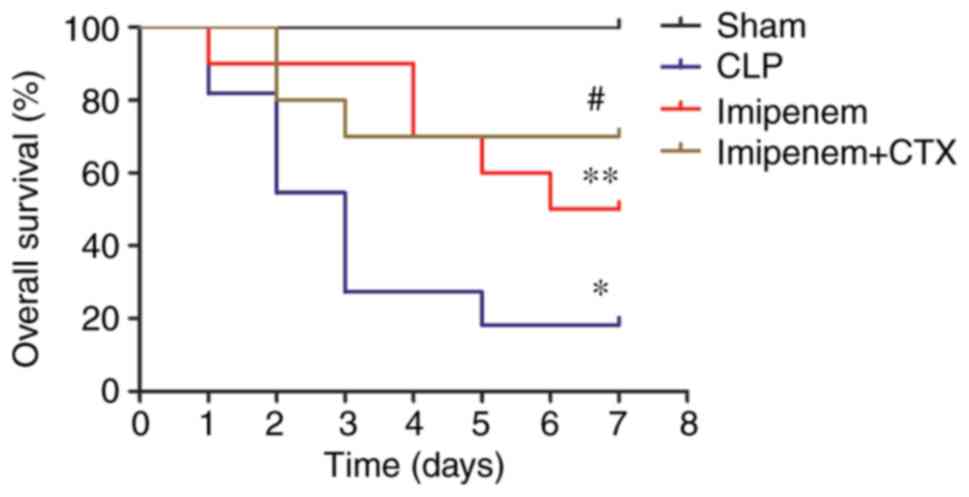
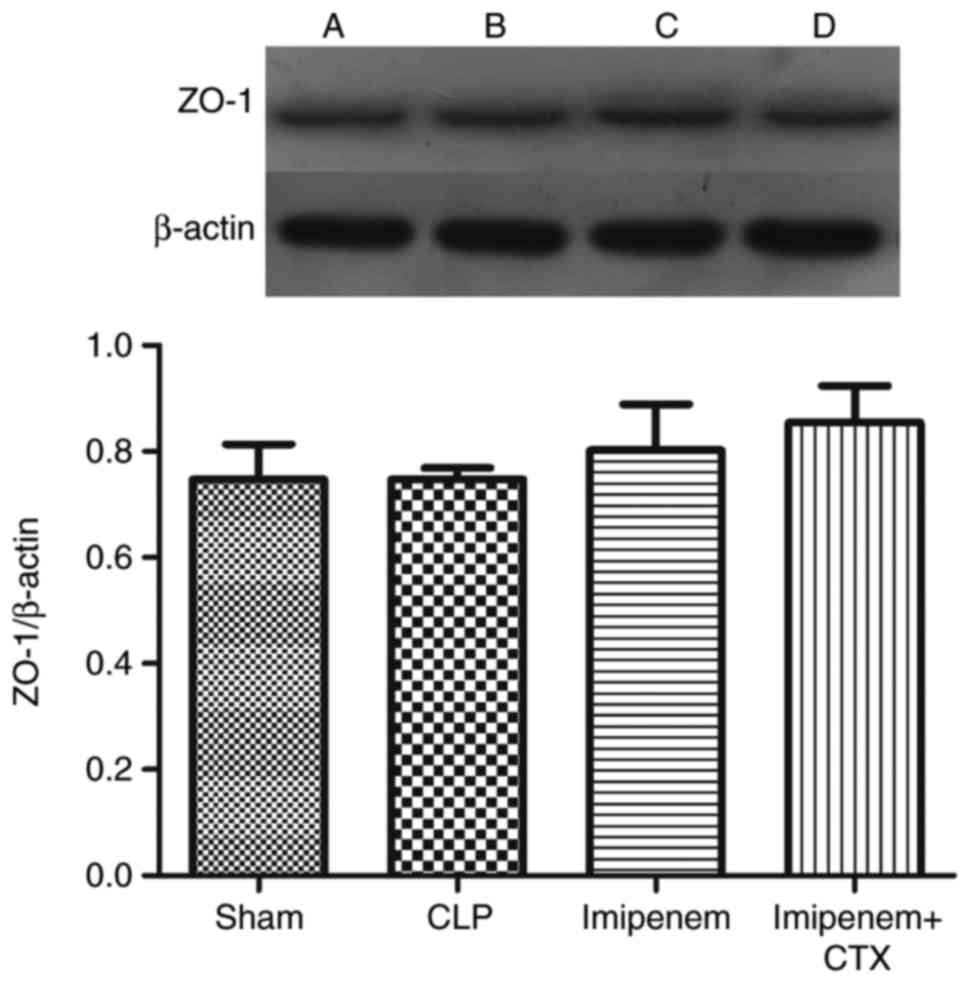
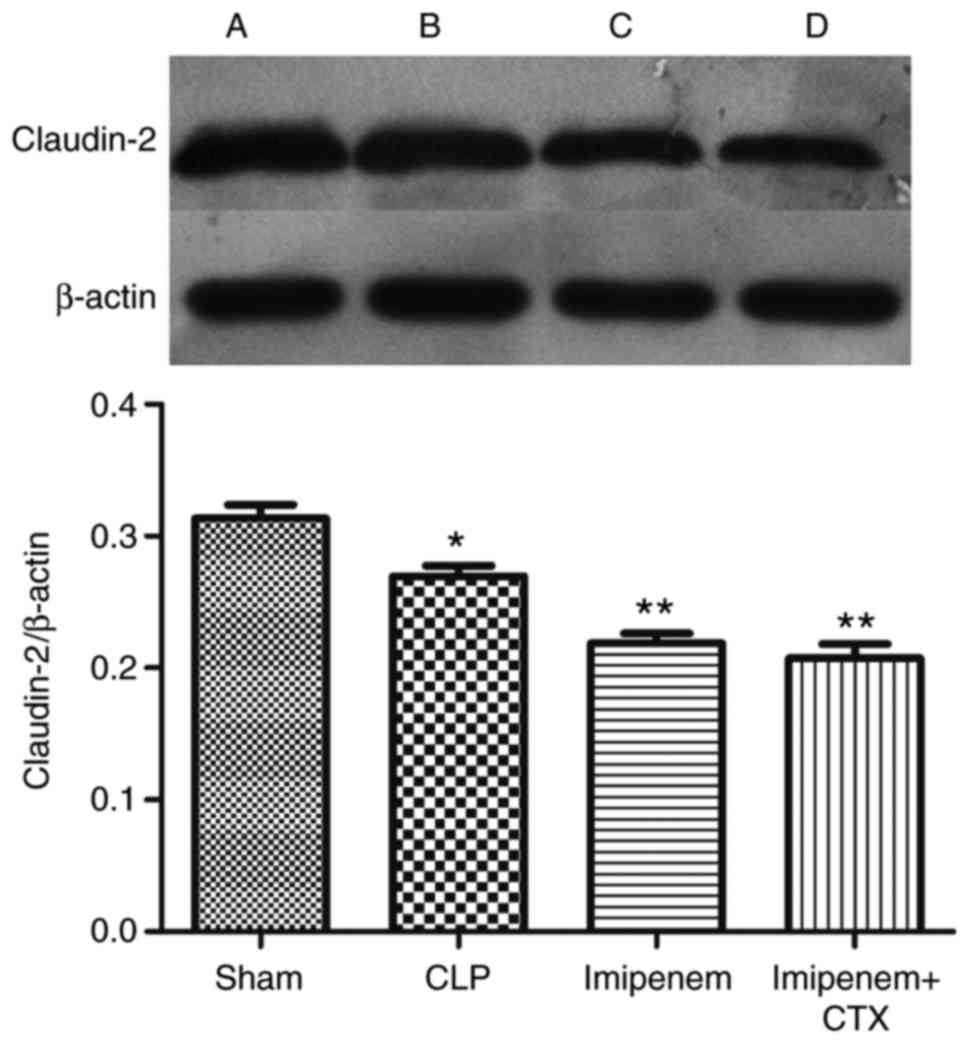
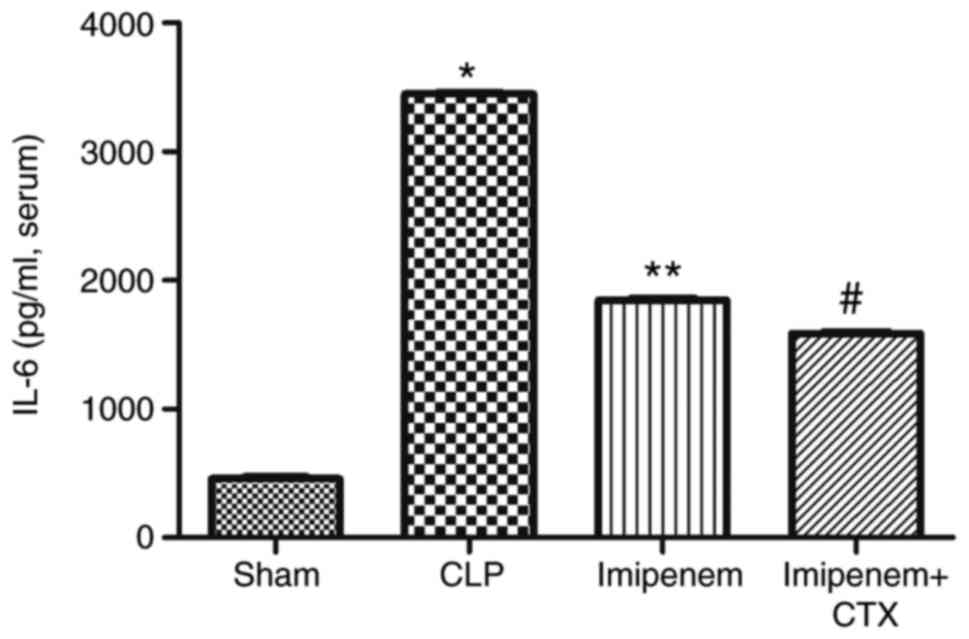
|
1
|
Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM,
Antonelli M, Ferrer R, Kumar A, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Nunnally
ME, et al: Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for
management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Crit Care Med.
45:486–552. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J,
Clermont G, Carcillo J and Pinsky MR: Epidemiology of severe sepsis
in the United States: Analysis of incidence, outcome, and
associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 29:1303–1310. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NK,
Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P, Angus DC and Reinhart K:
International Forum of Acute Care Trialists: Assessment of global
incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. Current
estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 193:259–272.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stoller J, Halpin L, Weis M, Aplin B, Qu
W, Georgescu C and Nazzal M: Epidemiology of severe sepsis:
2008–2012. J Crit Care. 31:58–62. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hotchkiss RS and Opal S: Immunotherapy for
sepsis-a new approach against an ancient foe. N Engl J Med.
363:87–89. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Weighardt H, Heidecke CD, Emmanuilidis K,
Maier S, Bartels H, Siewert JR and Holzmann B: Sepsis after major
visceral surgery is associated with sustained and
interferon-gamma-resistant defects of monocyte cytokine production.
Surgery. 127:309–315. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zeni F, Freeman B and Natanson C:
Anti-inflammatory therapies to treat sepsis and septic shock: A
reassessment. Crit Care Med. 25:1095–1100. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brown I, Bellevue O, Shawo A, Woldesemayat
H, Lyo V, Rayikanti B, Lee M, Uzosike ED, Kasravi S and Harris HW:
Low-dose cyclophosphamide improves survival in a murine treatment
model of sepsis. Shock. 43:92–98. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wei ZR, Wang DL and Liu Q: Effects of low
dose of cyclophosphamide on acute lung injury in sepsis sats. Chin
J Crit Care Med. 26:124–126. 2006.
|
|
10
|
Waymack JP and Alexander JW:
Immunomodulators for the prevention of infections in burned guinea
pigs. J Burn Care Rehabil. 8:363–365. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fibbe WE, van der Meer JW, Falkenburg JH,
Hamilton MS, Kluin PM and Dinarello CA: A single low dose of human
recombinant interleukin 1 accelerates the recovery of neutrophils
in mice with cyclophosphamide-induced neutropenia. Exp Hematol.
17:805–808. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
van Vliet MJ, Tissing WJ, Dun CA, Meessen
NE, Kamps WA, de Bont ES and Harmsen HJ: Chemotherapy treatment in
pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia receiving
antimicrobial prophylaxis leads to a relative increase of
colonization with potentially pathogenic bacteria in the gut. Clin
Infect Dis. 49:262–270. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang J, Liu KX, Qu JM and Wang XD: The
changes induced by cyclophosphamide in intestinal barrier and
microflora in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 714:120–124. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nord CE and Edlund C: Impact of
antimicrobial agents on human intestinal microflora. J Chemother.
2:218–237. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Matsumoto T, Ishikawa H, Tateda K,
Yaeshima T, Ishibashi N and Yamaguchi K: Oral administration of
Bifidobacterium longum prevents gut-derived Pseudomonas aeruginosa
sepsis in mice. J Appl Microbiol. 104:672–680. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dancygier H and Frick B: Crohn's disease
of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Endoscopy. 24:555–558. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fahal AH, el Razig SA, Suliman SH, Ibrahim
SZ and Tigani AE: Gastrointestinal tract cancer in association with
hepatitis and HIV infection. East Afr Med J. 72:424–426.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wells CL: Relationship between intestinal
microecology and the translocation of intestinal bacteria. Antonie
Van Leeuwenhoek. 58:87–93. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Udall JN, Pang K, Fritze L, Kleinman R and
Walker WA: Development of gastrointestinal mucosal barrier. I. The
effect of age on intestinal permeability to macromolecules. Pediatr
Res. 15:241–244. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu H, Liu Z, Zhao S, Sun C and Yang M:
Effect of BML-111 on the intestinal mucosal barrier in sepsis and
its mechanism of action. Mol Med Rep. 12:3101–3106. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Berg RD and Garlington AW: Translocation
of certain indigenous bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract to
the mesenteric lymph nodes and other organs in a gnotobiotic mouse
model. Infect Immun. 23:403–411. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gao M, Jiang Y, Xiao X, Peng Y, Xiao X and
Yang M: Protective effect of pioglitazone on sepsis-induced
intestinal injury in a rodent model. J Surg Res. 195:550–558. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao W and Sun GZ: Random grouping of
experimental animals is often used. Xu Mu Shou Yi Ke Ji Xin Xi.
2009:61–62. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
24
|
Rittirsch D, Huber-Lang MS, Flierl MA and
Ward PA: Immunodesign of experimental sepsis by cecal ligation and
puncture. Nat Protoc. 4:31–36. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma LQ, Chen DC and Liu SZ: Influence of
broad-spectrum antibiotics on the gut microflora in sepsis in rats.
Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi. 20:520–522. 2008.(In
Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Ulluwishewa D, Anderson RC, McNabb WC,
Moughan PJ, Wells JM and Roy NC: Regulation of tight junction
permeability by intestinal bacteria and dietary components. J Nutr.
141:769–776. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Deitch EA: Gut lymph and lymphatics: A
source of factors leading to organ injury and dysfunction. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1207 Suppl 1:E103–E111. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sharma R, Tepas JJ III, Hudak ML, Mollitt
DL, Wludyka PS, Teng RJ and Premachandra BR: Neonatal gut barrier
and multiple organ failure: Role of endotoxin and proinflammatory
cytokines in sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg.
42:454–461. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Costantini TW, Loomis WH, Putnam JG,
Drusinsky D, Deree J, Choi S, Wolf P, Baird A, Eliceiri B, Bansal V
and Coimbra R: Burn-induced gut barrier injury is attenuated by
phosphodiesterase inhibition: Effects on tight junction structural
proteins. Shock. 31:416–422. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Song D, Shi B, Xue H, Li Y, Yang X, Yu B,
Xu Z, Liu F and Li J: Confirmation and prevention of intestinal
barrier dysfunction and bacterial translocation caused by
methotrexate. Dig Dis Sci. 51:1549–1556. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Thakre-Nighot M and Blikslager AT:
Indomethacin induces increase in gastric epithelial tight junction
permeability via redistribution of occludin and activation of p38
MAPK in MKN-28 Cells. Tissue Barriers. 4:e11873252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Munjal C, Tyagi N, Lominadze D and Tyagi
SC: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 in homocysteine-induced intestinal
microvascular endothelial paracellular and transcellular
permeability. J Cell Biochem. 113:1159–1169. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gu L, Li N, Gong J, Li Q, Zhu W and Li J:
Berberine ameliorates intestinal epithelial tight-junction damage
and down-regulates myosin light chain kinase pathways in a mouse
model of endotoxinemia. J Infect Dis. 203:1602–1612. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Costantini TW, Bansal V, Peterson CY,
Loomis WH, Putnam JG, Rankin F, Wolf P, Eliceiri BP, Baird A and
Coimbra R: Efferent vagal nerve stimulation attenuates gut barrier
injury after burn: Modulation of intestinal occludin expression. J
Trauma. 68:1349–1356. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Al-Sadi R, Guo S, Ye D and Ma TY: TNF-α
modulation of intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier is
regulated by ERK1/2 activation of Elk-1. Am J Pathol.
183:1871–1884. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang R, Han X, Uchiyama T, Watkins SK,
Yaguchi A, Delude RL and Fink MP: IL-6 is essential for development
of gut barrier dysfunction after hemorrhagic shock and
resuscitation in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
285:G621–G629. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun X, Yang H, Nose K, Nose S, Haxhija EQ,
Koga H, Feng Y and Teitelbaum DH: Decline in intestinal mucosal
IL-10 expression and decreased intestinal barrier function in a
mouse model of total parenteral nutrition. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 294:G139–G147. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Arrieta MC, Madsen K, Doyle J and Meddings
J: Reducing small intestinal permeability attenuates colitis in the
IL10 gene-deficient mouse. Gut. 58:41–48. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu Z, Zhang P, Ma Y, Chen H, Zhou Y,
Zhang M, Chu Z and Qin H: Lactobacillus plantarum prevents the
development of colitis in IL-10-deficient mouse by reducing the
intestinal permeability. Mol Biol Rep. 38:1353–1361. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Arrieta MC, Madsen KL, Field CJ and
Meddings JB: Increasing small intestinal permeability worsens
colitis in the IL-10-/- mouse and prevents the induction of oral
tolerance to ovalbumin. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 21:8–18. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zahs A, Bird MD, Ramirez L, Choudhry MA
and Kovacs EJ: Anti-IL-6 antibody treatment but not IL-6 knockout
improves intestinal barrier function and reduces inflammation after
binge ethanol exposure and burn injury. Shock. 39:373–379. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang Q, Fang CH and Hasselgren PO:
Intestinal permeability is reduced and IL-10 levels are increased
in septic IL-6 knockout mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp
Physiol. 281:R1013–R1023. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|