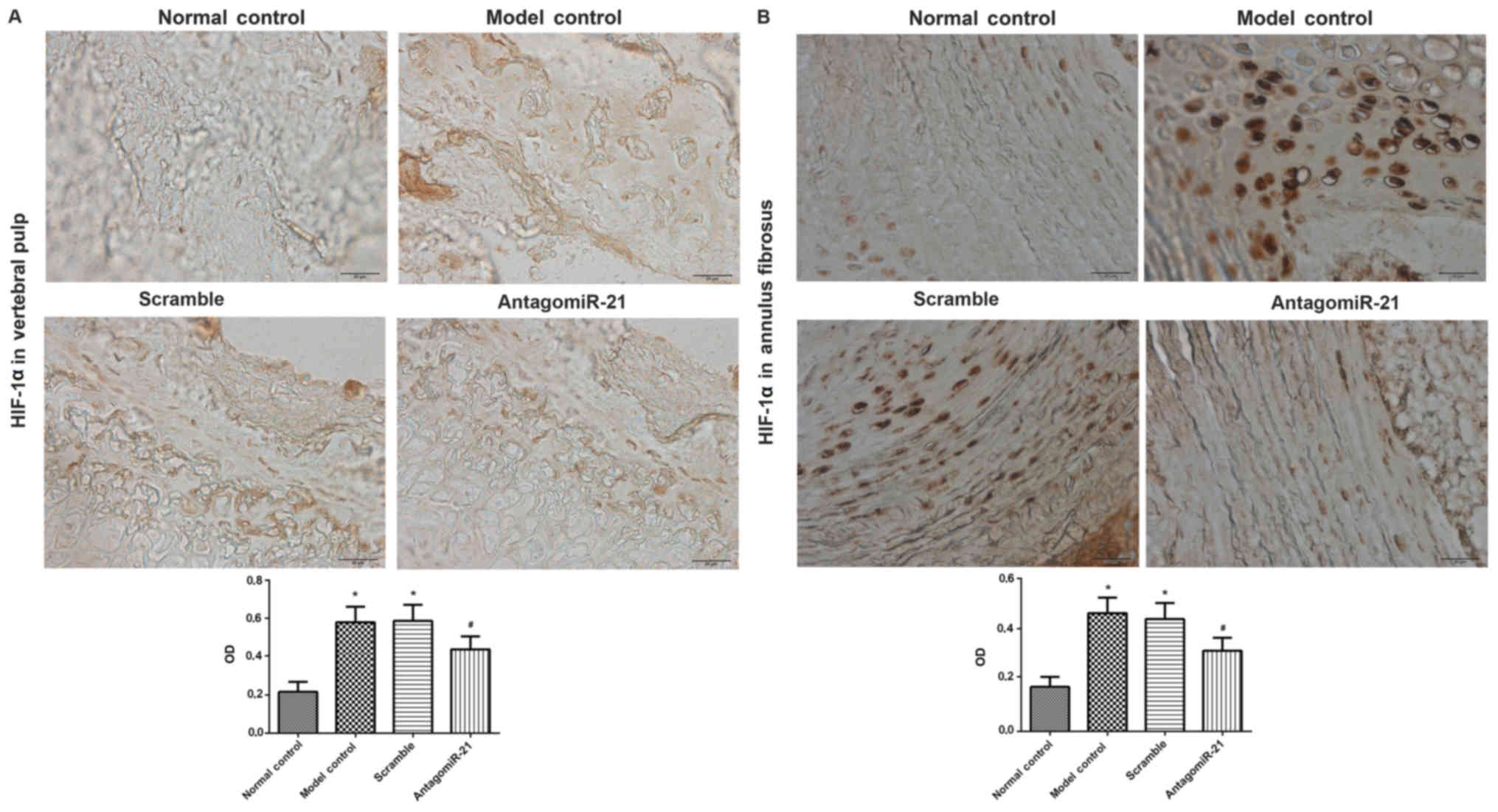
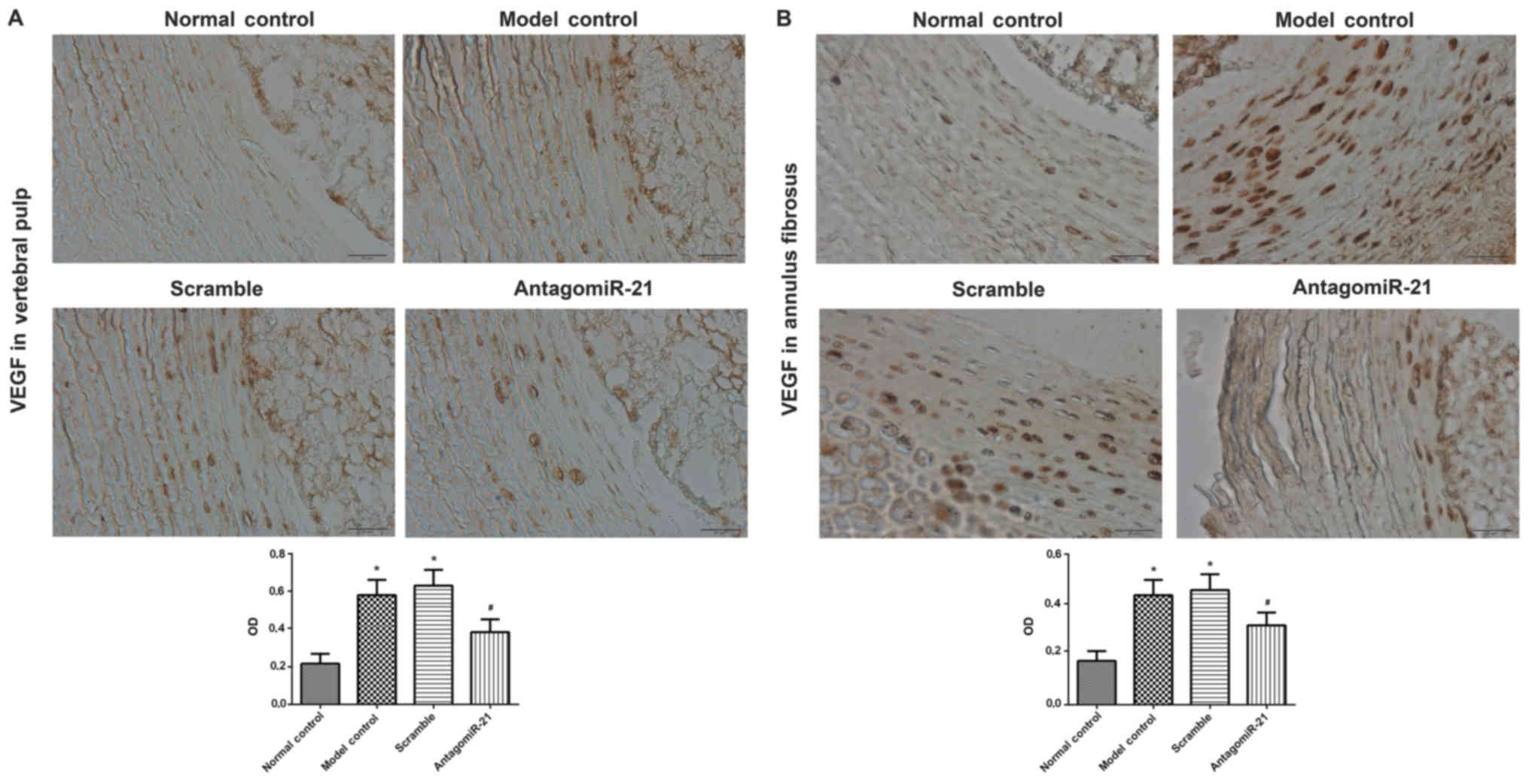
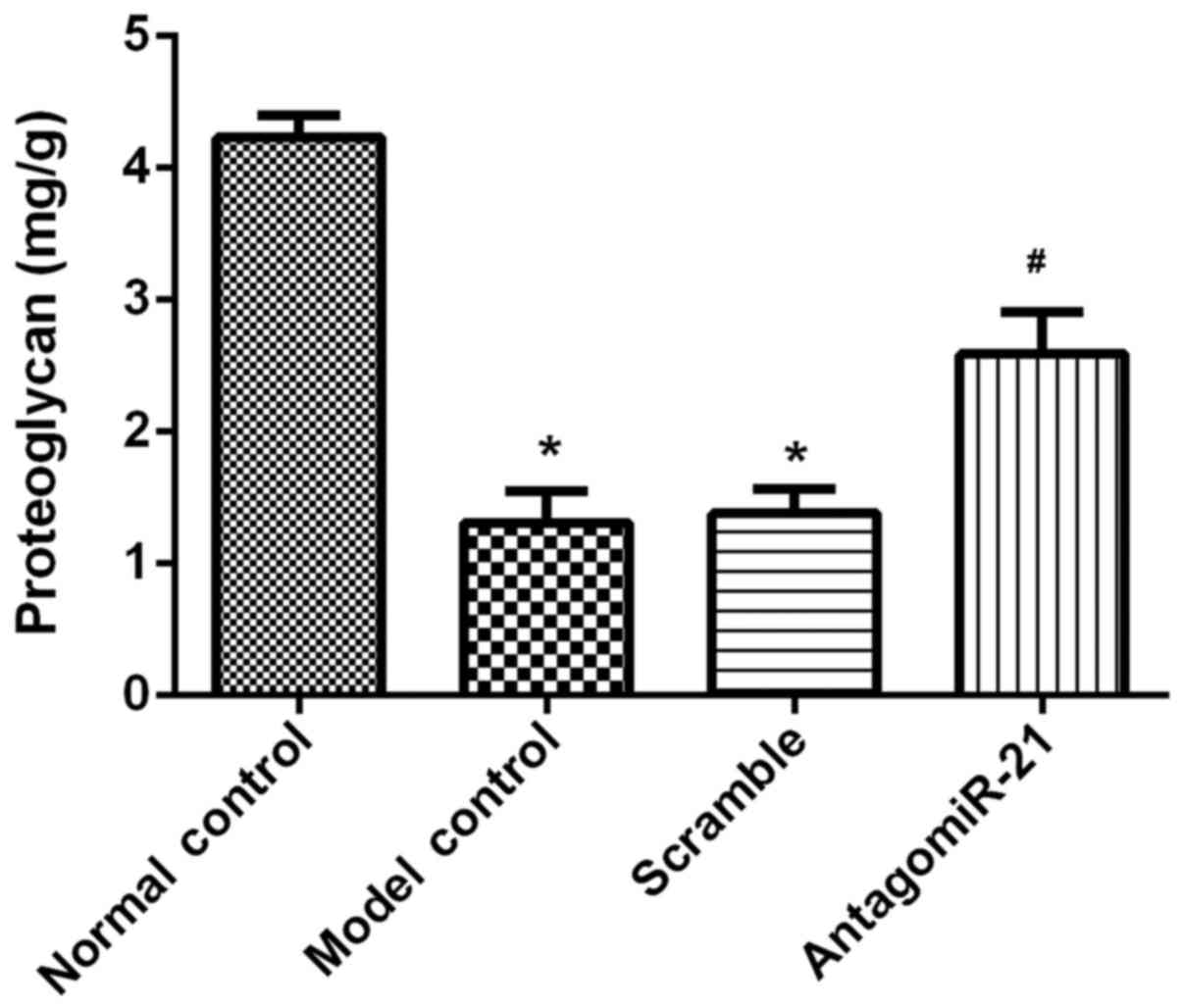
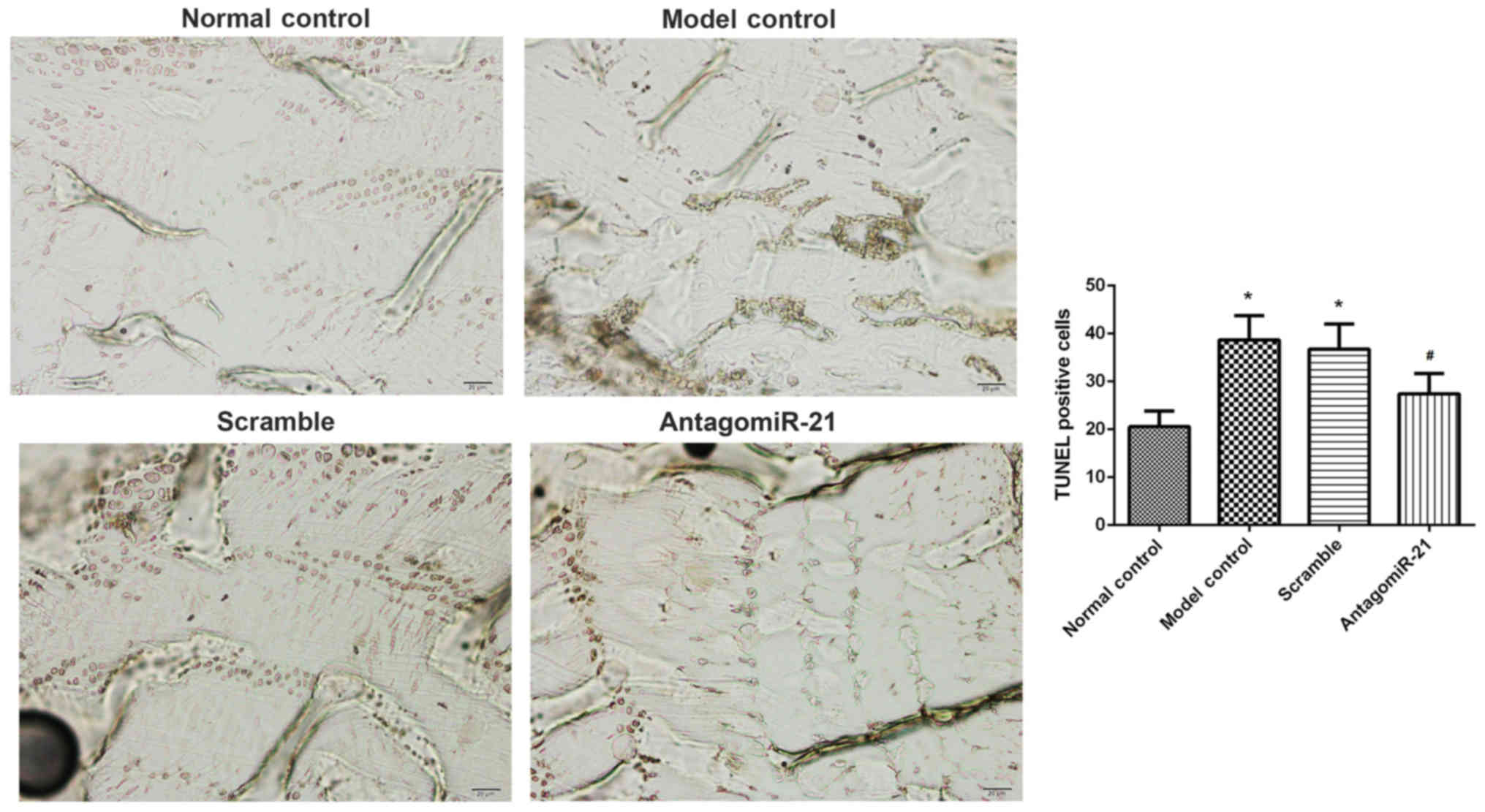
|
1
|
Kang JD, Stefanovic-Racic M, Mcintyre LA,
Georgescu HI and Evans CH: Toward a biochemical understanding of
human intervertebral disc degeneration and herniation.
Contributions of nitric oxide, interleukins, prostaglandin E2, and
matrix metalloproteinases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 22:1065–1073.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Luoma K, Riihimäki H, Luukkonen R,
Raininko R, Viikari-Juntura E and Lamminen A: Low back pain in
relation to lumbar disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
25:487–492. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Freemont AJ, Watkins A, Le Maitre C,
Jeziorska M and Hoyland JA: Current understanding of cellular and
molecular events in intervertebral disc degeneration: Implications
for therapy. J Pathol. 196:374–379. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fairbank J: Clinical importance of the
intervertebral disc, or back pain for biochemists. Biochem Soc
Trans. 30:829–831. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Adams MA and Roughley PJ: What is
intervertebral disc degeneration, and what causes it? Spine (Phila
Pa 1976). 31:2151–2161. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Binch ALA, Phillips KL, Chiverton N, Cole
A, Michael AR, Breakwell L, Cross AK and Le Maitre CL: Role of
semaphorins in angiogenesis and innervation in human intervertebral
disc degeneration. Global Spine Journal. 04:1834–1841. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ali R, Le-Maitre CL, Richardson SM,
Hoyland JA and Freemont AJ: Connective tissue growth factor
expression in human intervertebral disc: Implications for
angiogenesis in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biotech
Histochem. 83:239–245. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee JM, Song JY, Baek M, Jung HY, Kang H,
Han IB, Kwon YD and Shin DE: Interleukin-1β induces angiogenesis
and innervation in human intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop
Res. 29:265–269. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang J, Chen H, Yuan W, Cao P, Shi L, Li R
and Zang F: Analysis on angiogenesis in degenerative intervertebral
disc and relevant factors. Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 35:1200–1205.
2015.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
David G, Ciurea AV, Iencean SM and Mohan
A: Angiogenesis in the degeneration of the lumbar intervertebral
disc. J Med Life. 3:154–161. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao Y, Xu Y, Luo F, Xu W, Wang B, Pang Y,
Zhou J, Wang X and Liu Q: Angiogenesis, mediated by miR-21, is
involved arsenite-induced carcinogenesis. Toxicol Lett. 223:35–41.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sabatel C, Malvaux L, Bovy N, Deroanne C,
Lambert V, Gonzalez ML, Colige A, Rakic JM, Noël A, Martial JA and
Struman I: MicroRNA-21 exhibits antiangiogenic function by
targeting RhoB expression in endothelial cells. PLoS One.
6:e169792011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu LZ, Li C, Chen Q, Jing Y, Carpenter R,
Jiang Y, Kung HF, Lai L and Jiang BH: MiR-21 induced angiogenesis
through AKT and ERK activation and HIF-1α expression. PLoS One.
6:e191392011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen X, Liu J, He B, Li Y, Liu S, Wu B,
Wang S, Zhang S, Xu X and Wang J: Vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF) regulation by hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha
(HIF1A) starts and peaks during endometrial breakdown, not repair,
in a mouse menstrual-like model. Hum Reprod. 30:2160–2170. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu WJ, Zhang XK, Zheng XF, Yang YH, Jiang
SD and Jiang LS: SHH-dependent knockout of HIF-1 alpha accelerates
the degenerative process in mouse intervertebral disc. Int J
Immunopathol Pharmacol. 26:601–609. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bayne K: Revised guide for the care and
use of laboratory animals available. american physiological
society. Physiologist. 39(199): 208–111. 1996.
|
|
18
|
Zhao CQ, Zhang YH, Jiang SD, Jiang LS and
Dai LY: Both endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria are involved in
disc cell apoptosis and intervertebral disc degeneration in rats.
Age (Dordr). 32:161–177. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu B, Meng C, Wang H, Jia C and Zhao Y:
Proteoglycan and collagen type II in the adjacent intervertebral
disc of the cervical instability models. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng
Yanjiu. 17:5421–5426. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Wei A, Brisby H, Chung SA and Diwan AD:
Bone morphogenetic protein-7 protects human intervertebral disc
cells in vitro from apoptosis. Spine J. 8:466–474. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu H, Huang X, Liu X, Xiao S, Zhang Y,
Xiang T, Shen X, Wang G and Sheng B: miR-21 promotes human nucleus
pulposus cell proliferation through PTEN/AKT signaling. Int J Mol
Sci. 15:4007–4018. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao D, Tu Y, Wan L, Bu L, Huang T, Sun X,
Wang K and Shen B: In vivo monitoring of angiogenesis inhibition
via down-regulation of mir-21 in a VEGFR2-luc murine breast cancer
model using bioluminescent imaging. PLoS One. 8:e714722013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Semenza GL: Vascular responses to hypoxia
and ischemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 30:648–652. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA and Semenza GL:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS
heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 92:5510–5514. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rey S and Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible
factor-1-dependent mechanisms of vascularization and vascular
remodelling. Cardiovasc Res. 86:236–242. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhu L, Ye W and Cao Y: The relationship
between the expression of cyclooxygenase-2, hypoxia-inducible
factor-1α and angiogenesis in lumbar intervertebral disc
degeneration of rats. Jiang Yaotong Zazhi. 33:174–178. 2012.(In
Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Lyons G, Eisenstein SM and Sweet MB:
Biochemical changes in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 673:443–453. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kohyama K, Saura R, Doita M and Mizuno K:
Intervertebral disc cell apoptosis by nitric oxide: Biological
understanding of intervertebral disc degeneration. Kobe J Med Sci.
46:283–295. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|