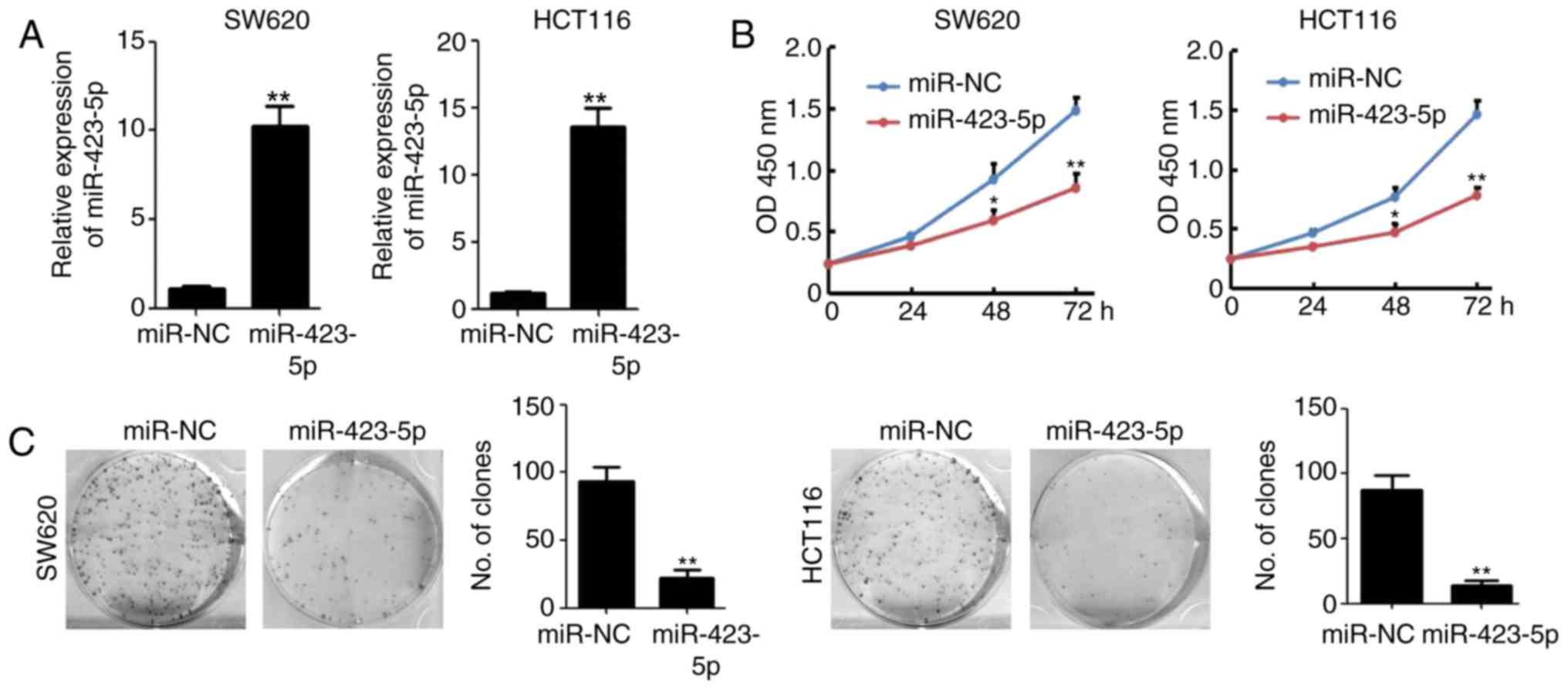
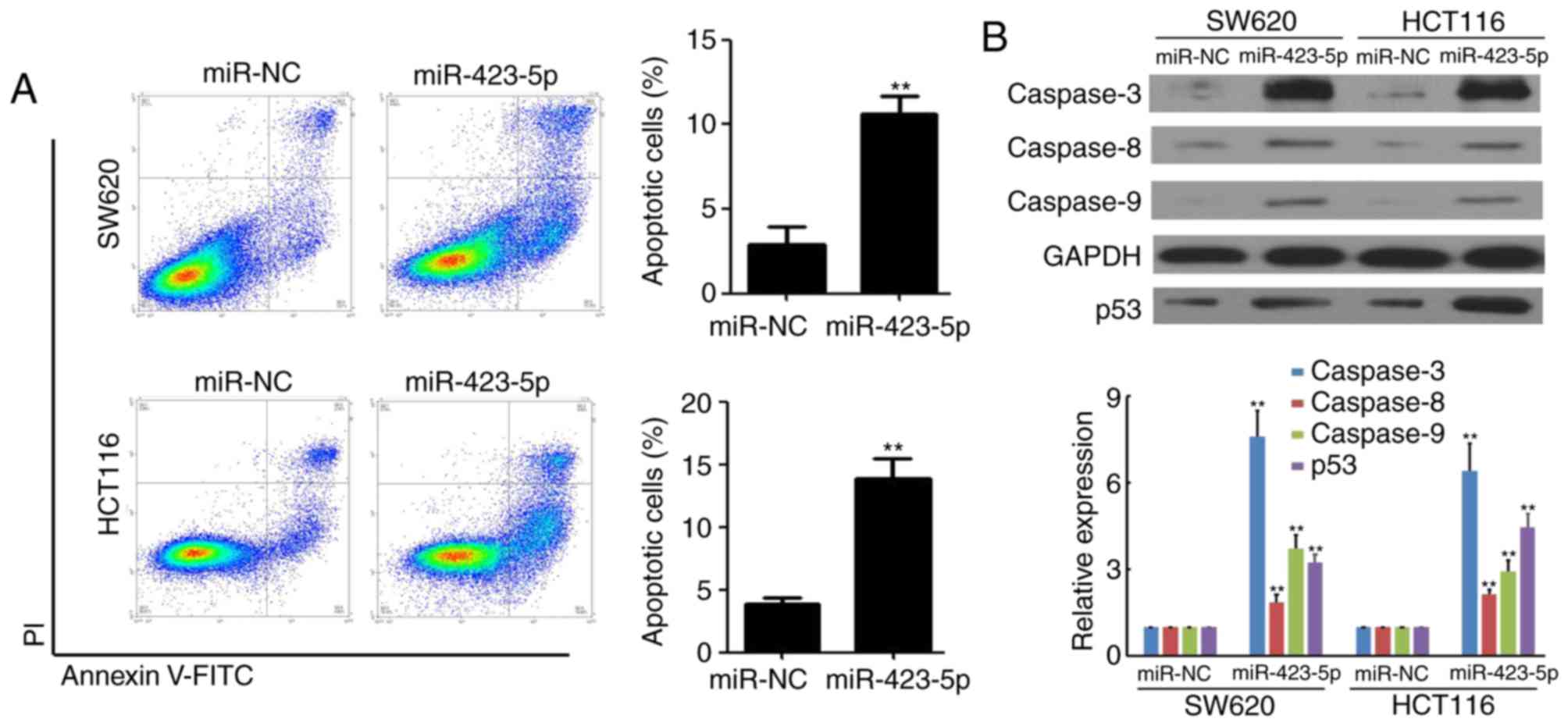
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jonas S, Thelen A, Benckert C, Spinelli A,
Sammain S, Neumann U, Rudolph B and Neuhaus P: Extended resections
of liver metastases from colorectal cancer. World J Surg.
31:511–521. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Smith JJ, Deane NG, Dhawan P and Beauchamp
RD: Regulation of metastasis in colorectal adenocarcinoma: A
collision between development and tumor biology. Surgery.
144:353–366. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moore MJ, Scheel TK, Luna JM, Park CY, Fak
JJ, Nishiuchi E, Rice CM and Darnell RB: miRNA-target chimeras
reveal miRNA 3′-end pairing as a major determinant of Argonaute
target specificity. Nat Commun. 6:88642015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Slezak-Prochazka I, Durmus S, Kroesen BJ
and van den Berg A: MicroRNAs, macrocontrol: Regulation of miRNA
processing. RNA. 16:1087–1095. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rupaimoole R, Wu SY, Pradeep S, Ivan C,
Pecot CV, Gharpure KM, Nagaraja AS, Armaiz-Pena GN, McGuire M, Zand
B, et al: Hypoxia-mediated downregulation of miRNA biogenesis
promotes tumour progression. Nat Commun. 5:52022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu SY, Rupaimoole R, Shen F, Pradeep S,
Pecot CV, Ivan C, Nagaraja AS, Gharpure KM, Pham E, Hatakeyama H,
et al: A miR-192-EGR1-HOXB9 regulatory network controls the
angiogenic switch in cancer. Nat Commun. 7:111692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tajima K, Yae T, Javaid S, Tam O, Comaills
V, Morris R, Wittner BS, Liu M, Engstrom A, Takahashi F, et al:
SETD1A modulates cell cycle progression through a miRNA network
that regulates p53 target genes. Nat Commun. 6:82572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fang Z, Tang J, Bai Y, Lin H, You H, Jin
H, Lin L, You P, Li J, Dai Z, et al: Plasma levels of microRNA-24,
microRNA-320a, and microRNA-423-5p are potential biomarkers for
colorectal carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lu X and Lu J: The significance of
detection of serum miR-423-5p and miR-484 for diagnosis of
colorectal cancer. Clin Lab. 61:187–190. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kumarswamy R, Anker SD and Thum T:
MicroRNAs as circulating biomarkers for heart failure: Questions
about MiR-423-5p. Circ Res. 106:e8author reply e9. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nabiałek E, Wańha W, Kula D, Jadczyk T,
Krajewska M, Kowalówka A, Dworowy S, Hrycek E, Wludarczyk W, Parma
Z, et al: Circulating microRNAs (miR-423-5p, miR-208a and miR-1) in
acute myocardial infarction and stable coronary heart disease.
Minerva Cardioangiol. 61:627–637. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bauters C, Kumarswamy R, Holzmann A,
Bretthauer J, Anker SD, Pinet F and Thum T: Circulating miR-133a
and miR-423-5p fail as biomarkers for left ventricular remodeling
after myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 168:1837–1840. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Luo P, He T, Jiang R and Li G:
MicroRNA-423-5p targets O-GlcNAc transferase to induce apoptosis in
cardiomyocytes. Mol Med Rep. 12:1163–1168. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stiuso P, Potenza N, Lombardi A,
Ferrandino I, Monaco A, Zappavigna S, Vanacore D, Mosca N,
Castiello F, Porto S, et al: MicroRNA-423-5p promotes autophagy in
cancer cells and is increased in serum from hepatocarcinoma
patients treated with sorafenib. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
4:e2332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wan Y, Fei X, Wang Z, Jiang D, Chen H,
Wang M and Zhou S: miR-423-5p knockdown enhances the sensitivity of
glioma stem cells to apigenin through the mitochondrial pathway.
Tumour Biol. 39:10104283176955262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dai L, Cui X, Zhang X, Cheng L, Liu Y,
Yang Y, Fan P, Wang Q, Lin Y, Zhang J, et al: SARI inhibits
angiogenesis and tumour growth of human colon cancer through
directly targeting ceruloplasmin. Nat Commun. 7:119962016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Offit K, Kohut K, Clagett B, Wadsworth EA,
Lafaro KJ, Cummings S, White M, Sagi M, Bernstein D and Davis JG:
Cancer genetic testing and assisted reproduction. J Clin Oncol.
24:4775–4782. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Calvert PM and Frucht H: The genetics of
colorectal cancer. Ann Intern Med. 137:603–612. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wei EK, Wolin KY and Colditz GA: Time
course of risk factors in cancer etiology and progression. J Clin
Oncol. 28:4052–4057. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
O'Connell MJ: Oxaliplatin or irinotecan as
adjuvant therapy for colon cancer: The results are in. J Clin
Oncol. 27:3082–3084. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dienstmann R, Salazar R and Tabernero J:
Personalizing colon cancer adjuvant therapy: Selecting optimal
treatments for individual patients. J Clin Oncol. 33:1787–1796.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|