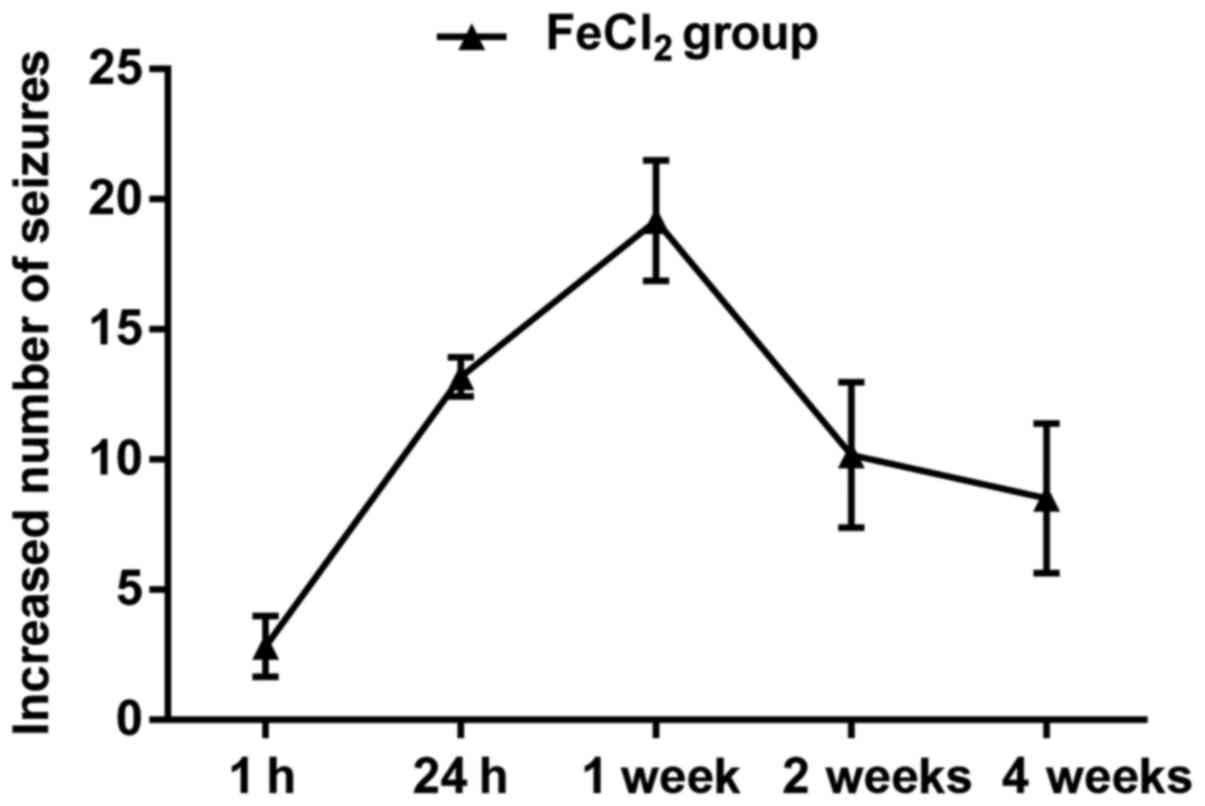
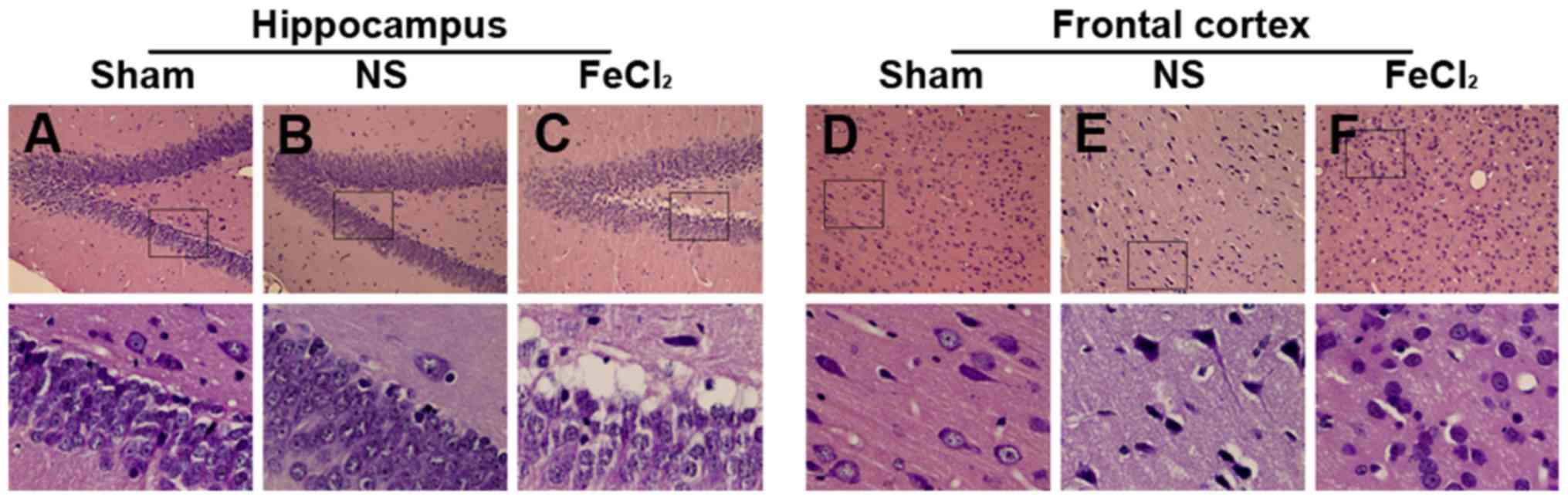
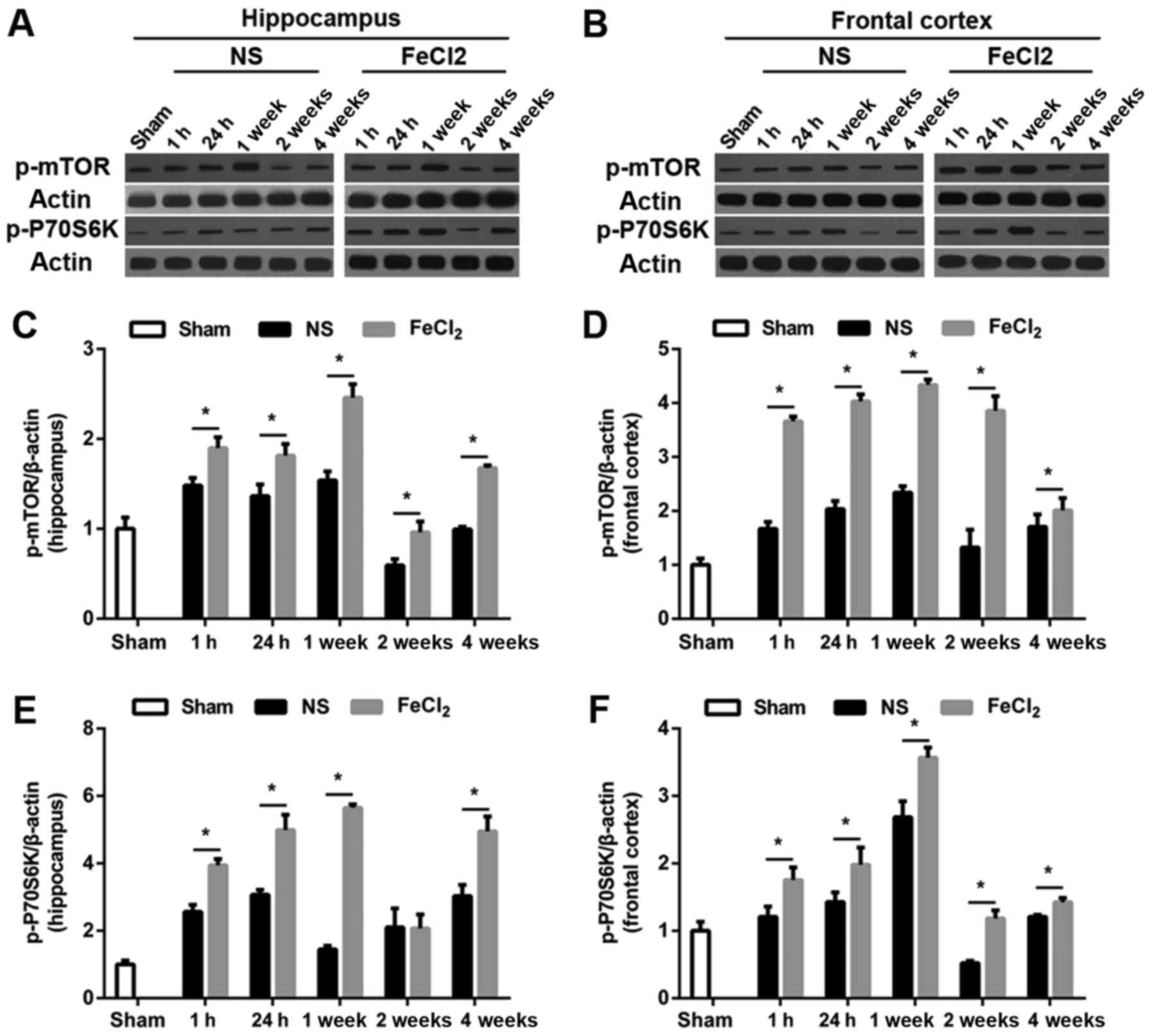
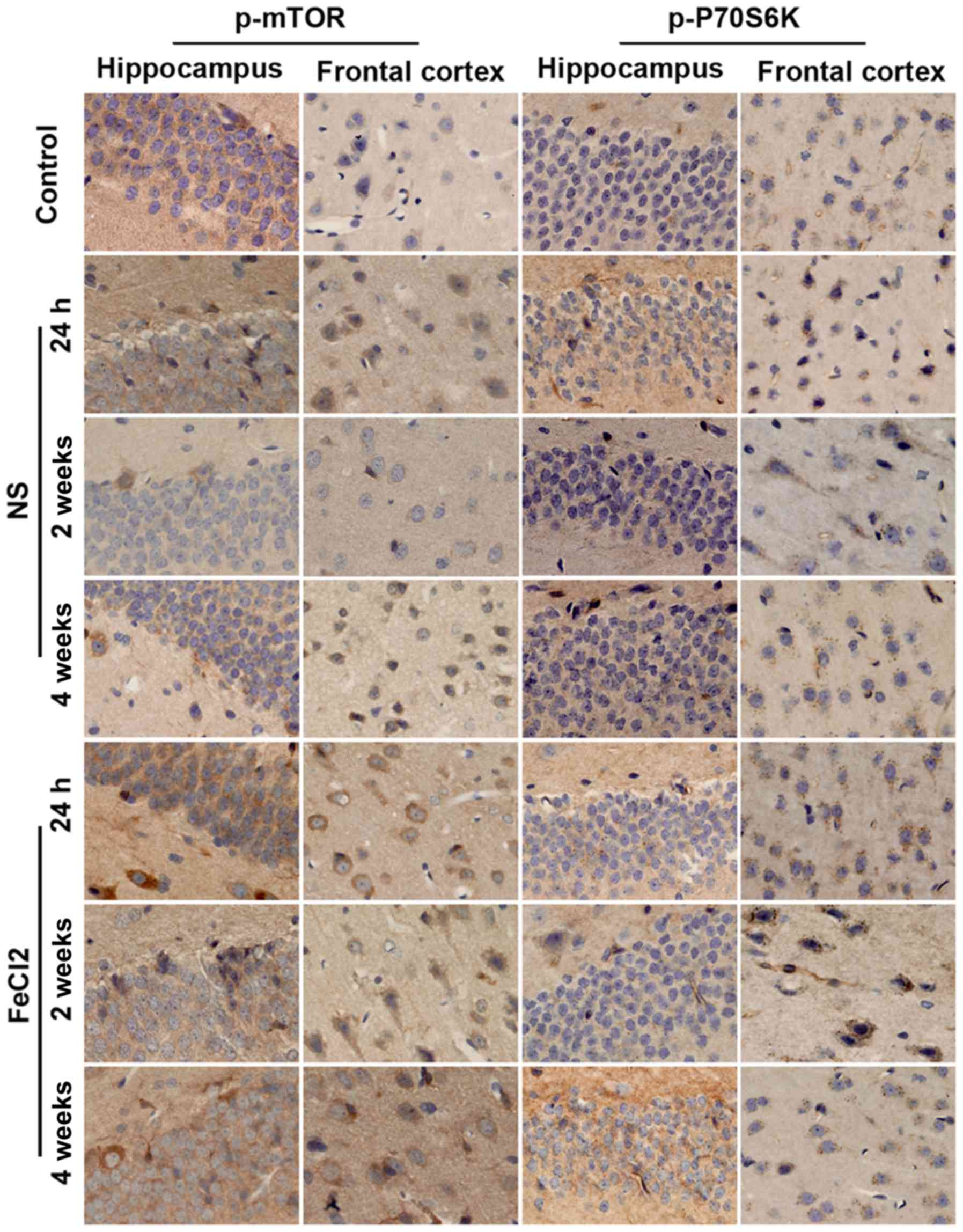
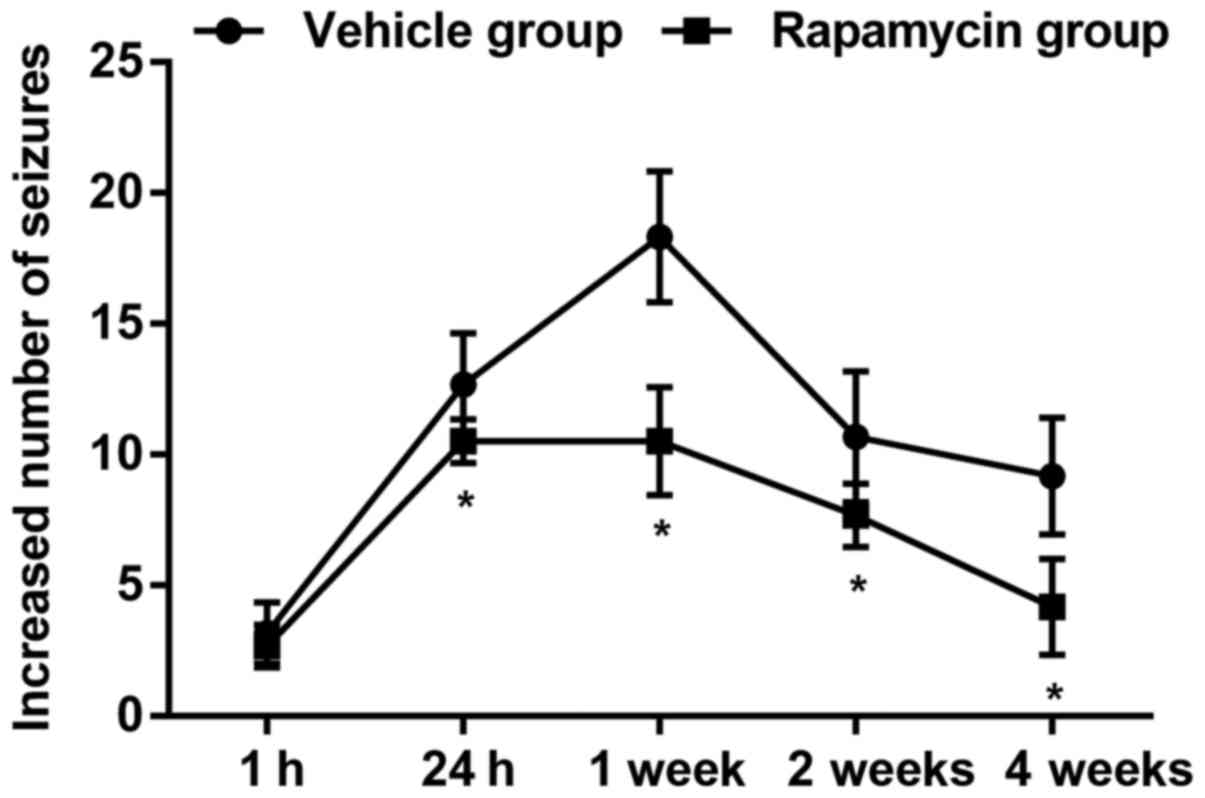
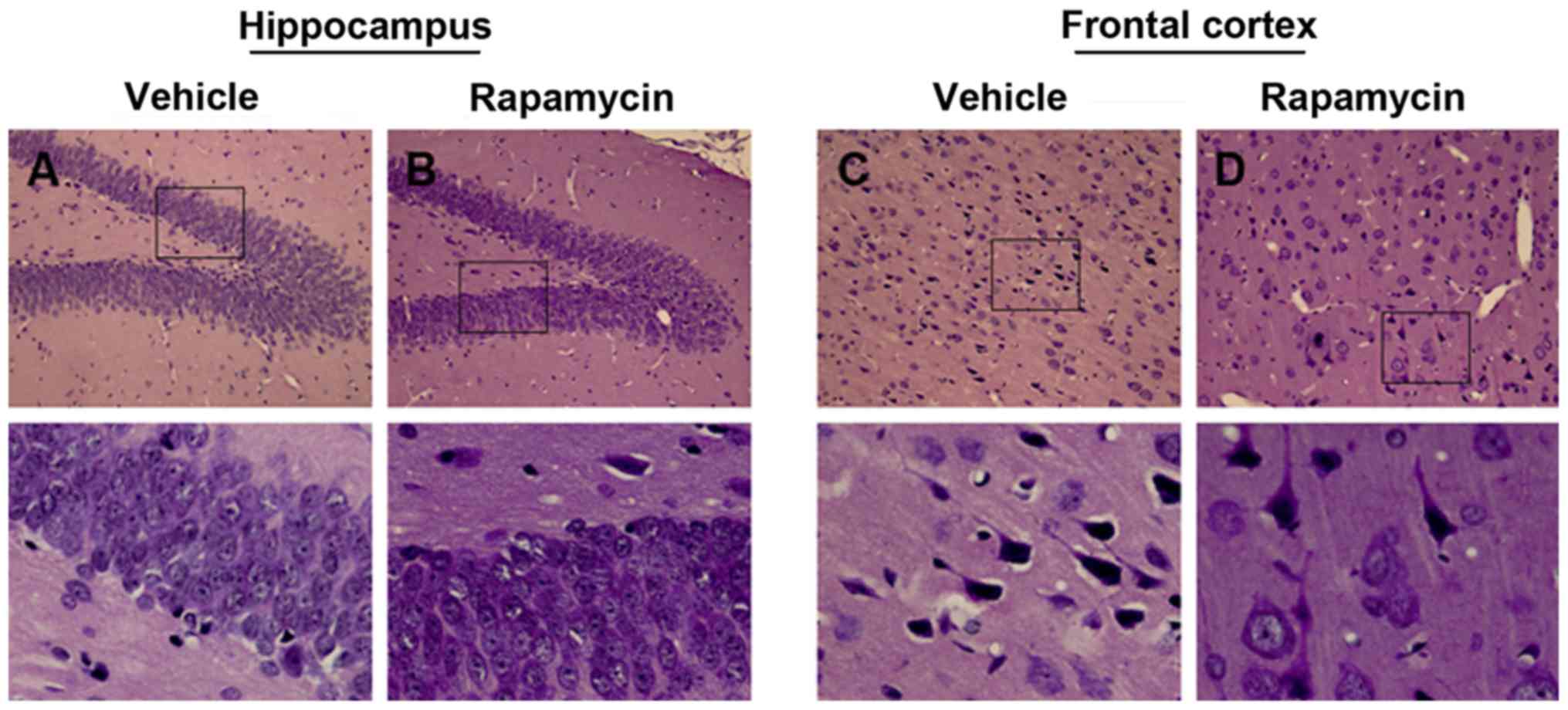
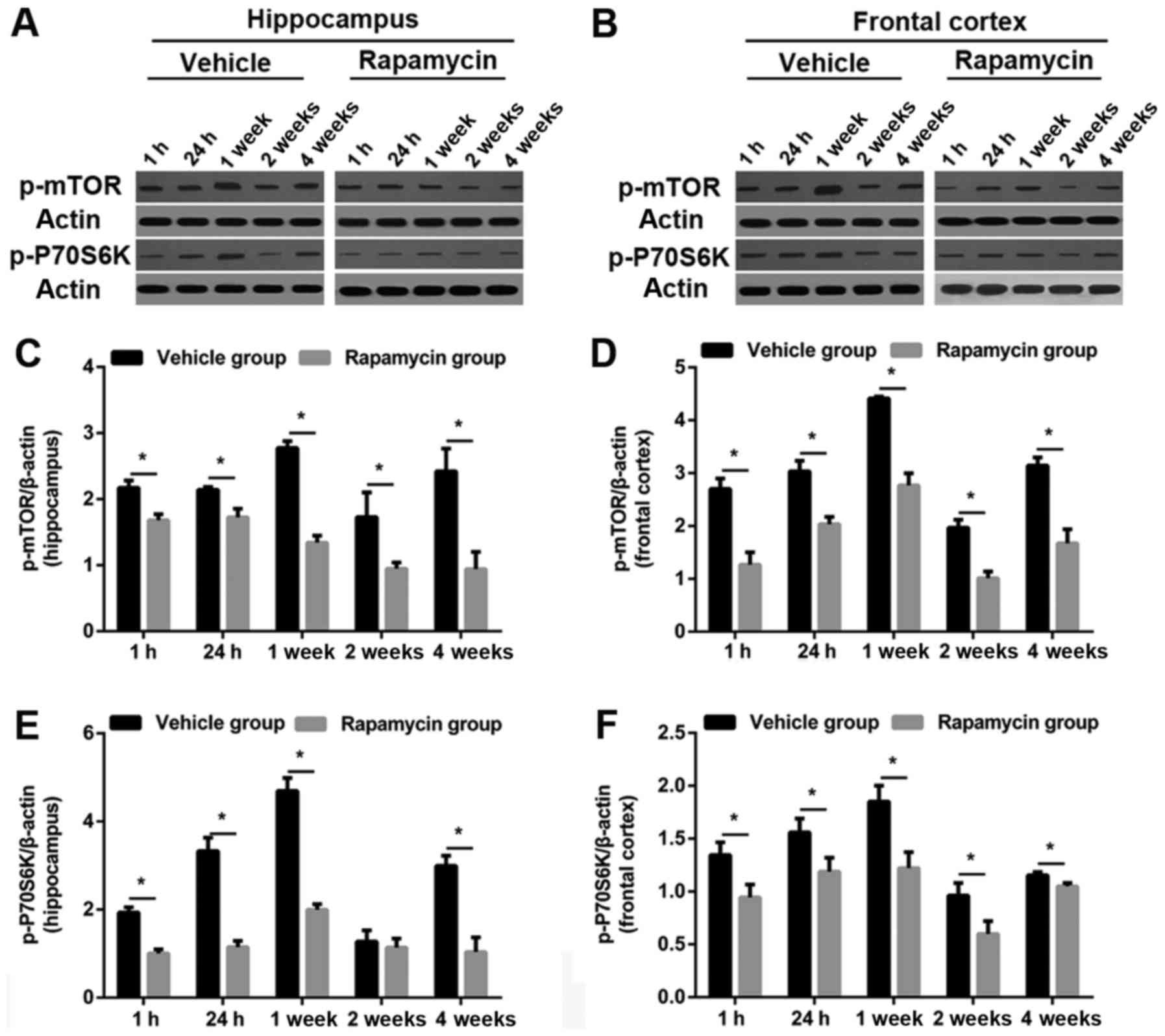
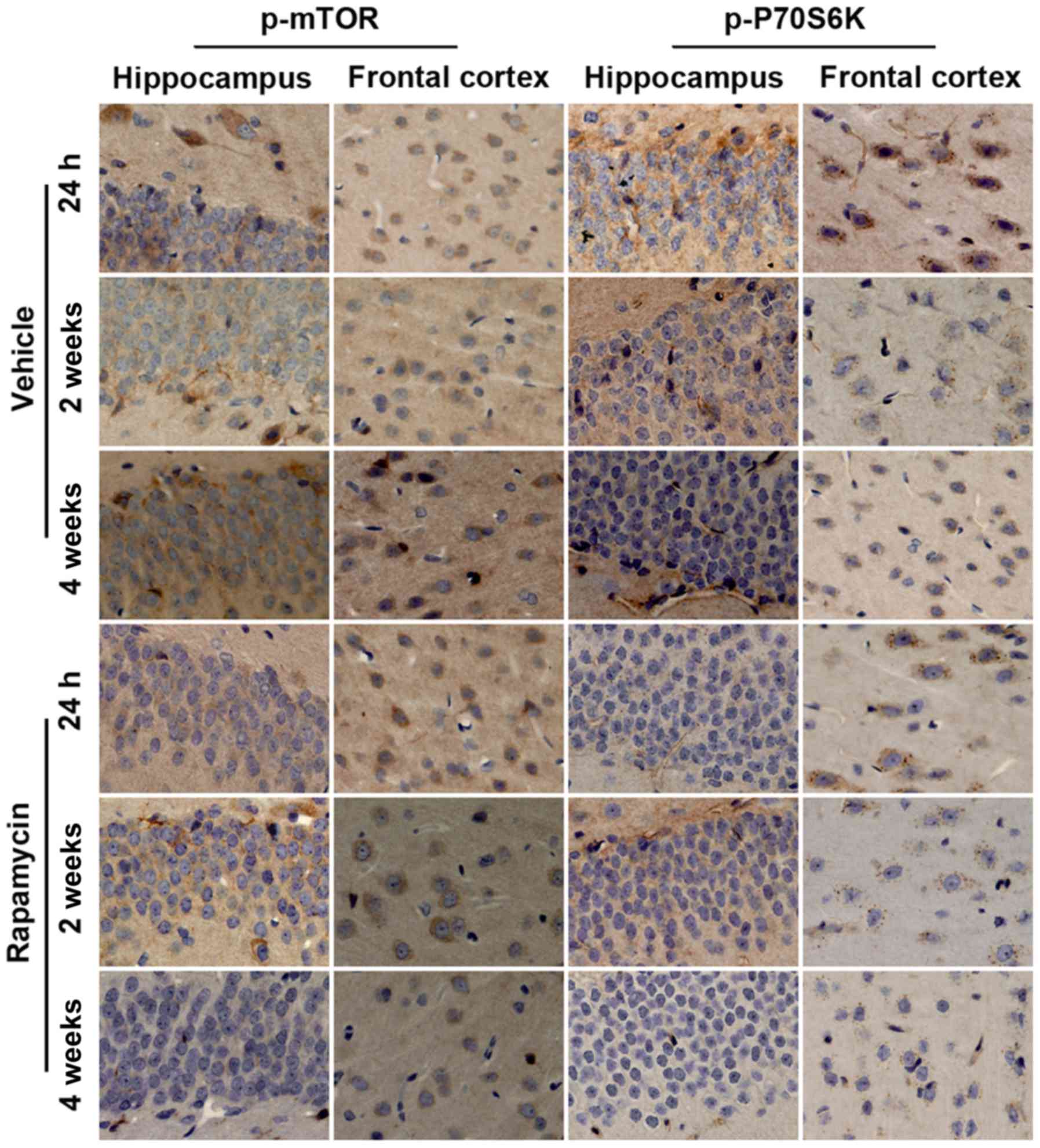
|
1
|
Gupta PK, Sayed N, Ding K, Agostini MA,
Van Ness PC, Yablon S, Madden C, Mickey B, D'Ambrosio R and
Diaz-Arrastia R: Subtypes of post-traumatic epilepsy: Clinical,
electrophysiological, and imaging features. J Neurotrauma.
31:1439–1443. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bhuyan P, Patel DC, Wilcox KS and Patel M:
Oxidative stress in murine Theiler's virus-induced temporal lobe
epilepsy. Exp Neurol. 271:329–334. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Irimia A and Van Horn JD: Epileptogenic
focus localization in treatment-resistant post-traumatic epilepsy.
J Clin Neurosci. 22:627–631. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Christensen J, Pedersen MG, Pedersen CB,
Sidenius P, Olsen J and Vestergaard M: Long-term risk of epilepsy
after traumatic brain injury in children and young adults: A
population-based cohort study. Lancet. 373:1105–1110. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
in growth control and disease. Cell. 149:274–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wong M: Mammalian target of rapamycin
(mTOR) pathways in neurological diseases. Biomed J. 36:40–50. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cho CH: Frontier of epilepsy research-mTOR
signaling pathway. Exp Mol Med. 43:231–274. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Crino PB: The mTOR signalling cascade:
Paving new roads to cure neurological disease. Nat Rev Neurol.
12:379–392. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nguyen LH, Brewster AL, Clark ME,
Regnier-Golanov A, Sunnen CN, Patil VV, D'Arcangelo G and Anderson
AE: mTOR inhibition suppresses established epilepsy in a mouse
model of cortical dysplasia. Epilepsia. 56:636–646. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sha LZ, Xing XL, Zhang D, Yao Y, Dou WC,
Jin LR, Wu LW and Xu Q: Mapping the spatio-temporal pattern of the
mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) activation in temporal lobe
epilepsy. PLoS One. 7:e391522012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu P, Yang X, Hei C, Meli Y, Niu J, Sun T
and Li PA: Rapamycin reduced ischemic brain damage in diabetic
animals is associated with suppressions of mTOR and ERK1/2
Signaling. Int J Biol Sci. 12:1032–1040. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Berdichevsky Y, Dryer AM, Saponjian Y,
Mahoney MM, Pimentel CA, Lucini CA, Usenovic M and Staley KJ:
PI3K-Akt signaling activates mTOR-mediated epileptogenesis in
organotypic hippocampal culture model of post-traumatic epilepsy. J
Neurosci. 33:9056–9067. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sancho-Rieger J and Parra-Martinez J:
Preventive and therapeutic attitude in post-traumatic epileptic
seizures. Rev Neurol. 35 Suppl 1:S39–S42. 2002.(In Spanish).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Talos DM, Sun H, Zhou X, Fitzgerald EC,
Jackson MC, Klein PM, Lan VJ, Joseph A and Jensen FE: The
interaction between early life epilepsy and autistic-like
behavioral consequences: A role for the mammalian target of
rapamycin (mTOR) pathway. PLoS One. 7:e358852012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Galanopoulou AS, Gorter JA and Cepeda C:
Finding a better drug for epilepsy: The mTOR pathway as an
antiepileptogenic target. Epilepsia. 53:1119–1130. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Willmore LJ and Triggs WJ: Effect of
phenytoin and corticosteroids on seizures and lipid peroxidation in
experimental posttraumatic epilepsy. J Neurosurg. 60:467–472. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ueda Y, Willmore J and Triggs WJ:
Amygdalar injection of FeCl3 causes spontaneous recurrent seizures.
Exp Neurol. 153:123–127. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Racine RJ: Modification of seizure
activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure.
Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 32:281–294. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Butler CR, Boychuk JA and Smith BN:
Effects of rapamycin treatment on neurogenesis and synaptic
reorganization in the dentate gyrus after controlled cortical
impact injury in mice. Front Syst Neurosci. 9:1632015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rankin-Gee EK, McRae PA, Baranov E, Rogers
S, Wandrey L and Porter BE: Perineuronal net degradation in
epilepsy. Epilepsia. 56:1124–1133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou C, Xie G, Wang C, Zhang Z, Chen Q,
Zhang L, Wu L, Wei Y, Ding H, Hang C, et al: Decreased progranulin
levels in patients and rats with subarachnoid hemorrhage: A
potential role in inhibiting inflammation by suppressing neutrophil
recruitment. J Neuroinflammation. 12:2002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kelly KM, Miller ER, Lepsveridze E,
Kharlamov EA and Mchedlishvili Z: Posttraumatic seizures and
epilepsy in adult rats after controlled cortical impact. Epilepsy
Res. 117:104–116. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gong XW, Li JB, Lu QC, Liang PJ and Zhang
PM: Effective connectivity of hippocampal neural network and its
alteration in Mg2+-free epilepsy model. PLoS One. 9:e929612014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chauvette S, Soltani S, Seigneur J and
Timofeev I: In vivo models of cortical acquired epilepsy. J
Neurosci Methods. 260:185–201. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lloyd BA, Hake HS, Ishiwata T, Farmer CE,
Loetz EC, Fleshner M, Bland ST and Greenwood BN: Exercise increases
mTOR signaling in brain regions involved in cognition and emotional
behavior. Behav Brain Res. 323:56–67. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee HJ, Koh SH, Song KM, Seol IJ and Park
HK: The Akt/mTOR/p70S6K pathway is involved in the neuroprotective
effect of erythropoietin on hypoxic/ischemic brain injury in a
neonatal rat model. Neonatology. 110:93–100. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fan W, Wang W, Mao X, Chu S, Feng J, Xiao
D, Zhou J and Fan S: Elevated levels of p-Mnk1, p-eIF4E and
p-p70S6K proteins are associated with tumor recurrence and poor
prognosis in astrocytomas. J Neurooncol. 131:485–493. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lippman-Bell JJ, Rakhade SN, Klein PM,
Obeid M, Jackson MC, Joseph A and Jensen FE: AMPA receptor
antagonist NBQX attenuates later-life epileptic seizures and
autistic-like social deficits following neonatal seizures.
Epilepsia. 54:1922–1932. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ding K, Wang H, Wu Y, Zhang L, Xu J, Li T,
Ding Y, Zhu L and He J: Rapamycin protects against apoptotic
neuronal death and improves neurologic function after traumatic
brain injury in mice via modulation of the mTOR-p53-Bax axis. J
Surg Res. 194:239–247. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Buckmaster PS and Wen X: Rapamycin
suppresses axon sprouting by somatostatin interneurons in a mouse
model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia. 52:2057–2064. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Stoica L, Zhu PJ, Huang W, Zhou H, Kozma
SC and Costa-Mattioli M: Selective pharmacogenetic inhibition of
mammalian target of Rapamycin complex I (mTORC1) blocks long-term
synaptic plasticity and memory storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:3791–3796. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
van Vliet EA, Otte WM, Wadman WJ, Aronica
E, Kooij G, de Vries HE, Dijkhuizen RM and Gorter JA: Blood-brain
barrier leakage after status epilepticus in rapamycin-treated rats
II: Potential mechanisms. Epilepsia. 57:70–78. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zeng LH, Rensing NR and Wong M: The
mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway mediates
epileptogenesis in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci.
29:6964–6972. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|