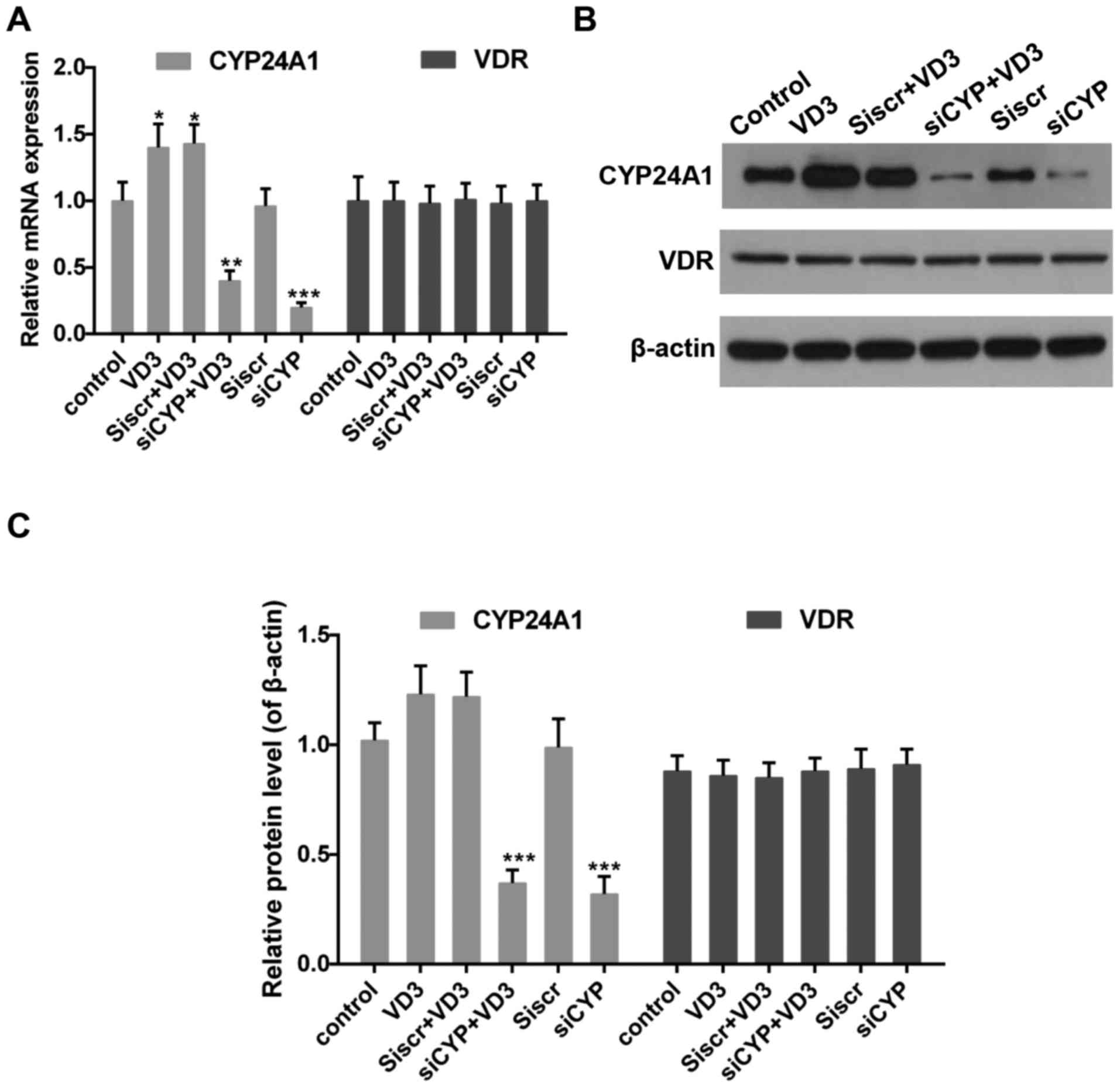
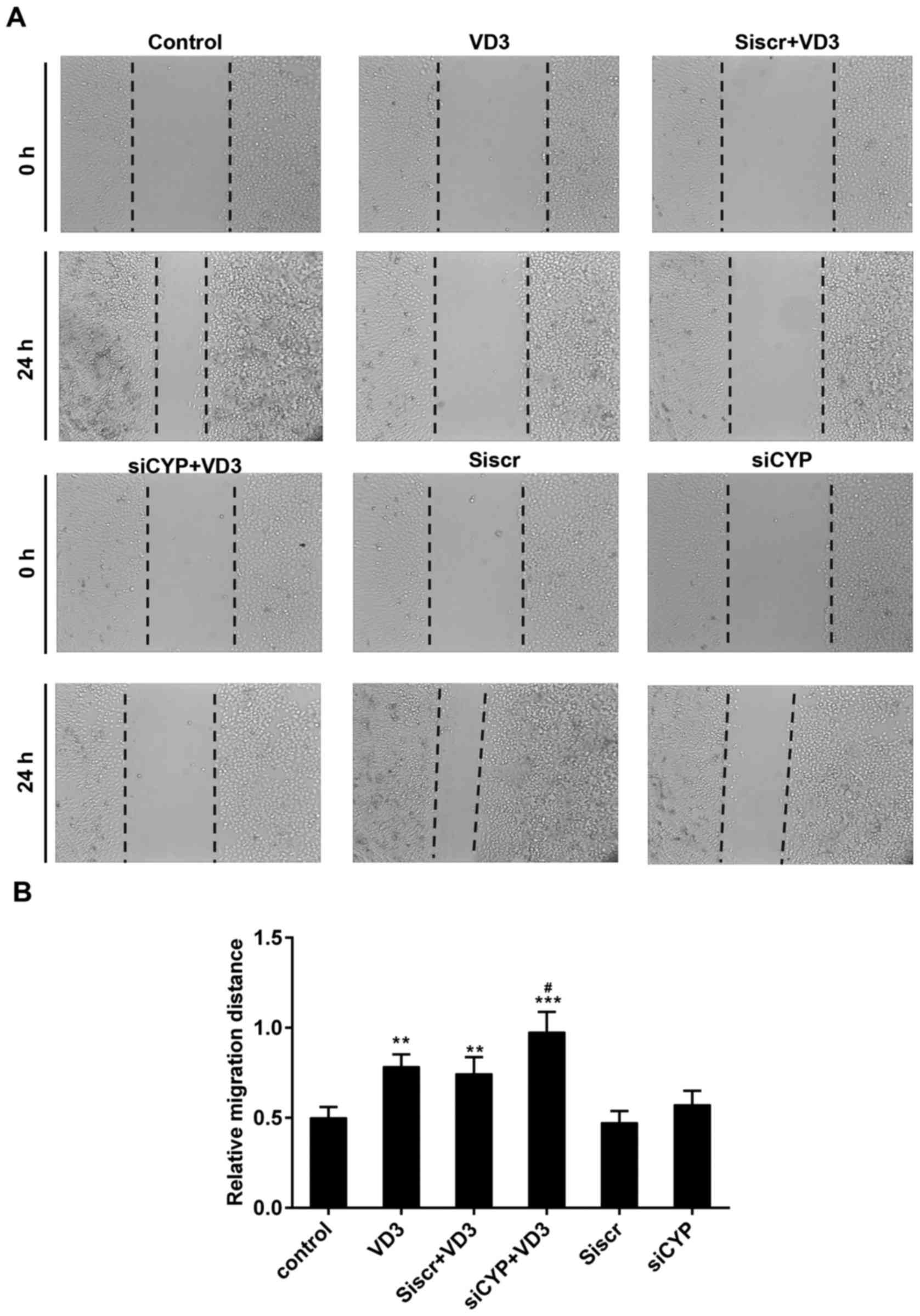
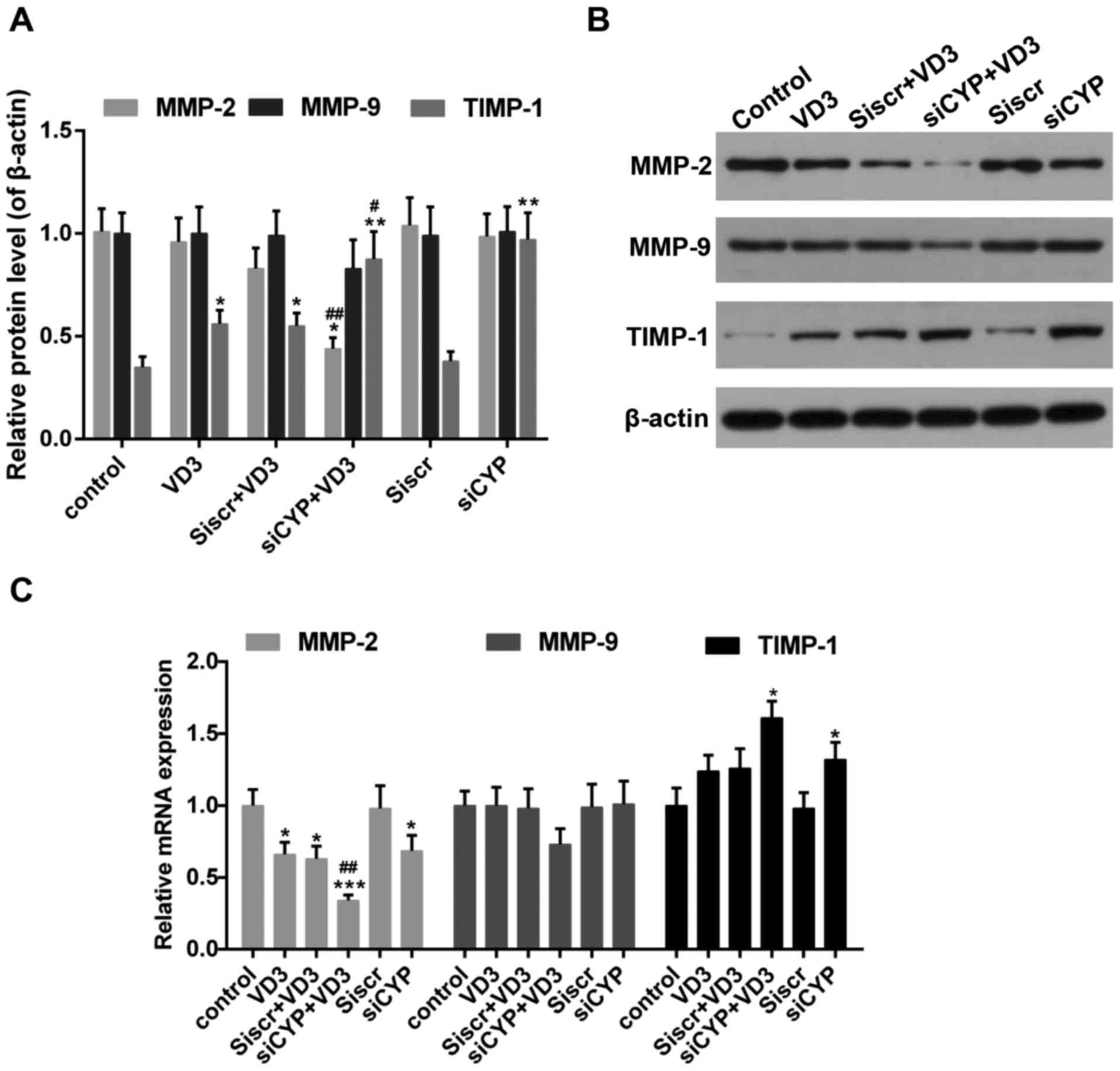
|
1
|
Davies L and Welch HG: Increasing
incidence of thyroid cancer in the United States, 1973-2002. JAMA.
295:2164–2167. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sherma SI: Thyroid carcinoma. Lancet.
361:501–511. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dobrinja C: Papillary thyroid cancer
gender disparity. 2014.
|
|
4
|
Kapiteijn E, Schneider TC, Morreau H,
Gelderblom H, Nortier JW and Smit JW: New treatment modalities in
advanced thyroid cancer. Ann Oncol. 23:10–18. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Boot AC: Vitamin-D deficiency. Ned
Tijdschr Geneeskd. 150:1315–1316. 2006.(In Dutch). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Deeb KK, Trump DL and Johnson CS: Vitamin
D signalling pathways in cancer: Potential for anticancer
therapeutics. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:684–700. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Clinckspoor I, Verlinden L, Mathieu C,
Bouillon R, Verstuyf A and Decallonne B: Vitamin D in thyroid
tumorigenesis and development. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 48:65–98.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Balla B, Tobias B, Kósa JP, Podani J,
Horváth P, Nagy Z, Horanyi J, Jaray B, Szekely E, Krenács L, et al:
Vitamin D-neutralizing CYP24A1 expression, oncogenic mutation
states and histological findings of human papillary thyroid cancer.
J Endocrinol Invest. 38:313–321. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hershberger PA, Modzelewski RA, Shurin ZR,
Rueger RM, Trump DL and Johnson CS: 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol
(1,25-D3) inhibits the growth of squamous cell carcinoma and
down-modulates p21(Waf1/Cip1) in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res.
59:2644–2649. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bises G, Kállay E, Weiland T, Wrba F,
Wenzl E, Bonner E, Kriwanek S, Obrist P and Cross HS:
25-hydroxyvitamin D3-1alpha-hydroxylase expression in normal and
malignant human colon. J Histochem Cytochem. 52:985–989. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Trump DL, Potter DM, Muindi J, Brufsky A
and Johnson CS: Phase II trial of high-dose, intermittent
calcitriol (1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3) and dexamethasone in
androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer. 106:2136–2142. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bennett RG, Wakeley SE, Hamel FG, High RR,
Korch C and Goldner WS: Gene expression of vitamin D metabolic
enzymes at baseline and in response to vitamin D treatment in
thyroid cancer cell lines. Oncology. 83:264–272. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stepien T, Krupinski R, Sopinski J, Kuzdak
K, Komorowski J, Lawnicka H and Stepien H: Decreased 1–25
dihydroxyvitamin D3 concentration in peripheral blood serum of
patients with thyroid cancer. Arch Med Res. 41:190–194. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Peehl DM and Feldman D: Interaction of
nuclear receptor ligands with the Vitamin D signaling pathway in
prostate cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 92:307–315. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ma Y, Trump DL and Johnson CS: Vitamin D
in combination cancer treatment. J Cancer. 1:101–107. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Evans TR, Colston KW, Lofts FJ, Cunningham
D, Anthoney DA, Gogas H, de Bono JS, Hamberg KJ, Skov T and Mansi
JL: A phase II trial of the vitamin D analogue Seocalcitol (EB1089)
in patients with inoperable pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer.
86:680–685. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dalhoff K, Dancey J, Astrup L, Skovsgaard
T, Hamberg KJ, Lofts FJ, Rosmorduc O, Erlinger S, Hansen JB,
Steward WP, et al: A phase II study of the vitamin D analogue
Seocalcitol in patients with inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma.
Br J Cancer. 89:252–257. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mikhail N: Clinical significance of
vitamin D deficiency in primary hyperparathyroidism, and safety of
vitamin D therapy. South Med J. 104:29–33. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cho YL, Christensen C, Saunders DE,
Lawrence WD, Deppe G, Malviya VK and Malone JM: Combined effects of
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and platinum drugs on the growth of MCF-7
cells. Cancer Res. 51:2848–2853. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu G, Hu X and Chakrabarty S: Vitamin D
mediates its action in human colon carcinoma cells in a
calcium-sensing receptor-dependent manner: Downregulates malignant
cell behavior and the expression of thymidylate synthase and
survivin and promotes cellular sensitivity to 5-FU. Int J Cancer.
126:631–639. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tanaka H, Abe E, Miyaura C, Kuribayashi T,
Konno K, Nishii Y and Suda T: 1 alpha,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol
and a human myeloid leukaemia cell line (HL-60). Biochem J.
204:713–719. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lechner D, Kállay E and Cross HS:
1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 downregulates CYP27B1 and induces
CYP24A1 in colon cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 263:55–64. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jones G, Prosser DE and Kaufmann M:
Cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism of vitamin D. J Lipid Res.
55:13–31. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Barry EL, Rees JR, Peacock JL, Mott LA,
Amos CI, Bostick RM, Figueiredo JC, Ahnen DJ, Bresalier RS, Burke
CA and Baron JA: Genetic variants in CYP2R1, CYP24A1, and VDR
modify the efficacy of vitamin D3 supplementation for increasing
serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in a randomized controlled trial.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 99:E2133–E2137. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bareis P, Kállay E, Bischof MG, Bises G,
Hofer H, Pötzi C, Manhardt T, Bland R and Cross HS: Clonal
differences in expression of 25-hydroxyvitamin
D(3)-1alpha-hydroxylase, of 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3)-24-hydroxylase,
and of the vitamin D receptor in human colon carcinoma cells:
Effects of epidermal growth factor and 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin
D(3). Exp Cell Res. 276:320–327. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Leevers SJ, Vanhaesebroeck B and
Waterfield MD: Signalling through phosphoinositide 3-kinases: The
lipids take centre stage. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 11:219–225. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J,
Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C and González-Barón M: PI3K/Akt signalling
pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 30:193–204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mandal M, Kim S, Younes MN, Jasser SA,
El-Naggar AK, Mills GB and Myers JN: The Akt inhibitor KP372-1
suppresses Akt activity and cell proliferation and induces
apoptosis in thyroid cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 92:1899–1905. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hou P, Liu D, Shan Y, Hu S, Studeman K,
Condouris S, Wang Y, Trink A, El-Naggar AK, Tallini G, et al:
Genetic alterations and their relationship in the
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway in thyroid cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 13:1161–1170. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Abbosh PH and Nephew KP: Multiple
signaling pathways converge on beta-catenin in thyroid cancer.
Thyroid. 15:551–561. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rubinfeld B, Albert I, Porfiri E,
Munemitsu S and Polakis P: Loss of beta-catenin regulation by the
APC tumor suppressor protein correlates with loss of structure due
to common somatic mutations of the gene. Cancer Res. 57:4624–4630.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Morin PJ, Sparks AB, Korinek V, Barker N,
Clevers H, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW: Activation of
beta-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in
beta-catenin or APC. Science. 275:1787–1790. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Korinek V, Barker N, Morin PJ, van Wichen
D, de Weger R, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B and Clevers H: Constitutive
transcriptional activation by a beta-catenin-Tcf complex in APC-/-
colon carcinoma. Science. 275:1784–1787. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Garcia-Rostan G, Camp RL, Herrero A,
Carcangiu ML, Rimm DL and Tallini G: Beta-catenin dysregulation in
thyroid neoplasms: Down-regulation, aberrant nuclear expression,
and CTNNB1 exon 3 mutations are markers for aggressive tumor
phenotypes and poor prognosis. Am J Pathol. 158:987–996. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kramer C, Seltmann H, Seifert M, Tilgen W,
Zouboulis CC and Reichrath J: Characterization of the vitamin D
endocrine system in human sebocytes in vitro. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 113:9–16. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tokar EJ and Webber MM: Cholecalciferol
(vitamin D3) inhibits growth and invasion by up-regulating nuclear
receptors and 25-hydroxylase (CYP27A1) in human prostate cancer
cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. 22:275–284. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ordoñez-Morán P and Muñoz A: Nuclear
receptors: Genomic and non-genomic effects converge. Cell Cycle.
8:1675–1680. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kósa JP, Horváth P, Wölfling J, Kovács D,
Balla B, Mátyus P, Horváth E, Speer G, Takács I, Nagy Z, et al:
CYP24A1 inhibition facilitates the anti-tumor effect of vitamin D3
on colorectal cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol. 19:2621–2628.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nieto MA: Epithelial plasticity: A common
theme in embryonic and cancer cells. Science. 342:12348502013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tam WL and Weinberg RA: The epigenetics of
epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in cancer. Nat Med. 19:1438–1449.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu F, Gu LN, Shan BE, Geng CZ and Sang
MX: Biomarkers for EMT and MET in breast cancer: An update. Oncol
Lett. 12:4869–4876. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yoo YA, Kang MH, Lee HJ, Kim BH, Park JK,
Kim HK, Kim JS and Oh SC: Sonic hedgehog pathway promotes
metastasis and lymphangiogenesis via activation of Akt, EMT, and
MMP-9 pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 71:7061–7070. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kawamata H, Kawai K, Kameyama S, Johnson
MD, Stetler-Stevenson WG and Oyasu R: Over-expression of tissue
inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases (TIMP1 and TIMP2) suppresses
extravasation of pulmonary metastasis of a rat bladder carcinoma.
Int J Cancer. 63:680–687. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Baryawno N, Sveinbjörnsson B, Eksborg S,
Chen CS, Kogner P and Johnsen JI: Small-molecule inhibitors of
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling inhibit
Wnt/beta-catenin pathway cross-talk and suppress medulloblastoma
growth. Cancer Res. 70:266–276. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tashiro K, Abe T, Oue N, Yasui W and Ryoji
M: Characterization of vitamin D-mediated induction of the CYP 24
transcription. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 226:27–32. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bates RC and Mercurio AM: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and colorectal cancer
progression. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:365–370. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu Y, Sun X, Feng J, Deng LL, Liu Y, Li
B, Zhu M, Lu C and Zhou L: MT2-MMP induces proteolysis and leads to
EMT in carcinomas. Oncotarget. 7:48193–48205. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li J and Zhou BP: Activation of β-catenin
and Akt pathways by Twist are critical for the maintenance of EMT
associated cancer stem cell-like characters. BMC Cancer. 11:492011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sastre-Perona A, Riesco-Eizaguirre G,
Zaballos MA and Santisteban P: β-catenin signaling is required for
RAS-driven thyroid cancer through PI3K activation. Oncotarget.
7:49435–49449. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lee G, Goretsky T, Managlia E, Dirisina R,
Singh AP, Brown JB, May R, Yang GY, Ragheb JW, Evers BM, et al:
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling mediates beta-catenin
activation in intestinal epithelial stem and progenitor cells in
colitis. Gastroenterology. 139:869–881.e1-e9. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|