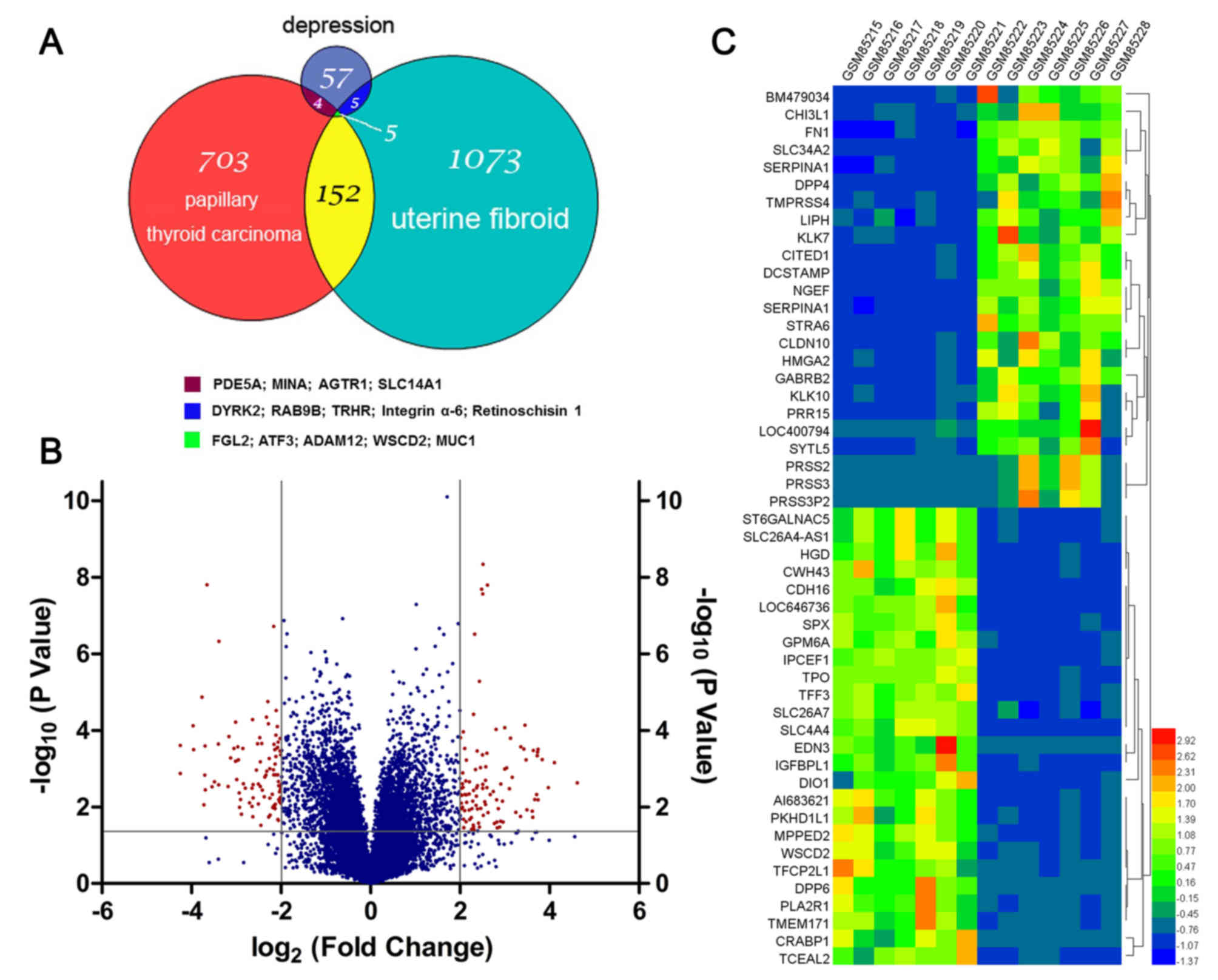
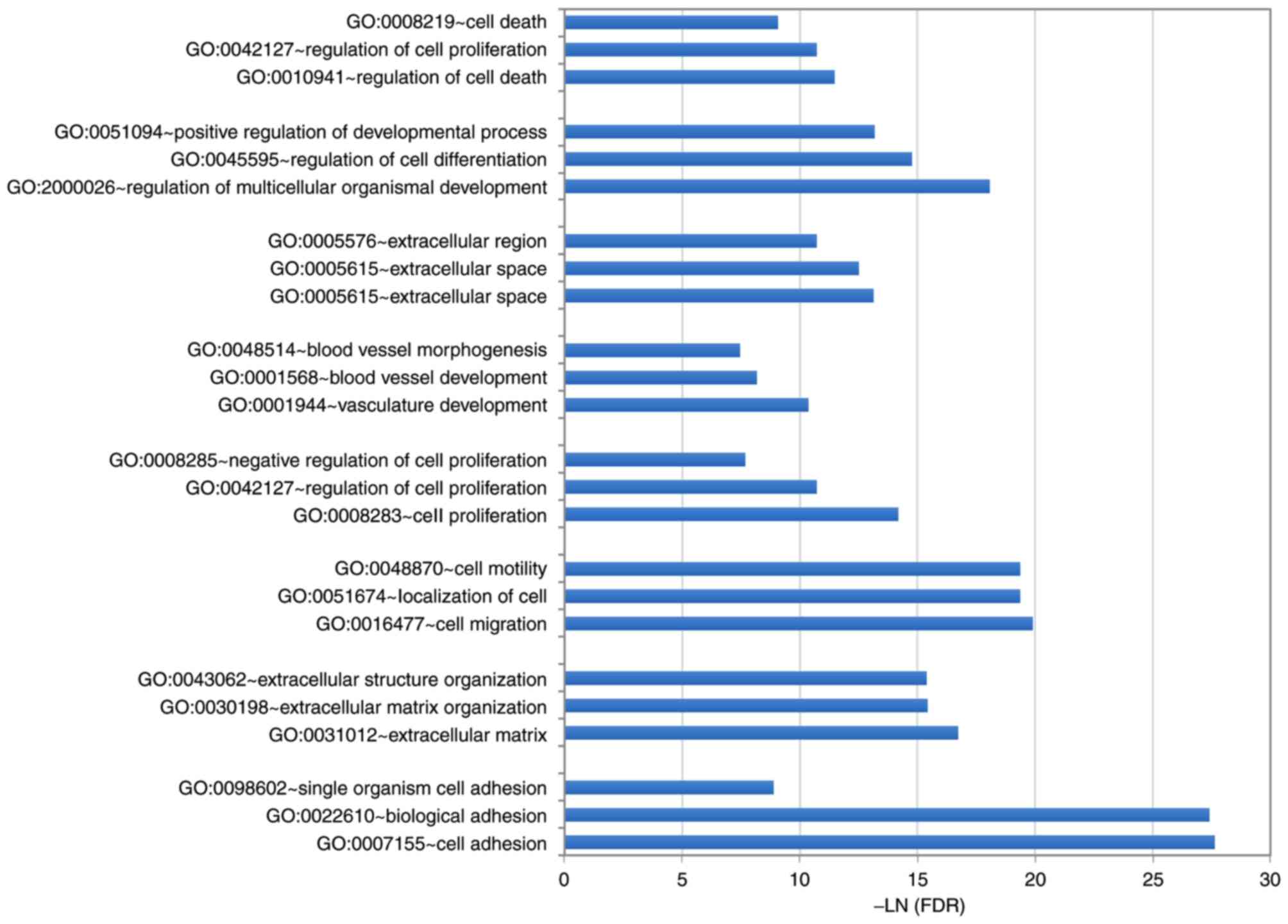
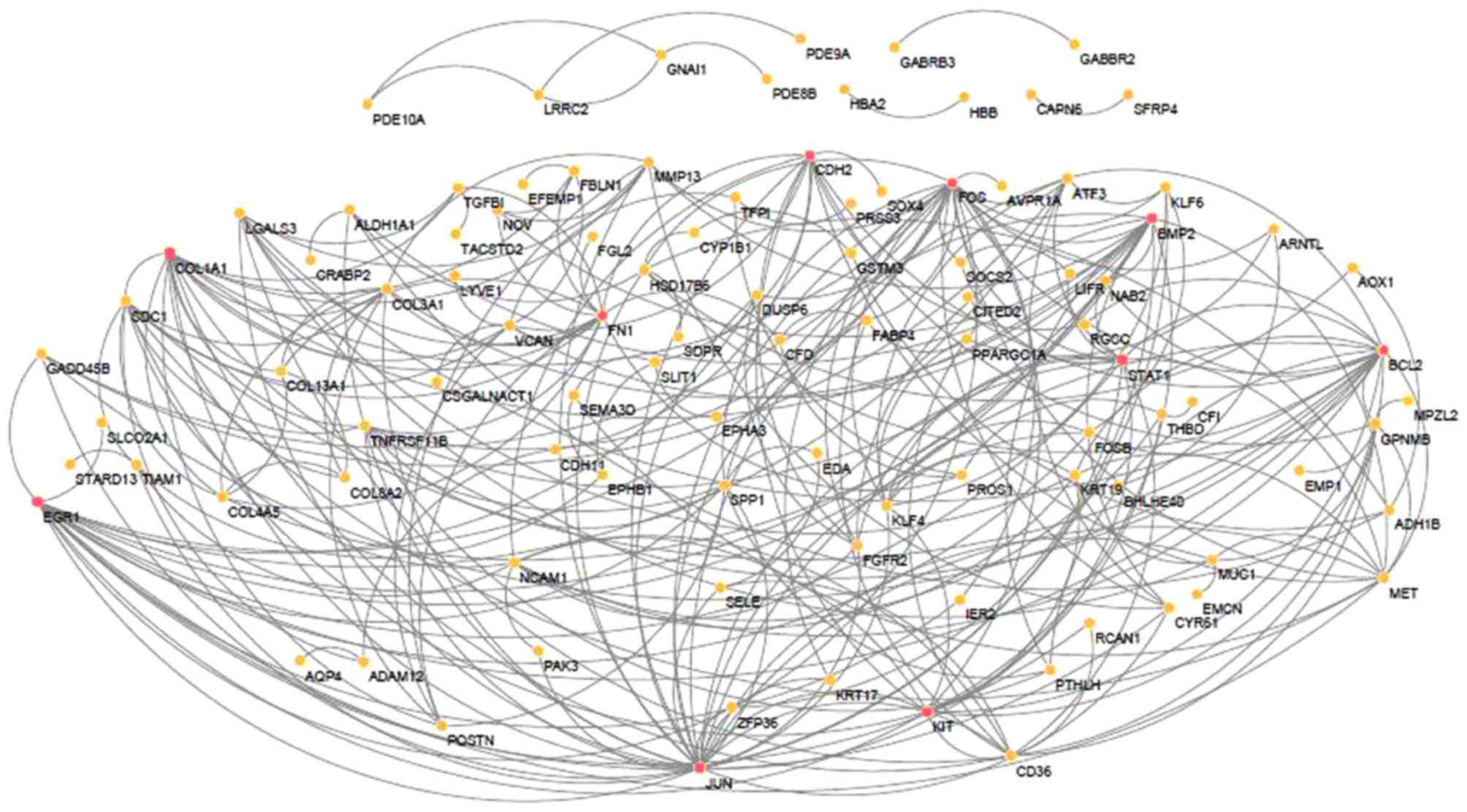
|
1
|
Min W, Liu C, Yang Y and Sun X, Zhang B,
Xu L and Sun X: Alterations in
hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal/thyroid (HPA/HPT) axes correlated
with the clinical manifestations of depression. Prog
Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 39:206–211. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sun Y, Yuan K, Zhang P, Ma R, Zhang QW and
Tian XS: Crosstalk analysis of pathways in breast cancer using a
network model based on overlapping differentially expressed genes.
Exp Ther Med. 10:743–748. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Morris LG, Sikora AG, Tosteson TD and
Davies L: The increasing incidence of thyroid cancer: The influence
of access to care. Thyroid. 23:885–891. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stewart EA: Clinical practice. Uterine
fibroids. N Engl J Med. 372:1646–1655. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sweet MG, Schmidt-Dalton TA, Weiss PM and
Madsen KP: Evaluation and management of abnormal uterine bleeding
in premenopausal women. Am Fam Physician. 85:35–43. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim TH, Choi SJ, Lee YH, Song GG and Ji
JD: Gene expression profile predicting the response to anti-TNF
treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis; analysis of GEO
datasets. Joint Bone Spine. 81:325–330. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xiong H, Zhang D, Martyniuk CJ, Trudeau VL
and Xia X: Using Generalized Procrustes Analysis (GPA) for
normalization of cDNA microarray data. Bmc Bioinformatics.
9:252008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao P, Hu W, Wang H, Yu S, Li C, Bai J,
Gui S and Zhang Y: Identification of differentially expressed genes
in pituitary adenomas by integrating analysis of microarray data.
Int J Endocrinol. 2015:1640872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liang B, Li C and Zhao J: Identification
of key pathways and genes in colorectal cancer using bioinformatics
analysis. Med Oncol. 33:1112016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gene Ontology Consortium: Gene ontology
consortium: Going forward. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:D1049–D1056. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Furumichi M
and Tanabe M: KEGG for integration and interpretation of
large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:D109–D114.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen EY, Tan CM, Kou Y, Duan Q, Wang Z,
Meirelles GV, Clark NR and Ma'ayan A: Enrichr: Interactive and
collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC
Bioinformatics. 14:1282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Heinzel A, Mühlberger I, Fechete R, Mayer
B and Perco P: Functional molecular units for guiding biomarker
panel design. Biomeds Mol Biol. 1159:109–133. 2014.
|
|
16
|
Ding X, Wang W, Peng X and Wang J: Mining
protein complexes from PPI networks using the minimum vertex cut.
Tsing Sci Technol. 17:674–681. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hoffman PJ, Milliken DB, Gregg LC, Davis
RR and Gregg JP: Molecular characterization of uterine fibroids and
its implication for underlying mechanisms of pathogenesis. Fertil
Steril. 82:639–649. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Iwamoto K, Kakiuchi C, Bundo M, Ikeda K
and Kato T: Molecular characterization of bipolar disorder by
comparing gene expression profiles of postmortem brains of major
mental disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 9:406–416. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ito Y, Nikiforov YE, Schlumberger M and
Vigneri R: Increasing incidence of thyroid cancer: Controversies
explored. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 9:178–184. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang XL and Qian LX: Ultrasonic features
of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma and non-microcarcinoma. Exp
Ther Med. 8:1335–1339. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kehuan S, Zhengzhi W, Meiqun C, Xiaoli Z,
Yinghong L, Anming W, Yu J and Zhibin R: A preliminary non-invasive
salivary proteomics diagnostic model for TCM syndrome
differentiation in thyroid cancer based on SELDI and bioinformatics
techniques. Int Sympos Med Edu. 1:508–511. 2011.
|
|
22
|
Cheng F, Wang X, Song W, Lu Y, Li X, Zhang
H and Wang Q: Biologic basis of TCM syndromes and the
standardization of syndrome classification. J Trad Chinese Med Sci.
1:92–97. 2014.
|
|
23
|
Hsu PY, Yang SH, Tsang NM, Fan KH, Hsieh
CH, Lin JR, Hong JH, Lin YC, Chen HY, Yang CT, et al: Efficacy of
traditional chinese medicine in xerostomia and quality of life
during radiotherapy for head and neck cancer: A prospective pilot
study. Evid Based Complement Altern Med: 8359251. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhu J, Xia T and Liu ZJ: Experimental
study of effect of liver Qi Stagnation-psychological stress on sex
hormone and immune factors in uterine leiomyomas animal model. J
Liaon Univers Trad Chinese Med. 9:252011.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Vidal AP, Andrade BM, Vaisman F, Cazarin
J, Pinto LF, Breitenbach MM, Corbo R, Caroli-Bottino A, Soares F,
Vaisman M and Carvalho DP: AMP-activated protein kinase signaling
is upregulated in papillary thyroid cancer. Eur J Endocrinol.
169:521–528. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xing M: Molecular pathogenesis and
mechanisms of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:184–199. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Faustino A, Couto JP, Pópulo H, Rocha AS,
Pardal F, Cameselle-Teijeiro JM, Lopes JM, Sobrinho-Simões M and
Soares P: mTOR pathway overactivation in BRAF mutated papillary
thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:E1139–E1149. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nozhat Z and Hedayati M: PI3K/AKT pathway
and its mediators in thyroid carcinomas. Mol Diagn Ther. 20:13–26.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mcwilliams MM and Chennathukuzhi VM:
Recent advances in uterine fibroid etiology. Semin Reprod Med.
35:181–189. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
CONVERGE consortium: Sparse whole genome
sequencing identifies two loci for major depressive disorder.
Nature. 523:588–591. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tzivion G, Dobson M and Ramakrishnan G:
FoxO transcription factors; Regulation by AKT and 14-3-3 proteins.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:1938–1945. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Peng Y, Kim JM, Park HS, Yang A, Islam C,
Lakatta EG and Lin L: AGE-RAGE signal generates a specific NF-κB
RelA ‘barcode’ that directs collagen I expression. Sci Rep.
6:188222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim HS, Kim DH, Kim JY, Jeoung NH, Lee IK,
Bong JG and Jung ED: Microarray analysis of papillary thyroid
cancers in korean. Korean J Int Med. 25:399–407. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Reierson GW, Guo S, Mastronardi C, Licinio
J and Wong ML: cGMP signaling, phosphodiesterases and major
depressive disorder. Curr Neuropharmacol. 9:715–727. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Taylor WD, Benjamin S, McQuoid DR, Payne
ME, Krishnan RR, MacFall JR and Ashley-Koch A: AGTR1 gene
variation: Association with depression and frontotemporal
morphology. Psychiatry Res. 202:104–109. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vriens MR, Schreinemakers JM, Suh I,
Guerrero MA and Clark OH: Diagnostic markers and prognostic factors
in thyroid cancer. Future Oncol. 5:1283–1293. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cui H, Guo M, Xu D, Ding ZC, Zhou G, Ding
HF, Zhang J, Tang Y and Yan C: The stress-responsive gene ATF3
regulates the histone acetyltransferase Tip60. Nat Commun.
6:67522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kufe DW: MUC1-C oncoprotein as a target in
breast cancer: Activation of signaling pathways and therapeutic
approaches. Oncogene. 32:1073–1081. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hwang I, Kang YN, Kim JY, DO YR, Song HS
and Park KU: Prognostic significance of membrane-associated mucins
1 and 4 in gastric adenocarcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 4:311–316. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pavlovsky AA, Boehning D, Li D, Zhang Y,
Fan X and Green TA: Psychological stress, cocaine and natural
reward each induce endoplasmic reticulum stress genes in rat brain.
Neuroscience. 246:160–169. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lo MT, Hinds DA, Tung JY, Franz C, Fan CC,
Wang Y, Smeland OB, Schork A, Holland D, Kauppi K, et al:
Genome-wide analyses for personality traits identify six genomic
loci and show correlations with psychiatric disorders. Nat Genet.
49:152–156. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mehan S, Meena H, Sharma D and Sankhla R:
JNK: A stress-activated protein kinase therapeutic strategies and
involvement in Alzheimer's and various neurodegenerative
abnormalities. J Mol Neurosci. 43:376–390. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Qiao Y, He H, Jonsson P, Sinha I, Zhao C
and Dahlman-Wright K: AP-1 is a key regulator of proinflammatory
cytokine TNFα-mediated triple-negative breast cancer progression. J
Biol Chem. 291:183092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Uluçkan Ö, Guineaviniegra J, Jimenez M and
Wagner EF: Signalling in inflammatory skin disease by AP-1
(Fos/Jun). Clin Exp Rheumatol. 33 4 Suppl 92:S44–S49. 2015.
|
|
45
|
Delbridge AR, Grabow S, Strasser A and
Vaux DL: Thirty years of BCL-2: Translating cell death discoveries
into novel cancer therapies. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:99–109. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Schreiber RD, Old LJ and Smyth MJ: Cancer
immunoediting: Integrating immunity's roles in cancer suppression
and promotion. Science. 331:1565–1570. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Schroeder AC and Privalsky ML: Thyroid
hormones, t3 and t4, in the brain. Front endocrinol (Lausanne).
5:402014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Vissenberg R, Manders V, Mastenbroek S,
Fliers E, Afink GB, Ris-Stalpers C, Goddijn M and Bisschop PH:
Pathophysiological aspects of thyroid hormone disorders/thyroid
peroxidase autoantibodies and reproduction. Hum Reprod Update.
21:378–387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hage MP and Azar ST: The link between
thyroid function and depression. J Thyroid Res.
2012:5906482011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tasneem A, Fatima I, Ali A, Mehmood N and
Amin MK: The incidence of hyperprolactinaemia and associated
hypothyroidism: Local experience from Lahore. Pak J Nuclear Med.
1:49–55. 2011.
|
|
51
|
Su Q, Cheng Y, Jin K, Cheng J, Lin Y, Lin
Z, Wang L and Shao B: Estrogen therapy increases BDNF expression
and improves post-stroke depression in ovariectomy-treated rats.
Exp Ther Med. 12:1843–1848. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Heim C and Binder EB: Current research
trends in early life stress and depression: Review of human studies
on sensitive periods, gene-environment interactions and
epigenetics. Exp Neurol. 233:102–111. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Khan AT, Shehmar M and Gupta JK: Uterine
fibroids: Current perspectives. Int J Womens Health. 6:95–114.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang TS, Goffredo P, Sosa JA and Roman SA:
Papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: An over-treated malignancy? World
J Surg. 38:2297–2303. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Talaulikar VS and Manyonda IT: Ulipristal
acetate: A novel option for the medical management of symptomatic
uterine fibroids. Adv Ther. 29:655–663. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Divakar H: Asymptomatic uterine fibroids.
Best Pract Res Clin Obst Gynaecol. 22:643–654. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Ito Y, Nikiforov YE, Schlumberger M and
Vigneri R: Increasing incidence of thyroid cancer: Controversies
explored. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 9:178–184. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Philippi CL, Motzkin JC, Pujara MS and
Koenigs M: Subclinical depression severity is associated with
distinct patterns of functional connectivity for subregions of
anterior cingulate cortex. J Psychiatr Res. 71:103–111. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
de Castro Gonzalez D, Clarke PA,
Al-Lazikani B and Workman P: Personalized cancer medicine:
Molecular diagnostics, predictive biomarkers and drug resistance.
Clin Pharmacol Ther. 93:252–259. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Winter JM, Yeo CJ and Brody JR:
Diagnostic, prognostic and predictive biomarkers in pancreatic
cancer. J Surg Oncol. 107:15–22. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|