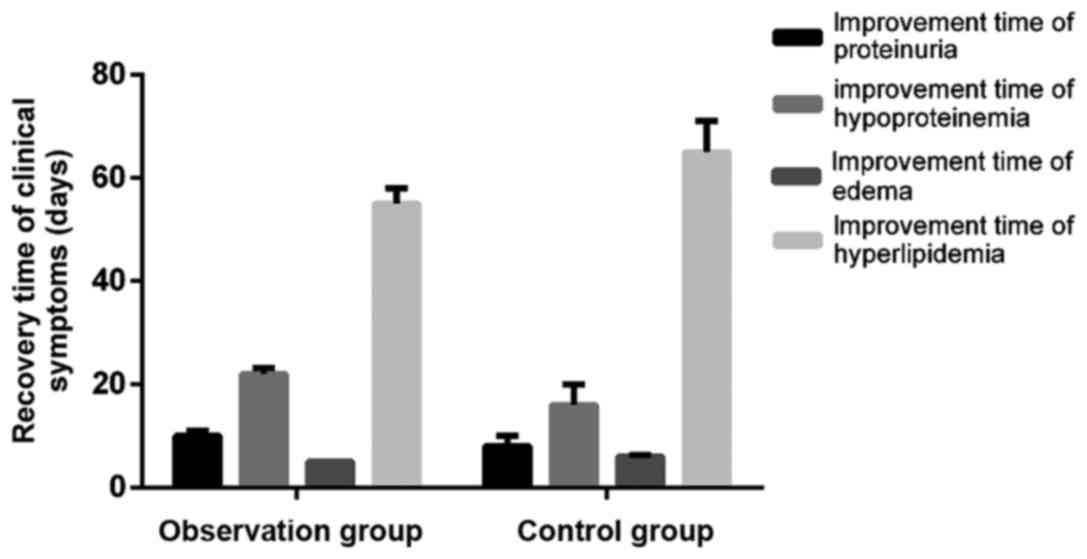
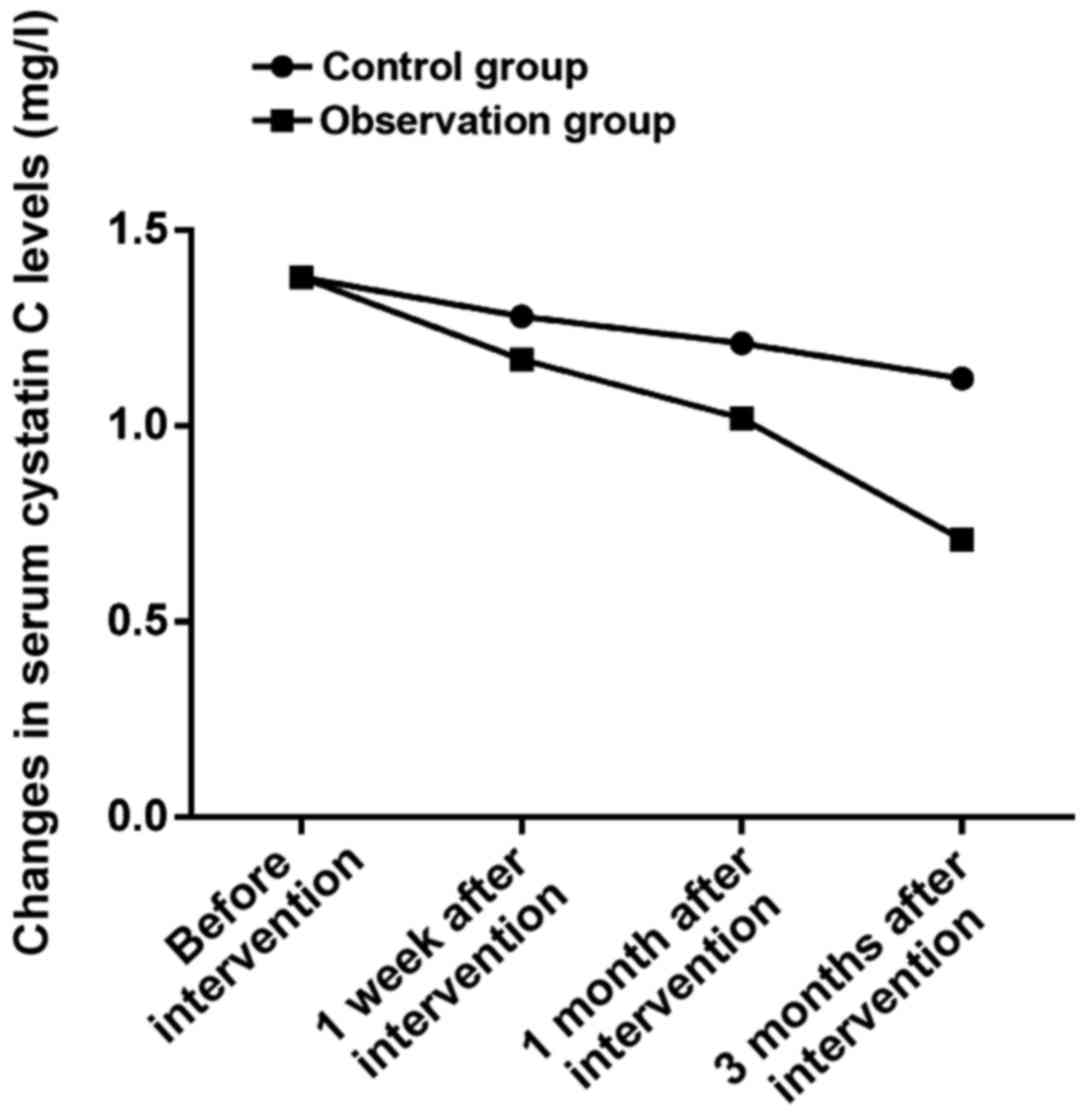
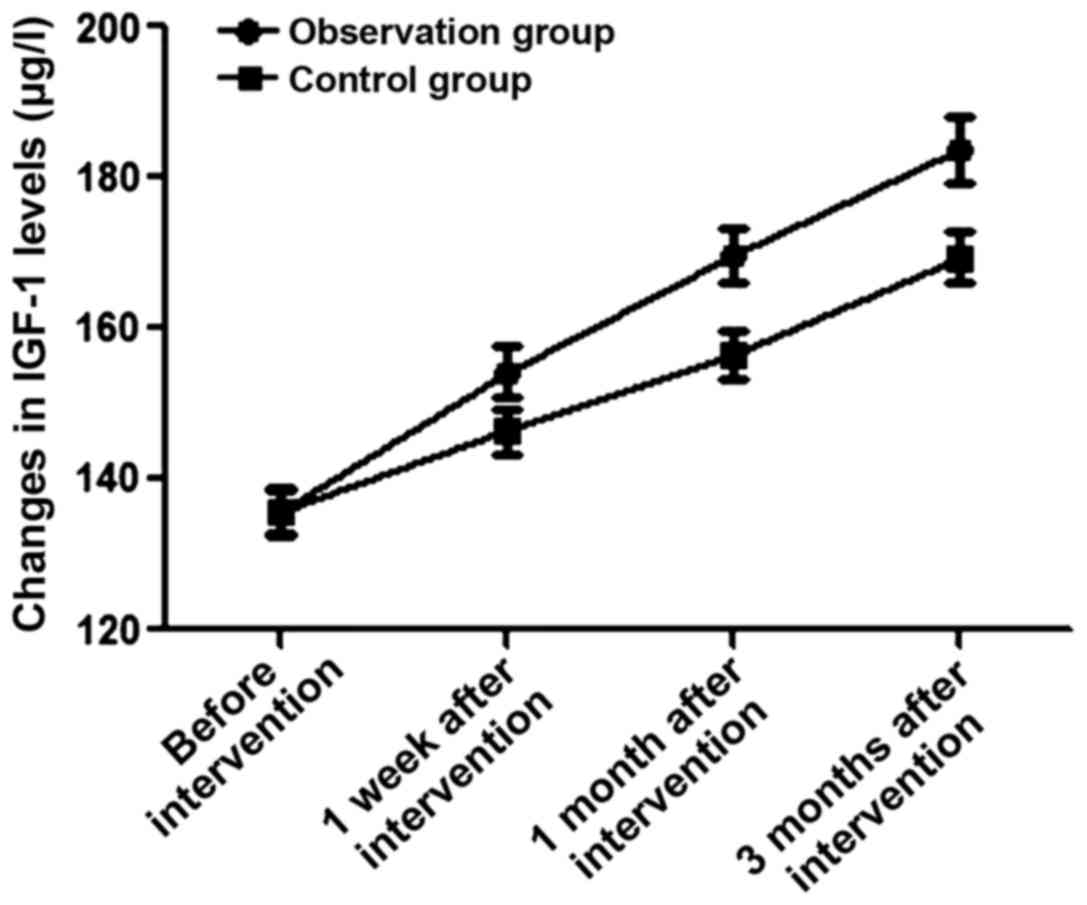
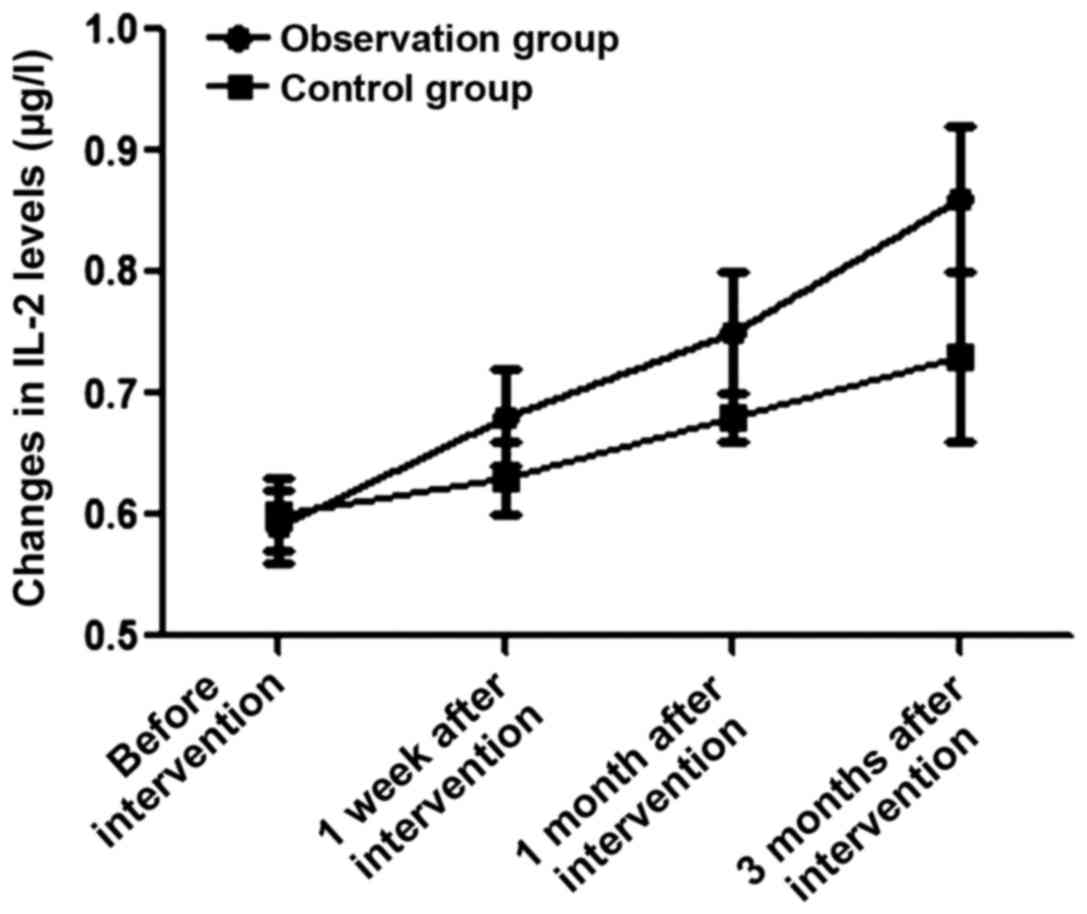
|
1
|
Akchurin OM, Kogon AJ, Kumar J, Sethna CB,
Hammad HT, Christos PJ, Mahan JD, Greenbaum LA and Woroniecki R:
Approach to growth hormone therapy in children with chronic kidney
disease varies across North America: The Midwest Pediatric
Nephrology Consortium report. BMC Nephrol. 18:1812017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cho SM, Lee SH, Lee D, Lee JH, Chang GT,
Kim H and Lee JY: The Korean herbal formulation Yukmijihwangtang
stimulates longitudinal bone growth in animal models. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 17:2392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cernaro V, Lucisano S, Canale V, Bruzzese
A, Caccamo D, Costantino G, Buemi M and Santoro D: Acetate-free
biofiltration to remove fibroblast growth factor 23 in hemodialysis
patients: A pilot study. J Nephrol. 11:1007–1010. 2017.
|
|
4
|
Johar DR and Bernstein LH: Biomarkers of
stress-mediated metabolic deregulation in diabetes mellitus.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 126:222–229. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hong JT, Son DJ, Lee CK, Yoon DY, Lee DH
and Park MH: Interleukin 32, inflammation and cancer. Pharmacol
Ther. 174:127–137. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stephen J, Vilboux T, Mian L, Kuptanon C,
Sinclair CM, Yildirimli D, Maynard DM, Bryant J, Fischer R,
Vemulapalli M, et al: NISC Comparative Sequencing Program:
Mutations in KIAA0753 cause Joubert syndrome associated with growth
hormone deficiency. Hum Genet. 136:399–408. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fragiadaki M, Lannoy M, Themanns M, Maurer
B, Leonhard WN, Peters DJ, Moriggl R and Ong AC: STAT5 drives
abnormal proliferation in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney
disease. Kidney Int. 91:575–586. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Othman EM, Naseem M, Awad E, Dandekar T
and Stopper H: The plant hormone cytokinin confers protection
against oxidative stress in mammalian cells. PLoS One.
11:e01683862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Curran IH, Liston V, Nunnikhoven A,
Caldwell D, Scuby MJ, Pantazopoulos P, Rawn DF, Coady L, Armstrong
C, Lefebvre DE, et al: Toxicologic effects of 28-day dietary
exposure to the flame retardant
1,2-dibromo-4-(1,2-dibromoethyl)-cyclohexane (TBECH) in F344 rats.
Toxicology. 377:1–13. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bu P, Le Y, Zhang Y and Cheng X: Hormonal
and chemical regulation of the Glut9 transporter in mice. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 360:206–214. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Y, Dutra EH, Reichenberger EJ and Chen
IP: Dietary phosphate supplement does not rescue skeletal phenotype
in a mouse model for craniometaphyseal dysplasia. J Negat Results
Biomed. 15:182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Batra J, Buttar RS, Kaur P, Kreimerman J
and Melamed ML: FGF-23 and cardiovascular disease: Review of
literature. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 23:423–429. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zvereva I, Semenistaya E, Krotov G and
Rodchenkov G: Comparison of various in vitro model systems of the
metabolism of synthetic doping peptides: Proteolytic enzymes, human
blood serum, liver and kidney microsomes and liver S9 fraction. J
Proteomics. 149:85–97. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liao S, Vickers MH, Evans A, Stanley JL,
Baker PN and Perry JK: Comparison of pulsatile vs. continuous
administration of human placental growth hormone in female C57BL/6J
mice. Endocrine. 54:169–181. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kobalava Z: SP 04-1 The role of
natriuretic peptides in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular
diseases. J Hypertens. 3 Suppl 1:e3772016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Morgan SJ, Neumann S, Marcus-Samuels B and
Gershengorn MC: Thyrotropin and insulin-like growth factor 1
receptor crosstalk upregulates sodium-iodide symporter expression
in primary cultures of human thyrocytes. Thyroid. 26:1794–1803.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
De Angelis M, Giesert F, Finan B,
Clemmensen C, Müller TD, Vogt-Weisenhorn D, Tschöp MH and Schramm
KW: Determination of thyroid hormones in mouse tissues by
isotope-dilution microflow liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
method. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
1033–1034:413–420. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Czarnecka AM, Matak D, Szymanski L,
Czarnecka KH, Lewicki S, Zdanowski R, Brzezianska-Lasota E and
Szczylik C: Triiodothyronine regulates cell growth and survival in
renal cell cancer. Int J Oncol. 49:1666–1678. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sexton DJ, O'Reilly MW, Geoghegan P,
Kinsella SM, Moran PJ and O'Regan AW: Serum fibroblastic growth
factor 23 in acute Sarcoidosis and normal kidney function.
Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 33:139–142. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nguyen-Yamamoto L, Karaplis AC, St-Arnaud
R and Goltzman D: Fibroblast growth factor 23 regulation by
systemic and local osteoblast-synthesized 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D.
J Am Soc Nephrol. 28:586–597. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|