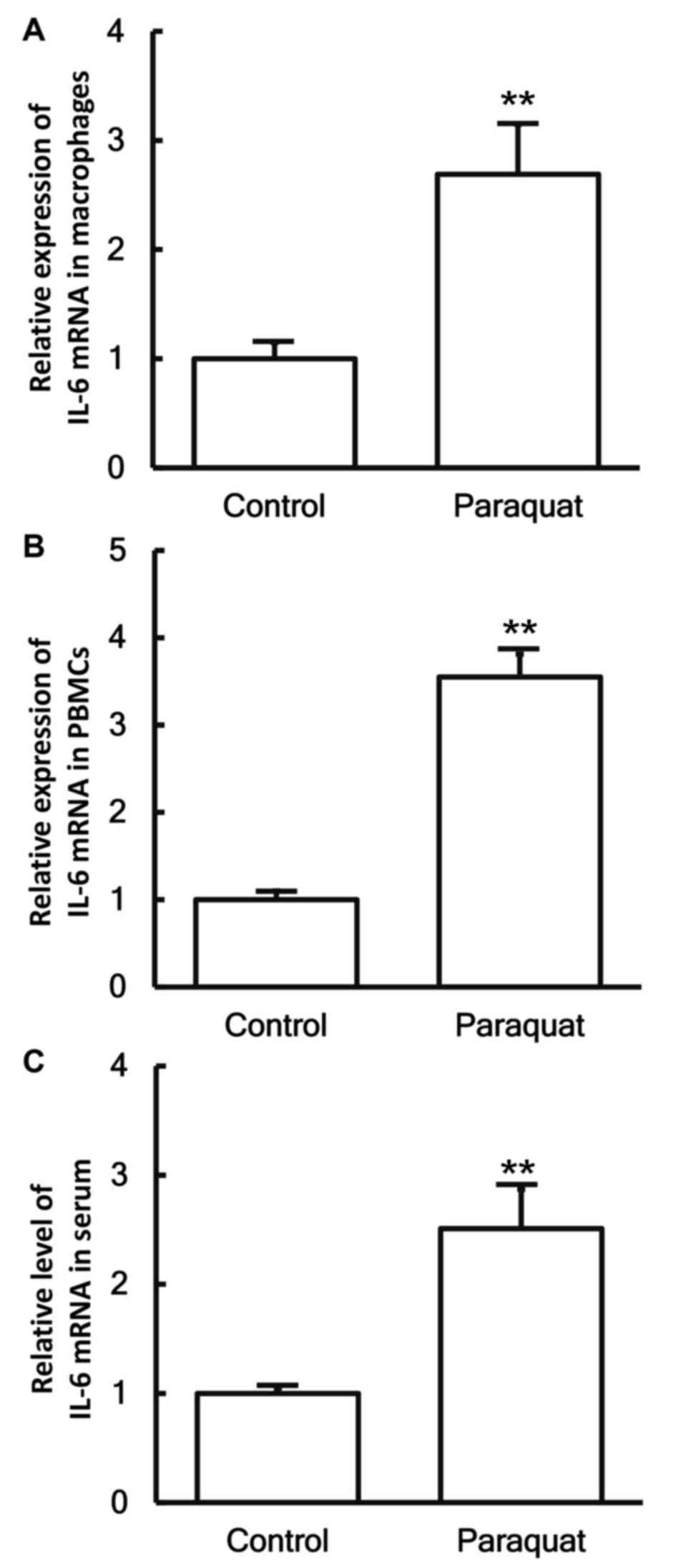
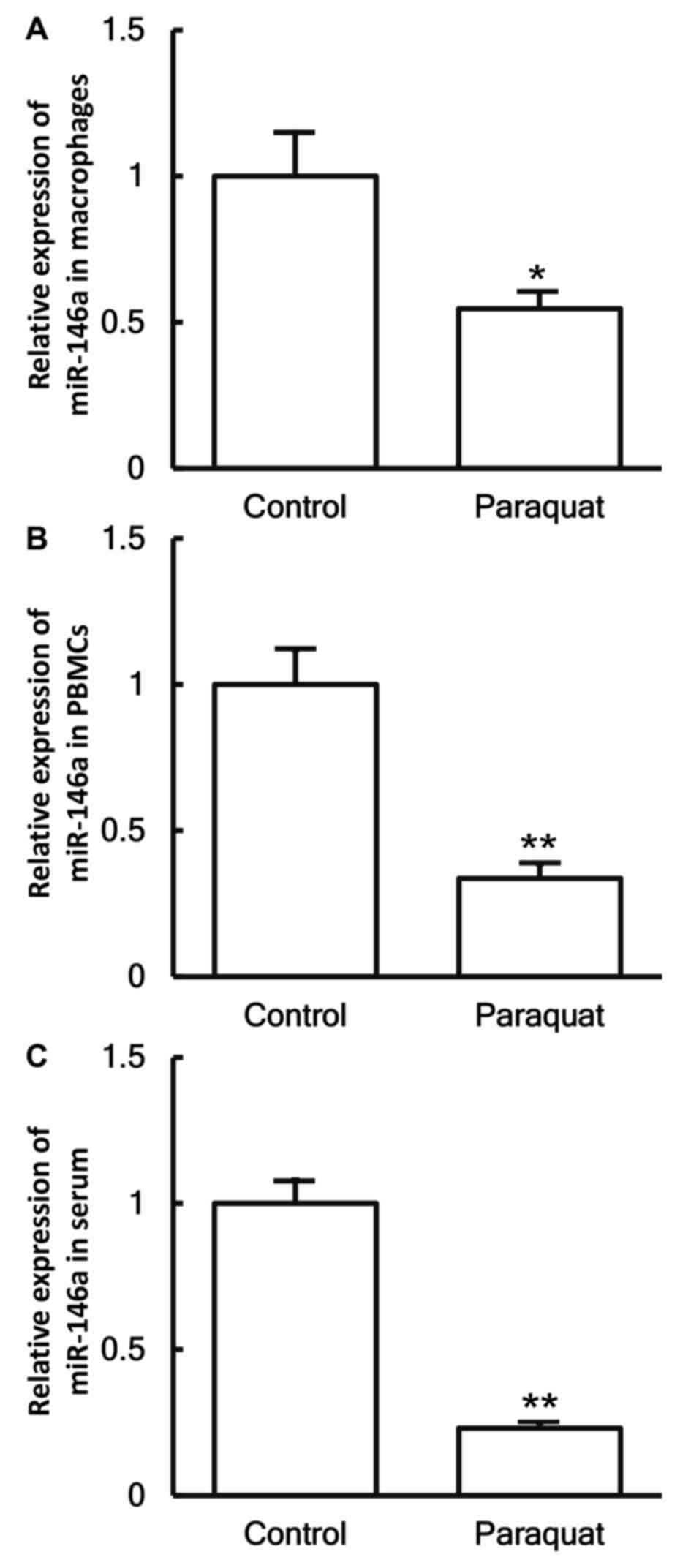
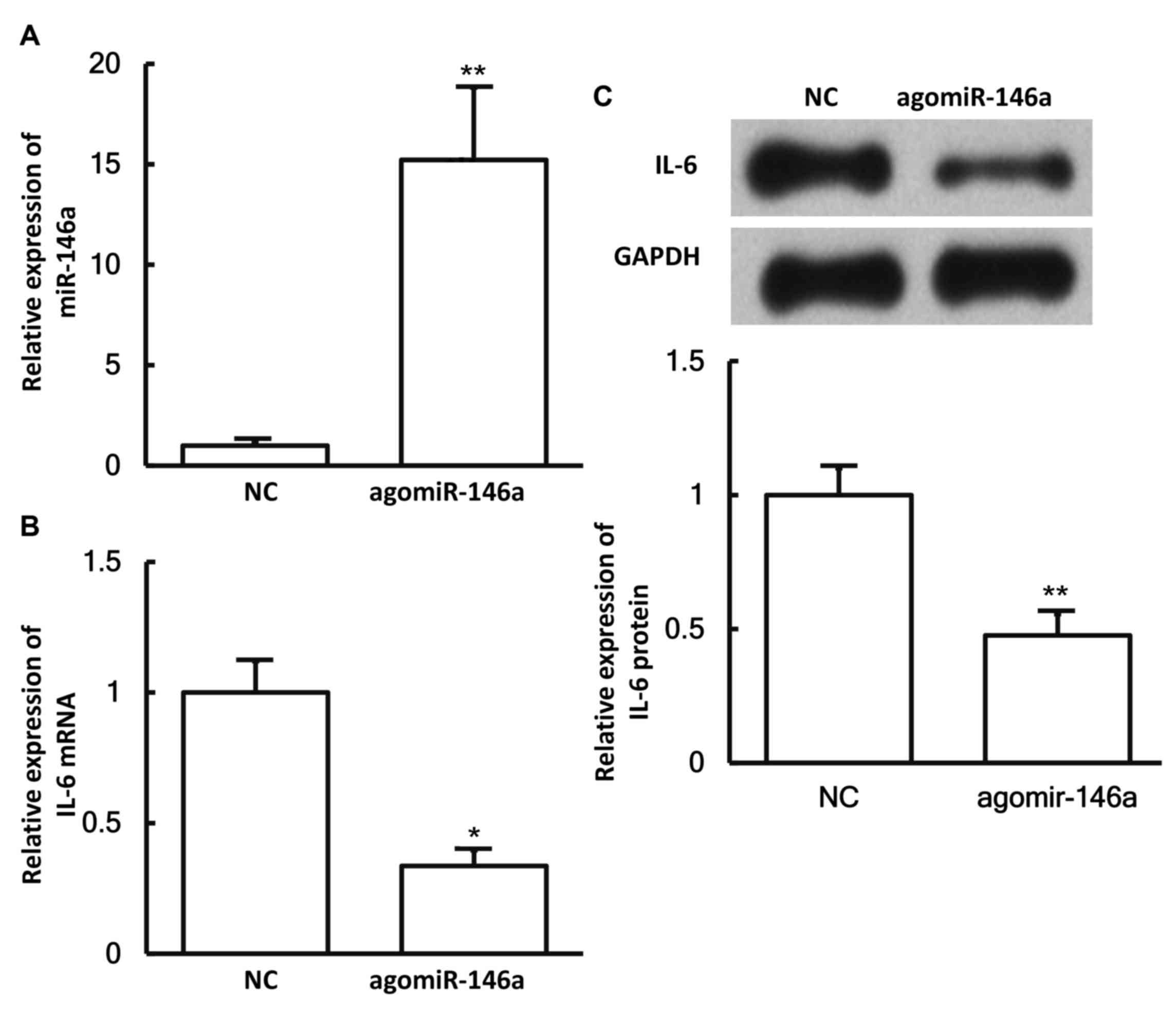
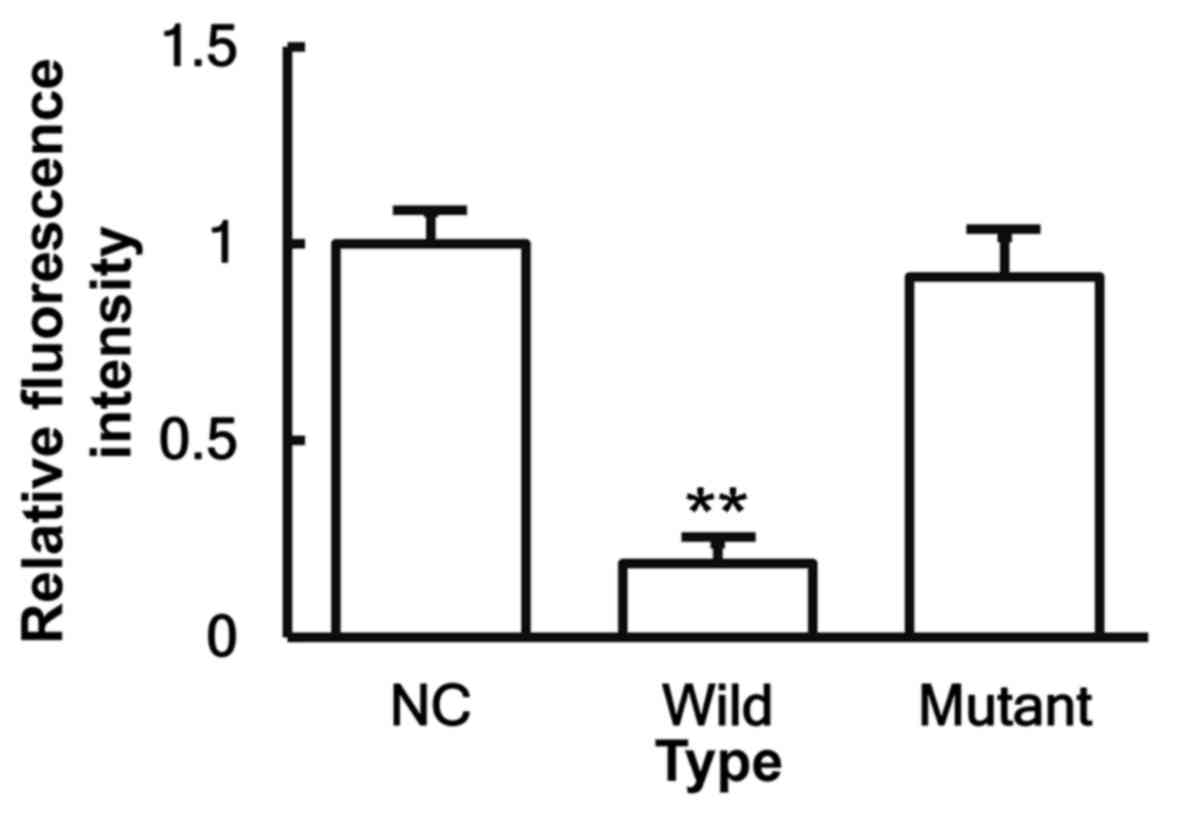
|
1
|
Mullick FG, Ishak KG, Mahabir R and
Stromeyer FW: Hepatic injury associated with paraquat toxicity in
humans. Liver. 1:209–221. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nagao M, Takatori T, Inoue K, Shimizu M,
Terazawa K and Akabane H: Immunohistochemical localization and
dynamics of paraquat in small intestine, liver and kidney.
Toxicology. 63:167–182. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Remião F, Duarte JA,
Ferreira R, Navarro Sánchez A, Bastos ML and Carvalho F:
P-glycoprotein induction: An antidotal pathway for paraquat-induced
lung toxicity. Free Radic Biol Med. 41:1213–1224. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hwang KY, Lee EY and Hong SY: Paraquat
intoxication in Korea. Arch Environ Health. 57:162–166. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yamashita M, Yamashita M and Ando Y: A
long-term follow-up of lung function in survivors of paraquat
poisoning. Hum Exp Toxicol. 19:99–103. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Anderson AE, Pratt AG, Sedhom MA, Doran
JP, Routledge C, Hargreaves B, Brown PM, Cao Lê KA, Isaacs JD and
Thomas R: IL-6-driven STAT signalling in circulating CD4+
lymphocytes is a marker for early anticitrullinated peptide
antibody-negative rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 75:466–473.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tezono K, Sarker KP, Kikuchi H, Nasu M,
Kitajima I and Maruyama I: Bioactivity of the vascular endothelial
growth factor trapped in fibrin clots: Production of IL-6 and IL-8
in monocytes by fibrin clots. Haemostasis. 31:71–79.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vila N, Reverter JC, Yagüe J and Chamorro
A: Interaction between interleukin-6 and the natural anticoagulant
system in acute stroke. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 20:325–329.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu Z, Xiao SB, Xu P, Xie Q, Cao L, Wang D,
Luo R, Zhong Y, Chen HC and Fang LR: miR-365, a novel negative
regulator of interleukin-6 gene expression, is cooperatively
regulated by Sp1 and NF-kappaB. J Biol Chem. 286:21401–21412. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sonkoly E, Ståhle M and Pivarcsi A:
MicroRNAs and immunity: Novel players in the regulation of normal
immune function and inflammation. Semin Cancer Biol. 18:131–140.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ye EA and Steinle JJ: miR-146a suppresses
STAT3/VEGF pathways and reduces apoptosis through IL-6 signaling in
primary human retinal microvascular endothelial cells in high
glucose conditions. Vision Res. 139:15–22. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Aspelund Stjärne A, Hammarström H,
Inghammar M, Larsson H, Hansson L, Christensson B and Påhlman LI:
Heparin-binding protein, lysozyme, and inflammatory cytokines in
bronchoalveolar lavage fluid as diagnostic tools for pulmonary
infection in lung transplanted patients. Am J Transplant.
18:444–452. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
He X, Ping J and Wen D: MicroRNA-186
regulates the invasion and metastasis of bladder cancer via
vascular endothelial growth factor C. Exp Ther Med. 14:3253–3258.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu H, Song J and Ma J: Paraquat is
approved for continued use in the European Union. Pest Sci
Administ. 25:36–37. 2004.
|
|
16
|
Yamamoto M, Toda M, Tanaka K, Sugita T,
Sasaki S, Uneyama C and Morikawa K: Study on usage of pesticides in
various countries. Kokuritsu Iyakuhin Shokuhin Eisei Kenkyusho
Hokoku. 92–100. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tang YH, Vital S, Russell J, Seifert H and
Granger DN: Interleukin-6 mediates enhanced thrombus development in
cerebral arterioles following a brief period of focal brain
ischemia. Exp Neurol. 271:351–357. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Suzuki Y, Matsui T, Ito H, Ashida T,
Nakamura S, Motoya S, Matsumoto T, Sato N, Ozaki K, Watanabe M and
Hibi T: Circulating interleukin 6 and albumin, and infliximab
levels are good predictors of recovering efficacy after dose
escalation infliximab therapy in patients with loss of response to
treatment for crohn's disease: A prospective clinical trial.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 21:2114–2122. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schaper F and Rose-John S: Interleukin-6:
Biology, signaling and strategies of blockade. Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 26:475–487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liz J and Esteller M: lncRNAs and
microRNAs with a role in cancer development. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1859:169–176. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Varshney J and Subramanian S: MicroRNAs as
potential target in human bone and soft tissue sarcoma
therapeutics. Front Mol Biosci. 2:312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Abou-Zeid A, Saad M and Soliman E:
MicroRNA 146a expression in rheumatoid arthritis: Association with
tumor necrosis factor-alpha and disease activity. Genet Test Mol
Biomarkers. 15:807–812. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pauley KM, Satoh M, Chan AL, Bubb MR,
Reeves WH and Chan EK: Upregulated miR-146a expression in
peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis
patients. Arthritis Res Ther. 10:R1012008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li X, Kroin JS, Kc R, Gibson G, Chen D,
Corbett GT, Pahan K, Fayyaz S, Kim JS, van Wijnen AJ, et al:
Altered spinal microRNA-146a and the microRNA-183 cluster
contribute to osteoarthritic pain in knee joints. J Bone Miner Res.
28:2512–2522. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li X, Gibson G, Kim JS, Kroin J, Xu S, van
Wijnen AJ and Im HJ: MicroRNA-146a is linked to pain-related
pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Gene. 480:34–41. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yamasaki K, Nakasa T, Miyaki S, Ishikawa
M, Deie M, Adachi N, Yasunaga Y, Asahara H and Ochi M: Expression
of MicroRNA-146a in osteoarthritis cartilage. Arthritis Rheum.
60:1035–1041. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Larner-Svensson HM, Williams AE, Tsitsiou
E, Perry MM, Jiang X, Chung KF and Lindsay MA: Pharmacological
studies of the mechanism and function of interleukin-1beta-induced
miRNA-146a expression in primary human airway smooth muscle. Respir
Res. 11:682010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cameron JE, Yin Q, Fewell C, Lacey M,
McBride J, Wang X, Lin Z, Schaefer BC and Flemington EK:
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 induces cellular
MicroRNA miR-146a, a modulator of lymphocyte signaling pathways. J
Virol. 82:1946–1958. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ and
Baltimore D: NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an
inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune
responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:12481–12486. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Curtale G, Citarella F, Carissimi C,
Goldoni M, Carucci N, Fulci V, Franceschini D, Meloni F, Barnaba V
and Macino G: An emerging player in the adaptive immune response:
microRNA-146a is a modulator of IL-2 expression and
activation-induced cell death in T lymphocytes. Blood. 115:265–273.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|