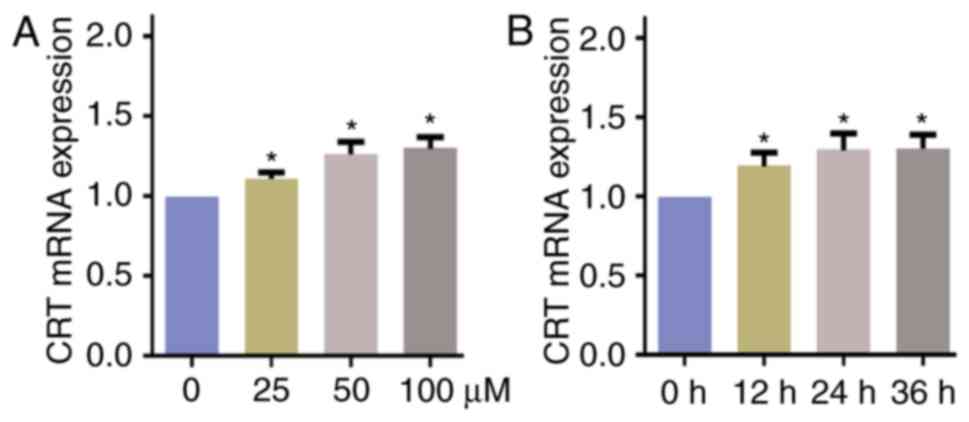
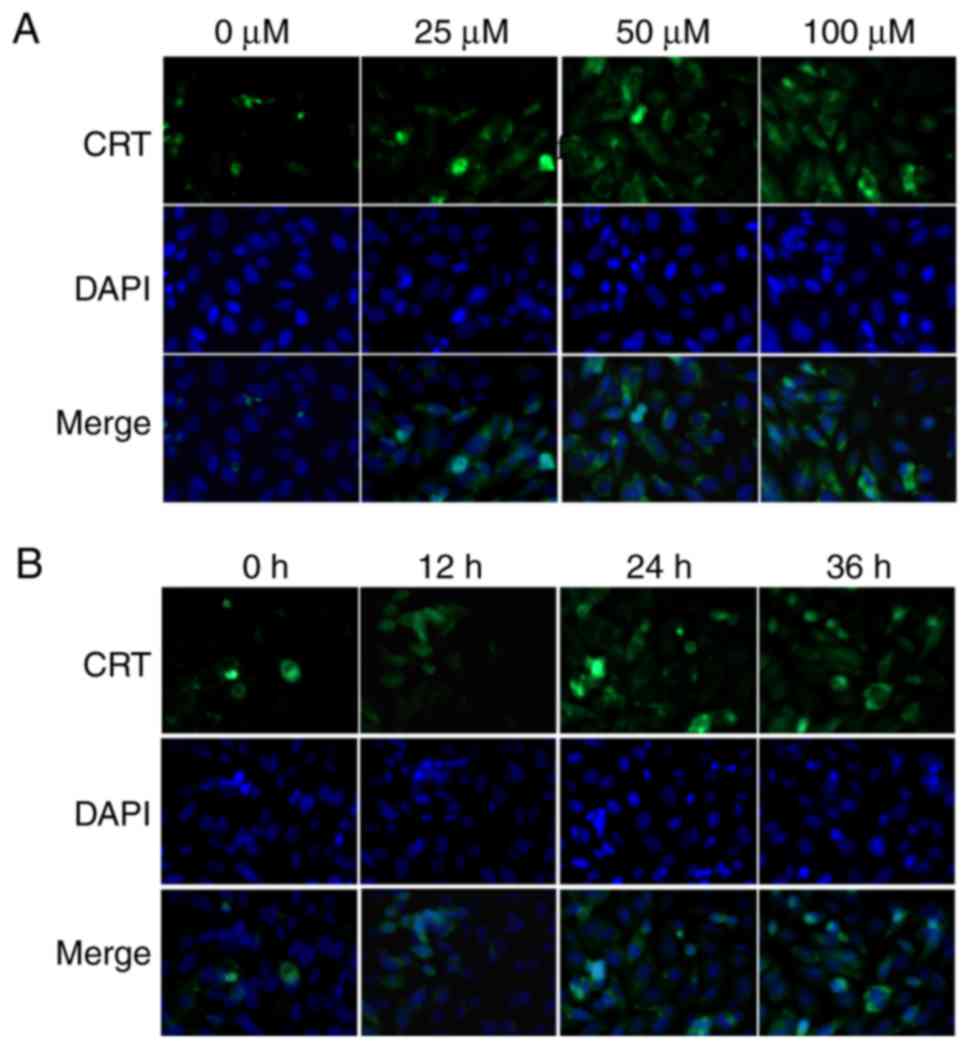
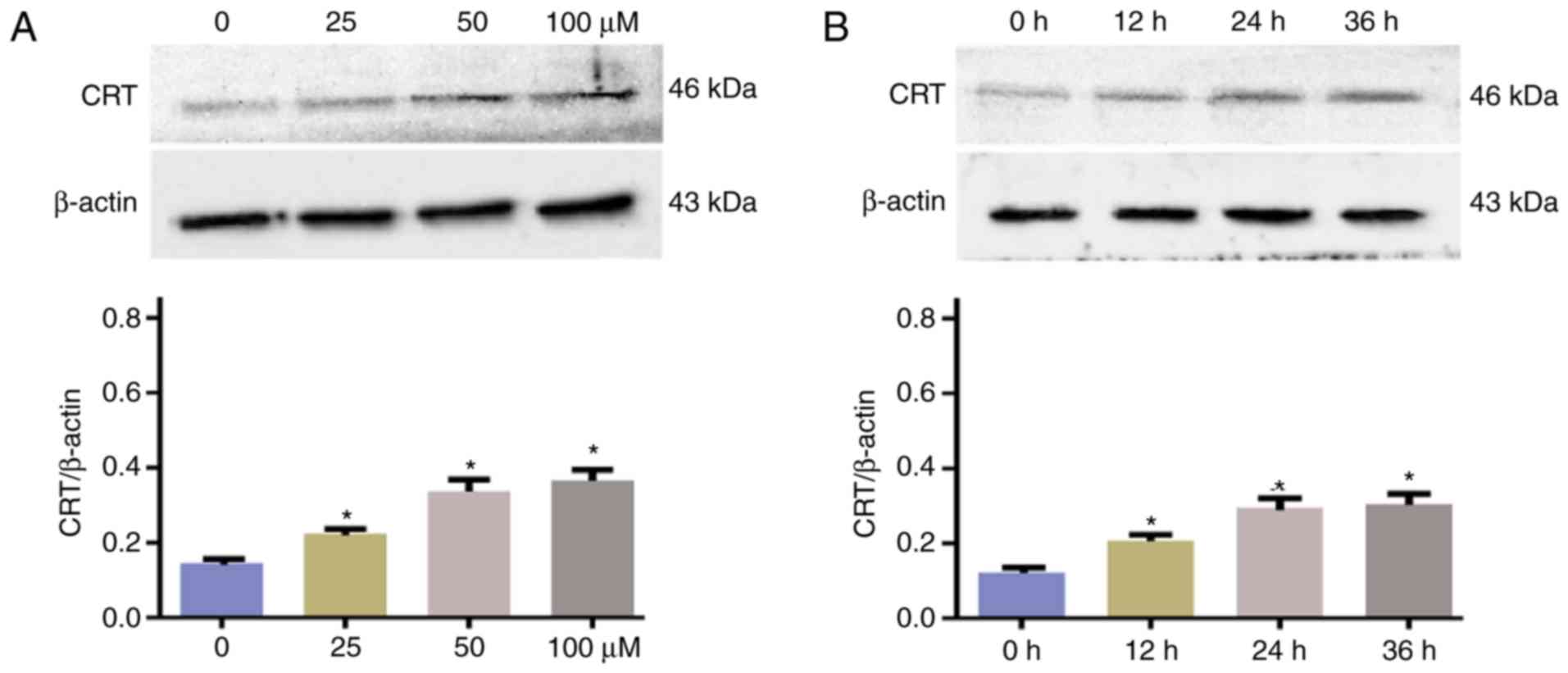
|
1
|
Chen N, Zhang R, Konishi T and Wang J:
Upregulation of NRF2 through autophagy/ERK 1/2 ameliorates ionizing
radiation induced cell death of human osteosarcoma U-2 OS. Mutat
Res. 813:10–17. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bielack SS, Hecker-Nolting S, Blattmann C
and Kager L: Advances in the management of osteosarcoma. F1000 Res.
5:27672016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Friebele JC, Peck J, Pan X, Abdel-Rasoul M
and Mayerson JL: Osteosarcoma: A meta-analysis and review of the
literature. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 44:547–553.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu K, Sun X, Zhang Y, Liu L and Yuan Q:
MiR-598: A tumor suppressor with biomarker significance in
osteosarcoma. Life Sci. 188:141–148. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Taran SJ, Taran R and Malipatil NB:
Pediatric osteosarcoma: An updated review. Indian J Med Paediatr
Oncol. 38:33–43. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen L, Pei H, Lu SJ, Liu ZJ, Yan L, Zhao
XM, Hu B and Lu HG: SPOP suppresses osteosarcoma invasion via
PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
22:609–615. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
He X, Gao Z, Xu H, Zhang Z and Fu P: A
meta-analysis of randomized control trials of surgical methods with
osteosarcoma outcomes. J Orthop Surg Res. 12:52017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Isakoff MS, Bielack SS, Meltzer P and
Gorlick R: Osteosarcoma: Current treatment and a collaborative
pathway to success. J Clin Oncol. 33:3029–3035. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Anderson ME: Update on survival in
osteosarcoma. Orthop Clin North Am. 47:283–292. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun J, Mu H, Dai K and Yi L: Calreticulin:
A potential anti-cancer therapeutic target. Pharmazie. 72:503–510.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Harada K, Takenawa T, Ferdous T, Kuramitsu
Y and Ueyama Y: Calreticulin is a novel independent prognostic
factor for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 13:4857–4862.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fucikova J, Truxova I, Hensler M, Becht E,
Kasikova L, Moserova I, Vosahlikova S, Klouckova J, Church SE,
Cremer I, et al: Calreticulin exposure by malignant blasts
correlates with robust anticancer immunity and improved clinical
outcome in AML patients. Blood. 128:3113–3124. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Obakan-Yerlikaya P, Arisan ED,
Coker-Gurkan A, Adacan K, Ozbey U, Somuncu B, Baran D and
Palavan-Unsal N: Calreticulin is a fine tuning molecule in
epibrassinolide-induced apoptosis through activating endoplasmic
reticulum stress in colon cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 56:1603–1619.
2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Matsukuma S, Yoshimura K, Ueno T, Oga A,
Inoue M, Watanabe Y, Kuramasu A, Fuse M, Tsunedomi R, Nagaoka S, et
al: Calreticulin is highly expressed in pancreatic cancer stem-like
cells. Cancer Sci. 107:1599–1609. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zamanian M, Hamadneh Qader LA,
Veerakumarasivam A, Rahman Abdul S, Shohaimi S and Rosli R:
Calreticulin mediates an invasive breast cancer phenotype through
the transcriptional dysregulation of p53 and MAPK pathways. Cancer
Cell Int. 16:562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fucikova J, Becht E, Iribarren K, Goc J,
Remark R, Damotte D, Alifano M, Devi P, Biton J, Germain C, et al:
Calreticulin expression in human non-small cell lung cancers
correlates with increased accumulation of antitumor immune cells
and favorable prognosis. Cancer Res. 76:1746–1756. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Feng R, Ye J, Zhou C, Qi L, Fu Z, Yan B,
Liang Z, Li R and Zhai W: Calreticulin down-regulation inhibits the
cell growth, invasion and cell cycle progression of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Diagn Pathol. 10:1492015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang MS, Wang HS, Wang BS, Li WH, Pang ZF,
Zou BK, Zhang X, Shi XT, Mu DB, Zhang DX, et al: A comparative
proteomic study identified calreticulin and prohibitin up-regulated
in adrenocortical carcinomas. Diagn Pathol. 8:582013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen CN, Chang CC, Su TE, Hsu WM, Jeng YM,
Ho MC, Hsieh FJ, Lee PH, Kuo ML, Lee H and Chang KJ: Identification
of calreticulin as a prognosis marker and angiogenic regulator in
human gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:524–533. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang XH, Zhang Y, Xie WP, Sun DS, Zhang
YK, Hao YK and Tan GQ: Expression and significance of calreticulin
in human osteosarcoma. Cancer Biomark. 18:405–411. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mikaili P, Maadirad S, Moloudizargari M,
Aghajanshakeri S and Sarahroodi S: Therapeutic uses and
pharmacological properties of garlic, shallot, and their
biologically active compounds. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 16:1031–1048.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Horn N, Miller G, Ajuwon KM and Adeola O:
Garlic diallyl disulfide and diallyl trisulfide mitigates effects
of pro-oxidant induced cellular stress and has immune modulatory
function in LPS-stimulated porcine epithelial cells. J Anim Sci.
95:4045–4051. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Antony ML and Singh SV: Molecular
mechanisms and targets of cancer chemoprevention by garlic-derived
bioactive compound diallyl trisulfide. Indian J Exp Biol.
49:805–816. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Seki T, Hosono T, Hosono-Fukao T, Inada K,
Tanaka R, Ogihara J and Ariga T: Anticancer effects of diallyl
trisulfide derived from garlic. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 17 Suppl
1:S249–S252. 2008.
|
|
25
|
Zhang YK, Zhang XH, Li JM, Sun DS, Yang Q
and Diao DM: A proteomic study on a human osteosarcoma cell line
Saos-2 treated with diallyl trisulfide. Anticancer Drugs.
20:702–712. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang YK, Li JM, Wang DL and Chen YQ:
Effects of diallyl trisulfide on cell cycle and apoptosis of human
osteosarcoma cell line Saos-2. Tumor. 33:214–222. 2013.(In
Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Yuan G, Chen J, Wu D and Gao C:
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy combined with limb salvage surgery in
patients with limb osteosarcoma of Enneking stage II: A
retrospective study. Onco Targets Ther. 10:2745–2750. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rosen G, Marcove RC, Caparros B, Nirenberg
A, Kosloff C and Huvos AG: Primary osteogenic sarcoma: The
rationale for preoperative chemotherapy and delayed surgery.
Cancer. 43:2163–2177. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Masood S: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in
breast cancers. Womens Health (Lond). 12:480–491. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Borkowska A, Knap N and Antosiewicz J:
Diallyl trisulfide is more cytotoxic to prostate cancer cells PC-3
than to noncancerous epithelial cell line PNT1A: A possible role of
p66Shc signaling axis. Nutr Cancer. 65:711–717. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pan Y, Lin S, Xing R, Zhu M, Lin B, Cui J,
Li W, Gao J, Shen L, Zhao Y, et al: Epigenetic upregulation of
metallothionein 2A by diallyl trisulfide enhances chemosensitivity
of human gastric cancer cells to docetaxel through attenuating
NF-κB activation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 24:839–854. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li W, Tian H, Li L, Li S, Yue W, Chen Z,
Qi L, Hu W, Zhu Y, Hao B, et al: Diallyl trisulfide induces
apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of A549 cells in vitro and in
vivo. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 44:577–583. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim SH, Kaschula CH, Priedigkeit N, Lee AV
and Singh SV: Forkhead box Q1 is a novel target of breast cancer
stem cell inhibition by diallyl trisulfide. J Biol Chem.
291:13495–13508. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lai KC, Hsu SC, Yang JS, Yu CC, Lein JC
and Chung JG: Diallyl trisulfide inhibits migration, invasion and
angiogenesis of human colon cancer HT-29 cells and umbilical vein
endothelial cells, and suppresses murine xenograft tumour growth. J
Cell Mol Med. 19:474–484. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Oommen S, Anto RJ, Srinivas G and
Karunagaran D: Allicin (from garlic) induces caspase-mediated
apoptosis in cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 485:97–103. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xu L, Yu J, Zhai D, Zhang D, Shen W, Bai
L, Cai Z and Yu C: Role of JNK activation and mitochondrial bax
translocation in allicin-induced apoptosis in human ovarian cancer
SKOV3 cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014:3786842014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li C, Lun W, Zhao X, Lei S, Guo Y, Ma J
and Zhi F: Allicin alleviates inflammation of
trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced rats and suppresses P38 and
JNK pathways in Caco-2 cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2015:4346922015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tufi R, Panaretakis T, Bianchi K, Criollo
A, Fazi B, Di Sano F, Tesniere A, Kepp O, Paterlini-Brechot P,
Zitvogel L, et al: Reduction of endoplasmic reticulum
Ca2+ levels favors plasma membrane surface exposure of
calreticulin. Cell Death Differ. 15:274–282. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chao MP, Jaiswal S, Weissman-Tsukamoto R,
Alizadeh AA, Gentles AJ, Volkmer J, Weiskopf K, Willingham SB,
Raveh T, Park CY, et al: Calreticulin is the dominant
pro-phagocytic signal on multiple human cancers and is
counterbalanced by CD47. Sci Transl Med. 2:63–94. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
No authors listed: Calreticulin inhibits
commitment to adipocyte differentiation. J Cell Biol. 208:249–250.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Martín N, Bardisa L, Pantoja C, Barra E,
Demetrio C, Valenzuela J, Barrios M and Sepúlveda MJ: Involvement
of calcium in the cardiac depressant actions of a garlic dialysate.
J Ethnopharmacol. 55:113–118. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|