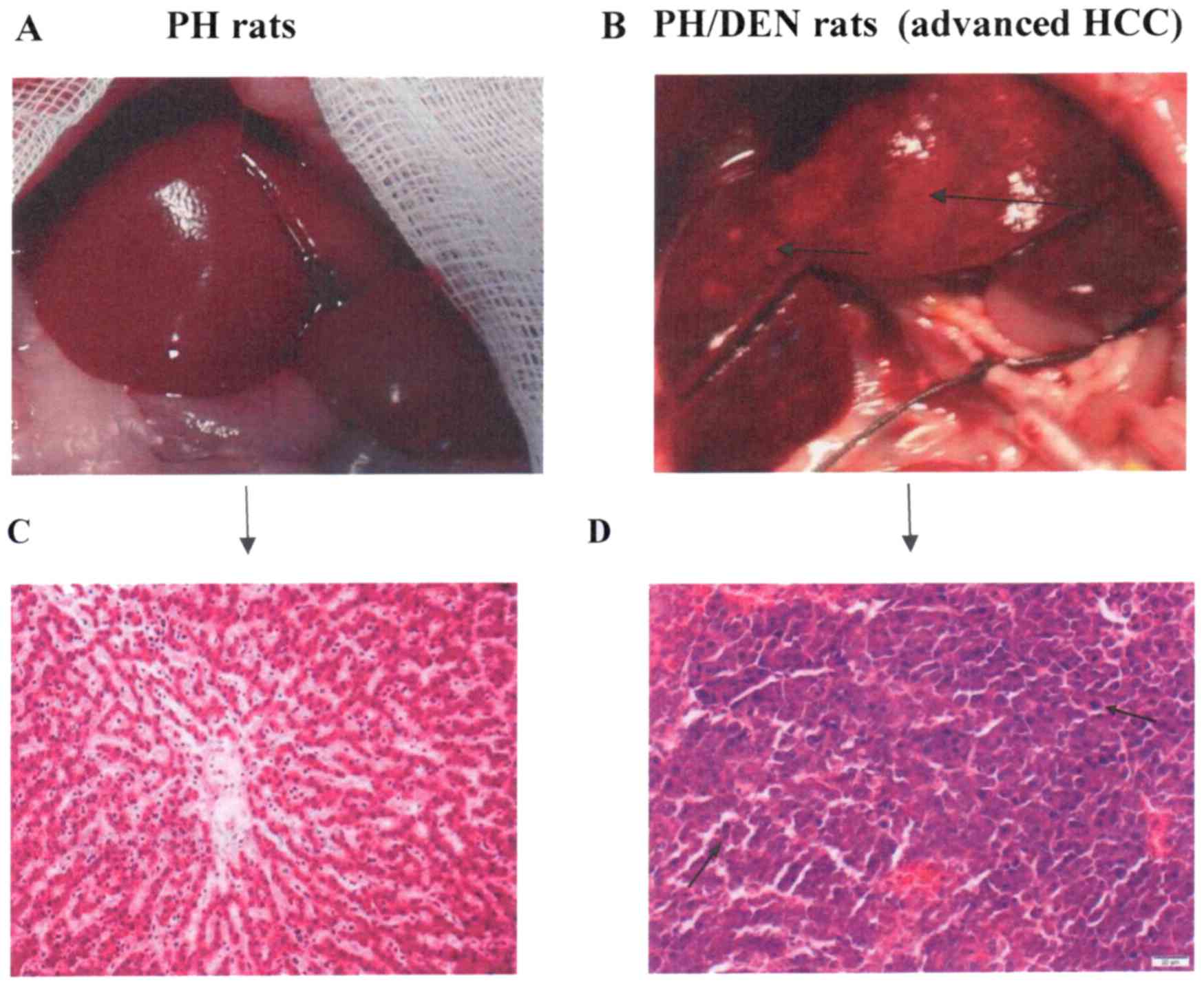
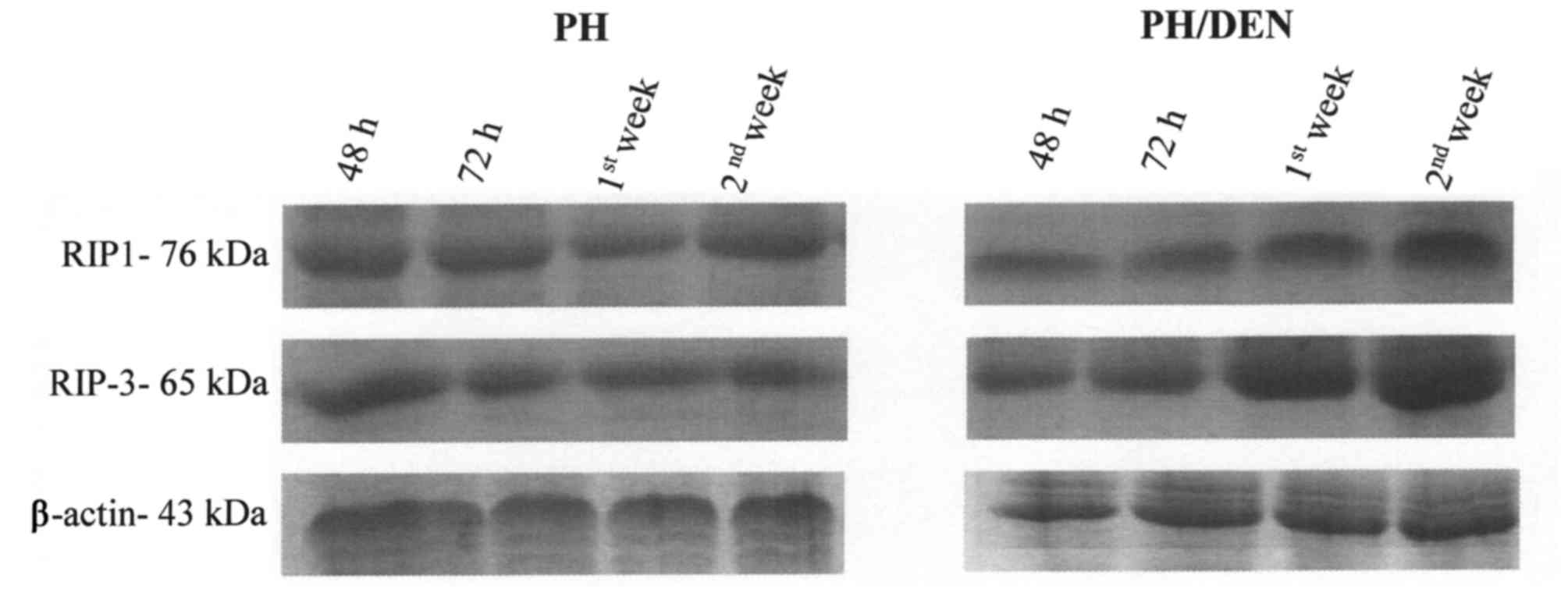
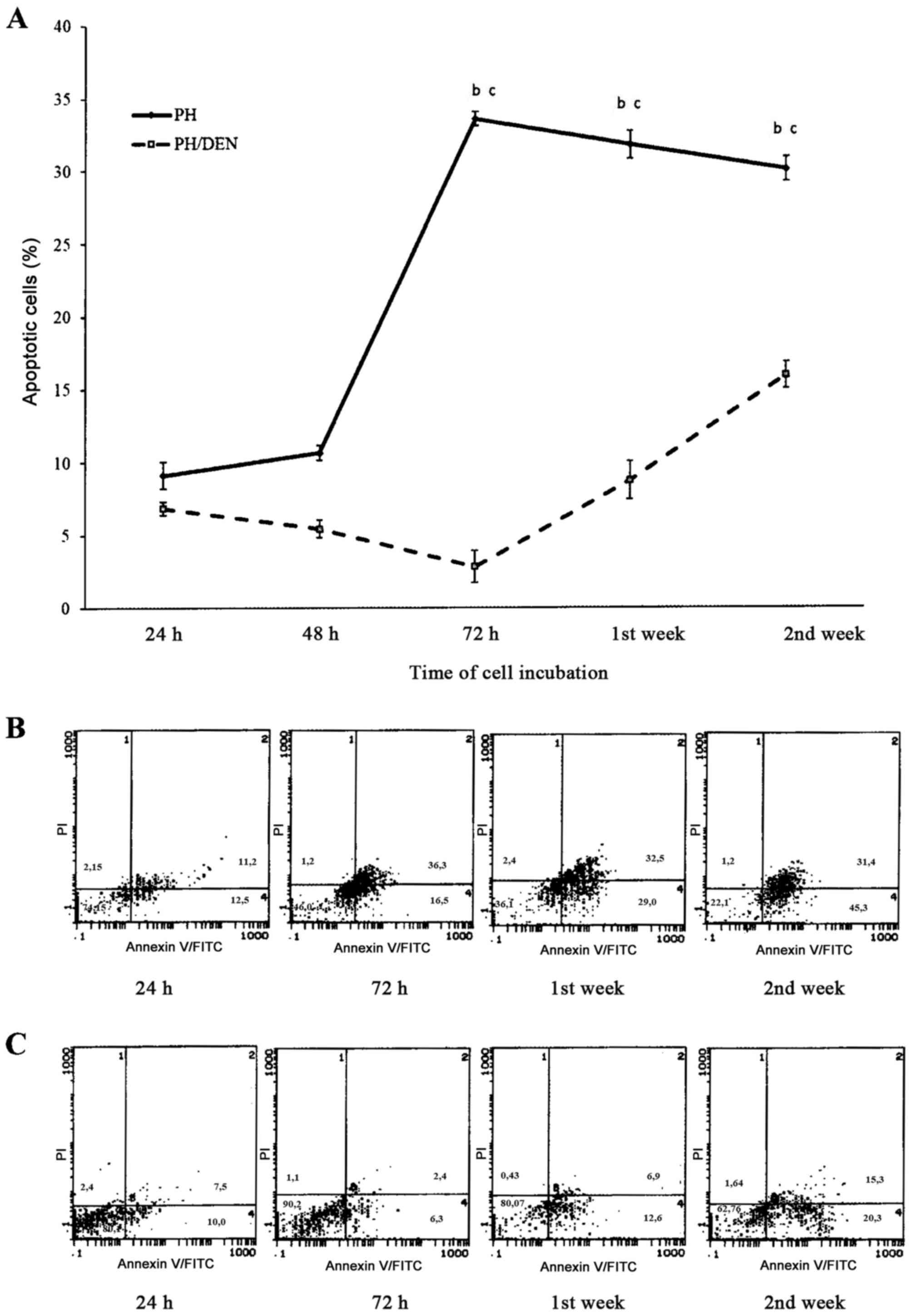
|
1
|
Schlageter M, Terracciano LM, D'Angelo S
and Sorrentino P: Histopatholgy of hepatocellular carcinoma. World
J Gastroenterol. 20:15955–15964. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zou C, Zhang H, Li Q, Xiao H, Yu L, Ke S,
Zhou L, Liu W, Wang W, Huang H, et al: Heme-oxygenase-1: A
molecular brake on hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration.
Carcinogenesis. 32:1840–1848. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee KP, Lee JH, Kim TS, Park HD, Byun JS,
Kim MC, Jeong WI, Calvisi DF, Kim JM and Lim DS: The Hippo-Salvador
pathway restrains hepatic oval cell proliferation, liver size, and
liver tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:8248–8253. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wójcik M, Bobowiec R and Martelli F:
Effect of carotenoids on in vitro proliferation and differentiation
of oval cells during neoplastic and non-neoplastic liver injures in
rats. J Physiol Pharmacol. 59 Suppl 2:S203–S213. 2008.
|
|
5
|
Zheng T, Wang J, Jiang H and Liu L: Hippo
signalling in oval cells and hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Lett.
302:91–99. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jin J, Jin X, Qian C, Ruan Y and Jiang H:
Signaling network of OSW-1-induced apoptosis and necroptosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 7:1646–1650. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fulda S: The mechanism of necroptosis in
normal and cancer cell. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:999–1004. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jouan-Lanhouet S, Riquet F, Duprez L,
Vanden Berhe T, Takahashi N and Vandenabeele P: Necroptosis, in
vivo detection in experimental disease models. Semin Cell Devel
Biol. 35:2–13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Schattenberg JM, Schumann M and Galle PR:
Cell death and hepatocarcinogenesis: Dysregulation of apoptosis
signaling pathways. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26 Suppl 1:S213–S219.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hu X, Han W and Li L: Targeting the weak
point of cancer by induction of necroptosis. Autophagy. 3:490–492.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jiang L, Kon N, Li T, Wang SJ, Su T,
Hibshoosh H, Baer R and Gu W: Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated
activity during tumor suppression. Nature. 520:57–62. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He S, Wang L, Miao L, Wang T, Du F, Zhao L
and Wang X: Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines
cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha. Cell. 137:1100–1111. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vandenabeele P, Galluzi L, Vanden Berghe T
and Kroemer G: Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis: An ordered
cellular explosion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 11:700–714. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fulda S: Therapeutic exploitation of
necroptosis for cancer therapy. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 35:51–56.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Saeed WK and Jun DW: Necroptosis: An
emerging type of cell death in liver diseases. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:12526–12532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Solt D and Farber E: New principle for the
analysis of chemical carcinogenesis. Narure. 263:701–703. 1976.
|
|
17
|
Higgins G and Anderson G: Experimental
pathology of the liver restoration of the liver of the white rat
following partial surgical removal. Arch Pathol (Chic). 12:186–202.
1931.
|
|
18
|
Shupe TD, Piscaglia AC, Oh SH, Gasbarrini
A and Petersen BE: Isolation and characterization of hepatic stem
cells, or ‘oval cells,’ from rat livers. Method Mol Biol.
482:387–405. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
He ZP, Tan WQ, Tang YF, Zhang HJ and Feng
MF: Activation, isolation, identification and in vitro
proliferation of oval cells from adult rat livers. Cell Prolif.
37:177–187. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Strober W: Trypan blue exclusion test of
cell viability. Curr Protoc Immunol. 21:3B:A.3B.1–A.3B.2. 2001.
|
|
21
|
Head KW, Cullen JM, Dubielzig RR, Else RW,
Misdorp W, Patnaik AK, Tateyama S and Van Der Gaag I: Histological
Classification of Tumors of the Alimentary System of Domestic
AnimalsSecond Series. WHO, Armed Forces Institute of Pathology;
Washington, DC: 2003
|
|
22
|
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J
Biol Chem. 193:265–275. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wójcik M, Bobowiec R, Lisiecka U and
Kostro K: Proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis of choline
deficient ethionine supplemented diet-rat oval cells under the
influence of 2-methoxyestradiol. J Physiol Pharmacol. 63:669–676.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wójcik M, Wessely-Szponder J and
Kosior-Korzecka U: Proliferative and oxidative response of
hepatocytes (Hep) and hepatic stellate cells (HSC) isolated from
rats exposed to ketogenic diet. Pol J Vet Sci. 17:703–711. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kearney CJ, Cullen SP, Clancy D and Martin
SJ: RIPK1 can function as an inhibitor rather than an initiator of
PIPK3-dependent necroptosis. FEBS J. 281:4921–4934. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Upton JW, Kaiser WJ and Mocarski ES:
DAI/ZBP1/DLM-1 complexes with RIP3 to mediate virus-induced
programmed necrosis that is targeted by murine cytomegalovirus
VIRA. Cell Host Microbe. 15:290–297. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Christofferson DE and Yuan J: Necroptosis
as an alternative form of programmed cell death. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 22:263–268. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Declercq W, Vanden Berghe T and
Vandenabeele P: RIP kinase at the crossroads of cell death and
survival. Cell. 138:229–232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Newton K: RIPK1 and RIPK3: Critical
regulators of inflammation and cell death. Trends Cell Biol.
25:347–353. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou W and Yuan J: Necroptosis in health
and diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 35:14–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|