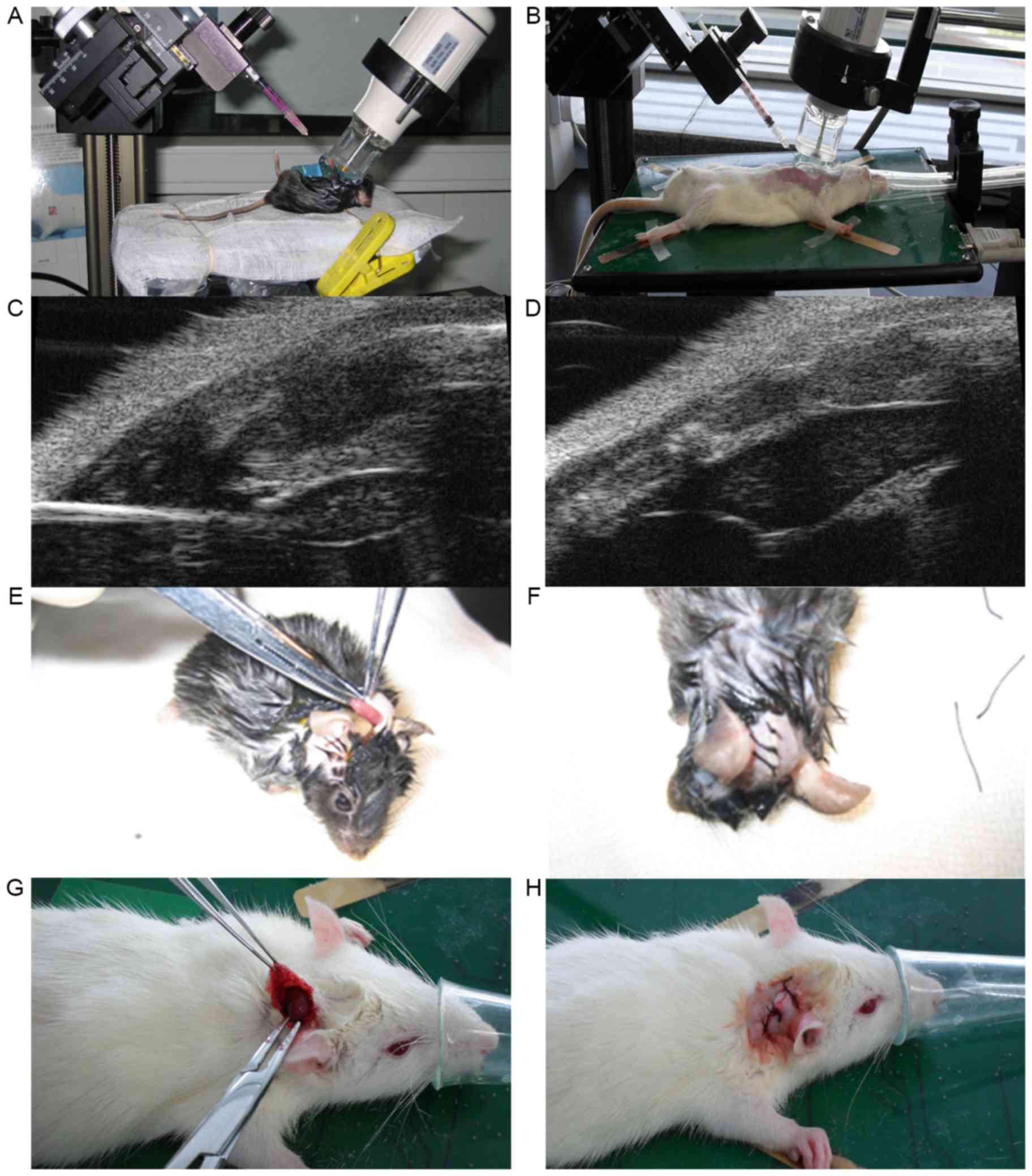
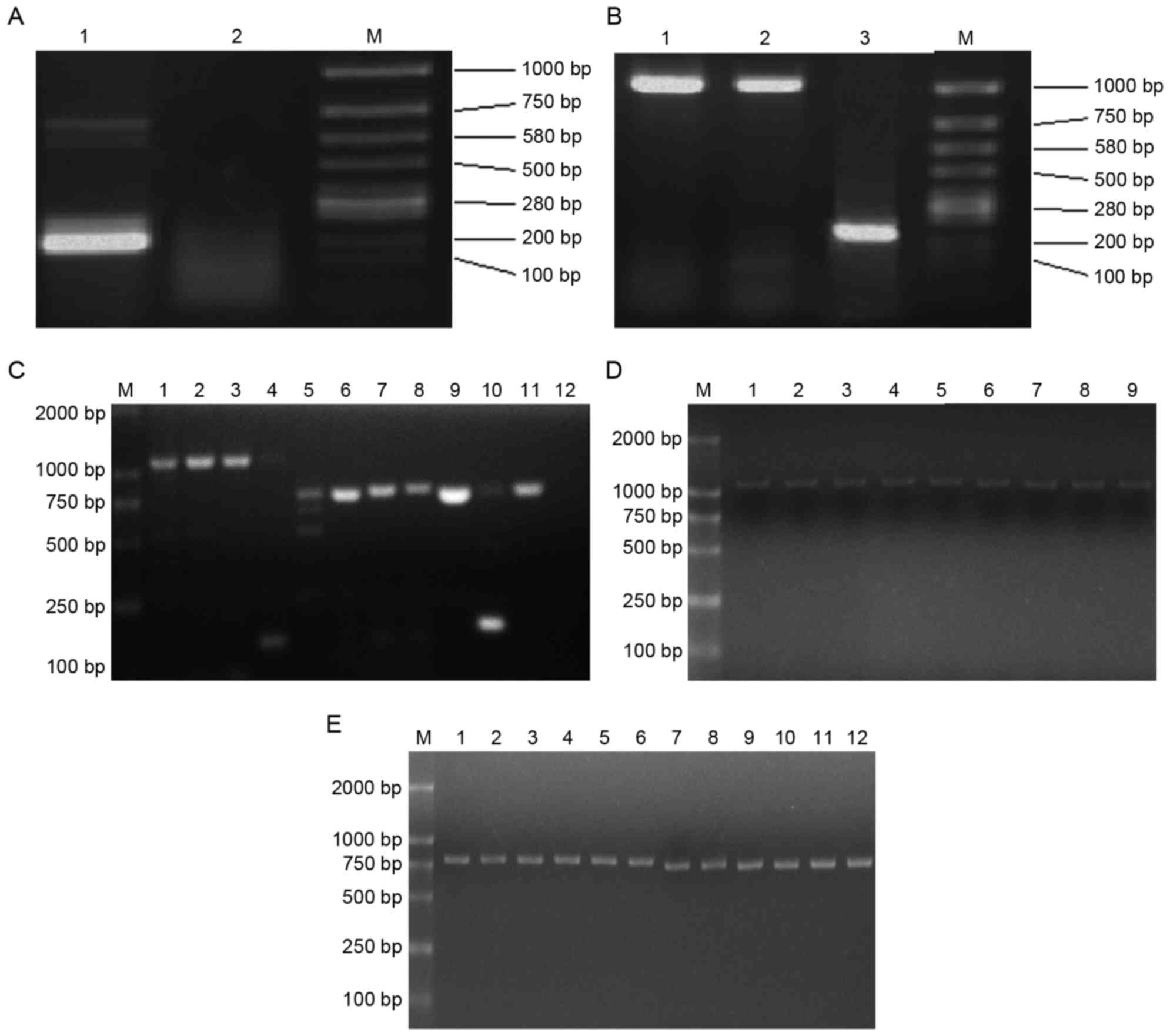
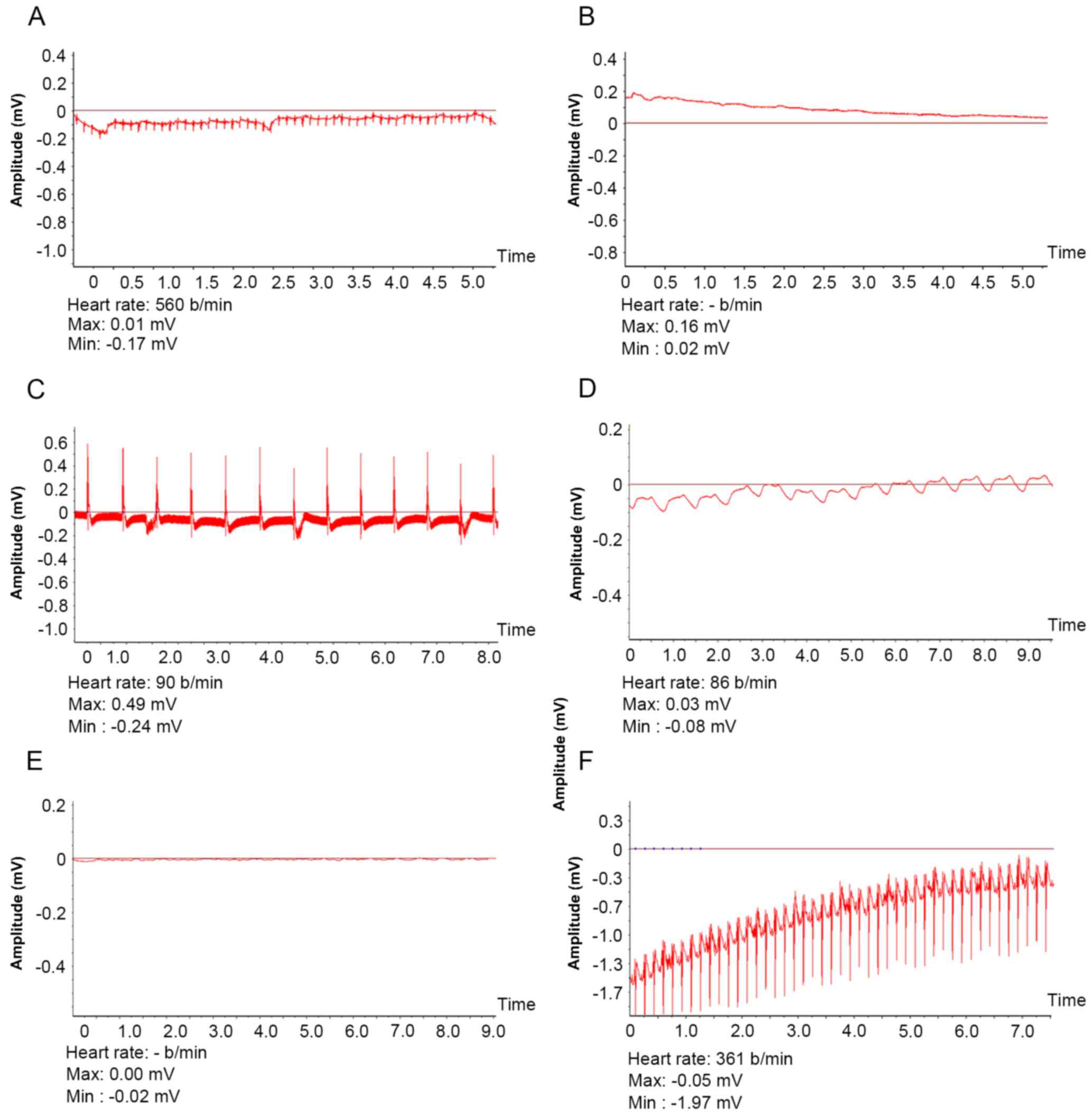
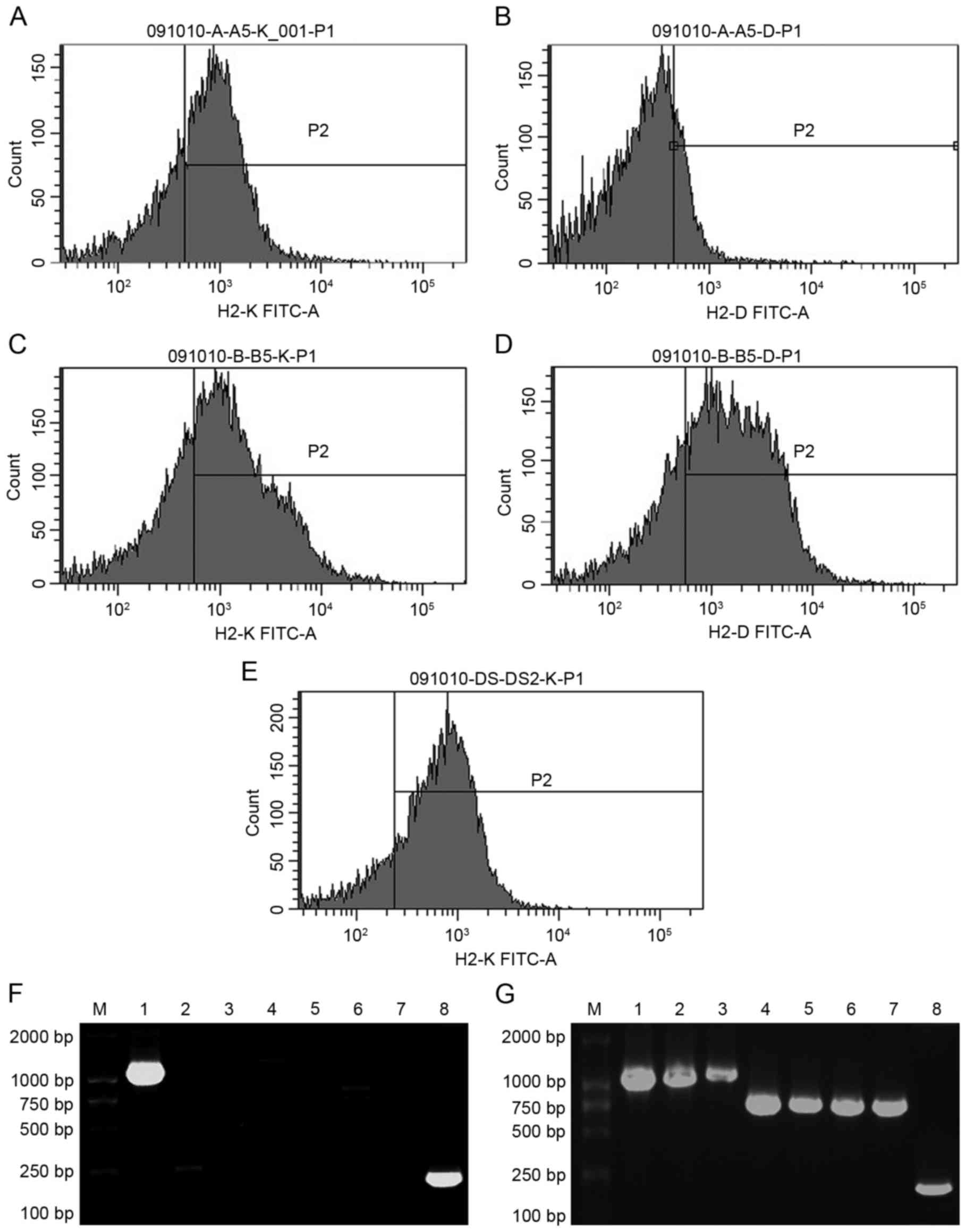
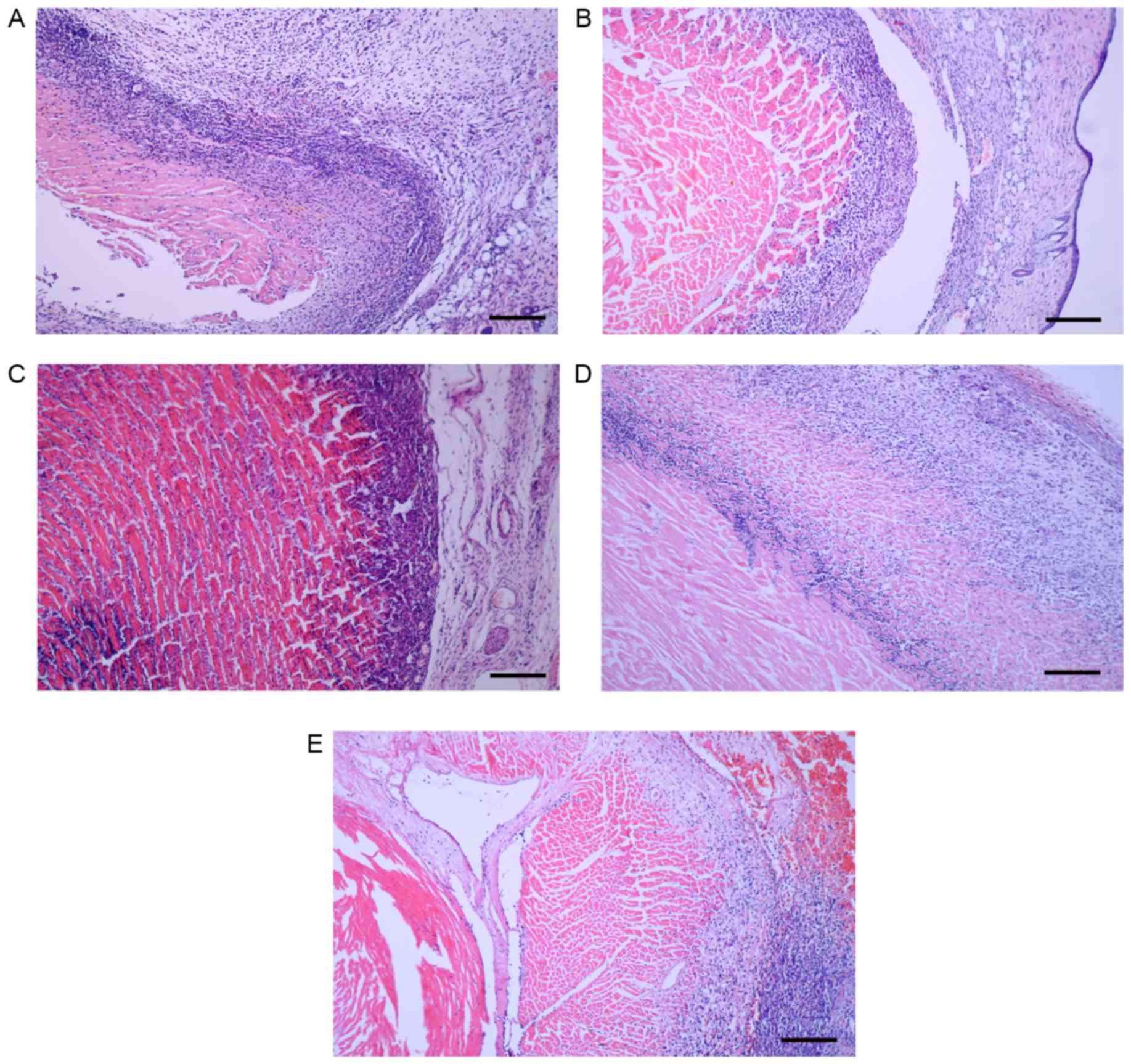
|
1
|
Bharat A, Kuo E, Steward N, Aloush A,
Hachem R, Trulock EP, Patterson GA, Meyers BF and Mohanakumar T:
Immunological link between primary graft dysfunction and chronic
lung allograft rejection. Ann Thorac Surg. 86:189–195. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Corris PA and Christie JD: Update in
transplantation 2007. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 177:1062–1067.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pham VV, Stichtenoth DO and Borlak J:
Graft rejection: Pharmacogenetic analysis or drug anamnesis? Br J
Clin Pharmacol. 65:959–960. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Peeters P, Van Laecke S and Vanholder R:
Acute kidney injury in solid organ transplant recipients. Acta Clin
Belg. 62 Suppl 2:S389–S392. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lechler RI, Sykes M, Thomson AW and Turka
LA: Organ transplantation-how much of the promise has been
realized? Nat Med. 11:605–613. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim JI, Sonawane SB, Lee MK, Lee SH, Duff
PE, Moore DJ, O'Connor MR, Lian MM, Deng S, Choi Y, et al: Blockade
of GITR-GITRL interaction maintains Treg function to prolong
allograft survival. Eur J Immunol. 40:1369–1374. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peugh WN, Superina RA, Wood KJ and Morris
PJ: The role of H-2 and non-H-2 antigens and genes in the rejection
of murine cardiac allografts. Immunogenetics. 23:30–37. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wood KJ: Principles of transplantation
immunologyOxford Textbook of Medicine. Oxford University Press;
Oxford: pp. 1082003
|
|
9
|
Beck S and Trowsdale J: The human major
histocompatability complex: Lessons from the DNA sequence. Annu Rev
Genomics Hum Genet. 1:117–137. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu CL: Major histocompatibility complex
(introduction)Modern Medical Immunology. Shanghai Medical
University Publishing House; Shanghai: pp. 168–169. 1998
|
|
11
|
Parmar S, Del Lima M, Zou Y, Patah PA, Liu
P, Cano P, Rondon G, Pesoa S, de Padua Silva L, Qazilbash MH, et
al: Donor-recipient mismatches in MHC class I chain-related gene A
in unrelated donor transplantation lead to increased incidence of
acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 114:2884–2887. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fang M and Shen GX: The differentiation of
T cellMedical Immunology. Gong FL: Science Publishing House;
Beijing: pp. 151–153. 2000
|
|
13
|
Maurice D, Hooper J, Lang G and Weston K:
c-Myb regulates lineage choice in developing thymocytes via its
target gene Gata3. EMBO J. 26:3629–3640. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Goldrath AW and Bevan MJ: Selecting and
maintaining a diverse T-cell repertoire. Nature. 402:255–262. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kishimoto H and Sprent J: The thymus and
central tolerance. Clin Immunol. 95:S3–S7. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kruskall MS: The major histocompatibility
complex: The value of extended haplotypes in the analysis of
associated immune diseases and disorders. Yale J Biol Med.
63:477–486. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li T, Yan J, Tan JL, Lv YP, Hou SC, Li ST,
Xu Q, Tong XH, Ding J, Zhang Zt and Li H: Donor MHC gene to
mitigate rejection of transplantation in recipient mice. Chin Med J
(Engl). 124:4279–4285. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Judd KP and Trentin JJ: Cardiac
transplantation in mice. Transplantation. 11:298–308.
1971.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Babang G, Morris RE, Babang I and Kates
RE: Evaluation of the in vivo dose-response relationship of
immunosuppressive drugs using a mouse heart transplant model:
Application to cyclosporine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 244:259–262.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fiedor P, Jin MX, Hardy MA and Oluwole SF:
Dependence of acquired systemic tolerance to rat islet allografts
induced by intrathymic soluble alloantigens on host responsiveness,
MHC differences, and transient immunosuppression in the high
responder recipient. Transplantation. 63:279–283. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Oluwole SF, Jin MX, Chowdhury NC,
Engelstad K, Ohajekwe OA and James T: Induction of peripheral
tolerance by intrathymic inoculation of soluble alloantigens:
Evidence for the role of host antigen-presenting cells and
suppressor cell mechanism. Cell Immunol. 162:33–41. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Otomo N, Motovama K, Yu S, Shimizu Y,
Margenthaler JA, Tu F and Flye MW: Intrathymic alloantigen-mediated
tolerant, completely MHC-mismatched mouse hearts are specifically
rejected by adoptively transferred in vitro-sensitized anti-class I
L(d+)-specific 2C cells. Transplant Proc. 33:159–160. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Strober S: Protective conditioning against
GVHD and graft rejection after combined organ and hematopoietic
cell transplantation. Blood Cell Mol Dis. 40:48–54. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Arima T, Lehmann M and Flye MW: Induction
of donor specific transplantation tolerance to cardiac allografts
following treatment with nondepleting (RIB 5/2) or depleting
(OX-38) anti-CD4 mAb plus intrathymic or intravenous donor
alloantigen. Transplantation. 63:284–292. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gopinathan R, DePaz HA, Oluwole OO, Ali
AO, Garrovillo M, Engelstad K, Hardy MA and Oluwole SF: Role of
reentry of in vivo alloMHC peptide-activated T cells into the adult
thymus in acquired systemic tolerance. Transplantation.
72:1533–1541. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hillebrands JL, Raué HP, Klatter FA,
Hylkema MN, Platteel I, Hardonk-Wubbena A, Nieuwenhuis P and Rozing
J: Intrathymic immune modulation prevents acute rejection but not
the development of graft arteriosclerosis (chronic rejection).
Transplantation. 71:914–924. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kobayashi E, Kamada N, Delriviere L, Lord
R, Goto S, Walker NI, Enosawa S and Miyata M: Migration of donor
cells into the thymus is not essential for induction and
maintenance of systemic tolerance after liver transplantation in
the rat. Immunology. 84:333–336. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Trani J, Moore DJ, Jarrett BP, Markmann
JW, Lee MK, Singer A, Lian MM, Tran B, Caton AJ and Markmann JF:
CD25+ immunoregulatory CD4 T cells mediate acquired central
transplantation tolerance. J Immunol. 170:279–286. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chowdhury NC, Murphy B, Sayegh MH, Hardy
MA and Oluwole SF: Induction of transplant tolerance by intrathymic
inoculation of synthetic MHC class I allopeptides. Transplant Proc.
29:11361997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sonntag KC, Emery DW, Yasumoto A, Haller
G, Germana S, Sablinski T, Shimizu A, Yamada K, Shimada H, Arn S,
et al: Tolerance to solid organ transplants through transfer of MHC
class II genes. J Clin Invest. 107:65–71. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Spriewald BM, Ensminger SM, Jenkins S,
Morris PJ and Wood KJ: Intrathymic delivery of plasmid-encoding
endoplasmic reticulum signal-sequence-deleted MHC class I
alloantigen can induce long-term allograft survival. Transpl Int.
17:458–462. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ando Y, Beck Y, Ichikawa N, Meigata K,
Nomura Y, Nishimura Y, Tomikawa S and Takiguchi M: Induction of
long-term heart graft survival in HLA class I transgenic mice by
intrathymic injection of HLA class I peptides. Transplant Proc.
30:3890–3891. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
del Rio ML, Pabst O, Ramirez P,
Penuelas-Rivas G, Förster R and Rodriguez-Barbosa JI: The thymus is
required for the ability of FTY720 to prolong skin allograft
survival across different histocompatibility MHC barriers. Transpl
Int. 20:895–903. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Siemionow M, Izycki D, Ozer K, Ozmen S and
Klimczak A: Role of thymus in operational tolerance induction in
limb allograft transplant model. Transplantation. 81:1568–1576.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yamamoto S, Teranishi K, Kamano C,
Samelson-Jones E, Arakawa H, Nobori S, Okumi M, Houser S, Shimizu
A, Sachs DH and Yamada K: Role of the thymus in transplantation
tolerance in miniature swine: V. Deficiency of the graft-to-thymus
pathway of tolerance induction in recipients of cardiac
transplants. Transplantation. 81:607–613. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yamada K, Vagefi PA, Utsugi R, Kitamura H,
Barth RN, LaMattina JC and Sachs DH: Thymic transplantation in
miniature swine: III. Induction of tolerance by transplantation of
composite thymokidneys across fully major histocompatibility
complex-mismatched barriers. Transplantation. 76:530–536. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nobori S, Samelson-Jones E, Shimizu A,
Hisashi Y, Yamamoto S, Kamano C, Teranishi K, Vagefi PA, Nuhn M,
Okumi M, et al: Long-term acceptance of fully allogeneic cardiac
grafts by cotransplantation of vascularized thymus in miniature
swine. Transplantation. 81:26–35. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Viret C, Sant'Angelo DB, He X, Ramaswamy H
and Janeway CA Jr: A Role for accessibility to
self-peptide-self-MHC complexes in intrathymic negative selection.
J Immunol. 166:4429–4437. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pullen JK, Horton RM, Cai ZL and Pease LR:
Structural diversity of the classical H-2 genes: K, D, and L. J
Immunol. 148:953–967. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chowdhury NC, Jin MX, Hardy MA and Oluwole
SF: Donor-specific unresponsiveness to murine cardiac allografts
induced by intrathymic-soluble alloantigens is dependent on
alternate pathway of antigen presentation. J Surg Res. 59:91–96.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Knechtle SJ, Wang J, Graeb C, Zhai Y, Hong
X, Fechner JH Jr and Geissler EK: Direct MHC class I complementary
DNA transfer to thymus induces donor-specific unresponsiveness,
which involves multiple immunologic mechanisms. J Immunol.
159:152–158. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Geissler EK, Scherer MN and Graeb C:
Soluble donor MHC class I gene transfer to thymus promotes
allograft survival in a high-responder heart transplant model.
Transpl Int. 13 Suppl 1:S452–S455. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|