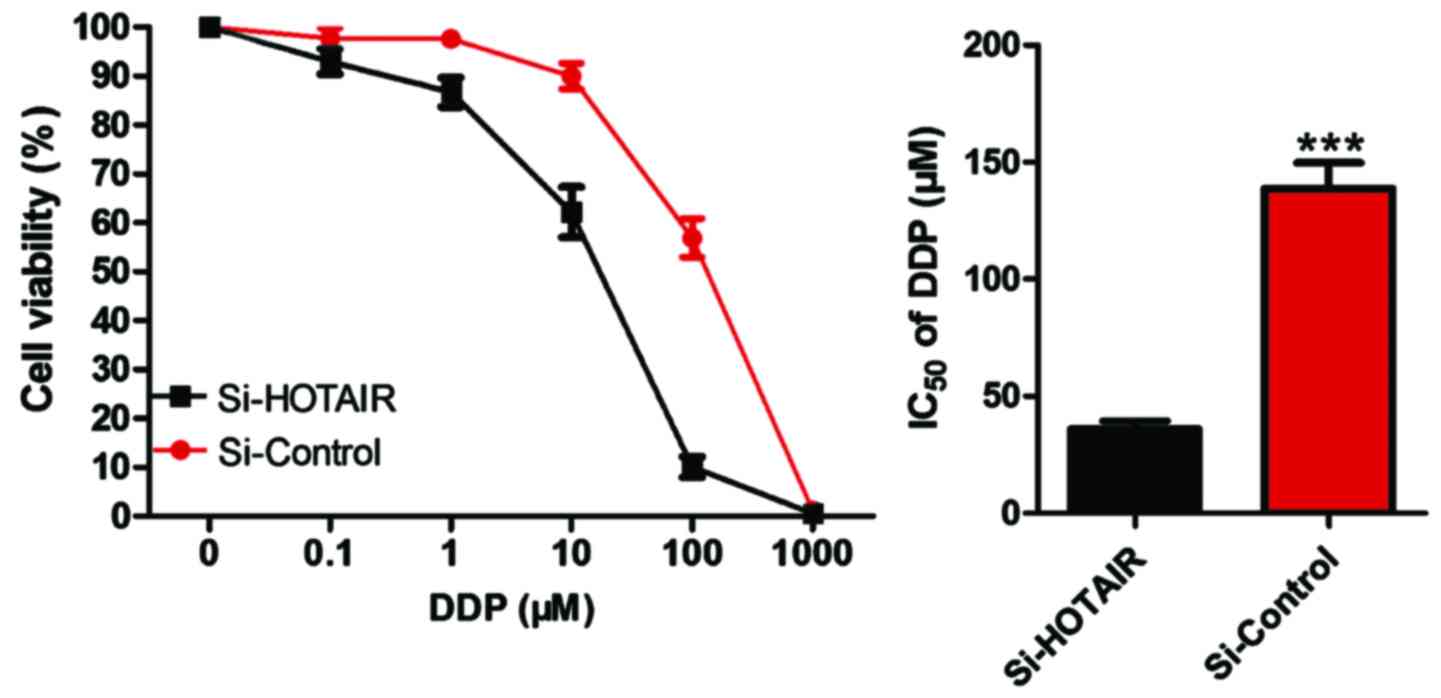
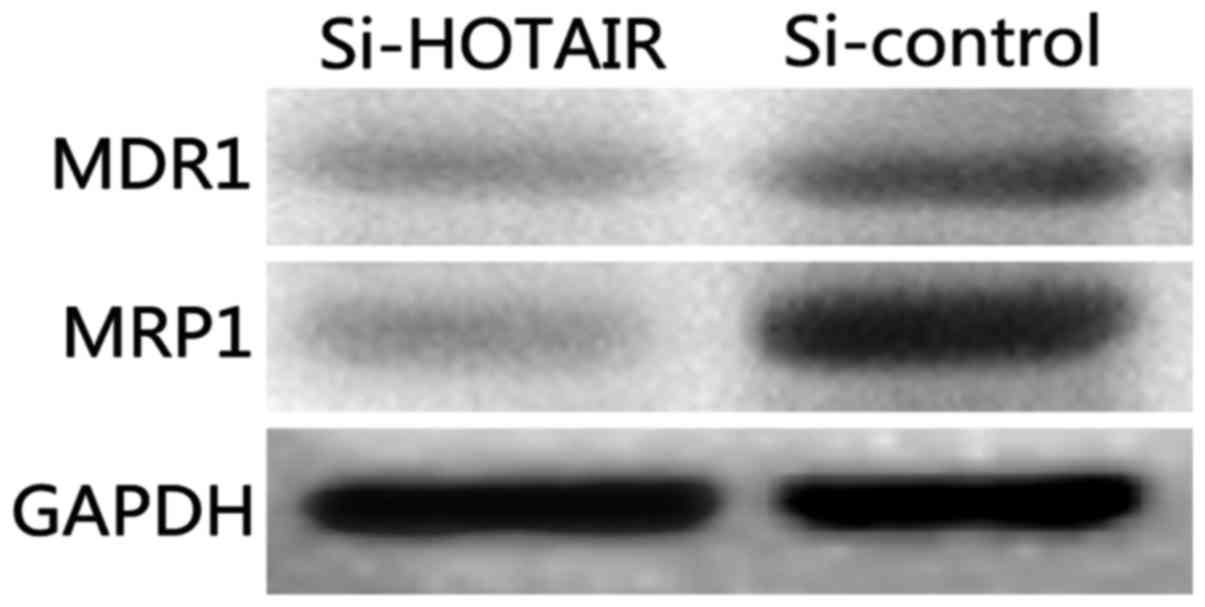
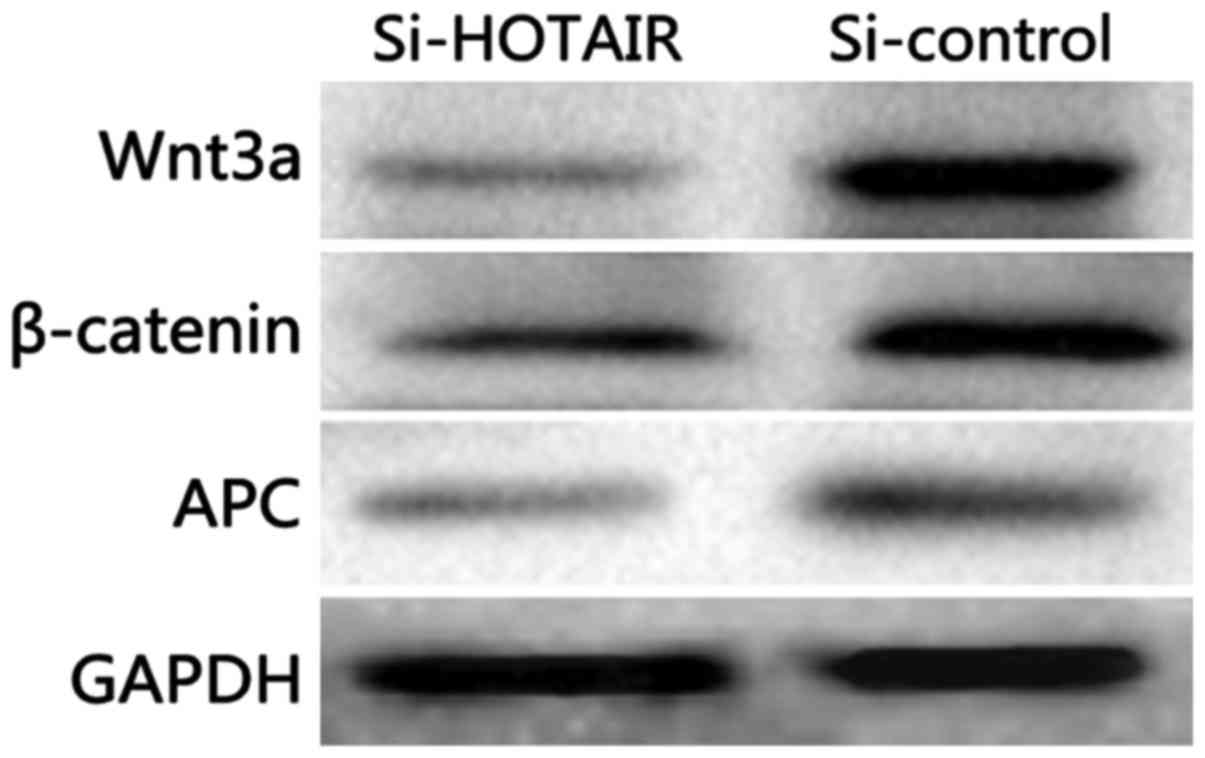
|
1
|
Hill C: Cancer prevention and screening.
Bull Cancer. 100:547–554. 2013.(In French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dearing KR, Sangal A and Weiss GJ:
Maintaining clarity: Review of maintenance therapy in non-small
cell lung cancer. World J Clin Oncol. 5:103–113. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ettinger DS, Akerley W, Borghaei H, Chang
AC, Cheney RT, Chirieac LR, D'Amico TA, Demmy TL, Ganti AK,
Govindan R, et al: NCCN (National Comprehensive Cancer Network):
Non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 10:1236–1271.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ettinger DS, Akerley W and Borghaei H:
Elemene increases autophagic apoptosis and drug sensitivity in
human cisplatin (DDP)-resistant lung cancer cell line SPC-A-1/DDP
by inducing Beclin-1 expression. Oncol Res Featuring Preclinical
Clin Cancer Ther. 4:502–510. 2017.
|
|
5
|
Xiao X, Yu S, Li S, Wu J, Ma R, Cao H, Zhu
Y and Feng J: Exosomes: Decreased sensitivity of lung cancer A549
cells to cisplatin. PLoS One. 9:e895342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shen W, Liang B, Yin J, Li X and Cheng J:
Noscapine increases the sensitivity of drug-resistant ovarian
cancer cell line SKOV3/DDP to cisplatin by regulating cell cycle
and activating apoptotic pathways. Cell Biochem Biophys.
72:203–213. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tang T, Song X, Liu YF and Wang WY: PEITC
reverse multi-drug resistance of human gastric cancer SGC7901/DDP
cell line. Cell Biol Int. 38:502–510. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pastan I and Gottesman M: Multiple-drug
resistance in human cancer. N Engl J Med. 316:1388–1393. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dean M, Fojo T and Bates S: Tumour stem
cells and drug resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:275–284. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Holohan C, Van Schaeybroeck S, Longley DB
and Johnston PG: Cancer drug resistance: an evolving paradigm. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:714–726. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Deng H, Zhang J, Shi J, Guo Z, He C, Ding
L, Tang JH and Hou Y: Role of long non-coding RNA in tumor drug
resistance. Tumour Biol. 37:11623–11631. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huarte M: The emerging role of lncRNAs in
cancer. Nat Med. 21:1253–1261. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li H, Yu B, Li J, Su L, Yan M, Zhu Z and
Liu B: Overexpression of lncRNA H19 enhances carcinogenesis and
metastasis of gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 5:2318–2329. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Engreitz JM, Pandya-Jones A, McDonel P,
Shishkin A, Sirokman K, Surka C, Kadri S, Xing J, Goren A, Lander
ES, et al: The Xist lncRNA exploits three-dimensional genome
architecture to spread across the X chromosome. Science.
341:12379732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang F, Zhou X and Xu Y: Assessment of
varied long noncoding RNA and messenger RNA expression levels in
adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 5:8031–8038.
2016.
|
|
16
|
Furió-Tarí P, Tarazona S, Gabaldón T,
Enright AJ and Conesa A: spongeScan: A web for detecting microRNA
binding elements in lncRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:W176–W180. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Clevers H: Wnt/β-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Clevers H, Loh KM and Nusse R: Stem cell
signaling. An integral program for tissue renewal and regeneration:
Wnt signaling and stem cell control. Science. 346:12480122014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fifis T, Tran BM, Schwab RHM, Johanson TM,
Warner N, Barker N and Vincan E: Wnt signaling regulation of tissue
architecture (EMT and MET) and morphogenesisWnt Signaling in
Development and Disease: Molecular Mechanisms and Biological
Functions. Hoppler S and Moon RT: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; pp.
315–328. 2014, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bhan A and Mandal SS: LncRNA HOTAIR: A
master regulator of chromatin dynamics and cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1856:151–164. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|