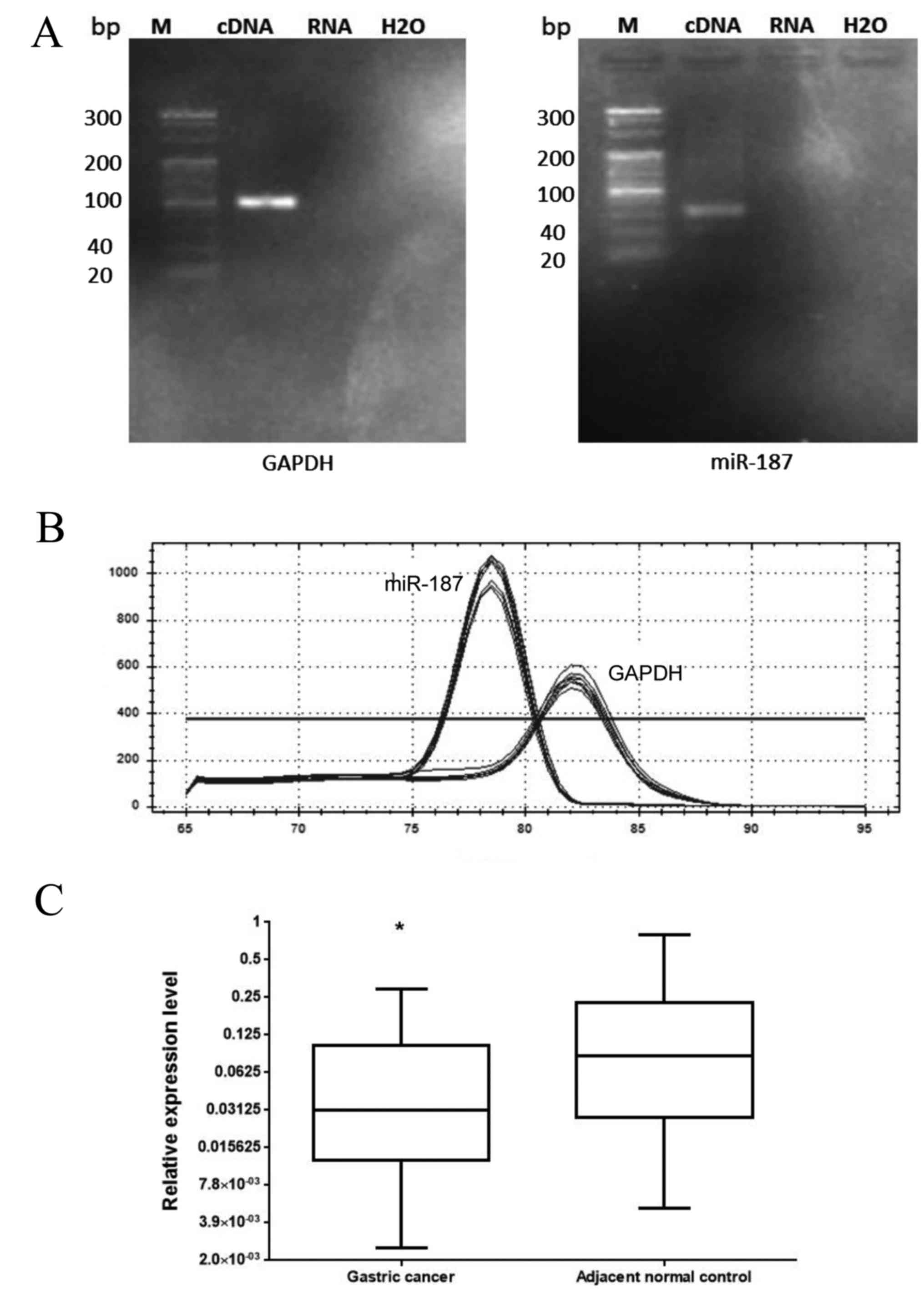
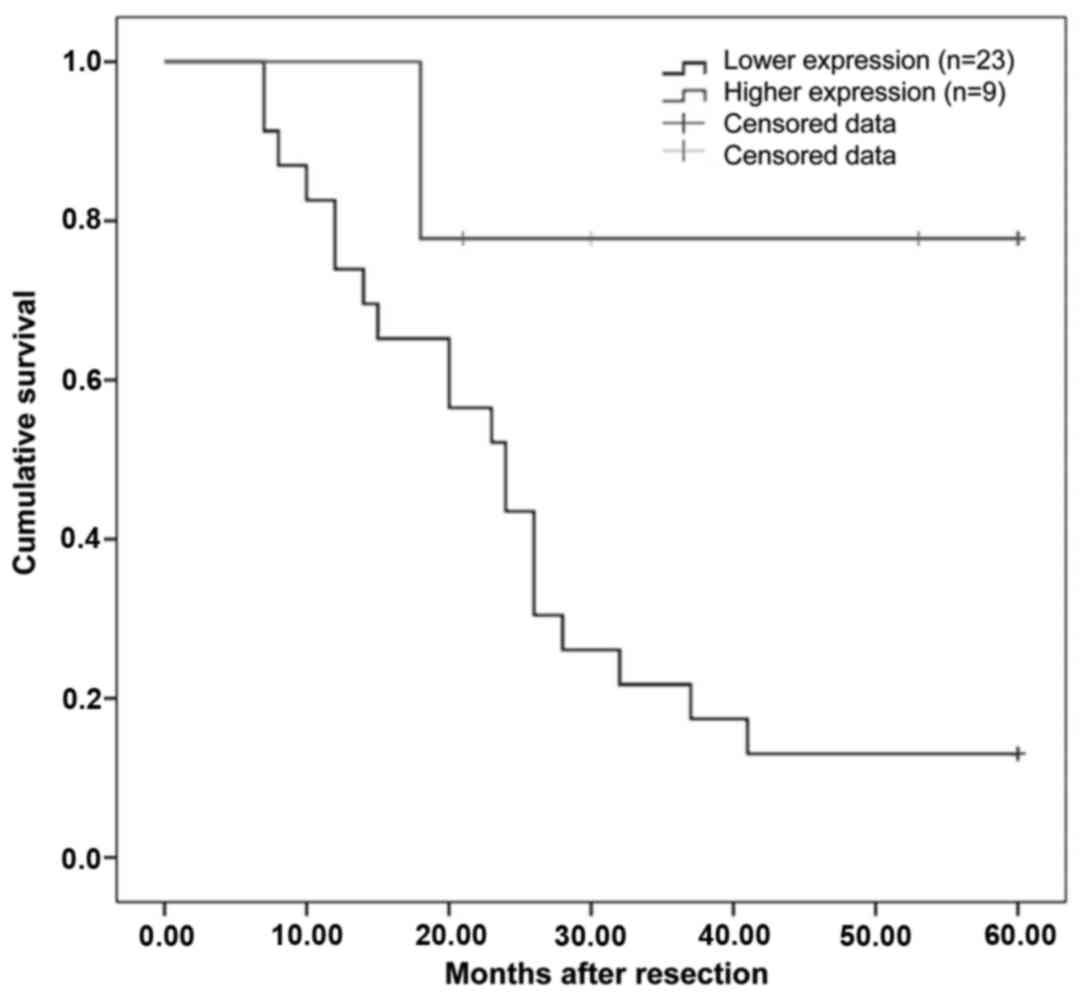
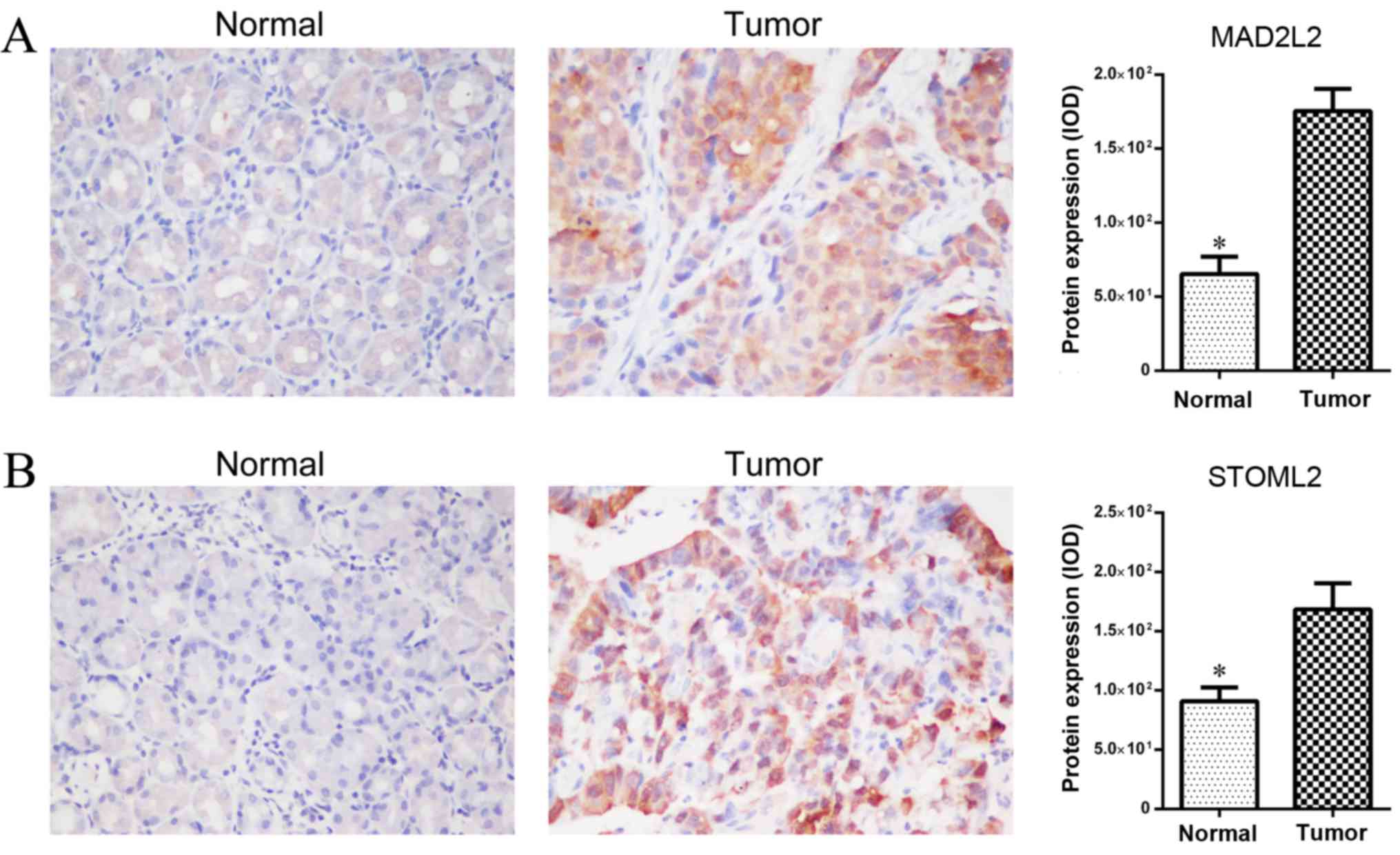
|
1
|
Crew KD and Neugut AI: Epidemiology of
gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 12:354–362. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM and Kosik KS:
MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells.
Cancer Res. 65:6029–6033. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Care A, Catalucci D, Felicetti F, Bonci D,
Addario A, Gallo P, Bang ML, Segnalini P, Gu Y, Dalton ND, et al:
MicroRNA-133 controls cardiac hypertrophy. Nat Med. 13:613–618.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wan HY, Guo LM, Liu T, Liu M, Li X and
Tang H: Regulation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB1 by
microRNA-9 in human gastric adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer. 9:162010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M
and Croce CM: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at
fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA-cancer
connection: The beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res. 66:7390–7394.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu T, Tang H, Lang Y, Liu M and Li X:
MicroRNA-27a functions as an oncogene in gastric adenocarcinoma by
targeting prohibitin. Cancer Lett. 273:233–242. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tie J, Pan Y, Zhao L, Wu K, Liu J, Sun S,
Guo X, Wang B, Gang Y, Zhang Y, et al: MiR-218 inhibits invasion
and metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting the Robo1 receptor.
PLoS Genet. 6:e10008792010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Z, Li Z, Gao C, Chen P, Chen J, Liu
W, Xiao S and Lu H: miR-21 plays a pivotal role in gastric cancer
pathogenesis and progression. Lab Invest. 88:1358–1366. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mulrane L, Madden SF, Brennan DJ, Gremel
G, McGee SF, McNally S, Martin F, Crown JP, Jirström K, Higgins DG,
et al: miR-187 is an independent prognostic factor in breast cancer
and confers increased invasive potential in vitro. Clin Cancer Res.
18:6702–6713. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao J, Lei T, Xu C, Li H, Ma W, Yang Y,
Fan S and Liu Y: MicroRNA-187, down-regulated in clear cell renal
cell carcinoma and associated with lower survival, inhibits cell
growth and migration though targeting B7-H3. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 438:439–444. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz AG,
Balch CM, Haller DG and Morrow M: AJCC Cancer staging manual: TNM
classification of malignant tumors. 6th. New York: Springer-Verlag;
2002, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xue X, Sun J, Zhang Q, Wang Z, Huang Y and
Pan W: Identification and characterization of novel microRNAs from
Schistosoma japonicum. PLoS One. 3:e40342008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu L and Eisenman RN: Regulation of c-Myc
protein abundance by a protein phosphatase 2A-Glycogen synthase
kinase 3β-Negative feedback pathway. Genes Cancer. 3:23–36. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Helwak A, Kudla G, Dudnakova T and
Tollervey D: Mapping the human miRNA interactome by CLASH reveals
frequent noncanonical binding. Cell. 153:654–665. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cheng AM, Byrom MW, Shelton J and Ford LP:
Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an
involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids
Res. 33:1290–1297. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Park SY, Lee JH, Ha M, Nam JW and Kim VN:
miR-29 miRNAs activate p53 by targeting p85α and CDC42. Nat Struct
Mol Biol. 16:23–29. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nikiforova MN, Tseng GC, Steward D, Diorio
D and Nikiforov YE: MicroRNA expression profiling of thyroid
tumors: Biological significance and diagnostic utility. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 93:1600–1608. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen HC, Chen GH, Chen YH, Liao WL, Liu
CY, Chang KP, Chang YS and Chen SJ: MicroRNA deregulation and
pathway alterations in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Br J Cancer.
100:1002–1011. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wijnhoven B, Hussey DJ, Watson DI, Tsykin
A, Smith C and Michael MZ: South Australian Oesophageal Research
Group; MicroRNA profiling of Barrett's oesophagus and oesophageal
adenocarcinoma. Br J Surg. 97:853–861. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F,
Volinia S, Alder H, Hagan JP, Liu CG, Bhatt D, Taccioli C and Croce
CM: MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic
adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA.
297:1901–1908. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen Y and Stallings RL: Differential
patterns of microRNA expression in neuroblastoma are correlated
with prognosis, differentiation, and apoptosis. Cancer Res.
67:976–983. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chao A, Lin CY, Lee YS, Tsai CL, Wei PC,
Hsueh S, Wu TI, Tsai CN, Wang CJ, Chao AS, et al: Regulation of
ovarian cancer progression by microRNA-187 through targeting
Disabled homolog-2. Oncogene. 31:764–775. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Evan GI and Vousden KH: Proliferation,
cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature. 411:342–348. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sánchez CA, Rodríguez E, Varela E, Zapata
E, Paez A, Massó FA, Montaño LF and Lóopez-Marure R: Statin-induced
inhibition of MCF-7 breast cancer cell proliferation is related to
cell cycle arrest and apoptotic and necrotic cell death mediated by
an enhanced oxidative stress. Cancer Invest. 26:698–707. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Park WH, Lee YY, Kim ES, Seol JG, Jung CW,
Lee CC and Kim BK: Lovastatin-induced inhibition of HL-60 cell
proliferation via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Anticancer Res.
19:3133–3140. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zamore PD and Haley B: Ribo-gnome: The big
world of small RNAs. Science. 309:1519–1524. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mattick JS and Makunin IV: Non-coding RNA.
Hum Mol Genet. 15:R17–R29. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sirotkin AV, Lauková M, Ovcharenko D,
Brenaut P and Mlynček M: Identification of microRNAs controlling
human ovarian cell proliferation and apoptosis. J Cell Physiol.
223:49–56. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rimkus C, Friederichs J, Rosenberg R,
Holzmann B, Siewert JR and Janssen KP: Expression of the mitotic
checkpoint gene MAD2L2 has prognostic significance in colon cancer.
Int J Cancer. 120:207–211. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cao W, Zhang B, Liu Y, Li H, Zhang S, Fu
L, Niu Y, Ning L, Cao X, Liu Z and Sun B: High-level SLP-2
expression and HER-2/neu protein expression are associated with
decreased breast cancer patient survival. Am J Clin Pathol.
128:430–436. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cao WF, Zhang LY, Liu MB, Tang PZ, Liu ZH
and Sun BC: Prognostic significance of stomatin-like protein 2
overexpression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: Clinical,
histologic, and immunohistochemistry analyses with tissue
microarray. Hum Pathol. 38:747–752. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Y, Cao W, Yu Z and Liu Z:
Downregulation of a mitochondria associated protein SLP-2 inhibits
tumor cell motility, proliferation and enhances cell sensitivity to
chemotherapeutic reagents. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:1651–1658. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang L, Ding F, Cao W and Liu Z, Liu W,
Yu Z, Wu Y, Li W, Li Y and Liu Z: Stomatin-like protein 2 is
overexpressed in cancer and involved in regulating cell growth and
cell adhesion in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:1639–1646. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu D, Zhang L, Shen Z, Tan F, Hu Y, Yu J
and Li G: Increased levels of SLP-2 correlate with poor prognosis
in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 16:498–504. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Brennecke J, Stark A, Russell RB and Cohen
SM: Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Biol.
3:e852005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Brodersen P and Voinnet O: Revisiting the
principles of microRNA target recognition and mode of action. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:141–148. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|