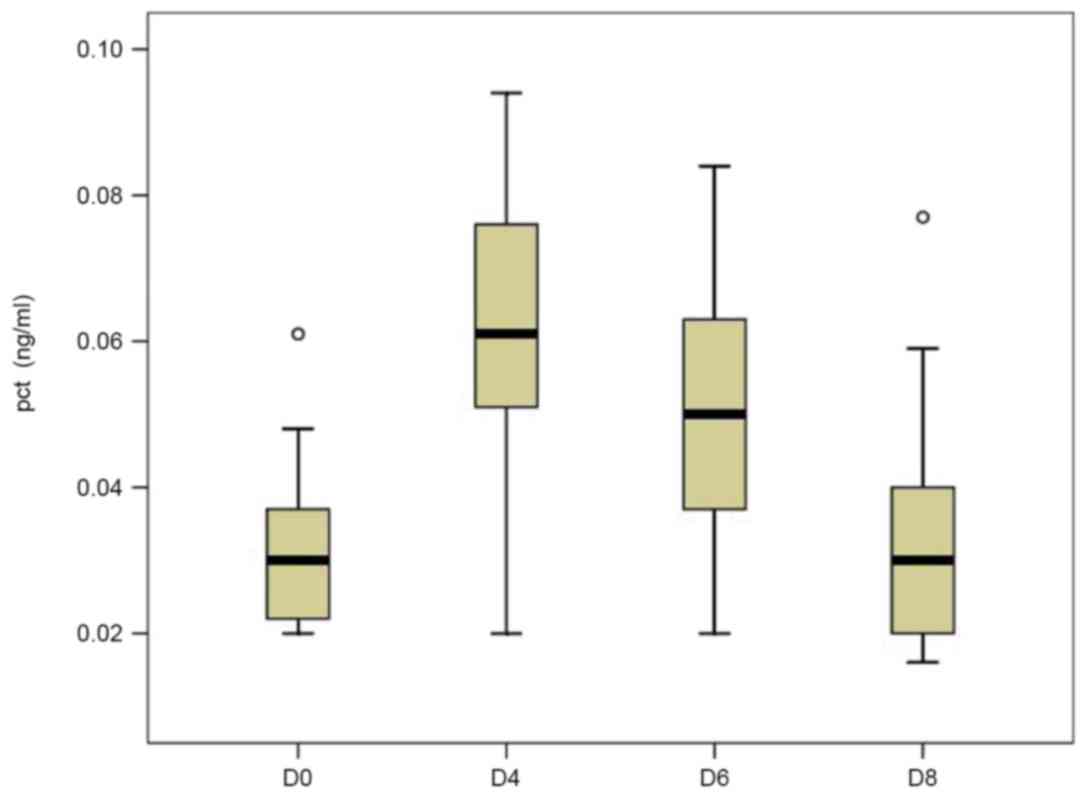
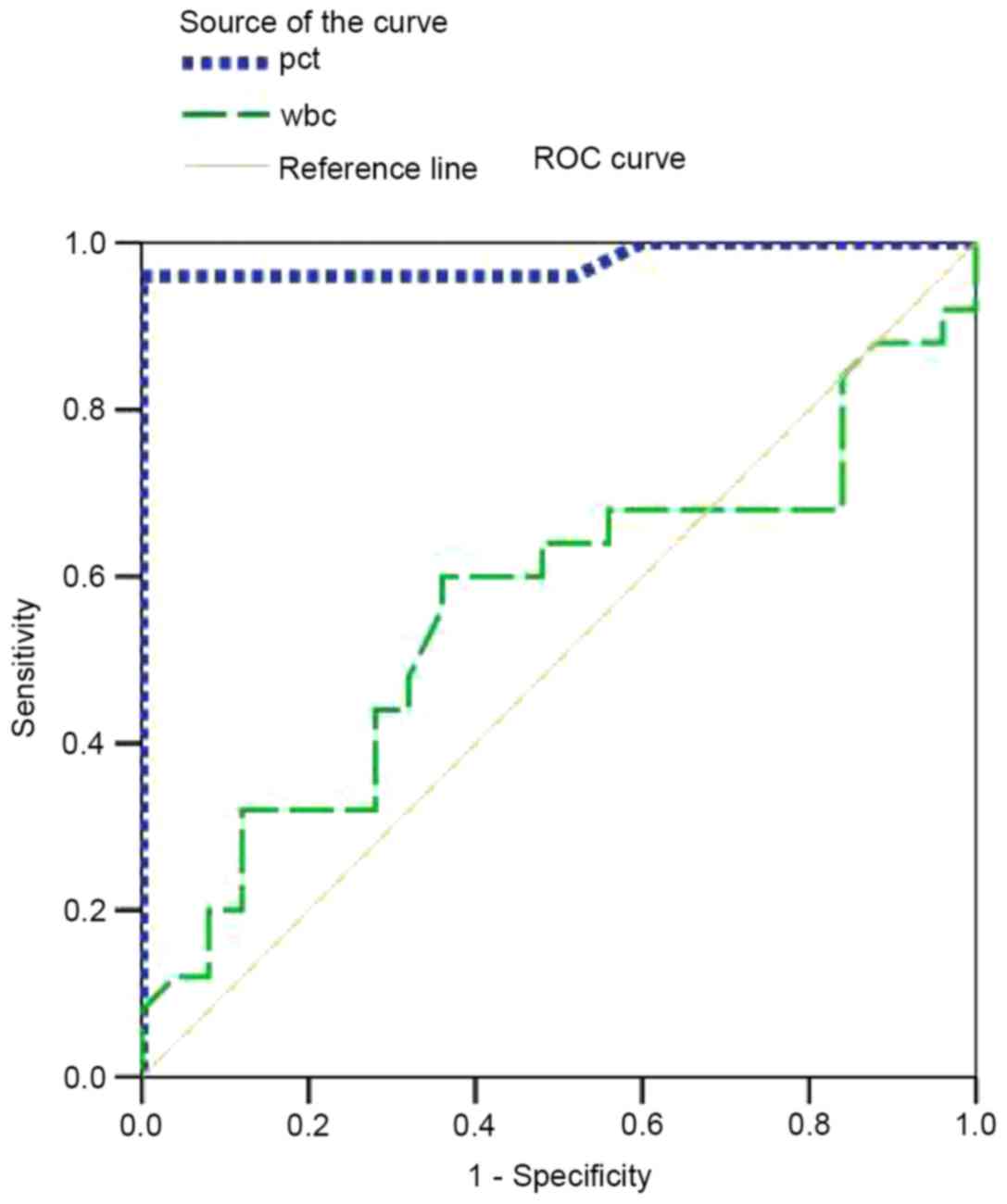
|
1
|
Dale H, Hallan G, Hallan G, Espehaug B,
Havelin LI and Engesaeter LB: Increasing risk of revision due to
deep infection after hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 80:639–645.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Costerton JW, Post JC, Ehrlich GD, Hu FZ,
Kreft R, Nistico L, Kathju S, Stoodley P, Hall-Stoodley L, Maale G,
et al: New methods for the detection of orthopedic and other
biofilm infection. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 61:133–140. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Savarino L, Baldini N, Tarabusi C,
Pellacani A and Giunti A: Diagnosis of infection after total hip
replacement. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 70:139–145. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Van Kleunen JP, Knox D, Garino JP and Lee
GC: Irrigation and dèbridement and prosthesis retention for
treating acute periprosthetic infections. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
468:2024–2028. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
van Leeuwen MA and van Rijswijk MH: Acute
phase proteins in the monitoring of inflammatory disorders.
Baillieres Clin Rheumato. 8:531–552. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rafiq M, Worthington T, Tebbs SE, Treacy
RB, Dias R, Lambert PA and Elliott TS: Serological detection of
Gram-positive bacterial infection around prostheses. J Bone Joint
Surg Br. 82:1156–1161. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Itasaka T, Kawai A, Sato T, Mitani S and
Inoue H: Diagnosis of infection after total hip arthroplasty. J
Orthop Sci. 6:320–326. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Di Cesare PE, Chang E, Preston CF and Liu
CJ: Serum interleukin-6 as a marker of periprosthetic infection
following total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am.
87:1921–1927. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mitaka C: Clinical laboratory
differentiation of infectious versus non-infectious systemic
inflammatory response syndrome. Clin Chim Acta. 351:17–29. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Falcoz PE, Laluc F, Toubin MM, Puyraveau
M, Clement F, Mercier M, Chocron S and Etievent JP: Usefulness of
procalcitonin in the early detection of infection after thoracic
surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 27:1074–1078. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Delèvaux I, André M, Colombier M,
Albuisson E, Meylheuc F, Bègue RJ, Piette JC and Aumaître O: Can
procalcitonin measurement help in differentiating between bacterial
infection and other kinds of inflammatory processes? Ann Rheum Dis.
62:337–340. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Eberhard K, Haubitz M, Brunkhorst M, Kliem
V and Koch M: Usefulness of procalcitonin for differentiation
between activity of systemic autoimmune disease and invasive
bacterial infection. Arthritis Rheum. 40:1250–1256. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Becker KL, Snider R and Nylen ES:
Procalcitonin assay in systemic inflammation, infection and sepsis:
Clinical utility and limitations. Crit Care Med. 36:941–952. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dandona P, Nix D, Wilson MF, Aljada A,
Love J, Assicot M and Bohuon C: Procalcitonin increase after
endotoxin injection in normal subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
79:1605–1608. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Reinhart K, Karzai W and Meisner M:
Procalcitonin as a marker of the systemic inflammatory response to
infection. Intensive Care Med. 26:1193–1200. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Carrol ED, Thomson AP and Hart CA:
Procalcitonin as a marker of sepsis. Int J Antimicrob Agents.
20:1–9. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hunziker S, Hügle T, Schuchardt K,
Groeschl I, Schuetz P, Mueller B, Dick W, Eriksson U and Trampuz A:
The value of serum procalcitonin level for differentiation of
infectious from noninfectious causes of fever after orthopaedic
surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 92:138–148. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nascimento-Carvalho CM, Cardoso MR, Barral
A, Araujo-Neto CA, Guerin S, Saukkoriipi A, Paldanius M, Vainionpaa
R, Lebon P, Leinonen M, et al: Procalcitonin is useful in
identifying bacteraemia among children with pneumonia. Scand J
Infect Dis. 42:644–649. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pramod J and Singh A: Sepsis biomarkers.
Am J Med. 121:e112008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ruiz-Alvarez MJ, García-Valdecasas S, De
Pablo R, Sanchez García M, Coca C, Groeneveld TW, Roos A, Daha MR
and Arribas I: Diagnostic efficacy and prognostic value of serum
procalcitonin concentration in patients with suspected sepsis. J
Intensive Care Med. 24:63–71. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gendrel D and Bohuon C: Procalcitonin, a
marker of bacterial infection. Infection. 25:133–134. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Martinot M, Sordet C, Soubrier M, Puéchal
X, Saraux A, Lioté F, Guggenbuhl P, Legre V, Jaulhac B, Maillefert
JF, et al: Diagnostic value of serum and synovial procalcitonin in
acute arthritis: A prospective study of 42 patients. Clin Exp
Rheumato. 23:303–310. 2005.
|
|
23
|
Simon L, Gauvin F, Amre DK, Saint-Louis P
and Lacroix J: Serum procalcitonin and C-reactive protein levels as
markers of bacterial infection: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 39:206–217. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Foglar C and Lindsey RW: C-reactive
protein in orthopedics. Orthopedics. 21:687–691. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Meisner M, Tschaikowsky K, Hutzler A,
Schick C and Schüttler J: Postoperative plasma concentrations of
procalcitonin after different types of surgery. Intensive Care
Medicine. 24:680–684. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Garner JS, Jarvis WR, Emori TG, Horan TC
and Hughes JM: CDC definitions for nosocomial infections, 1988. Am
J Infect Control. 16:128–140. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
CDC: Surgical site infections: Resources
for patients and healthcare providers. http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dhqp/dpac_ssiMarch
10–2010
|
|
28
|
Mangram AJ, Horan TC, Pearson ML, Silver
LC and Jarvis WR: Guideline for prevention of surgical site
infection. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 20:247–264. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Pulido L, Ghanem E, Joshi A, Purtill JJ
and Parvizi J: Periprosthetic joint infection: The incidence,
timing, and predisposing factors. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
466:1710–1715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Choong PF, Dowsey MM, Carr D, Daffy J and
Stanley P: Risk factors associated with acute hip prosthetic joint
infections and outcome of treatment with a rifampinbased regimen.
Acta Orthop. 78:755–765. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Phillips JE, Crane TP, Noy M, Elliott TS
and Grimer RJ: The incidence of deep prosthetic infections in a
specialist orthopaedic hospital: A 15-year prospective survey. J
Bone Joint Surg Br. 88:943–948. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Assicot M, Gendrel D, Carsin H, Raymond J,
Guilbaud J and Bohuon C: High serum procalcitonin concentrations in
patients with sepsis and infection. Lancet. 341:515–518. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Laffey JG, Boylan JF and Cheng DC: The
systemic inflammatory response to cardiac surgery. Anesthesiology.
97:215–252. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jebali MA, Hausfater P, Abbes Z, Aouni Z,
Riou B and Ferjani M: Assessment of the accuracy of procalcitonin
to diagnose postoperative infection after cardiac surgery.
Anesthesiology. 107:232–238. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Laifer G, Wasner M, Sendi P, Graber P,
Gratzl O, Huber P, Fluckiger U and Zimmerli W: Dynamics of serum
procalcitonin in patients after major neurosurgery. Clin Microbiol
Infect. 11:679–681. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Oberhofer D, Rumenjak V, Lazić J and Vucić
N: Inflammatory indicators in patients after surgery of the large
intestine. Acta Medica Croatica. 60:429–433. 2006.(In Croatian).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lo E, Nicolle LE, Coffin SE, Gould C,
Maragakis LL, Meddings J, Pegues DA, Pettis AM, Saint S and Yokoe
DS: Strategies to prevent catheter-associated urinary tract
infections in acute care hospitals: 2014 update. Infect Control
Hosp Epidemiol. 35:464–479. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Foxman B: The epidemiology of urinary
tract infection. Nature Rev Urol. 7:653–660. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Carsin H, Assicot M, Feger F, Roy O,
Pennacino I, Le Bever H, Ainaud P and Bohuon C: Evolution and
significance of circulating procalcitonin levels compared with
IL-6, TNF alpha and endotoxin levels early after thermal injury.
Burns. 23:218–224. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wanner GA, Keel M, Steckholzer U, Beier W,
Stocker R and Ertel W: Relationship between procalcitonin plasma
levels and severity of injury, sepsis, organ failure and mortality
in injured patients. Crit Care Med. 28:950–957. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Uçkay I, Garzoni C, Ferry T, Harbarth S,
Stern R, Assal M, Hoffmeyer P, Lew D and Bernard L: Postoperative
serum pro-calcitonin and C-reactive protein levels in patients with
orthopedic infections. Swiss Med Wkly. 140:w131242010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Boussekey N, Leroy O, Georges H, Devos P,
D'Escrivan T and Guery B: Diagnostic and prognostic values of
admission procalcitonin levels in community-acquired pneumonia in
an intensive care unit. Infection. 33:257–263. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hügle T, Schuetz P, Mueller B, Laifer G,
Tyndall A, Regenass S and Daikeler T: Serum procalcitonin for
discrimination between septic and non-septic arthritis. Clin Exp
Rheumato. 26:453–456. 2008.
|
|
44
|
Fottner A, Birkenmaier C, von Schulze PC,
Wegener B and Jansson V: Can serum procalcitonin help to
differentiate between septic and nonseptic arthritis? Arthroscopy.
24:229–233. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Faesch S, Cojocaru B, Hennequin C, Pannier
S, Glorion C, Lacour B and Chéron G: Can procalcitonin measurement
help the diagnosis of osteomyelitis and septic arthritis? A
prospective trial. Ital J Pediatr. 35:332009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bottner F, Wegner A, Winkelmann W, Becker
K, Erren M and Götze C: Interleukin-6, procalcitonin and TNF-alpha:
Markers of peri-prosthetic infection following total joint
replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 89:94–99. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|