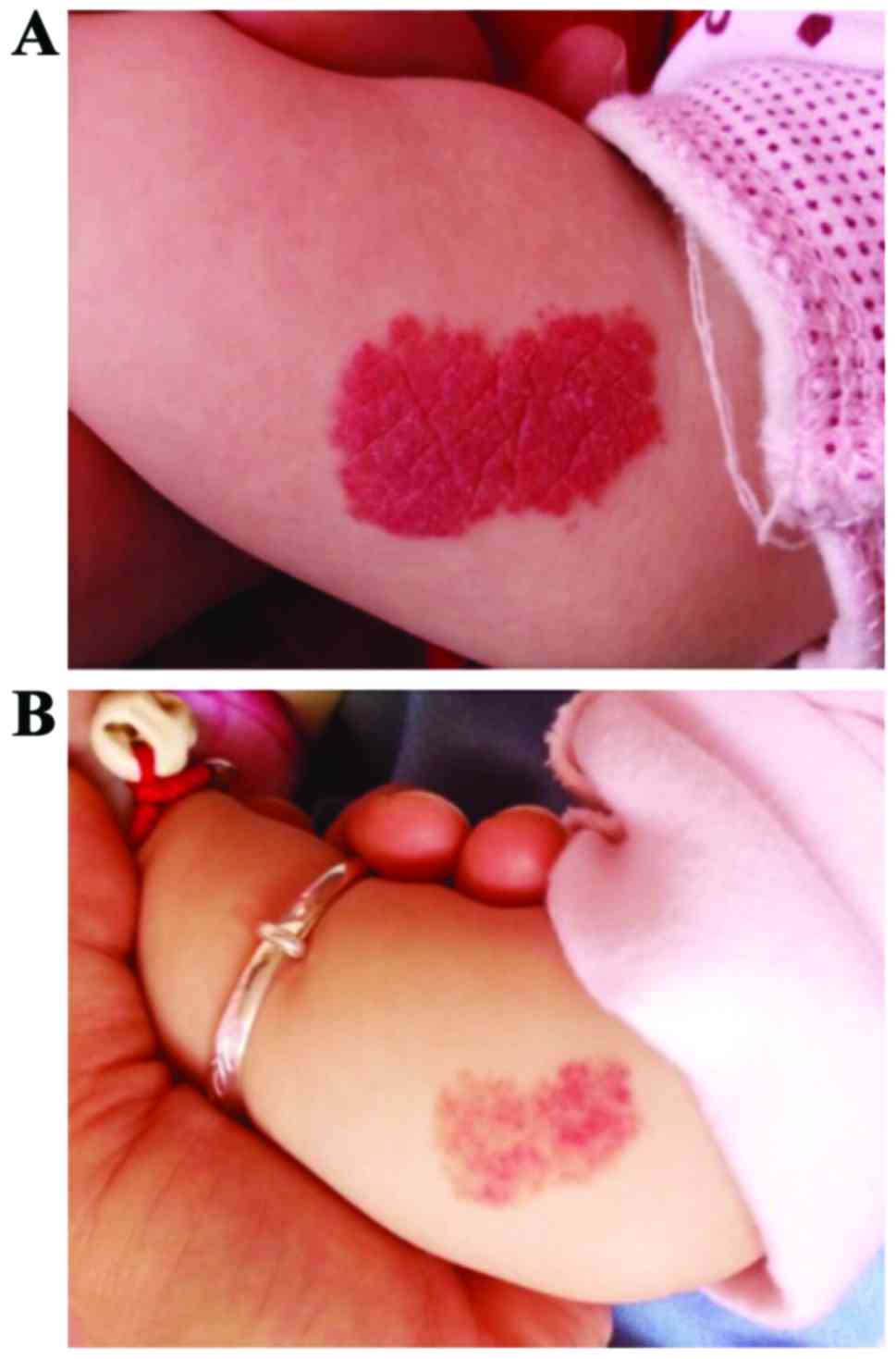
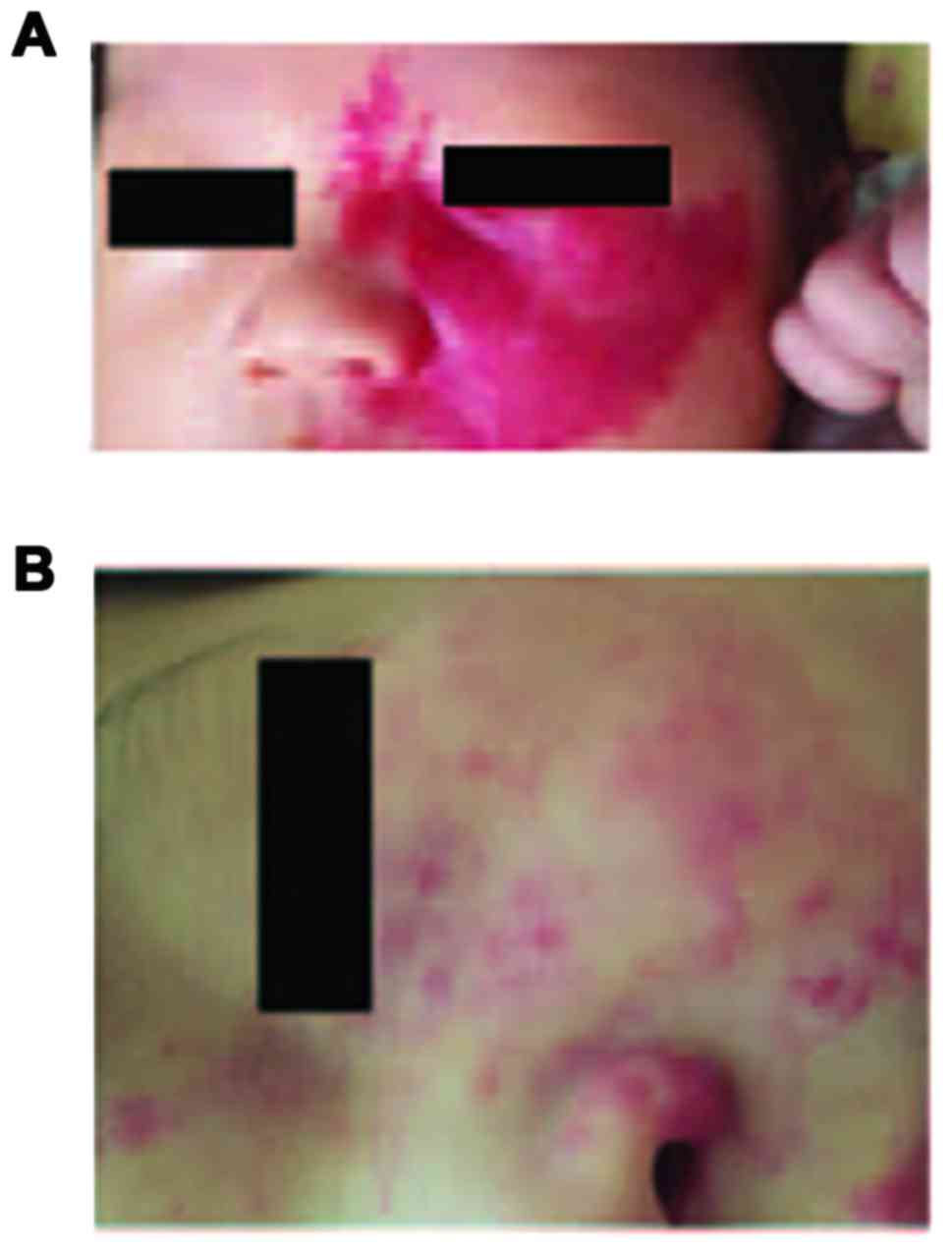
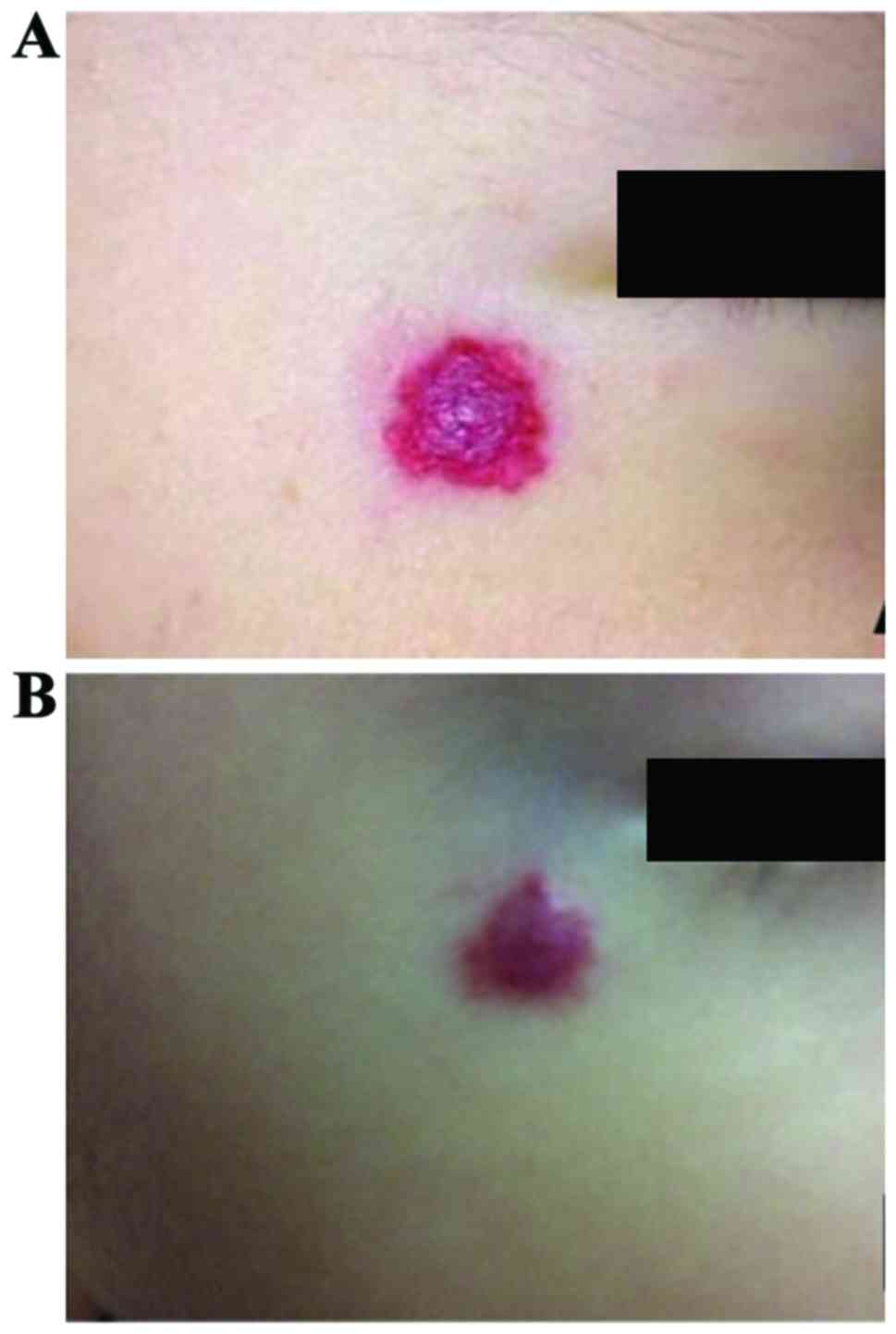
|
1
|
Fu Y, Yang ZG and Zhao LY: Angiogenesis
characteristics of infantile hemangioma and feasibility observation
of transplantation model of human hemangioma on mice. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 21:1276–1280. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de Graaf M, Breur JM, Raphaël MF, Vos M,
Breugem CC and Pasmans SG: Adverse effects of propranolol when used
in the treatment of hemangiomas: A case series of 28 infants. J Am
Acad Dermatol. 65:320–327. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eivazi B, Ardelean M, Bäumler W, Berlien
HP, Cremer H, Elluru R, Koltai P, Olofsson J, Richter G, Schick B,
et al: Update on hemangiomas and vascular malformations of the head
and neck. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 266:187–197. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chinnadurai S, Snyder K, Sathe N,
Fonnesbeck C, Morad A, Likis FE, Surawicz T, Ness G, Ficzere C and
McPheeters ML: Diagnosis and Management of Infantile Hemangioma
[Internet]Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Rockville,
MD: 2016
|
|
5
|
Sethuraman G, Yenamandra VK and Gupta V:
Management of infantile hemangiomas: Current trends. J Cutan
Aesthet Surg. 7:75–85. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Izadpanah A, Izadpanah A, Kanevsky J,
Belzile E and Schwarz K: Propranolol versus corticosteroids in the
treatment of infantile hemangioma: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 131:601–613. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Léauté-Labrèze C, de la Roque Dumas E,
Hubiche T, Boralevi F, Thambo JB and Taïeb A: Propranolol for
severe hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med. 358:2649–2651. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bruckner AL and Frieden IJ: Hemangiomas of
infancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 48:477–493; quiz 494–496. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsang MW, Garzon MC and Frieden IJ: How to
measure a growing hemangioma and assess response to therapy.
Pediatr Dermatol. 23:187–190. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Achauer BM, Chang CJ and Vander Kam VM:
Management of hemangioma of infancy: Review of 245 patients. Plast
Reconstr Surg. 99:1301–1308. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hogeling M, Adams S and Wargon O: A
randomized controlled trial of propranolol for infantile
hemangiomas. Pediatrics. 128:e259–e266. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chang LC, Haggstrom AN, Drolet BA, Baselga
E, Chamlin SL, Garzon MC, Horii KA, Lucky AW, Mancini AJ, Metry DW,
et al: Hemangioma Investigator Group: Growth characteristics of
infantile hemangiomas: Implications for management. Pediatrics.
122:360–367. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Storch CH and Hoeger PH: Propranolol for
infantile haemangiomas: Insights into the molecular mechanisms of
action. Br J Dermatol. 163:269–274. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zou HX, Jia J, Zhang WF, Sun ZJ and Zhao
YF: Propranolol inhibits endothelial progenitor cell homing: A
possible treatment mechanism of infantile hemangioma. Cardiovasc
Pathol. 22:203–210. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Siegfried EC, Keenan WJ and Al-Jureidini
S: More on propranolol for hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med.
359:2846–2847. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sánchez-Carpintero I, Ruiz-Rodriguez R and
López-Gutiérrez JC: Propranolol in the treatment of infantile
hemangioma: Clinical effectiveness, risks, and recommendations.
Actas Dermosifiliogr. 102:766–779. 2011.(In Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sans V, de la Roque ED, Berge J, Grenier
N, Boralevi F, Mazereeuw-Hautier J, Lipsker D, Dupuis E, Ezzedine
K, Vergnes P, et al: Propranolol for severe infantile hemangiomas:
Follow-up report. Pediatrics. 124:e423–e431. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang W, Chen G, Wang FQ, Ren JG, Zhu JY,
Cai Y, Zhao JH, Jia J and Zhao YF: Macrophages contribute to the
progression of infantile hemangioma by regulating the proliferation
and differentiation of hemangioma stem cells. J Invest Dermatol.
135:3163–3172. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rössler J, Wehl G and Niemeyer CM:
Evaluating systemic prednisone therapy for proliferating
haemangioma in infancy. Eur J Pediatr. 167:813–815. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Koay AC, Choo MM, Nathan AM, Omar A and
Lim CT: Combined low-dose oral propranolol and oral prednisolone as
first-line treatment in periocular infantile hemangiomas. J Ocul
Pharmacol Ther. 27:309–311. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|