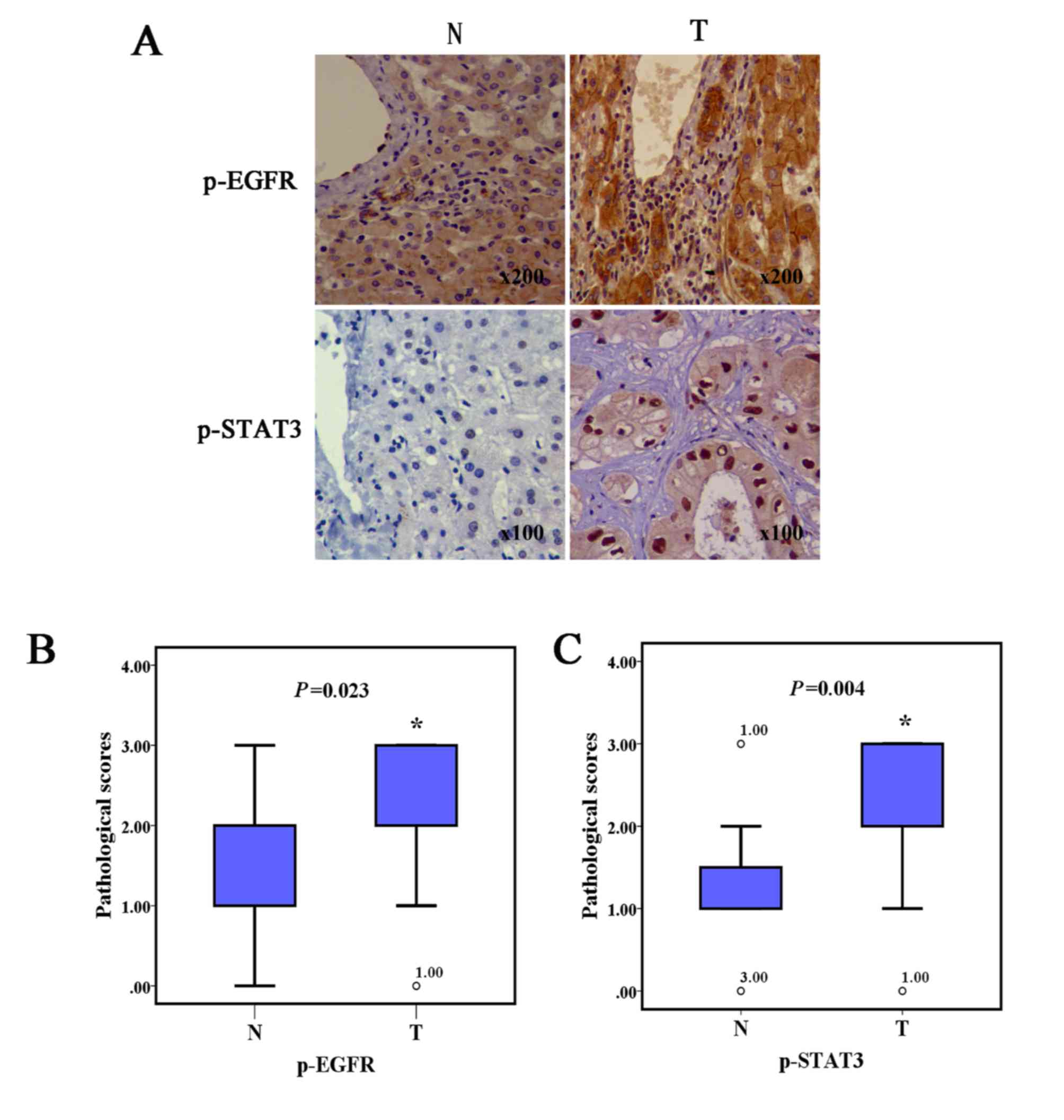
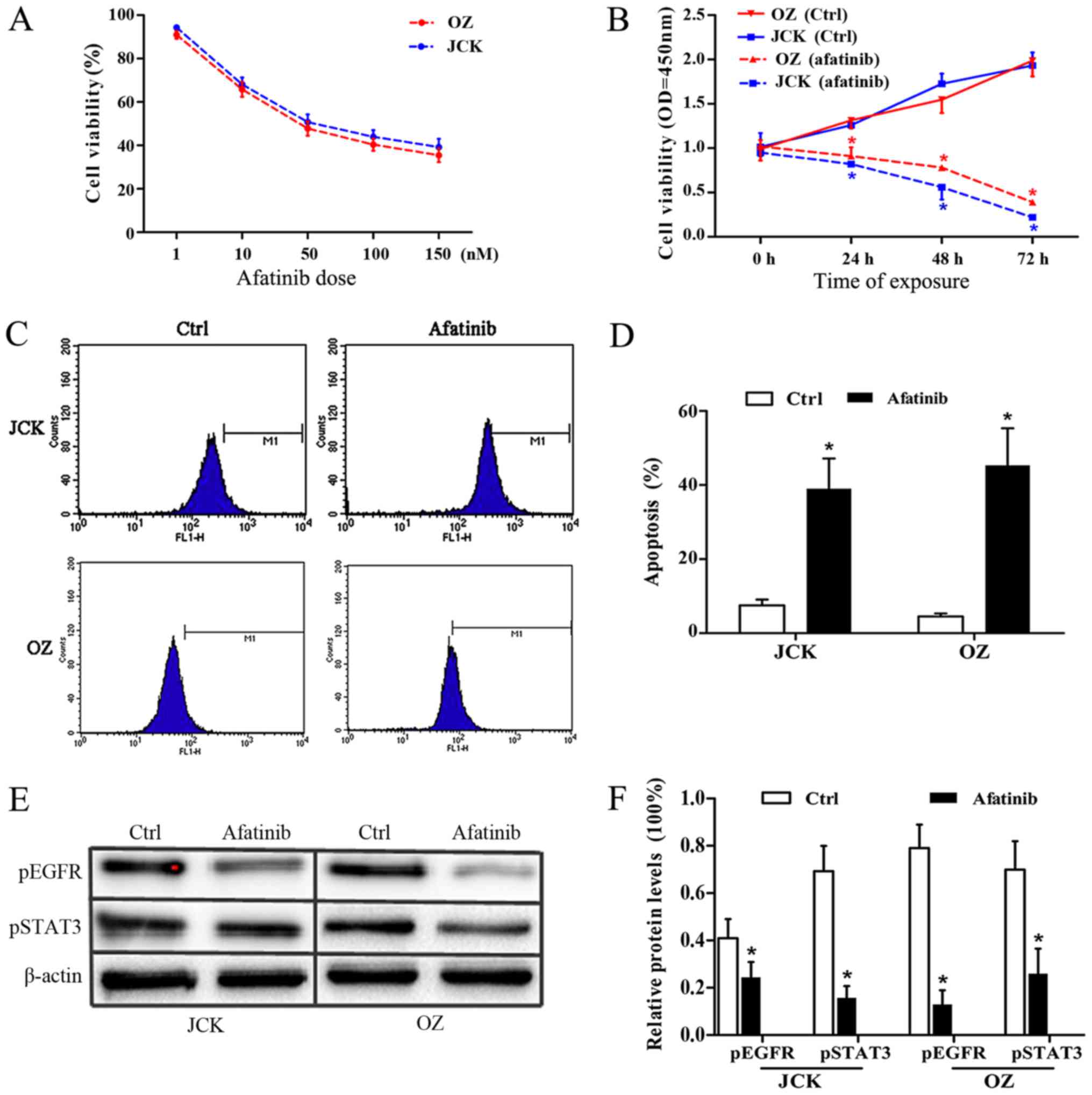
|
1
|
Shishir KM, Gamblin TC, Kamel I,
Corona-Villalobos CP, Thomas M and Pawlik TM: Multidisciplinary
approaches to intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer.
119:3929–3942. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sriputtha S, Khuntikeo N, Promthet S and
Kamsa-Ard S: Survival rate of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
patients after surgical treatment in Thailand. Asian Pacific J
Cancer Prev. 14:1107–1110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Robert R Jr: ErbB/HER protein-tyrosine
kinases: Structures and small molecule inhibitors. Pharmacol Res.
87:42–59. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bi WW, Zhang WH, Yin GH, Luo H, Wang SQ,
Wang H, Li C, Yan WQ and Nie DZ: Analysis of indoleamine 2–3
dioxygenase (IDO) and EGFR co-expression in breast cancer tissue by
immunohistochemistry. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:5535–5538. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhao X, Sun X and Li XL: Expression and
clinical significance of STAT3, p-STAT3, and VEGF-C in small cell
lung cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:2873–2877. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fang B: Genetic interactions of STAT3 and
anticancer drug development. Cancers (Basel). 6:494–525. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ung N, Putoczki TL, Stylli SS, Ng I,
Mariadason JM, Chan TA, Zhu HJ and Luwor RB: Anti-EGFR therapeutic
efficacy correlates directly with inhibition of STAT3 activity.
Cancer Biol Ther. 15:623–632. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chong CR and Jänne PA: The quest to
overcome resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in cancer. Nat Med.
19:1389–1400. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ioannou N, Seddon AM, Dalgleish A,
Mackintosh D and Modjtahedi H: Treatment with a combination of the
ErbB (HER) family blocker afatinib and the IGF-IR inhibitor,
NVP-AEW541 induces synergistic growth inhibition of human
pancreatic cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 13:412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Seiwert TY, Fayette J, Cupissol D, Del
Campo JM, Clement PM, Hitt R, Degardin M, Zhang W, Blackman A,
Ehrnrooth E and Cohen EE: A randomized, phase II study of afatinib
versus cetuximab in metastatic or recurrent squamous cell carcinoma
of the head and neck. Ann Oncol. 25:1813–1820. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lai WY, Chen CY, Yang SC, Wu JY, Chang CJ,
Yang PC and Peck K: Overcoming EGFR T790M-based tyrosine kinase
inhibitor resistance with an allele-specific DNAzyme. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 3:e1502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Machiels JP, Licitra LF, Haddad RI, Tahara
M and Cohen EE: Rationale and design of LUX-Head & Neck 1: A
randomised, Phase III trial of afatinib versus methotrexate in
patients with recurrent and/or metastatic head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma who progressed after platinum-based therapy. BMC
Cancer. 14:4732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Harder J, Waiz O, Otto F, Geissler M,
Olschewski M, Weinhold B, Blum HE, Schmitt-Graeff A and Opitz OG:
EGFR and HER2 expression in advanced biliary tract cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 15:4511–4517. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shen WF, Zhong W, Xu F, Kan T, Geng L, Xie
F, Sui CJ and Yang JM: Clinicopathological and prognostic analysis
of 429 patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 15:5976–5982. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yoshikawa D, Ojima H, Iwasaki M, Hiraoka
N, Kosuge T, Kasai S, Hirohashi S and Shibata T:
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of EGFR, VEGF, and
HER2 expression in cholangiocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 98:418–425.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Clapéron A, Mergey M, Aoudjehane L,
Ho-Bouldoires TH, Wendum D, Prignon A, Merabtene F, Firrincieli D,
Desbois-Mouthon C, Scatton O, et al: Hepatic myofibroblasts promote
the progression of human cholangiocarcinoma through activation of
epidermal growth factor receptor. Hepatology. 58:2001–2011. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nanda S: Cancer: A limited role for dual
EGFR and ErbB2 inhibition in cholangiocarcinoma? Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:5912010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu J, Patmore DM, Jousma E, Eaves DW,
Breving K, Patel AV, Schwartz EB, Fuchs JR, Cripe TP,
Stemmer-Rachamimov AO and Ratner N: EGFR-STAT3 signaling promotes
formation of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Oncogene.
33:173–180. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wendt MK, Balanis N, Carlin CR and
Schiemann WP: STAT3 and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in
carcinomas. JAKSTAT. 3:e289752014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qi QR and Yang ZM: Regulation and function
of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. World J Biol
Chem. 5:231–239. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mobahat M, Narendran A and Riabowol K:
Survivin as a preferential target for cancer therapy. Int J Mol
Sci. 15:2495–2516. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Concha-Benavente F, Srivastava RM, Ferrone
S and Ferris RL: EGFR-mediated tumor immunoescape: The imbalance
between phosphorylated STAT1 and phosphorylated STAT3.
Oncoimmunology. 2:e272152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou J, Liu Y, Wang T, Zhang H, Du M,
Zhang S, Wu S, Song S, Liu B, Zhang H and Jiang Z: Serum HER2 ECD
level and its clinical significance in advanced breast cancer
patients with different molecular subtypes. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.
94:1384–1387. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Parums DV: Current status of targeted
therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Drugs Today (Barc).
50:503–525. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|