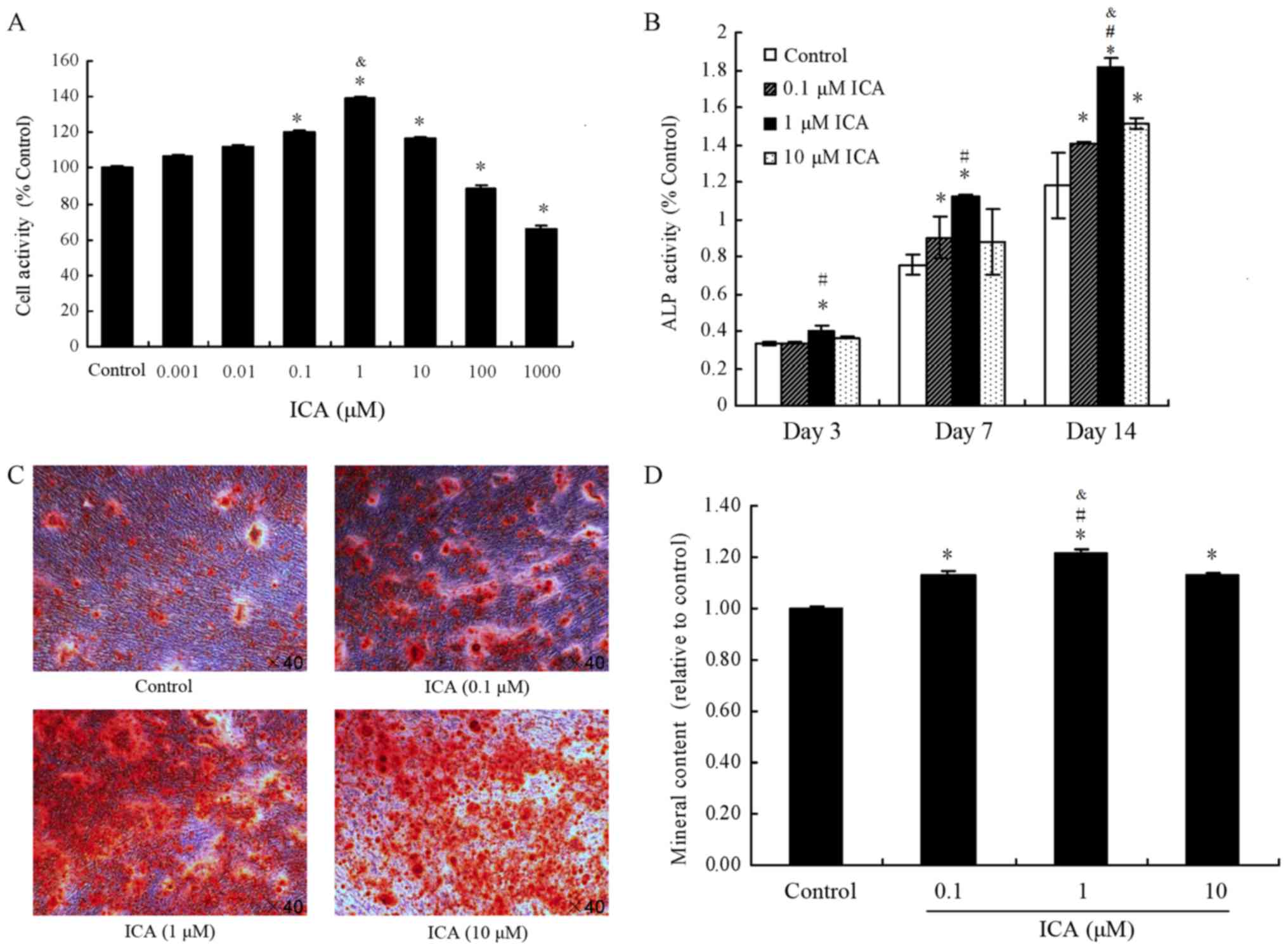
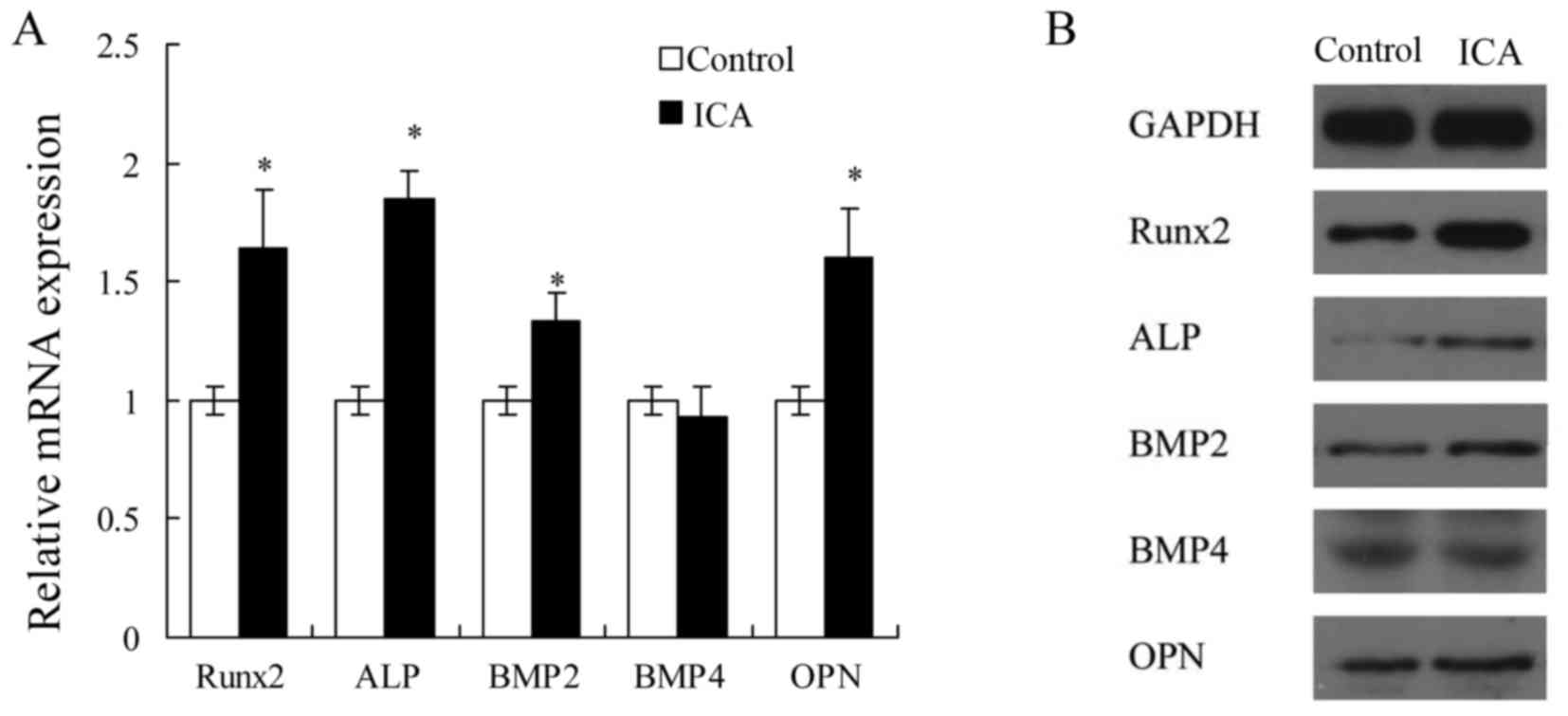
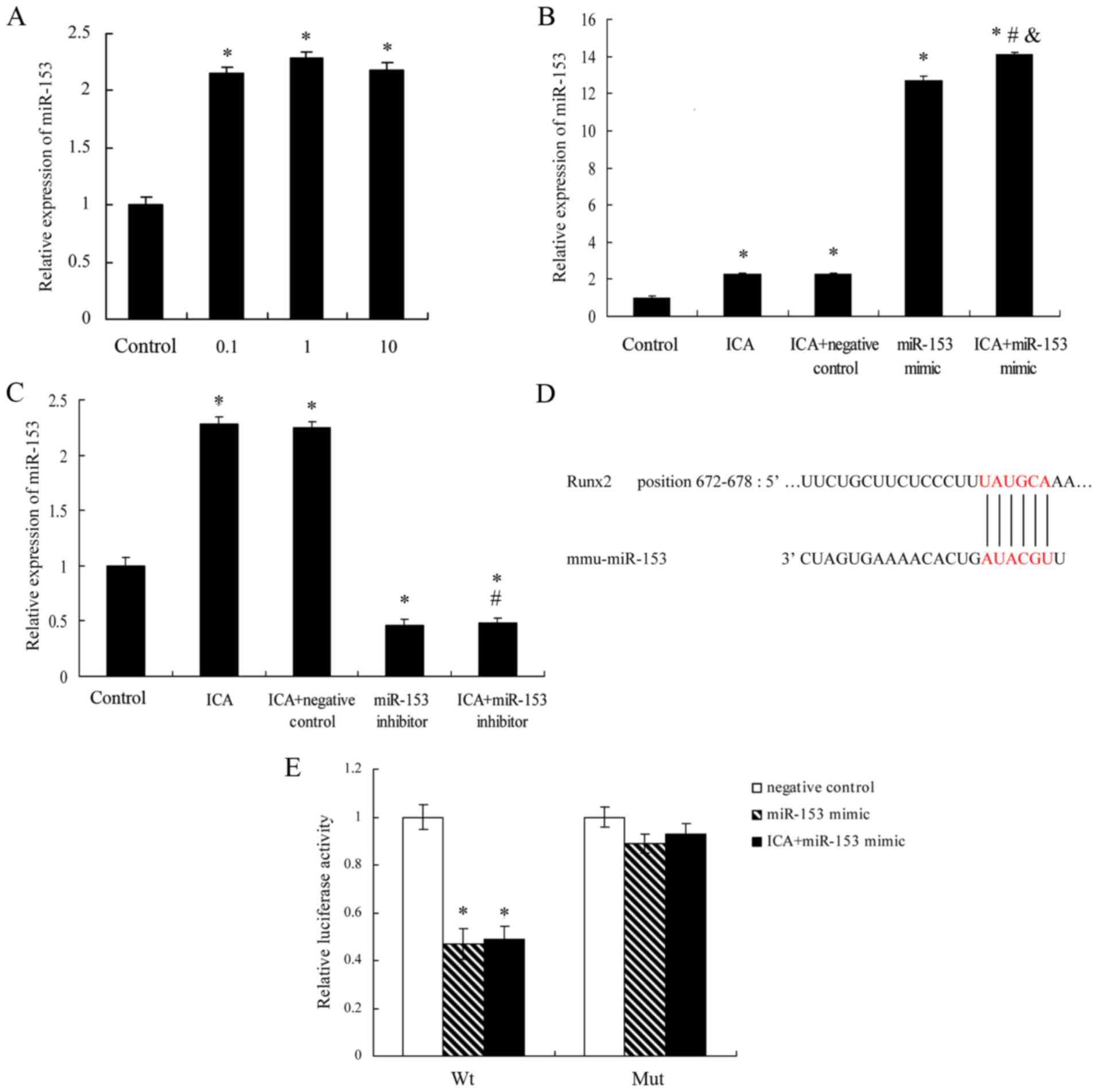
|
1
|
Zhao LJ, Liu XG, Liu YZ, Liu YJ, Papasian
CJ, Sha BY, Pan F, Guo YF, Wang L, Yan H, et al: Genome-wide
association study for femoral neck bone geometry. J Bone Miner Res.
25:320–329. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
An J, Yang H, Zhang Q, Liu C, Zhao J,
Zhang L and Chen B: Natural products for treatment of osteoporosis:
The effects and mechanisms on promoting osteoblast-mediated bone
formation. Life Sci. 147:46–58. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu YJ, Shen H, Xiao P, Xiong DH, Li LH,
Recker RR and Deng HW: Molecular genetic studies of gene
identification for osteoporosis: A 2004 update. J Bone Miner Res.
21:1511–1535. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Piscitelli P, Iolascon G, Gimigliano F,
Muratore M, Camboa P, Borgia O, Forcina B, Fitto F, Robaud V,
Termini G, et al: Incidence and costs of hip fractures compared to
acute myocardial infarction in the Italian population: A 4-year
survey. Osteoporos Int. 18:211–219. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Reginster JY and Burlet N: Osteoporosis: A
still increasing prevalence. Bone. 38 2 Suppl 1:4–9. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Budhia S, Mikyas Y, Tang M and Badamgarav
E: Osteoporotic fractures: A systematic review of U.S. healthcare
costs and resource utilization. Pharmacoeconomics. 30:147–170.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang Y, Du F, Ye W, Chen Y, Li J, Zhang J,
Nicely H and Burge R: Inpatient cost of treating osteoporotic
fractures in mainland China: A descriptive analysis. Clinicoecon
Outcomes Res. 7:205–212. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chan DC, Lee YS, Wu YJ, Tsou HH, Chen CT,
Hwang JS, Tsai KS and Yang RS: A 12-year ecological study of hip
fracture rates among older Taiwanese adults. Calcif Tissue Int.
93:397–404. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Melton LJ 3rd, Chrischilles EA, Cooper C,
Lane AW and Riggs BL: Perspective. How many women have
osteoporosis? J Bone Miner Res. 7:1005–1010. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Burge R, Dawson-Hughes B, Solomon DH, Wong
JB, King A and Tosteson A: Incidence and economic burden of
osteoporosis-related fractures in the United States, 2005–2025. J
Bone Miner Res. 22:465–475. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ahmed FE, Ahmed NC, Vos PW, Bonnerup C,
Atkins JN, Casey M, Nuovo GJ, Naziri W, Wiley JE, Mota H, et al:
Diagnostic microRNA markers to screen for sporadic human colon
cancer in stool: I. Proof of principle. Cancer Genomics Proteomics.
10:93–113. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
van Wijnen AJ, van de Peppel J, van
Leeuwen JP, Lian JB, Stein GS, Westendorf JJ, Oursler MJ, Im HJ,
Taipaleenmäki H, Hesse E, Riester S, et al: MicroRNA functions in
osteogenesis and dysfunctions in osteoporosis. Curr Osteoporos Rep.
11:72–82. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yamasaki K, Nakasa T, Miyaki S, Yamasaki
T, Yasunaga Y and Ochi M: Angiogenic microRNA-210 is present in
cells surrounding osteonecrosis. J Orthop Res. 30:1263–1270. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ukai T, Sato M, Akutsu H, Umezawa A and
Mochida J: MicroRNA-199a-3p, microRNA-193b, and microRNA-320c are
correlated to aging and regulate human cartilage metabolism. J
Orthop Res. 30:1915–1922. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W
and Tuschl T: Identification of novel genes coding for small
expressed RNAs. Science. 294:853–858. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG and Bartel
DP: An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles
in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 294:858–862. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee RC and Ambros V: An extensive class of
small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 294:862–864.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Duan Z, Choy E, Nielsen GP, Rosenberg A,
Iafrate J, Yang C, Schwab J, Mankin H, Xavier R and Hornicek FJ:
Differential expression of microRNA (miRNA) in chordoma reveals a
role for miRNA-1 in Met expression. J Orthop Res. 28:746–752.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dong S, Yang B, Guo H and Kang F:
MicroRNAs regulate osteogenesis and chondrogenesis. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 418:587–591. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li H, Xie H, Liu W, Hu R, Huang B, Tan YF,
Xu K, Sheng ZF, Zhou HD, Wu XP, et al: A novel microRNA targeting
HDAC5 regulates osteoblast differentiation in mice and contributes
to primary osteoporosis in humans. J Clin Invest. 119:3666–3677.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo J, Ren F, Wang Y, Li S, Gao Z, Wang X,
Ning H, Wu J, Li Y, Wang Z, et al: miR-764-5p promotes osteoblast
differentiation through inhibition of CHIP/STUB1 expression. J Bone
Miner Res. 27:1607–1618. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gao J, Yang T, Han J, Yan K, Qiu X, Zhou
Y, Fan Q and Ma B: MicroRNA expression during osteogenic
differentiation of human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells from
bone marrow. J Cell Biochem. 112:1844–1856. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Niu G, Li B, Sun L and An C: MicroRNA-153
inhibits osteosarcoma cells proliferation and invasion by targeting
TGF-β2. PLoS One. 10:e01192252015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu Z, He B, He J and Mao X: Upregulation
of miR-153 promotes cell proliferation via downregulation of the
PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human prostate cancer. Prostate.
73:596–604. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie L, Zhang Z, Tan Z, He R, Zeng X, Xie
Y, Li S, Tang G, Tang H and He X: MicroRNA-124 inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis by directly repressing EZH2 in
gastric cancer. Mol Cell Biochem. 392:153–159. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Song L, Duan P, Guo P, Li D, Li S, Xu Y
and Zhou Q: Downregulation of miR-223 and miR-153 mediates
mechanical stretch-stimulated proliferation of venous smooth muscle
cells via activation of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 528:204–211. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ming LG, Chen KM and Xian CJ: Functions
and action mechanisms of flavonoids genistein and icariin in
regulating bone remodeling. J Cell Physiol. 228:513–521. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang J, Yuan L, Wang X, Zhang TL and Wang
K: Icaritin and its glycosides enhance osteoblastic, but suppress
osteoclastic, differentiation and activity in vitro. Life
Sci. 81:832–840. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nian H, Ma MH, Nian SS and Xu LL:
Antiosteoporotic activity of icariin in ovariectomized rats.
Phytomedicine. 16:320–326. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao J, Ohba S, Shinkai M, Chung UI and
Nagamune T: Icariin induces osteogenic differentiation in
vitro in a BMP- and Runx2-dependent manner. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 369:444–448. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nash LA, Peters SJ, Sullivan PJ and Ward
WE: Supraphysiological levels of quercetin glycosides are required
to alter mineralization in Saos2 cells. Int J Environ Res Public
Health. 13:2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mok SK, Chen WF, Lai WP, Leung PC, Wang
XL, Yao XS and Wong MS: Icariin protects against bone loss induced
by oestrogen deficiency and activates oestrogen receptor-dependent
osteoblastic functions in UMR 106 cells. Br J Pharmacol.
159:939–949. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ma HP, Ming LG, Ge BF, Zhai YK, Song P,
Xian CJ and Chen KM: Icariin is more potent than genistein in
promoting osteoblast differentiation and mineralization in
vitro. J Cell Biochem. 112:916–923. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang D, Fong C, Jia Z, Cui L, Yao X and
Yang M: Icariin stimulates differentiation and suppresses
adipocytic transdifferentiation of primary osteoblasts through
estrogen receptor-mediated pathway. Calcif Tissue Int. 187–198.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li GW, Xu Z, Chang SX, Nian H, Wang XY and
Qin LD: Icariin prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss and lowers
marrow adipogenesis. Menopause. 21:1007–1016. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Meng YB, Li X, Li ZY, Zhao J, Yuan XB, Ren
Y, Cui ZD, Liu YD and Yang XJ: microRNA-21 promotes osteogenic
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by the PI3K/β-catenin
pathway. J Orthop Res. 33:957–964. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yuan Y, Du W, Wang Y, Xu C, Wang J, Zhang
Y, Wang H, Ju J, Zhao L, Wang Z, et al: Suppression of AKT
expression by miR-153 produced anti-tumor activity in lung cancer.
Int J Cancer. 136:1333–1340. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xu H, Abuhatzira L, Carmona GN, Vadrevu S,
Satin LS and Notkins AL: The Ia-2β intronic miRNA, miR-153, is a
negative regulator of insulin and dopamine secretion through its
effect on the Cacna1c gene in mice. Diabetologia. 58:2298–2306.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hua HW, Jiang F, Huang Q, Liao Z and Ding
G: MicroRNA-153 promotes Wnt/β-catenin activation in hepatocellular
carcinoma through suppression of WWOX. Oncotarget. 6:3840–3847.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liang W, Lin M, Li X, Li C, Gao B, Gan H,
Yang Z, Lin X, Liao L and Yang M: Icariin promotes bone formation
via the BMP-2/Smad4 signal transduction pathway in the hFOB 1.19
human osteoblastic cell line. Int J Mol Med. 30:889–895. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|