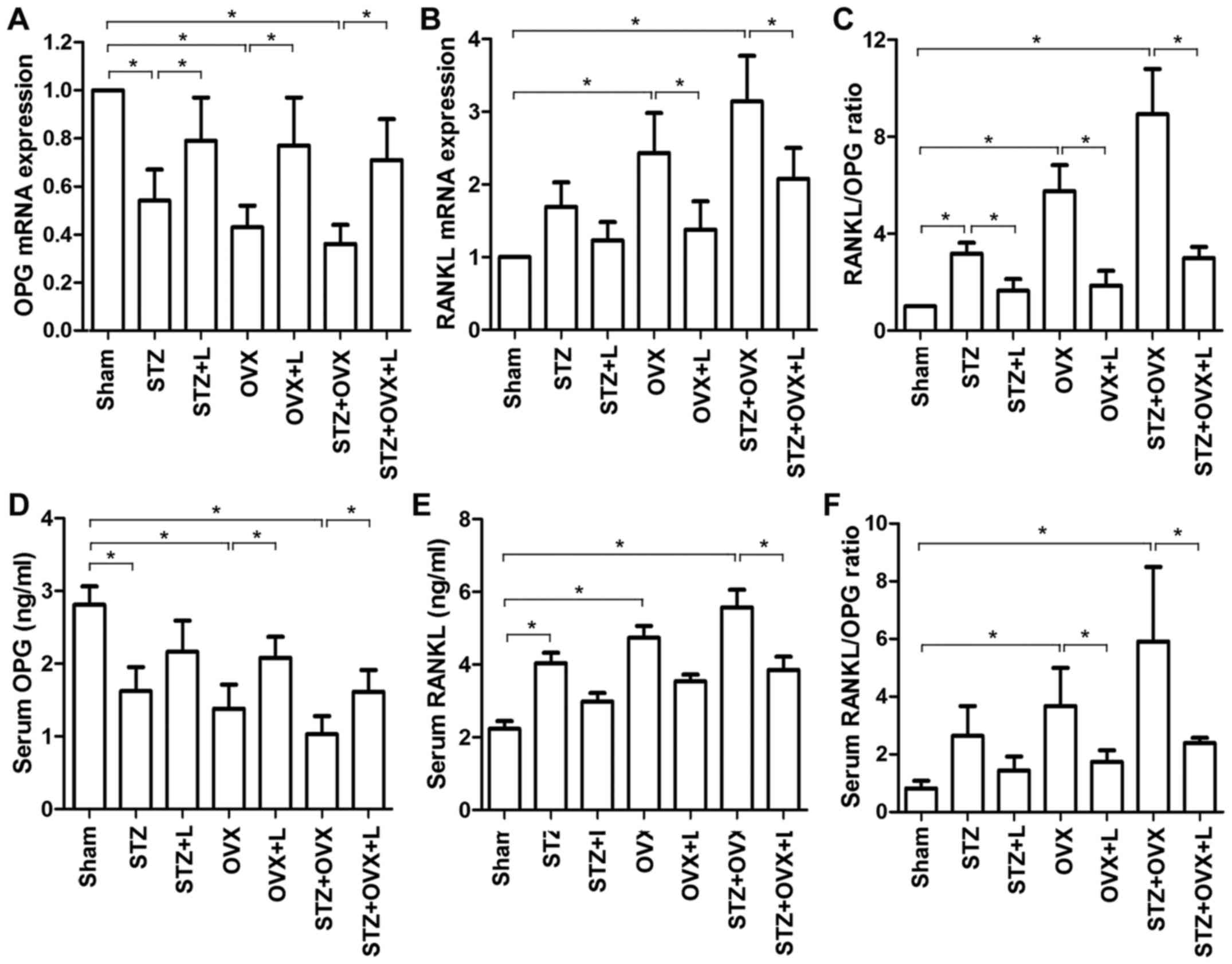
|
1
|
Vestergaard P: Discrepancies in bone
mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and type
2 diabetes-a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 18:427–444. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Janghorbani M, Van Dam RM, Willett WC and
Hu FB: Systematic review of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus and
risk of fracture. Am J Epidemiol. 166:495–505. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grey A: Skeletal consequences of
thiazolidinedione therapy. Osteoporos Int. 19:129–137. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rachner TD, Khosla S and Hofbauer LC:
Osteoporosis: Now and the future. Lancet. 377:1276–1287. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zaidi M: Skeletal remodeling in health and
disease. Nat Med. 13:791–801. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Berberoglu Z, Yazici AC and Demirag NG:
Effects of rosiglitazone on bone mineral density and remodelling
parameters in Postmenopausal diabetic women: A 2-year follow-up
study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 73:305–312. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Heilmeier U, Carpenter DR, Patsch JM,
Harnish R, Joseph GB, Burghardt AJ, Baum T, Schwartz AV, Lang TF
and Link TM: Volumetric femoral BMD, bone geometry and serum
sclerostin levels differ between type 2 diabetic postmenopausal
women with and without fragility fractures. Osteoporos Int.
26:1283–1293. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Henriksen DB, Alexandersen P, Hartmann B,
Adrian CL, Byrjalsen I, Bone HG, Holst JJ and Christiansen C:
Four-month treatment with GLP-2 significantly increases hip BMD: A
randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study in
postmenopausal women with low BMD. Bone. 45:833–842. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nicodemus KK and Folsom AR: Iowa Women's
Health Study: Type 1 and type 2 diabetes and incident hip fractures
in postmenopausal women. Diabetes Care. 24:1192–1197. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nauck MA: Incretin-based therapies for
type 2 diabetes mellitus: Properties, functions and clinical
implications. Am J Med. 124 Suppl 1:S3–S18. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Su B, Sheng H, Zhang M, Bu L, Yang P, Li
L, Li F, Sheng C, Han Y, Qu S and Wang J: Risk of bone fractures
associated with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists'
treatment: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Endocrine. 48:107–115. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Iepsen EW, Lundgren JR, Hartmann B,
Pedersen O, Hansen T, Jørgensen NR, Jensen JE, Holst JJ, Madsbad S
and Torekov SS: GLP-1 receptor agonist treatment increases bone
formation and prevents bone loss in weight-reduced obese women. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 100:2909–2917. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mansur SA, Mieczkowska A, Bouvard B, Flatt
PR, Chappard D, Irwin N and Mabilleau G: Stable incretin mimetics
counter rapid deterioration of bone quality in type 1 diabetes
mellitus. J Cell Physiol. 230:3009–3018. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun HX, Lu N, Luo X, Zhao L and Liu JM:
Liraglutide, the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, has
anabolic bone effects in diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. J Diabetes.
7:584–588. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lu N, Sun H, Yu J, Wang X, Liu D, Zhao L,
Sun L, Zhao H, Tao B and Liu J: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
agonist Liraglutide has anabolic bone effects in ovariectomized
rats without diabetes. PLoS One. 10:e01327442015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pereira M, Jeyabalan J, Jorgensen CS,
Hopkinson M, Al-Jazzar A, Roux JP, Chavassieux P, Orriss IR,
Cleasby ME and Chenu C: Chronic administration of Glucagon-like
peptide-1 receptor agonists improves trabecular bone mass and
architecture in ovariectomised mice. Bone. 81:459–467. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lasota A and Danowska-Klonowska D:
Experimental osteoporosis-different methods of ovariectomy in
female white rats. Rocz Akad Med Bialymst. 49 Suppl 1:S129–S131.
2004.
|
|
18
|
Moon YJ, Yun CY, Choi H, Ka SO, Kim JR,
Park BH and Cho ES: Smad4 controls bone homeostasis through
regulation of osteoblast/osteocyte viability. Exp Mol Med.
48:e2562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dempster DW, Compston JE, Drezner MK,
Glorieux FH, Kanis JA, Malluche H, Meunier PJ, Ott SM, Recker RR
and Parfitt AM: Standardized nomenclature, symbols and units for
bone histomorphometry: A 2012 update of the report of the ASBMR
histomorphometry nomenclature committee. J Bone Miner Res. 28:2–17.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kong YY, Yoshida H, Sarosi I, Tan HL,
Timms E, Capparelli C, Morony S, Oliveira-dos-Santos AJ, Van G,
Itie A, et al: OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis,
lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature.
397:315–323. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley
M, Chang MS, Luthy R, Nguyen HQ, Wooden S, Bennett L, Boone T, et
al: Osteoprotegerin: A novel secreted protein involved in the
regulation of bone density. Cell. 89:309–319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kazafeos K: Incretin effect: GLP-1, GIP,
DPP4. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 93 Suppl 1:S32–S36. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nuche-Berenguer B, Portal-Núñez S, Moreno
P, González N, Acitores A, López-Herradón A, Esbrit P, Valverde I
and Villanueva-Penacarrillo ML: Presence of a functional receptor
for GLP-1 in osteoblastic cells, independent of the cAMP-linked
GLP-1 receptor. J Cell Physiol. 225:585–592. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nuche-Berenguer B, Lozano D,
Gutierrez-Rojas I, Moreno P, Marinoso ML, Esbrit P and
Villanueva-Penacarrillo ML: GLP-1 and exendin-4 can reverse
hyperlipidic-related osteopenia. J Endocrinol. 209:203–210. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nuche-Berenguer B, Moreno P, Portal-Nuñez
S, Dapía S, Esbrit P and Villanueva-Penacarrillo ML: Exendin-4
exerts osteogenic actions in insulin-resistant and type 2 diabetic
states. Regul Pept. 159:61–66. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nuche-Berenguer B, Moreno P, Esbrit P,
Dapia S, Caeiro JR, Cancelas J, Haro-Mora JJ and
Villanueva-Penacarrillo ML: Effect of GLP-1 treatment on bone
turnover in normal, type 2 diabetic and insulin-resistant states.
Calcif Tissue Int. 84:453–461. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tantikanlayaporn D, Wichit P,
Weerachayaphorn J, Chairoungdua A, Chuncharunee A, Suksamrarn A and
Piyachaturawat P: Bone sparing effect of a novel phytoestrogen
diarylheptanoid from Curcuma comosa Roxb. in ovariectomized rats.
PLoS One. 8:e787392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Takano-Yamamoto T and Rodan GA: Direct
effects of 17 beta-estradiol on trabecular bone in ovariectomized
rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 87:2172–2176. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yamada C, Yamada Y, Tsukiyama K, Yamada K,
Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Tanaka K, Drucker DJ, Seino Y and Inagaki
N: The murine glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is essential for
control of bone resorption. Endocrinology. 149:574–579. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peng J, Hui K, Hao C, Peng Z, Gao QX, Jin
Q, Lei G, Min J, Qi Z, Bo C, et al: Low bone turnover and reduced
angiogenesis in streptozotocin-induced osteoporotic mice. Connect
Tissue Res. 57:277–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu SG, Zhang CJ, Xu XE, Sun JH, Zhang L
and Yu PF: Ursolic acid derivative ameliorates
streptozotocin-induced diabestic bone deleterious effects in mice.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:3681–3690. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ma B, Zhang Q, Wu D, Wang YL, Hu YY, Cheng
YP, Yang ZD, Zheng YY and Ying HJ: Strontium fructose
1,6-diphosphate prevents bone loss in a rat model of postmenopausal
osteoporosis via the OPG/RANKL/RANK pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
33:479–489. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sato T, Watanabe K, Masuhara M, Hada N and
Hakeda Y: Production of IL-7 is increased in ovariectomized mice,
but not RANKL mRNA expression by osteoblasts/stromal cells in bone
and IL-7 enhances generation of osteoclast precursors in vitro. J
Bone Miner Metab. 25:19–27. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|