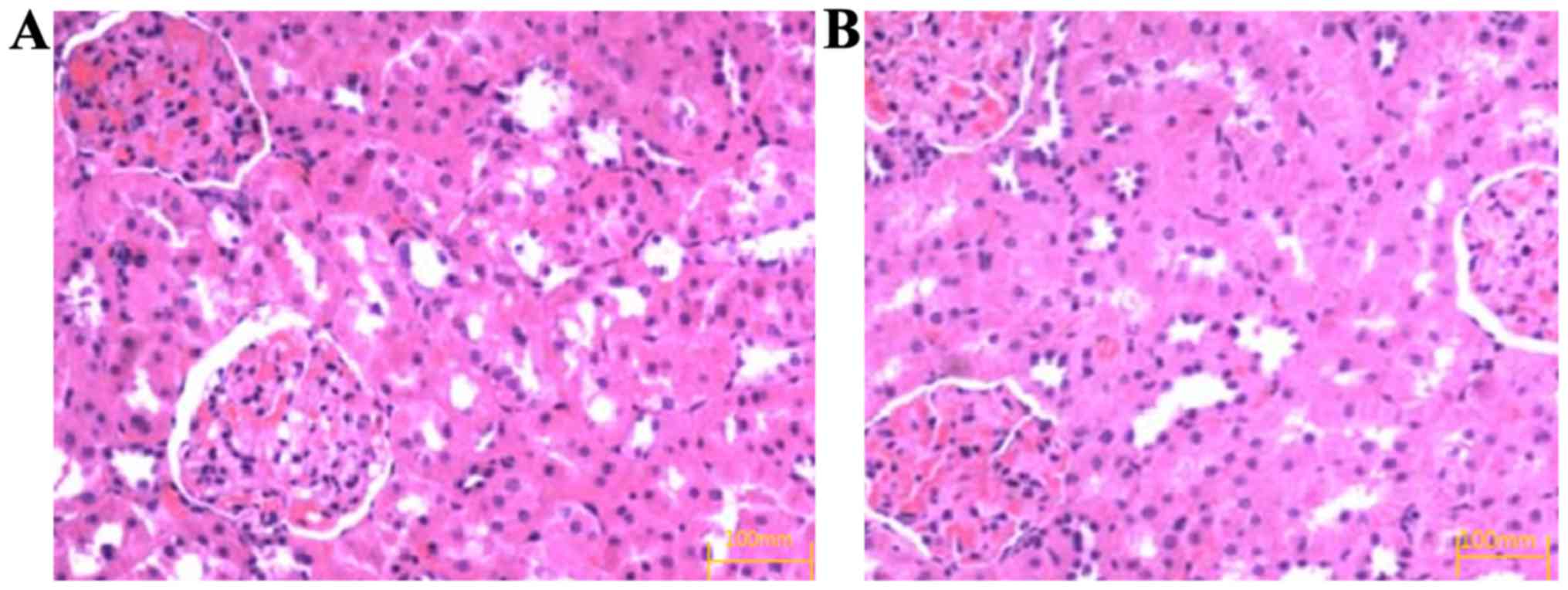
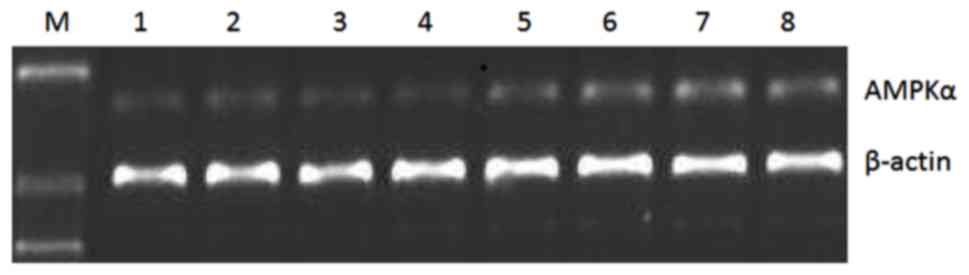
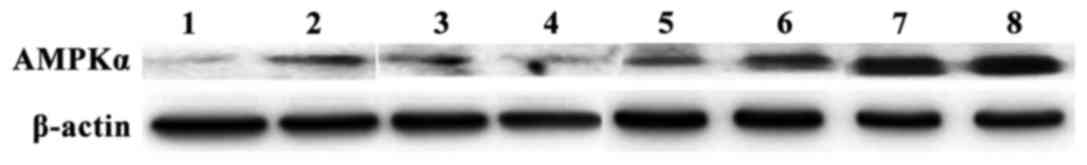
|
1
|
d'Emden MC, Shaw JE, Jones GR and Cheung
NW: Guidance concerning the use of glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) for
the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Med J Aust. 203:89–90. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mellitus D and Glucose O: American
Diabetes Association: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes
mellitus. Diabetes Care. 36 Suppl 1:S67–S74. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tsai SF, Su CW, Wu MJ, Chen CH, Fu CP, Liu
CS and Hsieh M: Urinary Cyclophilin A as a new marker for diabetic
nephropathy: A cross-sectional analysis of diabetes mellitus.
Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e18022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cooper ME, Gilbert RE and Epstein M:
Pathophysiology of diabetic nephropathy. Metabolism. 47 Suppl
1:3–6. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maezawa Y, Takemoto M and Yokote K: Cell
biology of diabetic nephropathy: Roles of endothelial cells,
tubulointerstitial cells and podocytes. J Diabetes Investig.
6:3–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pineda CT, Ramanathan S, Tacer Fon K, Weon
JL, Potts MB, Ou YH, White MA and Potts PR: Degradation of AMPK by
a cancer-specific ubiquitin ligase. Cell. 160:715–728. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liao L, Lei MX, Chen HL, Wu J and Guo LJ:
High-sensitive C-reactive protein and Type 2 diabetic nephropathy.
Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 29:627–630. 2004.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nimmerjahn F, Gordan S and Lux A: FcγR
dependent mechanisms of cytotoxic, agonistic, and neutralizing
antibody activities. Trends Immunol. 36:325–336. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ahmad J: Management of diabetic
nephropathy: Recent progress and future perspective. Diabetes Metab
Syndr. 9:343–358. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bangstad HJ, Osterby R, Rudberg S,
Hartmann A, Brabrand K and Hanssen KF: Kidney function and
glomerulopathy over 8 years in young patients with Type I
(insulin-dependent) diabetesmellitus and microalbuminuria.
Diabetologia. 45:253–261. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rigalleau V, Lasseur C, Raffaitin C,
Perlemoine C, Barthe N, Chauveau P, Combe C and Gin H: Glucose
control influencesglomerular filtration rate and its prediction in
diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care. 29:1491–1495. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Haneda M, Utsunomiya K, Koya D, Babazono
T, Moriya T, Makino H, Kimura K, Suzuki Y, Wada T, Ogawa S, et al:
A new classification of Diabetic Nephropathy 2014: A report from
Joint Committee on Diabetic Nephropathy. Clin Exp Nephrol. 19:1–5.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vincent EE, Coelho PP, Blagih J, Griss T,
Viollet B and Jones RG: Differential effects of AMPK agonists on
cell growth and metabolism. Oncogene. 34:3627–3639. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Blagih J, Coulombe F, Vincent EE, Dupuy F,
Galicia-Vázquez G, Yurchenko E, Raissi TC, van der Windt GJ,
Viollet B, Pearce EL, et al: The energy sensor AMPK regulates T
cell metabolic adaptation and effector responses in vivo. Immunity.
42:41–54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ford RJ, Fullerton MD, Pinkosky SL, Day
EA, Scott JW, Oakhill JS, Bujak AL, Smith BK, Crane JD, Blümer RM,
et al: Metformin and salicylate synergistically activate liver
AMPK, inhibit lipogenesis and improve insulin sensitivity. Biochem
J. 468:125–132. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shimoda M, Kaneto H, Yoshioka H, Okauchi
S, Hirukawa H, Kimura T, Kanda-Kimura Y, Kohara K, Kamei S,
Kawasaki F, et al: Influence of atherosclerosis-related risk
factors on serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels in
patients with type 2 diabetes: Comparison of their influence
between in obese and non-obese subjects. J Diabetes Investig.
7:197–205. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Varma V, Varma M, Varma A, Kumar R,
Bharosay A and Vyas S: Serum total sialic acid and highly sensitive
C-reactive protein: Prognostic markers for the diabetic
nephropathy. J Lab Physicians. 8:25–29. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Alam F, Fatima F, Orakzai S, Iqbal N and
Fatima SS: Elevated levels of ferritin and hs-CRP in type 2
diabetes. J Pak Med Assoc. 64:1389–1391. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bosques CJ and Manning AM: Fc-gamma
receptors: Attractive targets for autoimmune drug discovery
searching for intelligent therapeutic designs. Autoimmun Rev.
15:1081–1088. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Chan JC, Cooper ME,
Gansevoort RT, Haller H, Remuzzi G, Rossing P, Schmieder RE, Nowack
C, et al: Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist Tolerability Study
- Diabetic Nephropathy (ARTS-DN) Study Group: Effect of finerenone
on albuminuria in patients with diabetic nephropathy: A randomized
clinical trial. JAMA. 314:884–894. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu ZQ, Li QZ and Qin GJ: Effect of
Astragalus injection onplatelet function and plasma endothelin in
patients with earlystage diabetic nephropathy. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi
Jie He ZaZhi. 21:274–276. 2001.(In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Ford ES: Urinary albumin-creatinine ratio,
estimated glomerular filtration rate, and all-cause mortality among
US adults with obstructive lung function. Chest. 147:56–67. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Meneses MJ, Silva BM, Sousa M, Sá R,
Oliveira PF and Alves MG: Antidiabetic drugs: Mechanisms of action
and potential outcomes on cellular metabolism. Curr Pharm Des.
21:3606–3620. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|