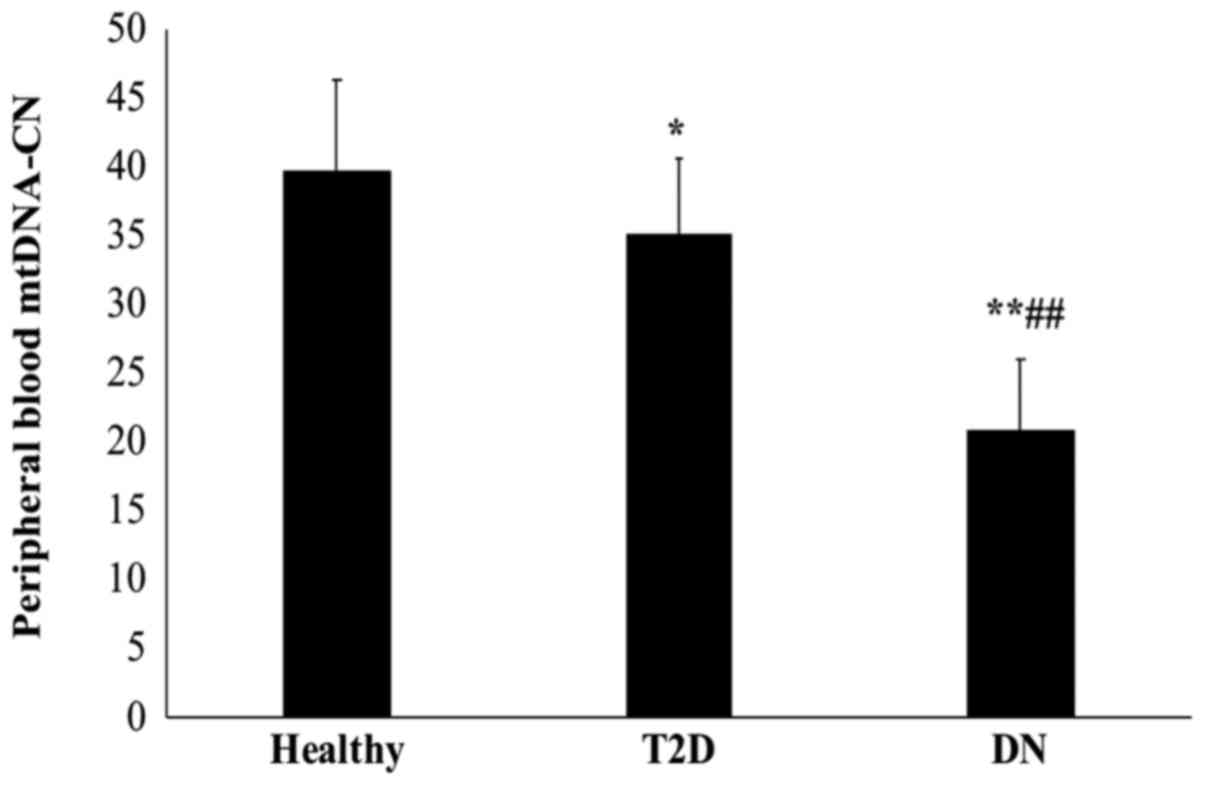
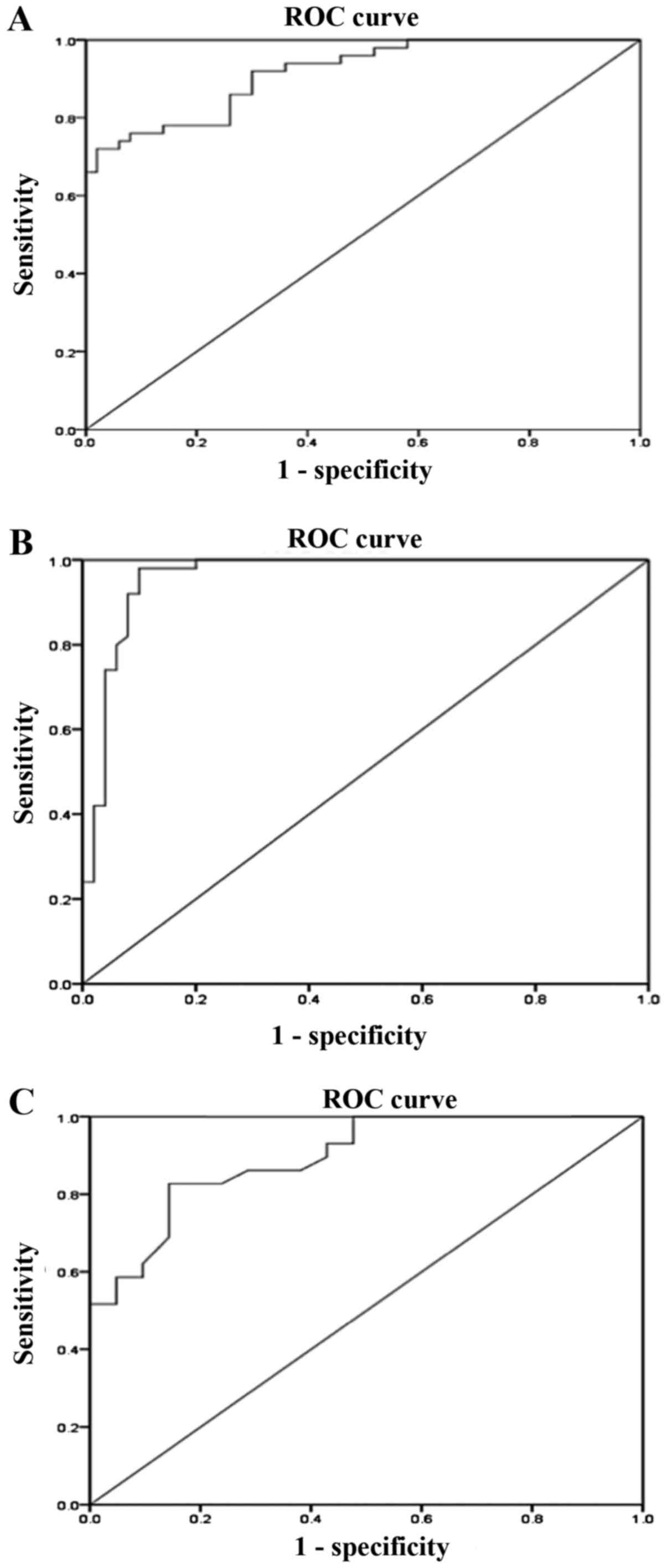
|
1
|
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R and
King H: Global prevalence of diabetes: Estimates for the year 2000
and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 27:1047–1053. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ghaderian SB, Hayati F, Shayanpour S and
Mousavi SSB: Diabetes and end-stage renal disease; a review article
on new concepts. J Renal Inj Prev. 4:28–33. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ritz E and Orth SR: Nephropathy in
patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med.
341:1127–1133. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Remuzzi G and Ruggenenti P: Slowing the
progression of diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 329:1496–1497.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nathan DM, Bayless M, Cleary P, Genuth S,
Gubitosi-Klug R, Lachin JM, Lorenzi G and Zinman B: DCCT/EDIC
Research Group; Diabetes control and complications
trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications
study at 30 years: Advances and contributions. Diabetes.
62:3976–3985. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Implications of the diabetes control
complications trial. American diabetes association. Diabetes.
42:1555–1558. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Forbes JM, Coughlan MT and Cooper ME:
Oxidative stress as a major culprit in kidney disease in diabetes.
Diabetes. 57:1446–1454. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sivitz WI and Yorek MA: Mitochondrial
dysfunction in diabetes: From molecular mechanisms to functional
significance and therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal.
12:537–577. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nishikawa T, Edelstein D, Du X L,
Yamagishi S, Matsumura T, Kaneda Y, Yorek MA, Beebe D, Oates PJ,
Hammes HP, et al: Normalizing mitochondrial superoxide production
blocks three pathways of hyperglycaemic damage. Nature.
404:787–790. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brownlee M: Biochemistry and molecular
cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 414:813–820. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Arora MK and Singh UK: Molecular
mechanisms in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy: An update.
Vascul Pharmacol. 58:259–271. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Parving HH, Smidt UM, Friisberg B,
Bonnevie-Nielsen V and Andersen AR: A prospective study of
glomerular filtration rate and arterial blood pressure in
insulin-dependent diabetics with diabetic nephropathy.
Diabetologia. 20:457–461. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Maclsaac RJ, Ekinici E and Jerums G:
Progressive diabetic nephropathy. How useful is microalbuminuria?
Contra'. Kidney Int. 86:50–57. 2014.
|
|
14
|
Glassock RJ: Is the presence of
microalbuminuria a relevant marker of kidney disease? Curr
Hypertens Rep. 12:364–368. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rigalleau V, Lasseur C, Raffaitin C,
Beauvieux MC, Barthe N, Chauveau P, Combe C and Gin H:
Normoalbuminuric renal-insufficient diabetic patients. Diabetes
Care. 30:2034–2039. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Clay-Montier LL, Deng JJ and Bai Y: Number
matters: Control of mammalian mitochondrial DNA copy number. J
Genet Genomics. 36:125–131. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Santos JH, Hunakova L, Chen Y, Bortner C
and Van Houten B: Cell sorting experiments link persistent
mitochondrial DNA damage with loss of mitochondrial membrane
potential and apoptotic cell death. J Biol Chem. 278:1728–1734.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee HC and Wei YH: Mitochondrial
biogenesis and mitochondrial DNA maintenance of mammalian cells
under oxidative stress. Int J Biochemy and Cell Biol. 37:822–834.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Al-Kafaji G and Golbahar J: High
glucose-induced oxidative stress increases the copy number of
mitochondrial DNA in human mesangial cells. Biomed Res Int.
2013:7549462013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Al-Kafaji G, Sabry MA and Bakhiet M:
Increased expression of mitochondrial DNA-encoded genes in human
renal mesangial cells in response to high glucose-induced reactive
oxygen species. Mol Med Rep. 13:1774–1780. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Al-Kafaji G, Sabry MA and Skrypnyk C:
Time-course effect of high glucose-induced reactive oxygen species
on mitochondrial biogenesis and function in human renal mesangial
cells. Cell Biol Int. 40:36–48. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee H, Song JH, Shine CS, Park DJ, Park
KS, Lee KU and Koh CS: Decreased mitochondrial DNA content in
peripheral blood precedes the development of non-insulin-dependent
diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 42:161–167. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gianotti TF, Sookoian S, Dieuzeide G,
Garcia S, Gemma C, González CD and Pirola CJ: A decreased
mitochondrial DNA content is related to insulin resistance in
adolescents. Obesity (Silver Spring). 16:1591–1595. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Song J, Oh JY, Sung YA, Pak YK, Park KS
and Lee HK: Peripheral blood mitochondrial DNA content is related
to insulin sensitivity in offspring of type 2 diabetic patients.
Diabetes Care. 24:865–869. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu FX, Zhou X, Shen F, Pang R and Liu SM:
Decreased peripheral blood mitochondrial DNA content is related to
HbA1c, fasting plasma glucose level and age of onset in type 2
diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 29:e47–e54. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hu L, Yao X and Shen Y: Altered
mitochondrial DNA copy number contributes to human cancer risk:
Evidence from an updated meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 6:358592016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu LP, Cheng K, Ning MA, Li HH, Wang HC,
Li F, Chen SY, Qu FL and Guo WY: Association between peripheral
blood cells mitochondrial DNA content and severity of coronary
heart disease. Atherosclerosis. 261:105–110. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Alberti KG and Zimmet PZ: Definition,
diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its
complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes
mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med.
15:539–553. 1998.
|
|
29
|
Mattix HJ, Hsu CY, Shaykevich S and Curhan
G: Use of the albumin/creatinine ratio to detect microalbuminuria:
Implications of sex and race. J Am Soc Nephrol. 13:1034–1039.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stoves J, Lindley EJ, Barnfield MC,
Burniston MT and Newstead CG: MDRD equation estimates of glomerular
filtration rate in potential living kidney donors and renal
transplant recipients with impaired graft function. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 17:2036–2037. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee JE, Park H, Ju YS, Kwak M, Kim J, Oh
HY and Seo JS: Higher mitochondrial DNA copy number is associated
with lower prevalence of microalbuminuria. Exp Mol Med. 41:253–258.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ide T, Tsutsui H, Hayashidani S, Kang D,
Suematsu N, Nakamura K, Utsumi H, Hamasaki N and Takeshita A:
Mitochondrial DNA damage and dysfunction associated with oxidative
stress in failing hearts after myocardial infarction. Circ Res.
88:529–535. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Catherwood MA, Powell LA, Anderson P,
McMaster D, Sharpe PC and Trimble ER: Glucose-induced oxidative
stress in mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 61:599–608. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ha H and Lee HB: Reactive oxygen species
amplify glucose signalling in renal cells cultured under high
glucose and in diabetic kidney. Nephrology (Carlton). 10
Suppl:S7–S10. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kakimoto M, Inoguchi T Sonta T, Yu HY,
Imamura M, Etoh T, Hashimoto T and Nawata H: Accumulation of
8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine and mitochondrial DNA deletion in kidney
of diabetic rats. Diabetes. 51:1588–1595. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pan HZ, Zhang L, Guo MY, Sui H, Li H, Wu
WH, Qu NQ, Liang MH and Chang D: The oxidative stress status in
diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy. Acta Diabetol. 47 Suppl
1:S71–S76. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Inci A, Olmaz R, Sarı F, Coban M, Ellidag
HY and Sarıkaya M: Increased oxidative stress in diabetic
nephropathy and its relationship with soluble Klotho levels.
Hiprokratia. 20:198–203. 2016.
|
|
38
|
Zhou M, Zhu L, Cui X, Feng L, Zhao X, He
S, Ping F, Li W and Li Y: Reduced peripheral blood mtDNA content is
associated with impaired glucose-stimulated islet β cell function
in a Chinese population with different degrees of glucose
tolerance. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 32:768–774. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Duran-Salgado MB and Rubio-Guerra AF:
Diabetic nephropathy and inflammation. World J Diabetes. 5:393–398.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cherry AD and Piantadosi CA: Regulation of
mitochondrial biogenesis and its intersection with inflammatory
responses. Antioxid Redox Signal. 22:965–976. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chawla A, Nguyen KD and Goh YP:
Macrophage-mediated inflammation in metabolic disease. Nat Rev
Immunol. 11:738–749. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu IC, Lin CC, Liu CS, Hus CC, Chen CY and
Hsiung CA: Interrelations between mitochondrial DNA copy number and
inflammation in older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.
72:937–944. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cossarizza A: Tests for mitochondrial
function and DNA: Potentials and pitfalls. Curr Opin Infect Dis.
16:5–10. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hurtado-Roca Y, Ledesma M, Gonzalez-Lazaro
M, Moreno-Loshuertos R, Fernandez-Silva P, Enriquez JA and
Laclaustra M: Adjusting MtDNA quantification in whole blood for
peripheral blood platelet and leukocyte counts. PLoS One.
11:e01637702016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Steinberg K, Beck J, Nickerson D,
Garcia-Closas M, Gallagher M, Caggana M, Reid Y, Cosentino M, Ji J,
Johnson D, et al: DNA banking for epidemiologic studies: A review
of current practices. Epidemiology. 13:246–254. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xia P, An H-X, Dang C-X, Radpour R, Kohler
C, Fokas E, Engenhart-Cabillic R, Holzgreve W and Zhong XY:
Decreased mitochondrial DNA content in blood samples of patients
with stage I breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 9:4542009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Demmer RT, Zuk AM, Rosenbaum M and
Desvarieux M: Prevalence of diagnosed and undiagnosed type 2
diabetes mellitus among US adolescents: Results from the continuous
NHANES, 1999-2010. Am J Epidemiol. 178:1106–1113. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gedebjerg A, Almdal TP, Berencsi K, Rungby
J, Nielsen JS, Witte DR, Friborg S, Brandslund I, Vaag A,
Beck-Nielsen H, et al: Prevalence of micro- and macrovascular
diabetes complications at time of type 2 diabetes diagnosis and
associated clinical characteristics: A cross-sectional baseline
study of 6,958 patients in the Danish DD2 cohort. J Diabetes
Complications. 32:34–40. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cho SB, Koh I, Nam HY, Jeon JP, Lee HK and
Han BG: Mitochondrial DNA copy number augments performance of A1C
and oral glucose tolerance testing in the prediction of type 2
diabetes. Sci Rep. 7:432032017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rao M, Li L, Demello C, Guo D, Jaber BL,
Pereira BJ and Balakrishnan VS: HEMO Study Group; Mitochondrial DNA
injury and mortality in hemodialysis patients. J Am Sco Nephrol.
20:189–196. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Mishra M, Lillvis J, Seyoum B and Kowluru
RA: Peripheral blood mitochondrial DNA damage as a potential
noninvasive biomarker of diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 57:4035–4044. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jayakumar RV: Risk factors in diabetic
nephropathy. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. 32:1–3. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Unsal A, Koc Y, Basturk T, Akgun AO,
Sakaci T and Ahbap E: Risk factors for progression of renal disease
in patient with diabetic nephropathy. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
16:878–883. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|