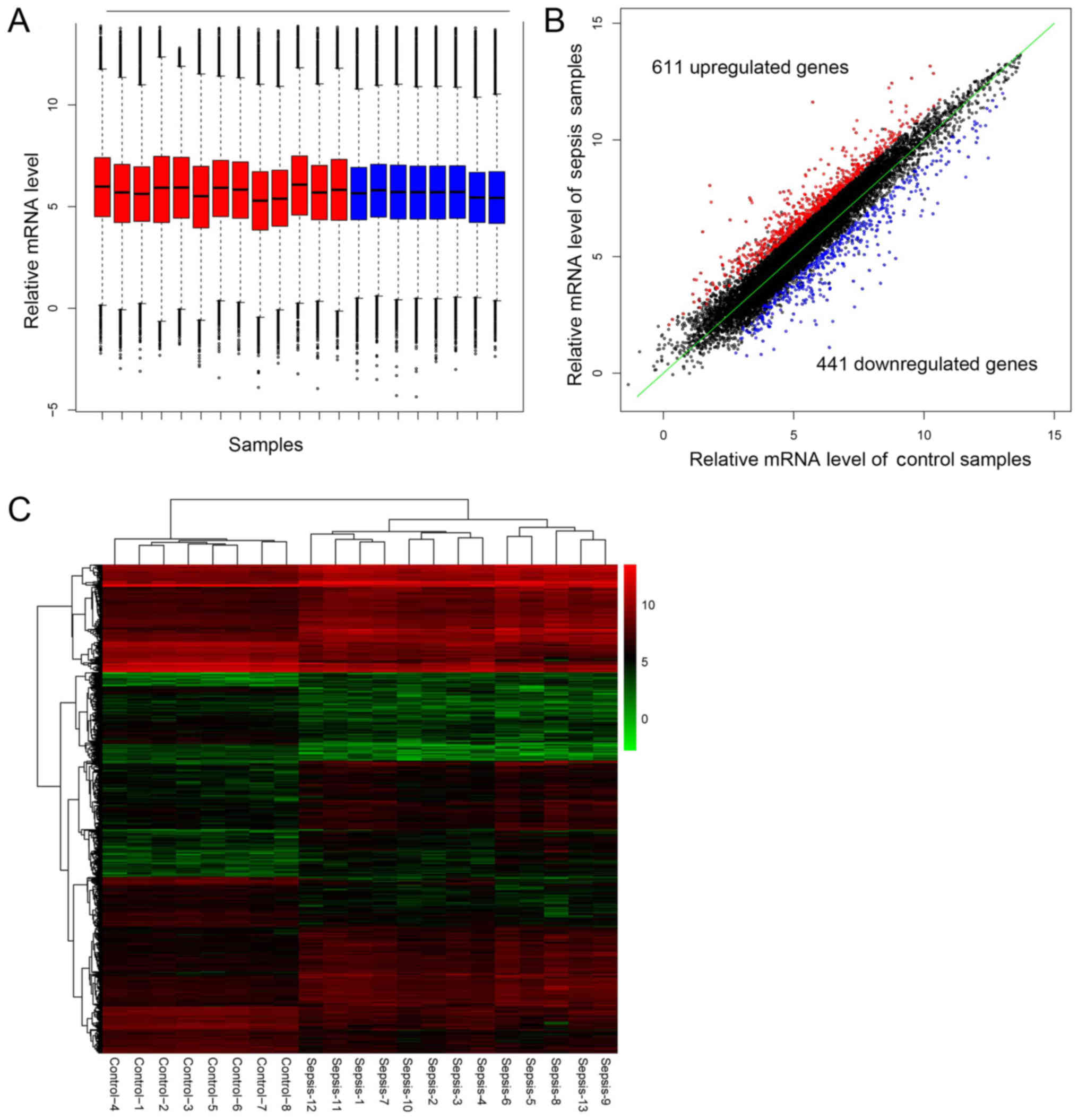
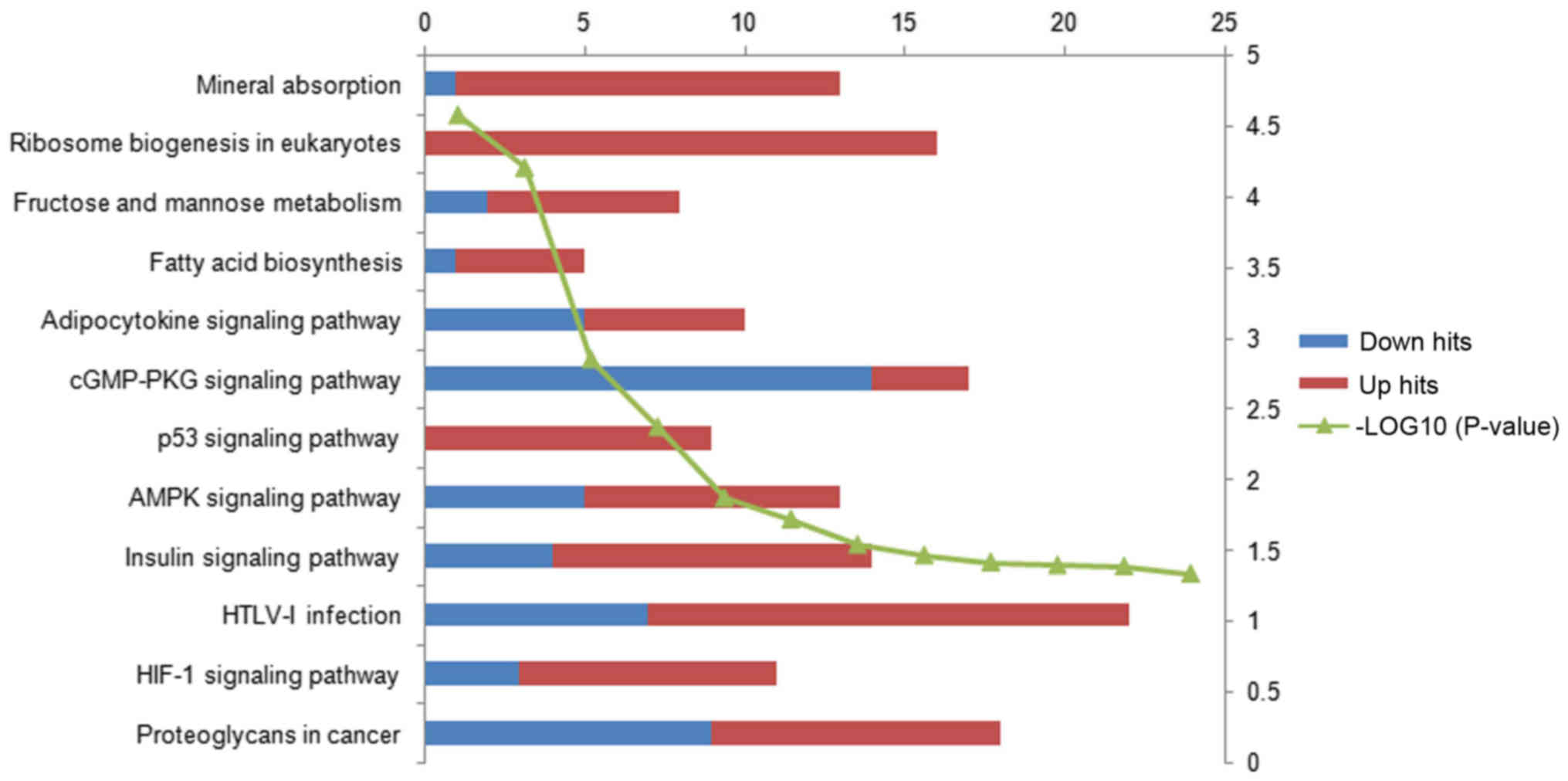
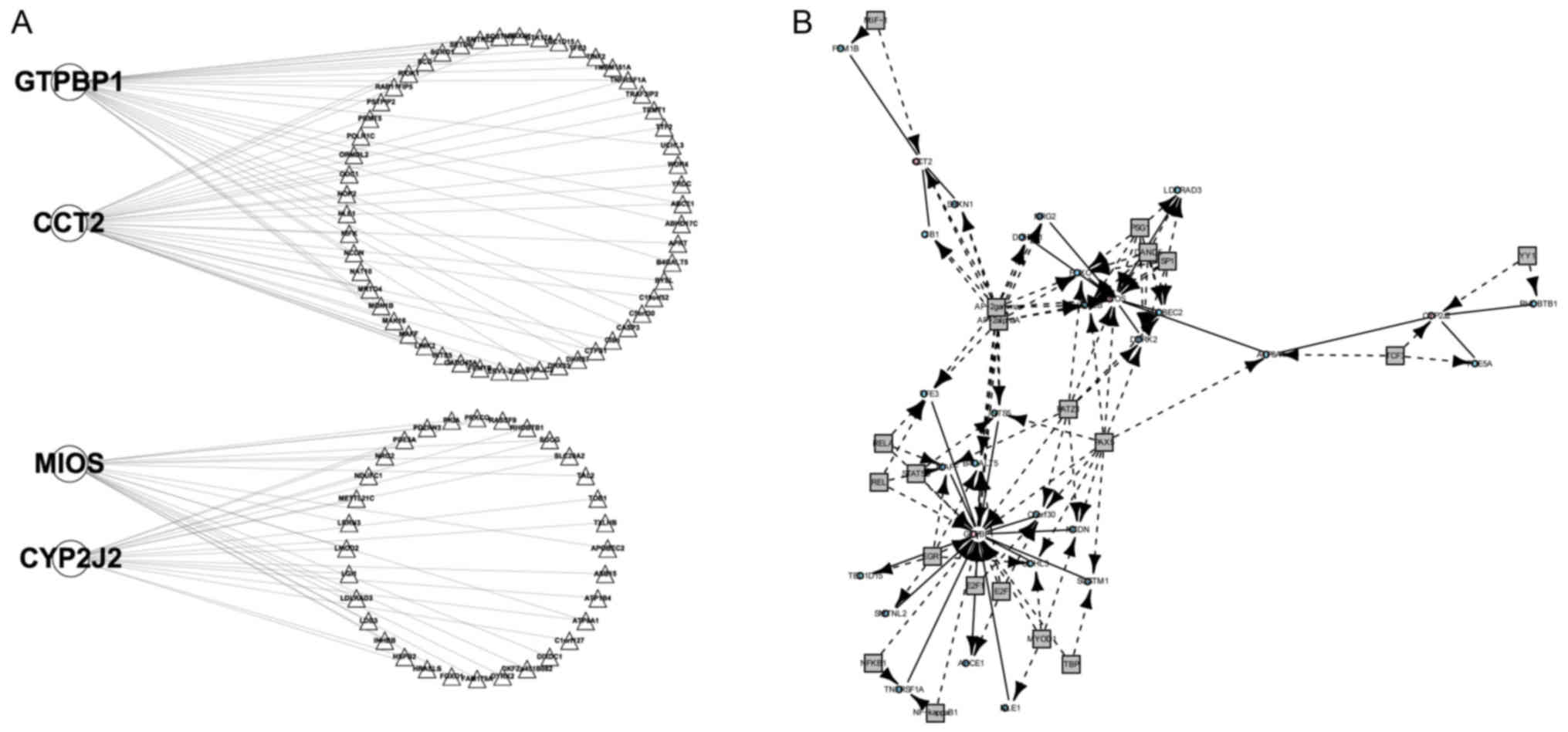
|
1
|
Evans CE and Zhao YY: Impact of thrombosis
on pulmonary endothelial injury and repair following sepsis. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 312:L441–L451. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Eisen DP, Moore EM, Leder K, Lockery J,
McBryde ES, McNeil JJ, Pilcher D, Wolfe R and Woods RL: AspiriN To
Inhibit SEPSIS (ANTISEPSIS) randomised controlled trial protocol.
BMJ Open. 7:e0136362017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sehgal V, Bajwa SJ, Consalvo JA and Bajaj
A: Clinical conundrums in management of sepsis in the elderly. J
Transl Int Med. 3:106–112. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Graziani AC, Stets MI, Lopes AL, Schluga
PHC, Marton S, Mendes IF, Andrade ASR, Krieger MA and Cardoso J:
High efficiency binding aptamers for a wide range of bacterial
sepsis agents. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 27:838–843. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tiru B, DiNino EK, Orenstein A, Mailloux
PT, Pesaturo A, Gupta A and McGee WT: The economic and humanistic
burden of severe sepsis. Pharmacoeconomics. 33:925–937. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Perner A, Rhodes A, Venkatesh B, Angus DC,
Martin-Loeches I, Preiser JC, Vincent JL, Marshall J, Reinhart K,
Joannidis M and Opal SM: Sepsis: Frontiers in supportive care,
organisation and research. Intensive Care Med. 43:496–508. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Midan DA, Abo El Fotoh WMM and El
Shalakany AH: The potential role of incorporating real-time PCR and
DNA sequencing for amplification and detection of 16S rRNA gene
signatures in neonatal sepsis. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med.
30:1476–1483. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ludwig KR and Hummon AB: Mass spectrometry
for the discovery of biomarkers of sepsis. Mol Biosyst. 13:648–664.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Scherag A, Schöneweck F, Kesselmeier M,
Taudien S, Platzer M, Felder M, Sponholz C, Rautanen A, Hill AVS,
Hinds CJ, et al: Genetic factors of the disease course after
sepsis: A genome-wide study for 28 day mortality. EBioMedicine.
12:239–246. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gosiewski T, Ludwig-Galezowska AH,
Huminska K, Sroka-Oleksiak A, Radkowski P, Salamon D, Wojciechowicz
J, Kus-Slowinska M, Bulanda M and Wolkow PP: Comprehensive
detection and identification of bacterial DNA in the blood of
patients with sepsis and healthy volunteers using next-generation
sequencing method-the observation of DNAemia. Eur J Clin Microbiol
Infect Dis. 36:329–336. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen Q, Xue H, Chen M, Gao F, Xu J, Liu Q,
Yang X, Zheng L and Chen H: High serum trypsin levels and the −409
T/T genotype of PRSS1 gene are susceptible to neonatal sepsis.
Inflammation. 37:1751–1756. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shibahashi K, Sugiyama K, Kashiura M and
Hamabe Y: Decreasing skeletal muscle as a risk factor for mortality
in elderly patients with sepsis: A retrospective cohort study. J
Intensive Care. 5:82017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bodine SC and Furlow JD: Glucocorticoids
and skeletal muscle. Adv Exp Med Biol. 872:145–176. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hansen ME, Simmons KJ, Tippetts TS,
Thatcher MO, Saito RR, Hubbard ST, Trumbull AM, Parker BA, Taylor
OJ and Bikman BT: Lipopolysaccharide disrupts mitochondrial
physiology in skeletal muscle via disparate effects on sphingolipid
metabolism. Shock. 44:585–592. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Steiner JL, Crowell KT, Kimball SR and
Lang CH: Disruption of REDD1 gene ameliorates sepsis-induced
decrease in mTORC1 signaling but has divergent effects on
proteolytic signaling in skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 309:E981–E994. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu GP, Cui P, Cheng Y, Lu ZJ, Zhang LE and
Kissoon N: Insulin control of blood glucose and GLUT4 expression in
the skeletal muscle of septic rats. West Indian Med J. 64:62–70.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang J, Yu H, Liu BH, Zhao Z, Liu L, Ma
LX, Li YX and Li YY: DCGL v2.0: An R package for unveiling
differential regulation from differential co-expression. PLoS One.
8:e797292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fredriksson K, Tjäder I, Keller P,
Petrovic N, Ahlman B, Schéele C, Wernerman J, Timmons JA and
Rooyackers O: Dysregulation of mitochondrial dynamics and the
muscle transcriptome in ICU patients suffering from sepsis induced
multiple organ failure. PLoS One. 3:e36862008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: affy-analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Diboun I, Wernisch L, Orengo CA and
Koltzenburg M: Microarray analysis after RNA amplification can
detect pronounced differences in gene expression using limma. BMC
Genomics. 7:2522006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Greenacre M: Ordination with any
dissimilarity measure: A weighted euclidean solution. Ecology.
98:2293–2300. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yan J,
Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zolfaghari PS, Carré JE, Parker N, Curtin
NA, Duchen MR and Singer M: Skeletal muscle dysfunction is
associated with derangements in mitochondrial bioenergetics (but
not UCP3) in a rodent model of sepsis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 308:E713–E725. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Crowell KT, Soybel DI and Lang CH:
Restorative mechanisms regulating protein balance in skeletal
muscle during recovery from sepsis. Shock. 47:463–473. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang J, Zhao L, Li Y, Feng S and Lv G: HuR
induces inflammatory responses in HUVECs and murine sepsis via
binding to HMGB1. Mol Med Rep. 17:1049–1056. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rontoyanni VG, Malagaris I, Herndon DN,
Rivas E, Capek KD, Delgadillo AD, Bhattarai N, Elizondo A, Voigt
CD, Finnerty CC, et al: Skeletal muscle mitochondrial function is
determined by burn severity, sex and sepsis and is associated with
glucose metabolism and functional capacity in burned children.
Shock. Dec 4–2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rocheteau P, Chatre L, Briand D, Mebarki
M, Jouvion G, Bardon J, Crochemore C, Serrani P, Lecci PP, Latil M,
et al: Sepsis induces long-term metabolic and mitochondrial muscle
stem cell dysfunction amenable by mesenchymal stem cell therapy.
Nat Commun. 6:101452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Figueiredo VC, Markworth JF, Durainayagam
BR, Pileggi CA, Roy NC, Barnett MP and Cameron-Smith D: Impaired
ribosome biogenesis and skeletal muscle growth in a murine model of
inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 22:268–278. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li R, Xu X, Chen C, Wang Y, Gruzdev A,
Zeldin DC and Wang DW: CYP2J2 attenuates metabolic dysfunction in
diabetic mice by reducing hepatic inflammation via the PPARγ. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 308:E270–E282. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen W, Yang S, Ping W, Fu X, Xu Q and
Wang J: CYP2J2 and EETs protect against lung ischemia/reperfusion
injury via anti-inflammatory effects in vivo and in vitro. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 35:2043–2054. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guest ST, Kratche ZR, Bollig-Fischer A,
Haddad R and Ethier SP: Two members of the TRiC chaperonin complex,
CCT2 and TCP1 are essential for survival of breast cancer cells and
are linked to driving oncogenes. Exp Cell Res. 332:223–235. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sung SJ, Walters JA, Hudson J and Gimble
JM: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mRNA accumulation in human
myelomonocytic cell lines. Role of transcriptional regulation by
DNA sequence motifs and mRNA stabilization. J Immunol.
147:2047–2054. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ye X and Liu SF: Lipopolysaccharide
regulates constitutive and inducible transcription factor
activities differentially in vivo in the rat. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 288:927–932. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang HJ, Hinney A, Song JY, Scherag A,
Meng XR, Grallert H, Illig T, Hebebrand J, Wang Y and Ma J:
Association of common variants identified by recent genome-wide
association studies with obesity in Chinese children: A
case-control study. BMC Med Genet. 17:72016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen Y, Sun D, Krishnamurthy VM and Rabkin
R: Endotoxin attenuates growth hormone-induced hepatic insulin-like
growth factor I expression by inhibiting JAK2/STAT5 signal
transduction and STAT5b DNA binding. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
292:E1856–E1862. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|