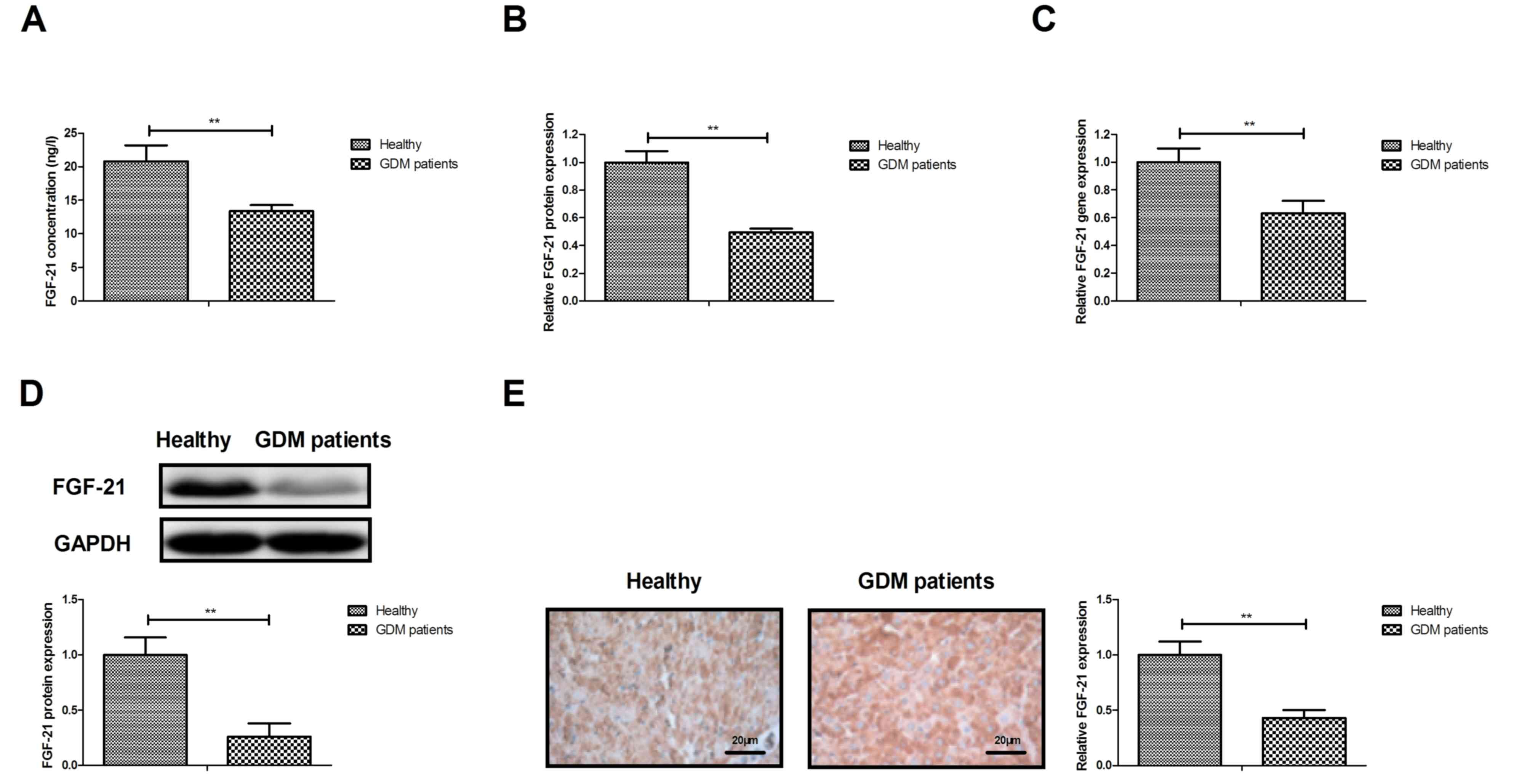
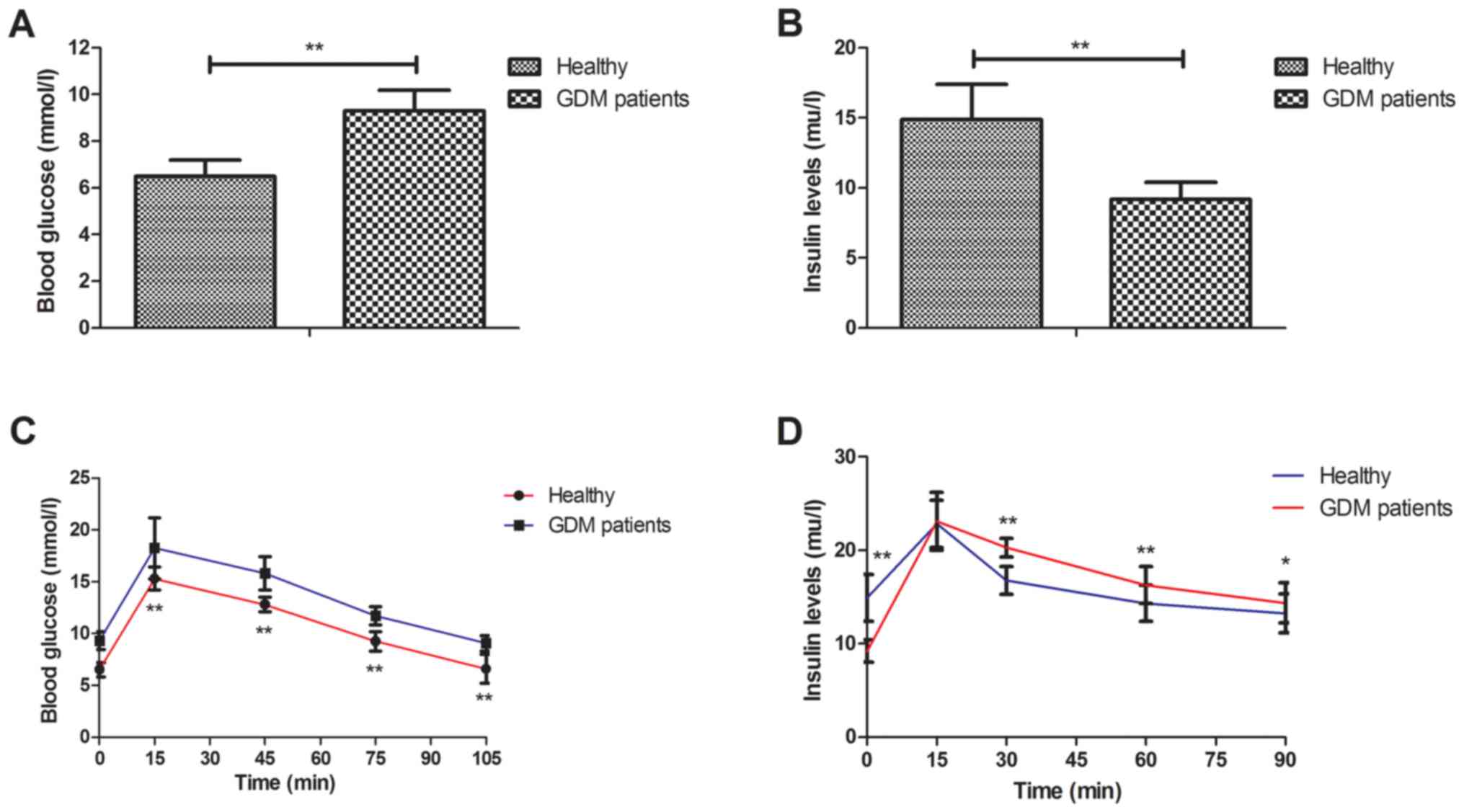
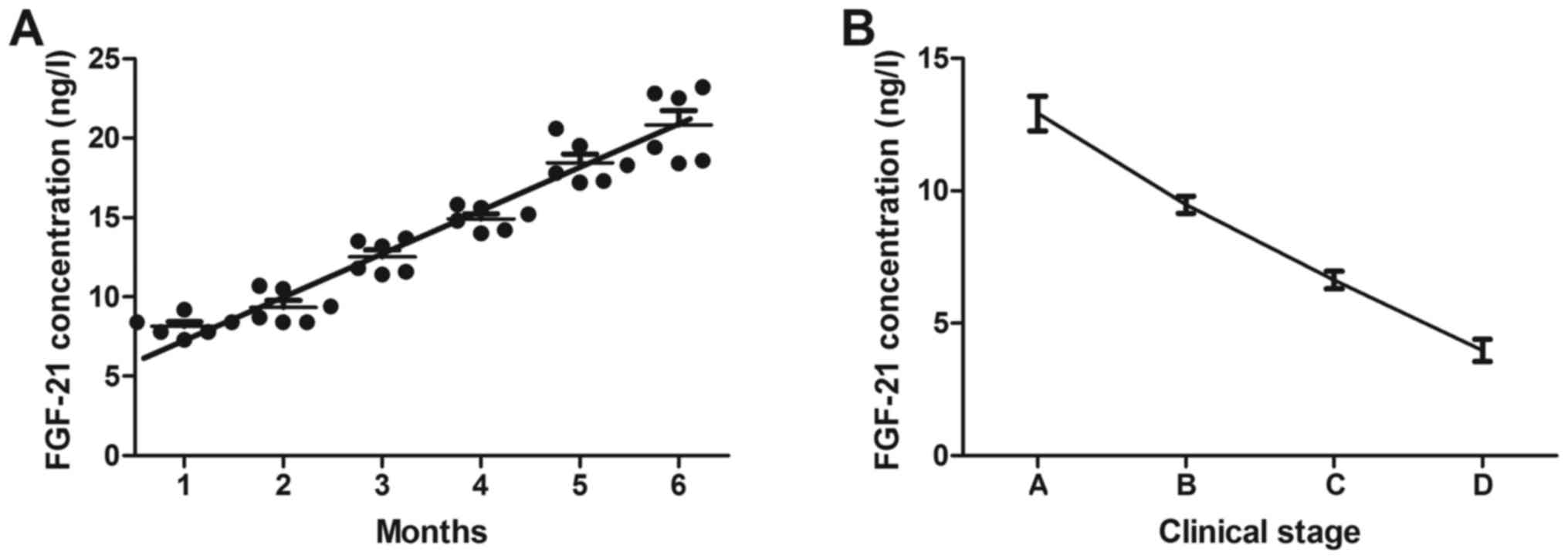
|
1
|
Popova P, Castorino K, Grineva EN and Kerr
D: Gestational diabetes mellitus diagnosis and treatment goals:
measurement and measures. Minerva Endocrinol. 41:421–432. 2016.
|
|
2
|
Khalafallah A, Phuah E, Al-Barazan AM,
Nikakis I, Radford A, Clarkson W, Trevett C, Brain T, Gebski V and
Corbould A: Glycosylated haemoglobin for screening and diagnosis of
gestational diabetes mellitus. BMJ Open. 6:e0110592016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hopmans TE, van Houten C, Kasius A,
Kouznetsova OI, Nguyen LA, Rooijmans SV, Voormolen DN, van Vliet
EO, Franx A and Koster MP: Increased risk of type II diabetes
mellitus and cardiovascular disease after gestational diabetes
mellitus: A systematic review. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd.
159:A80432015.(In Dutch). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wei Y, Yang H, Zhu W, Li H, Yan J and
Zhang C: International association of diabetes and pregnancy study
group criteria is suitable for gestational diabetes mellitus
diagnosis: Further evidence from China. Chin Med J (Engl).
127:3553–3556. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kalter-Leibovici O, Freedman LS, Olmer L,
Liebermann N, Heymann A, Tal O, Lerner-Geva L, Melamed N and Hod M:
Screening and diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus: Critical
appraisal of the new International Association of Diabetes in
pregnancy study group recommendations on a national level. Diabetes
Care. 35:1894–1896. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tan PC, Aziz AZ, Ismail IS and Omar SZ:
Gamma-glutamyltransferase, alanine transaminase and aspartate
transaminase levels and the diagnosis of gestational diabetes
mellitus. Clin Biochem. 45:1192–1196. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sagili H, Kamalanathan S, Sahoo J,
Lakshminarayanan S, Rani R, Jayalakshmi D and Kumar KT: Comparison
of different criteria for diagnosis of gestational diabetes
mellitus. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 19:824–828. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Askari G, Iraj B, Salehi-Abargouei A,
Fallah AA and Jafari T: The association between serum selenium and
gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 29:195–201. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Amin M, Suksomboon N, Poolsup N and Malik
O: Comparison of glyburide with metformin in treating gestational
diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Drug
Investig. 35:343–351. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhuo Z, Wang A and Yu H: Effect of
metformin intervention during pregnancy on the gestational diabetes
mellitus in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic
review and meta-analysis. J Diabetes Res. 2014:3812312014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Durovcová V, Marek J, Hána V, Matoulek M,
Zikán V, Haluzíková D, Kaválková P, Lacinová Z, Krsek M and Haluzík
M: Plasma concentrations of fibroblast growth factors 21 and 19 in
patients with Cushing's syndrome. Physiol Res. 59:415–422.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Eto K: FGF-21, a newcomer in the field of
hypertension research. J Hum Hypertens. 27:343–344. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Reinehr T, Woelfle J, Wunsch R and Roth
CL: Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF-21) and its relation to
obesity, metabolic syndrome, and nonalcoholic fatty liver in
children: A longitudinal analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
97:2143–2150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang F, Yu L, Lin X, Cheng P, He L, Li X,
Lu X, Tan Y, Yang H, Cai L and Zhang C: Minireview: Roles of
fibroblast growth factors 19 and 21 in metabolic regulation and
chronic diseases. Mol Endocrinol. 29:1400–1413. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang D, Zhu W, Li J, An C and Wang Z:
Serum concentrations of fibroblast growth factors 19 and 21 in
women with gestational diabetes mellitus: Association with insulin
resistance, adiponectin, and polycystic ovary syndrome history.
PloS One. 8:e811902013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Williams KJ, Picou AA, Kish SL, Giraldo
AM, Godke RA and Bondioli KR: Isolation and characterization of
porcine adipose tissue-derived adult stem cells. Cells Tissues
Organs. 188:251–258. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Selinger CI, Li BT, Pavlakis N, Links M,
Gill AJ, Lee A, Clarke S, Tran TN, Lum T, Yip PY, et al: Screening
for ROS1 gene rearrangements in non-small-cell lung cancers using
immunohistochemistry with FISH confirmation is an effective method
to identify this rare target. Histopathology. 70:402–411. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cariello M and Moschetta A: Fibroblast
growth factor 21: A new liver safeguard. Hepatology. 60:792–794.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Suomalainen A, Elo JM, Pietiläinen KH,
Hakonen AH, Sevastianova K, Korpela M, Isohanni P, Marjavaara SK,
Tyni T, Kiuru-Enari S, et al: FGF-21 as a biomarker for
muscle-manifesting mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiencies: A
diagnostic study. Lancet Neurol. 10:806–818. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lin Z, Wu Z, Yin X, Liu Y, Yan X, Lin S,
Xiao J, Wang X, Feng W and Li X: Serum levels of FGF-21 are
increased in coronary heart disease patients and are independently
associated with adverse lipid profile. PloS One. 5:e155342010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hart AW, Baeza N, Apelqvist A and Edlund
H: Attenuation of FGF signalling in mouse beta-cells leads to
diabetes. Nature. 408:864–868. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dushay J, Chui PC, Gopalakrishnan GS,
Varela-Rey M, Crawley M, Fisher FM, Badman MK, Martinez-Chantar ML
and Maratos-Flier E: Increased fibroblast growth factor 21 in
obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology.
139:456–463. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hotta Y, Nakamura H, Konishi M, Murata Y,
Takagi H, Matsumura S, Inoue K, Fushiki T and Itoh N: Fibroblast
growth factor 21 regulates lipolysis in white adipose tissue but is
not required for ketogenesis and triglyceride clearance in liver.
Endocrinology. 150:4625–4633. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang R, Yi X, Li X and Jiang X: Fibroblast
growth factor-21 is positively associated with atrial fibrosis in
atrial fibrillation patients with rheumatic heart disease. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:14901–14908. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen WW, Li L, Yang GY, Li K, Qi XY, Zhu
W, Tang Y, Liu H and Boden G: Circulating FGF-21 levels in normal
subjects and in newly diagnose patients with Type 2 diabetes
mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 116:65–68. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu MH: FGF-21 alleviates
diabetes-associated vascular complications: Inhibiting NF-kB/NLRP3
inflammasome-mediated inflammation? Int J Cardiol. 185:320–321.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu P, Zhang Y, Song L, Khoso MH, Li J,
Jiang X, He J, Li J, Ma X, Ren G and Li D: Efficacy of a
combination of high and low dosage of PEGylated FGF-21 in treatment
of diabetes in db/db mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:97–105. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|