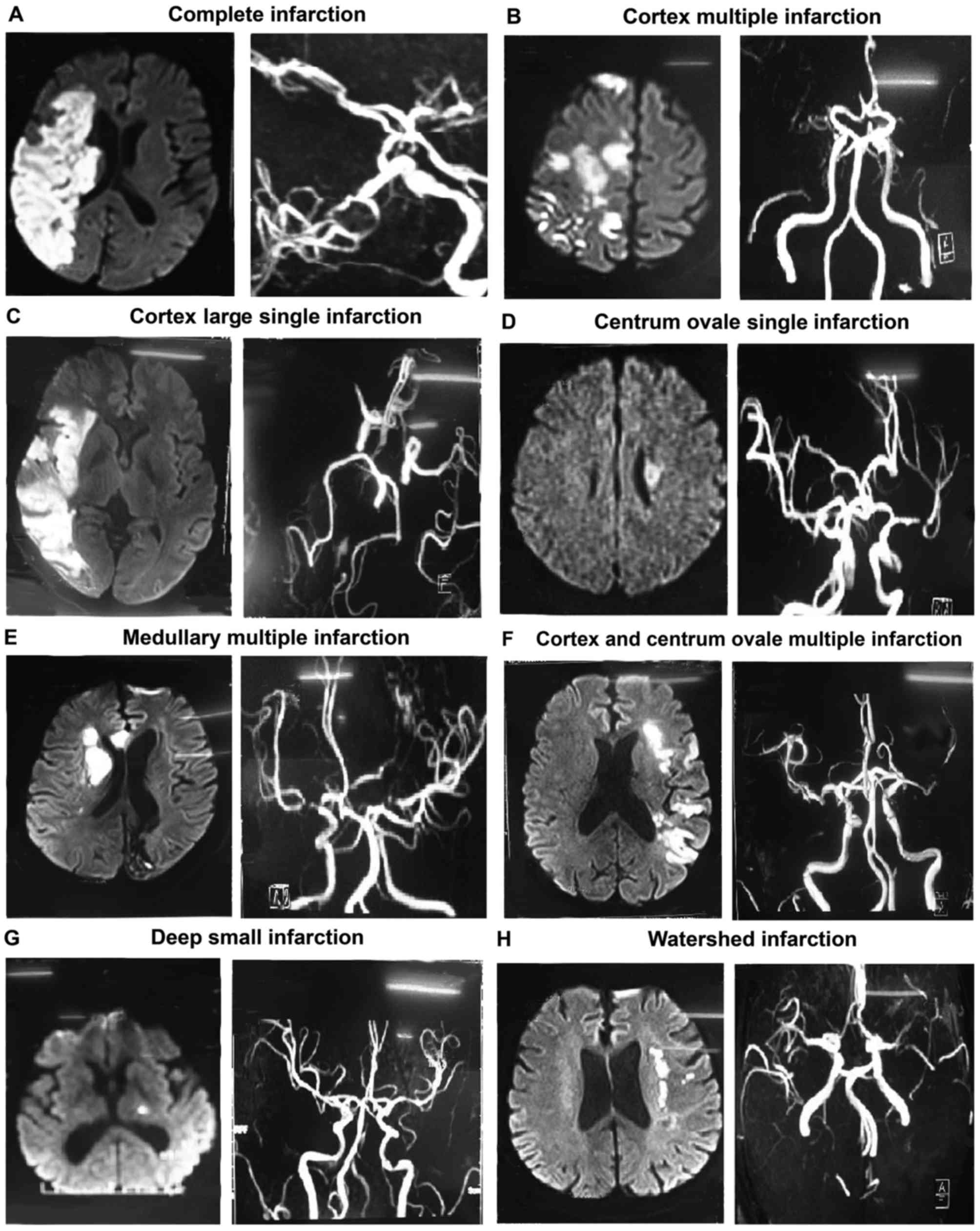
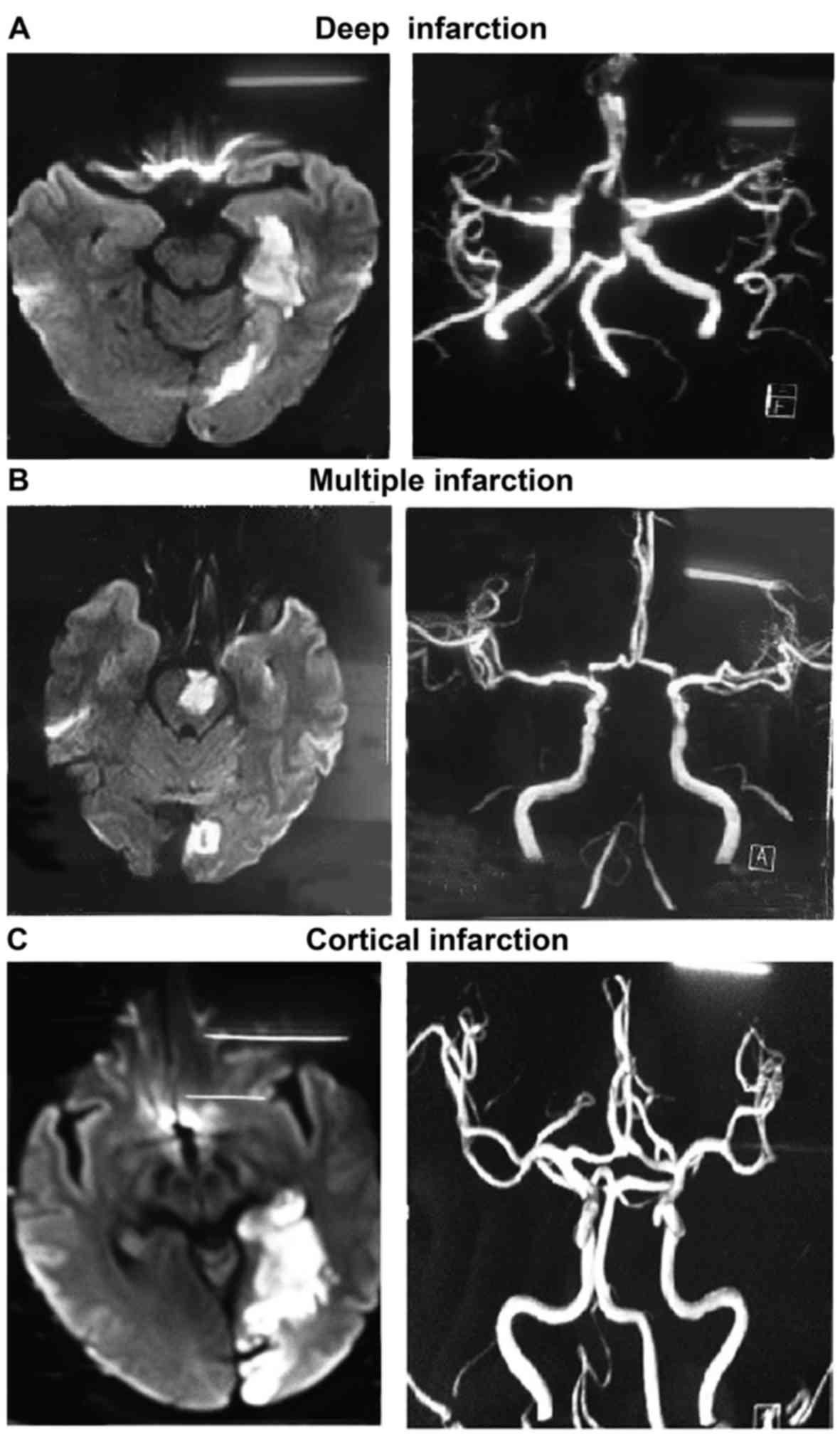
|
1
|
Ashrafi Ahmed SK, Suhail Z and Khambaty Y:
Postembolization infarction in juvenile nasopharyngeal
angiofibroma. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 21:115–116.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guidelines for secondary prevention of
ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack in China 2010. Chin J
Neurol. 43:154–160. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
3
|
Paciaroni M, Eliasziw M, Kappelle LJ,
Finan JW, Ferguson GG and Barnett HJ: Medical complications
associated with carotid endarterectomy. North American Symptomatic
Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET). Stroke. 30:1759–1763. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ferguson GG, Eliasziw M, Barr HW, Clagett
GP, Barnes RW, Wallace MC, Taylor DW, Haynes RB, Finan JW,
Hachinski VC and Barnett HJ: The North American symptomatic carotid
endarterectomy Trial: Surgical results in 1415 patients. Stroke.
30:1751–1758. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Koo J: The latest information on
intracranial atherosclerosis: Diagnosis and treatment. Interv
Neurol. 4:48–50. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yin P, Feng JC and Wang SC: Pathogenesis
of cerebral watershed infarction and the compensatory effect of
colleteral ability of the Willis circle. Chin J Cerebrovasc Dis.
5:102–106. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
7
|
Ma G, Jiang Z, He J, Liao Y, Zhu M, Huang
Z and Cui F: The value of DSA and CTA for diagnosis of carotid
artery stenosis. Clin Med Eng. 22:535–536. 2015.(In Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Khan M, Naqri L, Bansari A and Kamal AK:
Intracranial atherosclerotic disease. Stroke Res Treat.
2011:2828452011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Deng X, Liu W, Liu J and Zhong L: A study
of MRA for the diagnosis of occlusive and stenotic disorders of
intracranial arteries in ischemic cerebral vascular disease. J
Pract Med Tech. 14:1968–1970. 2007.
|
|
10
|
Qiu CC, Lu H, Wu Q and Yu JY:
Retrospective analysis of clinical value of early diagnosis in
brainstem infarction by magnetic resonance imaging characteristics
with MRI and DWI. Chin J Trauma Disabil Med. 21:22–24. 2013.(In
Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Wu CH and Liu B: The fourth Chinese
academic conference on cerebrovascular disease. Chin Med News.
4:1996.
|
|
12
|
Chen H, Hong H, Liu D, Xu G, Wang Y, Zeng
J, Zhang R and Liu X: Lesion patterns and mechanism of cerebral
infarction caused by severe atherosclerotic intracranial internal
carotid artery stenosis. J Neurol Sci. 307:79–85. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kang DW, Chu K, Ko SB, Kwon SJ, Yoon BW
and Roh JK: Lesion patterns and mechanism of ischemia in internal
carotid artery disease: A diffusion-weighted imaging study. Arch
Neurol. 59:1577–1582. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tatu L, Moulin T, Bogousslavsky J and
Duvernoy H: Arterial territories of the human brain: Cerebral
hemispheres. Neurology. 50:1699–1708. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu JY, Wei JH and Wang JR: Stroke pattern
analysis in patients with middle cerebral artery occlusive disease.
J Apoplexy Nerv Dis. 22:246–247. 2005.
|
|
16
|
Niizuma K, Shimizu H, Takada S and
Tominaga T: Middle cerebral artery plaque imaging using 3-Tesla
high-resolution MRI. J Clin Neurosci. 15:1137–1141. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bang OY, Heo JH, Kim JY, Park JH and Huh
K: Middle cerebral artery stenosis is a major clinical determinant
in striatocapsular small, deep infarction. Arch Neurol. 59:259–263.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wong KS, Gao S, Chan YL, Hansberg T, Lam
WW, Droste DW, Kay R and Ringelstein EB: Mechanisms of acute
cerebral infarctions in patients with middle cerebral artery
stenosis: A diffusion-weighted imaging and microemboli monitoring
study. Ann Neurol. 52:74–81. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li HF, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Pan XD, Zhao HQ
and Li H: Clinical and neuroradiological features of internal
watershed infarction and the occlusive diseases of carotid artery
system. Neurol Res. 32:1090–1096. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hallevi H, Chernyshev OY, EI khoury R,
Soileau MJ, Walker KC, Grotta JC and Savitz SI: Intracranial
atherosclerosis is associated with progression of neurological
deficit in subcortical stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis. 33:64–68. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Qiao Y, Liu L and Dong ZJ: The subtype of
watershed infarction and the internalcarotid artery/middle cerebral
artery steno-occlusion. Inner Mongolia Med J. 46:1427–1429.
2014.
|
|
22
|
Tan H and Yang Zhi: Types of infarction in
patients with different degrees of middle cerebral artery stenosis
and occlusion. Chin J Nervous Mental Dis. 36:427–429. 2010.
|
|
23
|
Masuda J: A pathologic study of carotid
artery disease as an embolicsource. Jpn J Stroke. 23:347–350. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gao S, Huang J, Huang Y and Li S:
Infarction pathogenesis of atherosclerotic middle cerebral artery
stenosis. Chin J Neurol. 36:155–157. 2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Shi MC, Wang SC, Zhou HW, Xing YQ, Cheng
YH, Feng JC and Wu J: Compensatory remodeling in symptomatic middle
cerebral atherosclerotic stenosis: A high-resolution MRI and
microemboli monitoring study. Neurol Res. 34:153–158.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ryoo S, Park JH, Kim SJ, Kim GM, Chung CS,
Lee KH, Kim JS and Bang OY: Branch occlusive disease: Clinical and
magnetic resonance angiography findings. Neurology. 78:888–896.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Katakami N, Takahara M, Kaneto H, Shimizu
I, Ohno K, Ishibashi F, Osonoi T, Kashiwagi A, Kawamori R,
Shimomura I, et al: Accumulation of gene polymorphisms related to
plaque disruption and thrombosis is associated with cerebral
infarction in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care.
33:390–395. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Caplan LR: Intracranial branch
atheromatous disease: A neglected, understudied, and underused
concept. Neurology. 39:1246–1250. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|