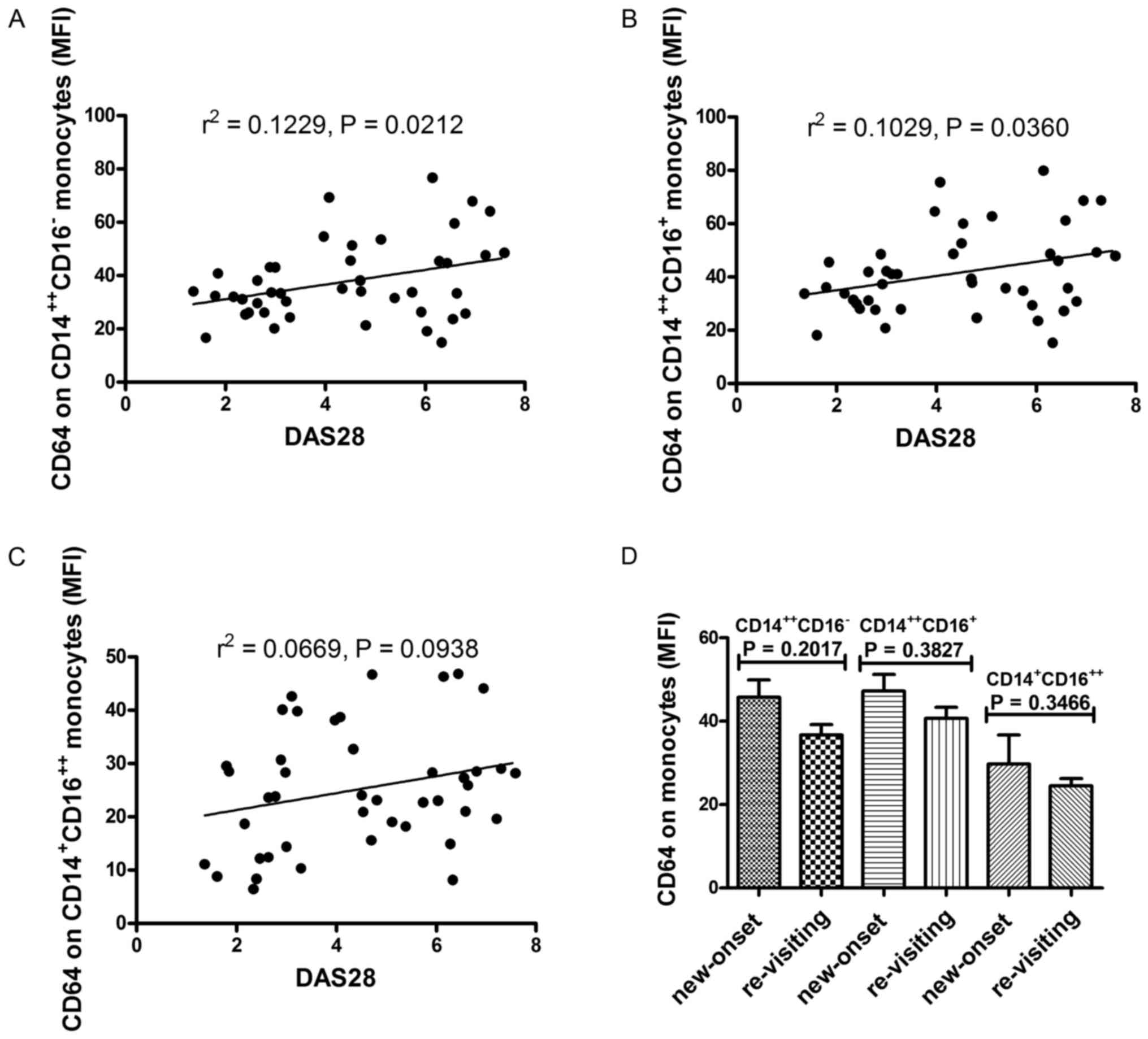
|
1
|
Li X, Yuan FL, Lu WG, Zhao YQ, Li CW, Li
JP and Xu RS: The role of interleukin-17 in mediating joint
destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
397:131–135. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yuan FL, Li X, Lu WG, Li CW, Xu RS and
Dong J: IL-33: A promising therapeutic target for rheumatoid
arthritis? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 15:529–534. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McInnes IB and Schett G: The pathogenesis
of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 365:2205–2219. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cascão R, Rosário HS, Souto-Carneiro MM
and Fonseca JE: Neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis: More than
simple final effectors. Autoimmun Rev. 9:531–535. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shi C and Pamer EG: Monocyte recruitment
during infection and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:762–774.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wong KL, Yeap WH, Tai JJ, Ong SM, Dang TM
and Wong SC: The three human monocyte subsets: Implications for
health and disease. Immunol Res. 53:41–57. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ziegler-Heitbrock L: The CD14+ CD16+ blood
monocytes: Their role in infection and inflammation. J Leukoc Biol.
81:584–592. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Skrzeczyńska-Moncznik J, Bzowska M, Loseke
S, Grage-Griebenow E, Zembala M and Pryjma J: Peripheral blood
CD14high CD16+ monocytes are main producers of IL-10. Scand J
Immunol. 67:152–159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rossol M, Kraus S, Pierer M, Baerwald C
and Wagner U: The CD14 (bright) CD16+ monocyte subset is expanded
in rheumatoid arthritis and promotes expansion of the Th17 cell
population. Arthritis Rheum. 64:671–677. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tsukamoto M, Seta N, Yoshimoto K, Suzuki
K, Yamaoka K and Takeuchi T: CD14brightCD16+ intermediate monocytes
are induced by interleukin-10 and positively correlate with disease
activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 19:282017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nimmerjahn F and Ravetch JV: Fcγ receptors
as regulators of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:34–47. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Amigorena S and Bonnerot C: Fc receptor
signalling and trafficking: A connection for antigen processing.
Immunol Rev. 172:279–284. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
García-García E and Rosales C: Signal
transduction during Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis. J Leukoc
Biol. 72:1092–1108. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Magnusson SE, Engström M, Jacob U, Ulfgren
AK and Kleinau S: High synovial expression of the inhibitory
FcgammaRIIb in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 9:R512007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van Vuuren AJ, van Roon JA, Walraven V,
Stuij I, Harmsen MC, McLaughlin PM, van de Winkel JG and Thepen T:
CD64-directed immunotoxin inhibits arthritis in a novel CD64
transgenic rat model. J Immunol. 176:5833–5838. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Matt P, Lindqvist U and Kleinau S:
Elevated membrane and soluble CD64: A novel marker reflecting
altered fcγr function and disease in early rheumatoid arthritis
that can be regulated by anti-rheumatic treatment. PLoS One.
10:e01374742015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Laurent L, Clavel C, Lemaire O, Anquetil
F, Cornillet M, Zabraniecki L, Nogueira L, Fournié B, Serre G and
Sebbag M: Fcγ receptor profile of monocytes and macrophages from
rheumatoid arthritis patients and their response to immune
complexes formed with autoantibodies to citrullinated proteins. Ann
Rheum Dis. 70:1052–1059. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hepburn AL, Mason JC and Davies KA:
Expression of Fcγ and complement receptors on peripheral blood
monocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 43:547–554. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane
DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS,
et al: The american rheumatism assocaition 1987 revised criteria
for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
31:315–324. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang J, Shan Y, Jiang Z, Feng J, Li C, Ma
L and Jiang Y: High frequencies of activated B cells and T
follicular helper cells are correlated with disease activity in
patients with new-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol.
174:212–220. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Prevoo ML, van't Hof MA, Kuper HH, van
Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LB and van Riel PL: Modified disease
activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development
and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with
rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 38:44–48. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mehta NN and Reilly MP: Monocyte mayhem:
Do subtypes modulate distinct atherosclerosis phenotypes? Circ
Cardiovasc Genet. 5:7–9. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mobley JL, Leininger M, Madore S, Baginski
TJ and Renkiewicz R: Genetic evidence of a functional monocyte
dichotomy. Inflammation. 30:189–197. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Auffray C, Sieweke MH and Geissmann F:
Blood monocytes: Development, heterogeneity and relationship with
dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 27:669–692. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Belge KU, Dayyani F, Horelt A, Siedlar M,
Frankenberger M, Frankenberger B, Espevik T and Ziegler-Heitbrock
L: The proinflammatory CD14 + CD16 + DR++ monocytes are a major
source of TNF. J Immunol. 168:3536–3542. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cros J, Cagnard N, Woollard K, Patey N,
Zhang SY, Senechal B, Puel A, Biswas SK, Moshous D, Picard C, et
al: Human CD14dim monocytes patrol and sense nucleic acids and
viruses via TLR7 and TLR8 receptors. Immunity. 33:375–386. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tsukamoto M, Seta N, Yoshimoto K, Suzuki
K, Yamaoka K and Takeuchi T: CD14brightCD16+ intermediate monocytes
are induced by interleukin-10 and positively correlate with disease
activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 19:282017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lacerte P, Brunet A, Egarnes B, Duchêne B,
Brown JP and Gosselin J: Overexpression of TLR2 and TLR9 on
monocyte subsets of active rheumatoid arthritis patients
contributes to enhance responsiveness to TLR agonists. Arthritis
Res Ther. 18:102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wijngaarden S, van Roon JA, Bijlsma JW,
van de Winkel JG and Lafeber FP: Fcgamma receptor expression levels
on monocytes are elevated in rheumatoid arthritis patients with
high erythrocyte sedimentation rate who do not use anti-rheumatic
drugs. Rheumatology (Oxford). 42:681–688. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rossol M, Kraus S, Pierer M, Baerwald C
and Wagner U: The CD14brightCD16 monocyte subset is expanded in
rheumatoid arthritis and promotes expansion of the th17 cell
population. Arthritis Rheum. 64:671–677. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bruhns P, Iannascoli B, England P,
Mancardi DA, Fernandez N, Jorieux S and Daëron M: Specificity and
affinity of human Fcgamma receptors and their polymorhic variants
for IgG subclasse. Blood. 113:3716–3725. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lu J, Marjon KD, Marnell LL, Wang R, Mold
C, Du Clos TW and Sun P: Recognition and functional activation of
the human IgA receptor (FcαRI) by C-reactive protein. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 108:4974–4979. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|