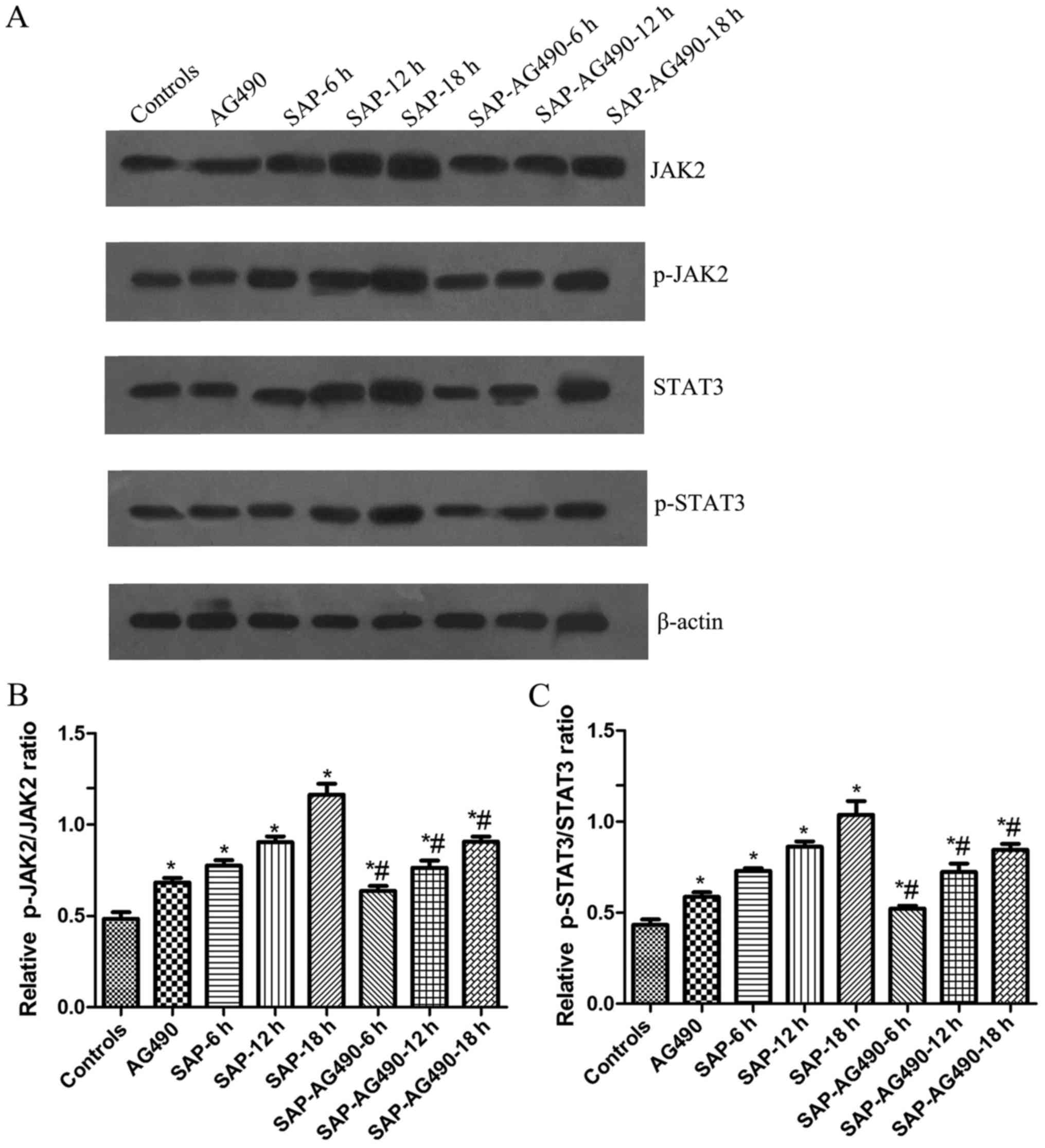
|
1
|
Shen HN, Lu CL and Li CY: Effect of
diabetes on severity and hospital mortality in patients with acute
pancreatitis: A national population-based study. Diabetes Care.
35:1061–1066. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen
HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, Tsiotos GG and Vege SS: Acute Pancreatitis
Classification Working Group: Classification of acute pancreatitis
2012: Revision of the atlanta classification and definitions by
international consensus. Gut. 62:102–111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu Y, Liao R, Qiang Z and Zhang C:
Pro-inflammatory cytokine-driven PI3K/Akt/Sp1 signalling and
H2S production facilitates the pathogenesis of severe
acute pancreatitis. Biosci Rep. 37:BSR201604832017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang J, Gallagher SF, Haines K,
Epling-Burnette PK, Bai F, Gower WR Jr, Mastorides S, Norman JG and
Murr MM: Kupffer cell-derived Fas ligand plays a role in liver
injury and hepatocyte death. J Gastrointest Surg. 8:166–174. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ou ZB, Miao CM, Ye MX, Xing DP, He K, Li
PZ, Zhu RT and Gong JP: Investigation for role of tissue factor and
blood coagulation system in severe acute pancreatitis and
associated liver injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 85:380–388. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang J, Fier A, Carter Y, Liu G,
Epling-Burnette PK, Bai F, Loughran TP Jr, Mastorides S, Norman JG
and Murr MM: Liver injury during acute pancreatitis: The role of
pancreatitis-associated ascitic fluid (PAAF), p38-MAPK, and
caspase-3 in inducing hepatocyte apoptosis. J Gastrointest Surg.
7:200–208. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Folch-Puy E: Importance of the liver in
systemic complications associated with acute pancreatitis: The role
of Kupffer cells. J Pathol. 211:383–388. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
O'Shea JJ, Schwartz DM, Villarino AV,
Gadina M, McInnes IB and Laurence A: The JAK-STAT pathway: Impact
on human disease and therapeutic intervention. Annu Rev Med.
66:311–328. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Roskoski R Jr: Janus kinase (JAK)
inhibitors in the treatment of inflammatory and neoplastic
diseases. Pharmacol Res. 111:784–803. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sakamori R, Takehara T, Ohnishi C, Tatsumi
T, Ohkawa K, Takeda K, Akira S and Hayashi N: Signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3 signaling within hepatocytes
attenuates systemic inflammatory response and lethality in septic
mice. Hepatology. 46:1564–1573. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Aho HJ, Koskensalo SM and Nevalainen TJ:
Experimental pancreatitis in the rat. Sodium taurocholate-induced
acute haemorrhagic pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 15:411–416.
1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schmidt J, Rattner DW, Lewandrowski K,
Compton CC, Mandavilli U, Knoefel WT and Warshaw AL: A better model
of acute pancreatitis for evaluating therapy. Ann Surg. 215:44–56.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Camargo CA Jr, Madden JF, Gao W, Selvan RS
and Clavien A: Interleukin-6 protects liver against warm
ischemia/reperfusion injury and promotes hepatocyte proliferation
in the rodent. Hepatology. 26:1513–1520. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kempuraj D, Twait EC, Williard DE, Yuan Z,
Meyerholz DK and Samuel I: The novel cytokine interleukin-33
activates acinar cell proinflammatory pathways and induces acute
pancreatic inflammation in mice. PLoS One. 8:e568662013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Geisler F, Algül H, Riemann M and Schmid
RM: Questioning current concepts in acute pancreatitis: Endotoxin
contamination of porcine pancreatic elastase is responsible for
experimental pancreatitis-associated distant organ failure. J
Immunol. 174:6431–6439. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang Y, An Y, Jiang D, Wu B, Yang Y and
Sun D: TNF-α regulating interleukin-33 induces acute pancreatic
inflammation in rats. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 46:54–59. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Martin MA, Saracibar E, Santamaria A,
Arranz E, Garrote JA, Almaraz A, del Olmo ML, García-Pajares F,
Fernández-Orcajo P, Velicia R, et al: Interleukin 18 (IL-18) and
other immunological parameters as markers of severity in acute
pancreatitis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 100:768–773. 2008.(In Spanish).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang XH, Li ML, Wang B, Guo MX and Zhu
RM: Caspase-1 inhibition alleviates acute renal injury in rats with
severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 20:10457–10463.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wenhong D, Jia Y, Weixing W, Xiaoyan C,
Chen C, Sheng X and Hao J: Zerumbone attenuates the severity of
acute necrotizing pancreatitis and pancreatitis-induced hepatic
injury. Mediators Inflamm. 2012:1565072012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang J, Gallagher SF, Haines K,
Epling-Burnette PK, Bai F, Gower WR Jr, Mastorides S, Norman JG and
Murr MM: Kupffer cell-derived Fas ligand plays a role in liver
injury and hepatocyte death. J Gastrointest Surg. 8:166–174. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen P, Huang L, Zhang Y, Qiao M, Yao W
and Yuan Y: The antagonist of the JAK-1/STAT-1 signaling pathway
improves the severity of cerulein-stimulated pancreatic injury via
inhibition of NF-κB activity. Int J Mol Med. 27:731–738.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Damm J, Harden L, Gerstberger R, Roth J
and Rummel C: The putative JAK-STAT inhibitor AG490 exacerbates
LPS-fever, reduces sickness behavior, and alters the expression of
pro- and anti-inflammatory genes in the rat brain.
Neuropharmacology. 71:98–111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu JH and Kim H: Role of janus
kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription in the
pathogenesis of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gut Liver.
6:417–422. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang C, Ma R, Sun S, Wei G, Fang Y, Liu R
and Li G: JAK2-STAT3 signaling pathway mediates thrombin-induced
proinflammatory actions of microglia in vitro. J Neuroimmunol.
204:118–125. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Agrawal S, Gollapudi S, Su H and Gupta S:
Leptin activates human B cells to secrete TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10
via JAK2/STAT3 and p38MAPK/ERK1/2 signaling pathway. J Clin
Immunol. 31:472–478. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang LY, Chen P, Xu LX, Zhou YF, Zhang YP
and Yuan YZ: Fractalkine upregulates inflammation through CX3CR1
and the Jak-Stat pathway in severe acute pancreatitis rat model.
Inflammation. 35:1023–1030. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gallmeier E, Schäfer C, Moubarak P, Tietz
A, Plössl I, Huss R, Göke B and Wagner AC: JAK and STAT proteins
are expressed and activated by IFN-gamma in rat pancreatic acinar
cells. J Cell Physiol. 203:209–216. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu L, Li H, Zheng SZ, Liu X, Cai H and Cai
BC: Da-Huang-Fu-Zi-Tang attenuates liver injury in rats with severe
acute pancreatitis. J Ethnopharmacol. 150:960–966. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu JH, Kim KH and Kim H: SOCS 3 and
PPAR-gamma ligands inhibit the expression of IL-6 and TGF-beta1 by
regulating JAK2/STAT3 signaling in pancreas. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 40:677–688. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Robinson K, Vona-Davis L, Riggs D, Jackson
B and McFadden D: Peptide YY attenuates STAT1 and STAT3 activation
induced by TNF-alpha in acinar cell line AR42J. J Am Coll Surg.
202:788–796. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu JH, Kim KH and Kim H: Suppression of
IL-1beta expression by the Jak 2 inhibitor AG490 in
cerulein-stimulated pancreatic acinar cells. Biochem Pharmacol.
72:1555–1562. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Surbatovic M and Radakovic S: Tumor
necrosis factor-α levels early in severe acute pancreatitis: Is
there predictive value regarding severity and outcome? J Clin
Gastroenterol. 47:637–643. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gallagher SF, Peng Y, Haines K, Baksh K,
Epling-Burnette PK, Yang J and Murr MM: Fas/FasL play a central
role in pancreatitis-induced hepatocyte apoptotis. J Gastrointest
Surg. 9:467–475. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
McCormack D, McDonald D and McFadden D:
Pterostilbene ameliorates tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced
pancreatitis in vitro. J Surg Res. 178:28–32. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ueda T, Takeyama Y, Yasuda T, Matsumura N,
Sawa H, Nakajima T, Ajiki T, Fujino Y, Suzuki Y and Kuroda Y:
Significant elevation of serum interleukin-18 levels in patients
with acute pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 41:158–165. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ning JW, Zhang Y, Yu MS, Gu ML, Xu J,
Usman A and Ji F: Emodin alleviates intestinal mucosal injury in
rats with severe acute pancreatitis via the caspase-1 inhibition.
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 16:431–436. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Segersvärd R, Tsai JA, Herrington MK and
Wang F: Obesity alters cytokine gene expression and promotes liver
injury in rats with acute pancreatitis. Obesity (Silver Spring).
16:23–28. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lv P, Fan LJ, Li HY, Meng QS and Liu J:
Protective effect of thalidomide on liver injury in rats with acute
pancreatitis via inhibition of oxidative stress. Ann Clin Lab Sci.
45:508–514. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|