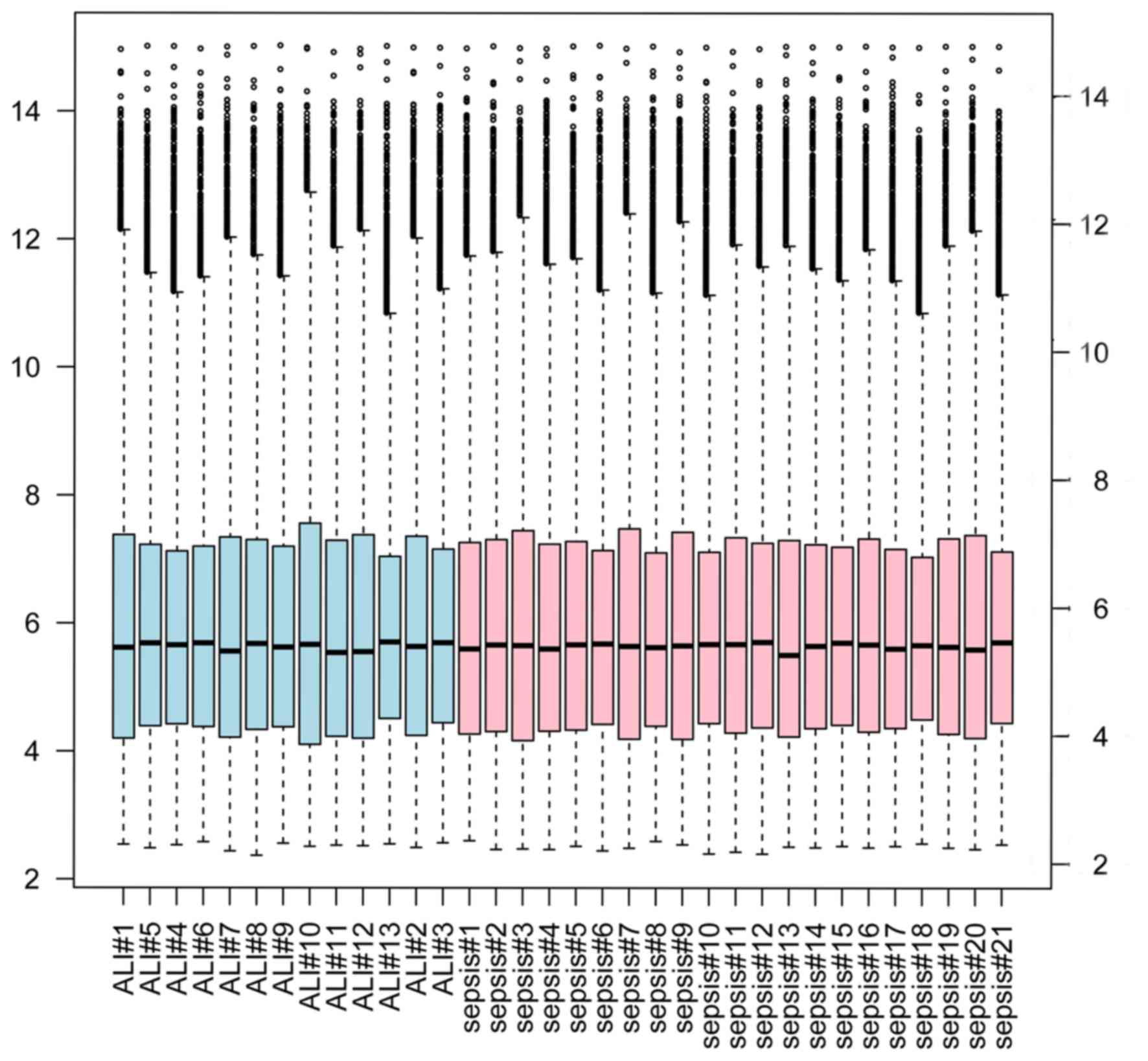
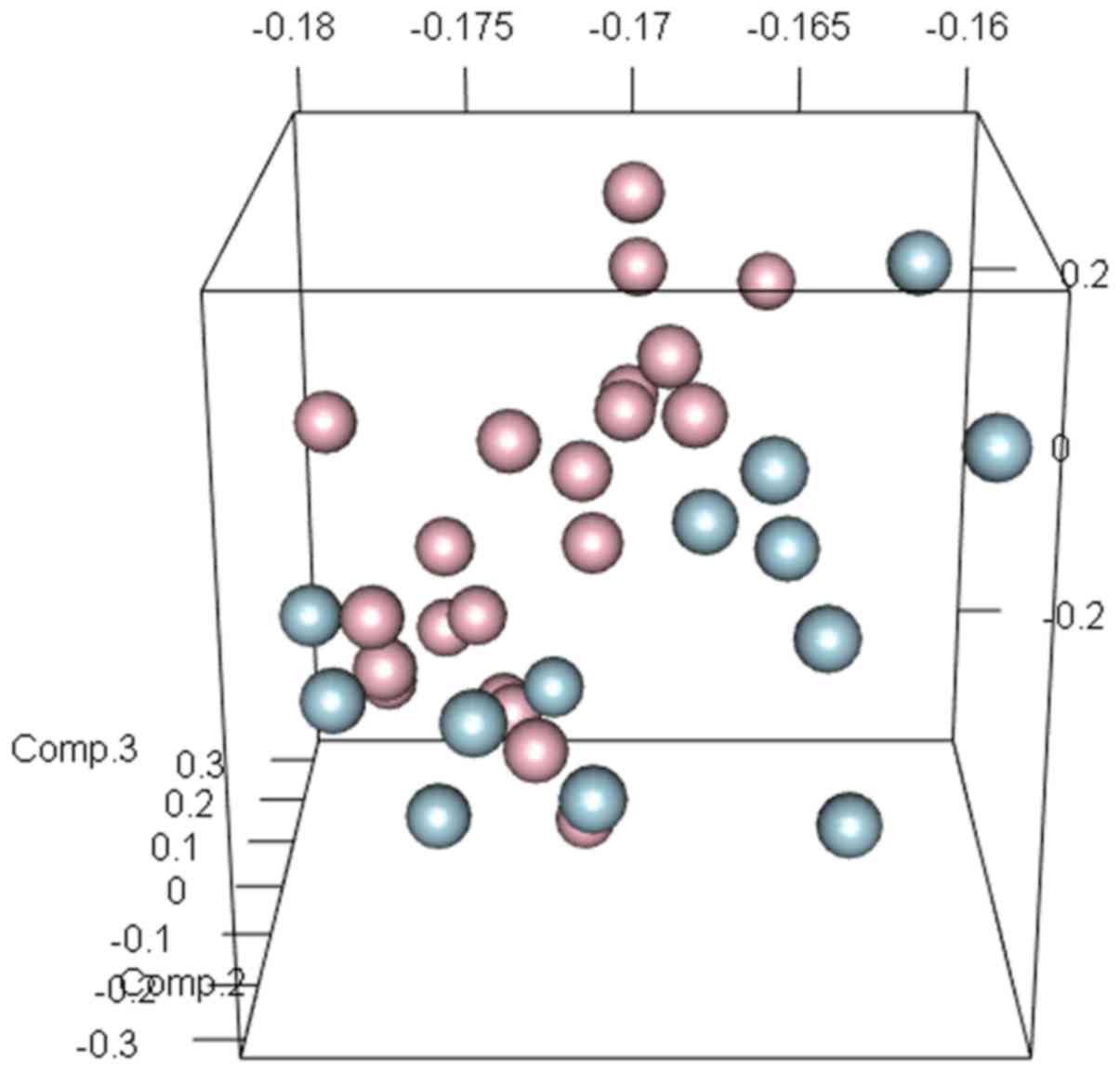
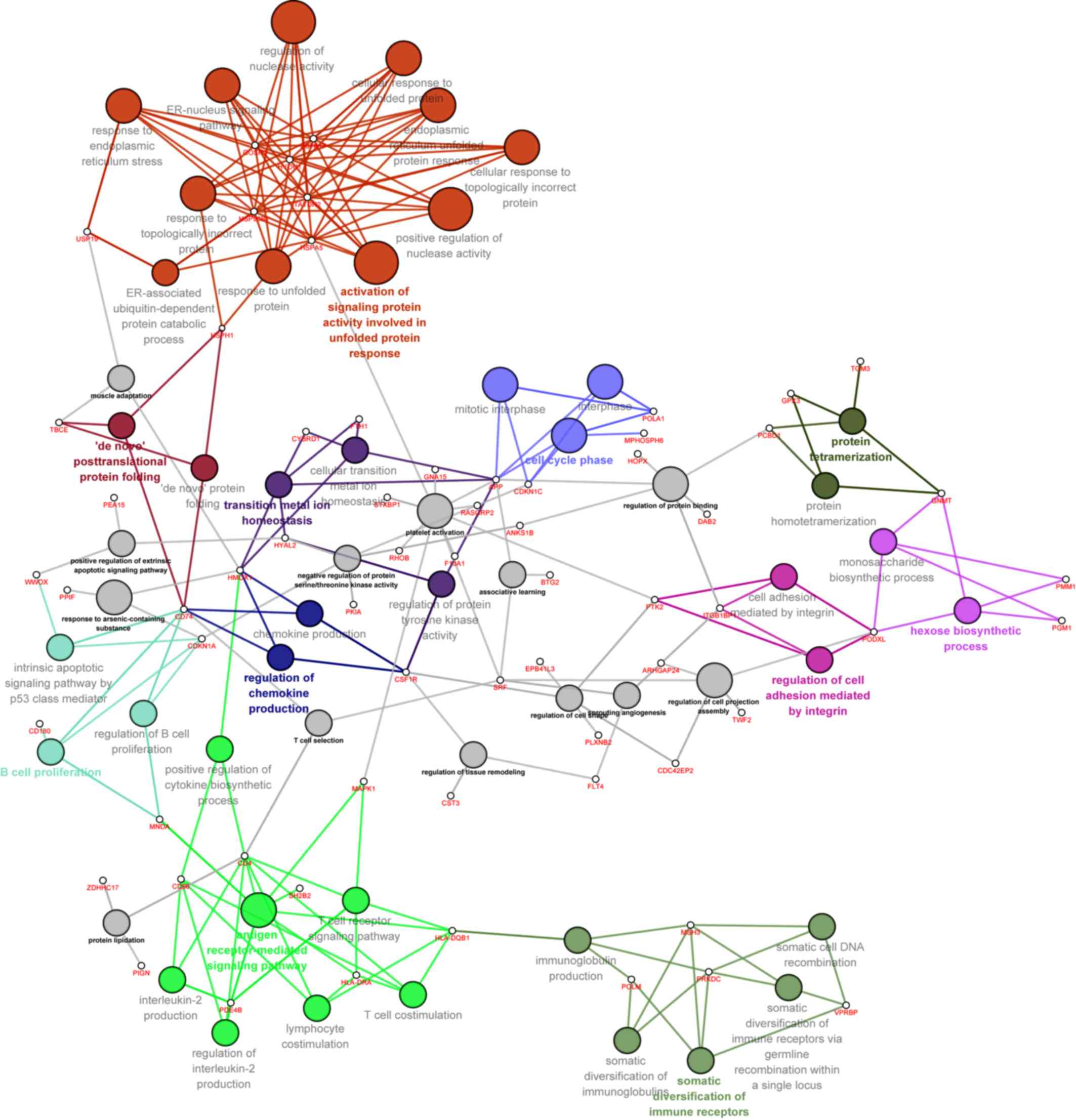
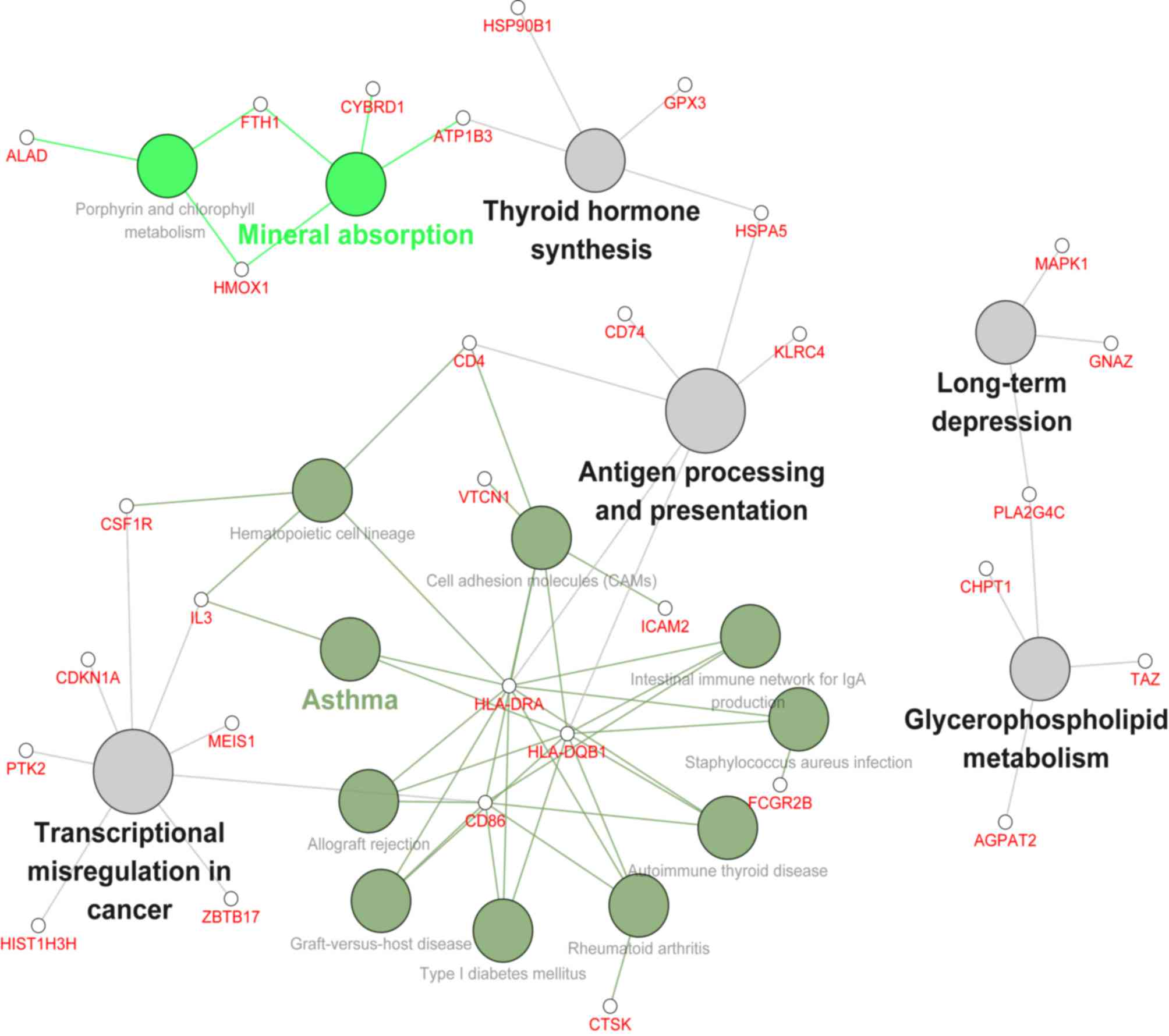
|
1
|
Jia Y, Chen K, Lin P, Lieber G, Nishi M,
Yan R, Wang Z, Yao Y, Li Y, Whitson BA, et al: Treatment of acute
lung injury by targeting MG53-mediated cell membrane repair. Nat
Commun. 5:43872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Memtsoudis SG, Bombardieri AM, Ma Y, Walz
JM, Chiu YL and Mazumdar M: Mortality of patients with respiratory
insufficiency and adult respiratory distress syndrome after surgery
the obesity paradox. J Intensive Care Med. 27:306–311. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Matthay MA, Ware LB and Zimmerman GA: The
acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest. 122:2731–2740.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Butt Y, Kurdowska A and Allen TC: Acute
lung injury: A clinical and molecular review. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
140:345–350. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Asaduzzaman M, Lavasani S, Rahman M, Zhang
S, Braun OO, Jeppsson B and Thorlacius H: Platelets support
pulmonary recruitment of neutrophils in abdominal sepsis. Crit Care
Med. 37:1389–1396. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sweeney RM, Griffiths M and Mcauley D:
Treatment of acute lung injury: current and emerging
pharmacological therapies. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 34:487–498.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dreyfuss D: Ventilation with lower tidal
volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung
injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med.
342:1301–1308. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guo Z, Zhao C and Wang Z: Gene expression
profiles analysis identifies key genes for acute lung injury in
patients with sepsis. Diagn Pathol. 9:1762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Howrylak JA, Dolinay T, Lucht L, Wang Z,
Christiani DC, Sethi JM, Xing EP, Donahoe MP and Choi AM: Discovery
of the gene signature for acute lung injury in patients with
sepsis. Physiol Genomics. 37:133–139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: Affy-analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Phipson B, Lee S, Majewski IJ, Alexander
WS and Smyth GK: Robust hyperparameter estimation protects against
hypervariable genes and improves power to detect differential
expression. Ann Appl Stat. 10:946–963. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H, Charoentong
P, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Fridman WH, Pagès F, Trajanoski Z and
Galon J: ClueGO: A Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally
grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks.
Bioinformatics. 25:1091–1093. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bindea G, Galon J and Mlecnik B: CluePedia
Cytoscape plugin: Pathway insights using integrated experimental
and in silico data. Bioinformatics. 29:661–663. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Maere S, Heymans K and Kuiper M: BiNGO: A
Cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of gene ontology
categories in biological networks. Bioinformatics. 21:3448–3449.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Griffith M, Griffith OL, Coffman AC,
Weible JV, McMichael JF, Spies NC, Koval J, Das I, Callaway MB,
Eldred JM, et al: DGIdb: Mining the druggable genome. Nat Methods.
10:1209–1210. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hu WC: Acute respiratory distress syndrome
is a TH17-like and Treg immune disease. Cornell University Library.
2013.https://arxiv.org/abs/1311.4384Nov 18–2013
|
|
18
|
Smits SL, van den Brand JM, de Lang A,
Leijten LM, van Ijcken WF, van Amerongen G, Osterhaus AD, Andeweg
AC and Haagmans BL: Distinct severe acute respiratory syndrome
coronavirus-induced acute lung injury pathways in two different
nonhuman primate species. J Virol. 85:4234–4245. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meduri GU, Annane D, Chrousos GP, Marik PE
and Sinclair SE: Activation and regulation of systemic inflammation
in ARDS: Rationale for prolonged glucocorticoid therapy. Chest.
136:1631–1643. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schneider A, Peukert K, Eilers M and Hänel
F: Association of Myc with the zinc-finger protein Miz-1 defines a
novel pathway for gene regulation by MycC-Myc in B-Cell Neoplasia.
Springer; New York, NY: pp. 137–146. 1997, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Staller P, Peukert K, Kiermaier A, Seoane
J, Lukas J, Karsunky H, Möröy T, Bartek J, Massagué J, Hänel F and
Eilers M: Repression of p15INK4b expression by Myc through
association with Miz-1. Nat Cell Biol. 3:392–399. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Möröy T, Saba I and Kosan C: The role of
the transcription factor Miz-1 in lymphocyte development and
lymphomagenesis-Binding Myc makes the difference. Semin Immunol.
23:379–387. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee SU and Maeda T: POK/ZBTB proteins: An
emerging family of proteins that regulate lymphoid development and
function. Immunol Rev. 247:107–119. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Verdaasdonk JS and Bloom K: Centromeres:
Unique chromatin structures that drive chromosome segregation. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:320–332. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guillet V, Knibiehler M, Gregory-Pauron L,
Remy MH, Chemin C, Raynaud-Messina B, Bon C, Kollman JM, Agard DA,
Merdes A and Mourey L: Crystal structure of γ-tubulin complex
protein GCP4 provides insight into microtubule nucleation. Nat
Struct Mol Biol. 18:915–919. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ducat D, Kawaguchi S, Liu H, Yates JR III
and Zheng Y: Regulation of microtubule assembly and organization in
mitosis by the AAA+ ATPase pontin. Mol Biol Cell. 19:3097–3110.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang X and Zhao YY: Transgenic expression
of FoxM1 promotes endothelial repair following lung injury induced
by polymicrobial sepsis in mice. PLoS One. 7:e500942012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
David Y, Ziv T, Admon A and Navon A: The
E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes direct polyubiquitination to
preferred lysines. J Biol Chem. 285:8595–8604. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hetz C: The unfolded protein response:
Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 13:89–102. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hendershot LM, Valentine VA, Lee AS,
Morris SW and Shapiro DN: Localization of the gene encoding human
BiP/GRP78, the endoplasmic reticulum cognate of the HSP70 family,
to chromosome 9q34. Genomics. 20:281–284. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pizzo P, Scapin C, Vitadello M, Florean C
and Gorza L: Grp94 acts as a mediator of curcumin-induced
antioxidant defence in myogenic cells. J Cell Mol Med. 14:970–981.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Omikorede O: The role of ER stress and the
unfolded protein response in obesity associated type 2 diabetes.
University of Leicester. 2012.
|
|
33
|
Lowe SL, Peter F, Subramaniam VN, Wong SH
and Hong W: A SNARE involved in protein transport through the Golgi
apparatus. Nature. 389:881–884. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moschos CB, Lahiri K, Lyons M, Weisse AB,
Oldewurtel HA and Regan TJ: Relation of microcirculatory thrombosis
to thrombus in the proximal coronary artery: Effect of aspirin,
dipyridamole and thrombolysis. Am Heart J. 86:61–68. 1973.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Das UN: Is insulin an antiinflammatory
molecule? Nutrition. 17:409–413. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee JS: Cytokine-mediated inflammation in
acute lung injury. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 14:523–535. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kremer JM, Dougados M, Emery P, Durez P,
Sibilia J, Shergy W, Steinfeld S, Tindall E, Becker JC, Li T, et
al: Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with the selective
costimulation modulator abatacept: Twelve-month results of a phase
IIb, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis
Rheum. 52:2263–2271. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|