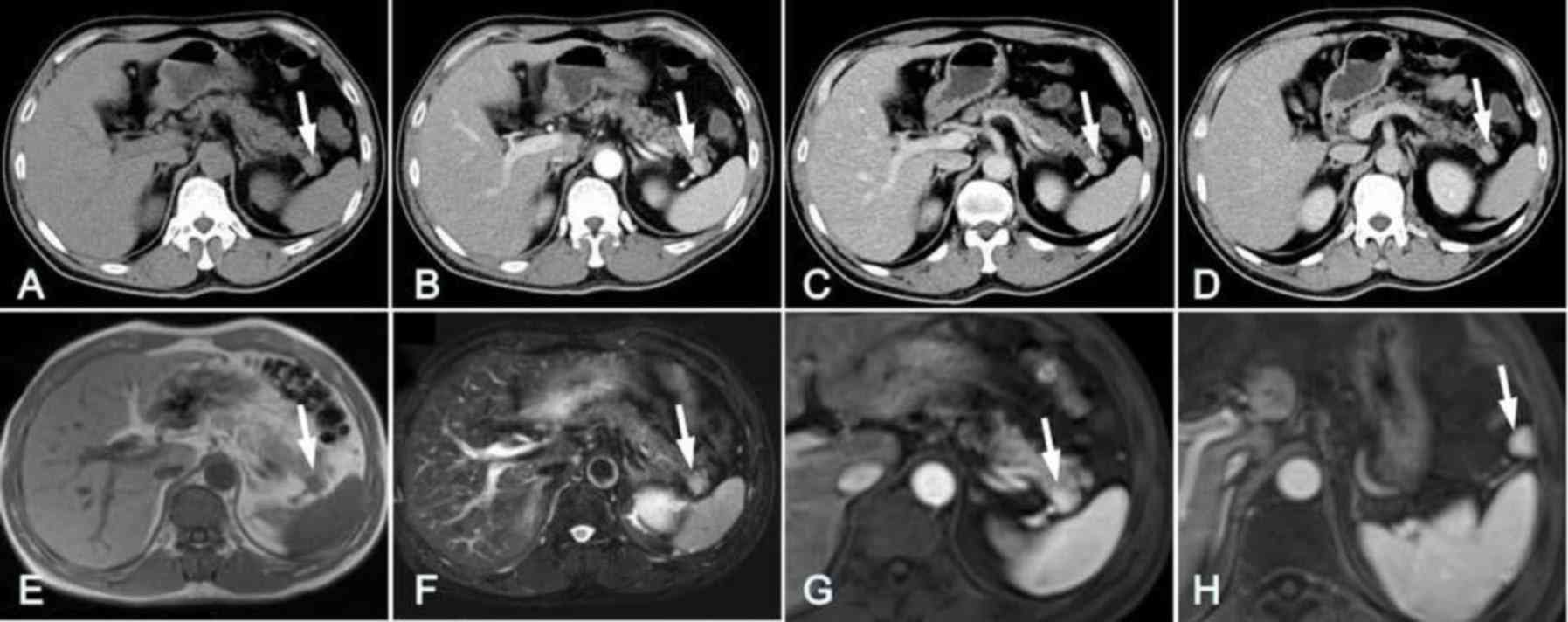
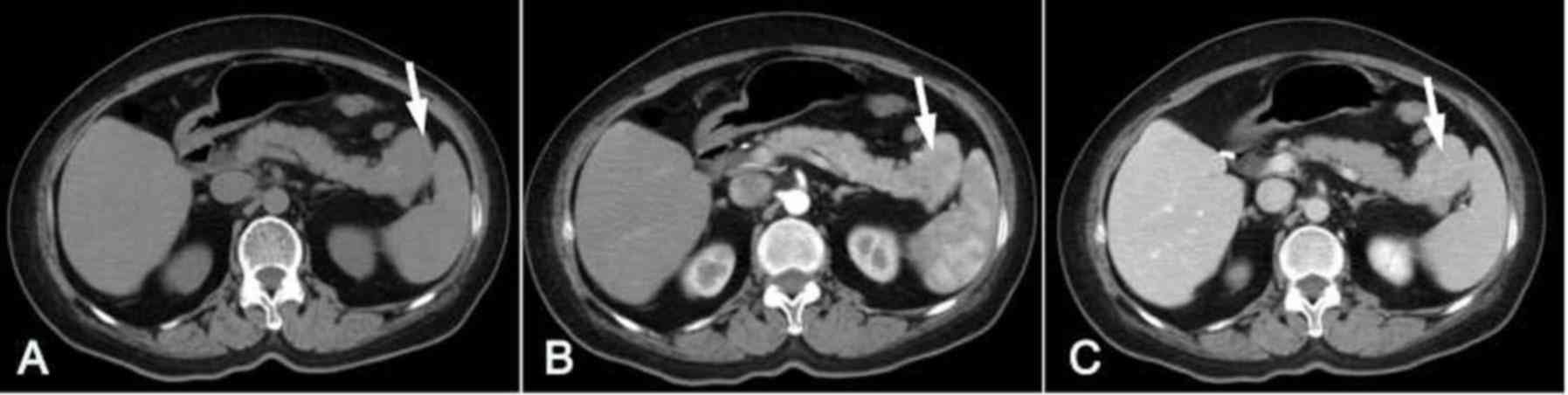
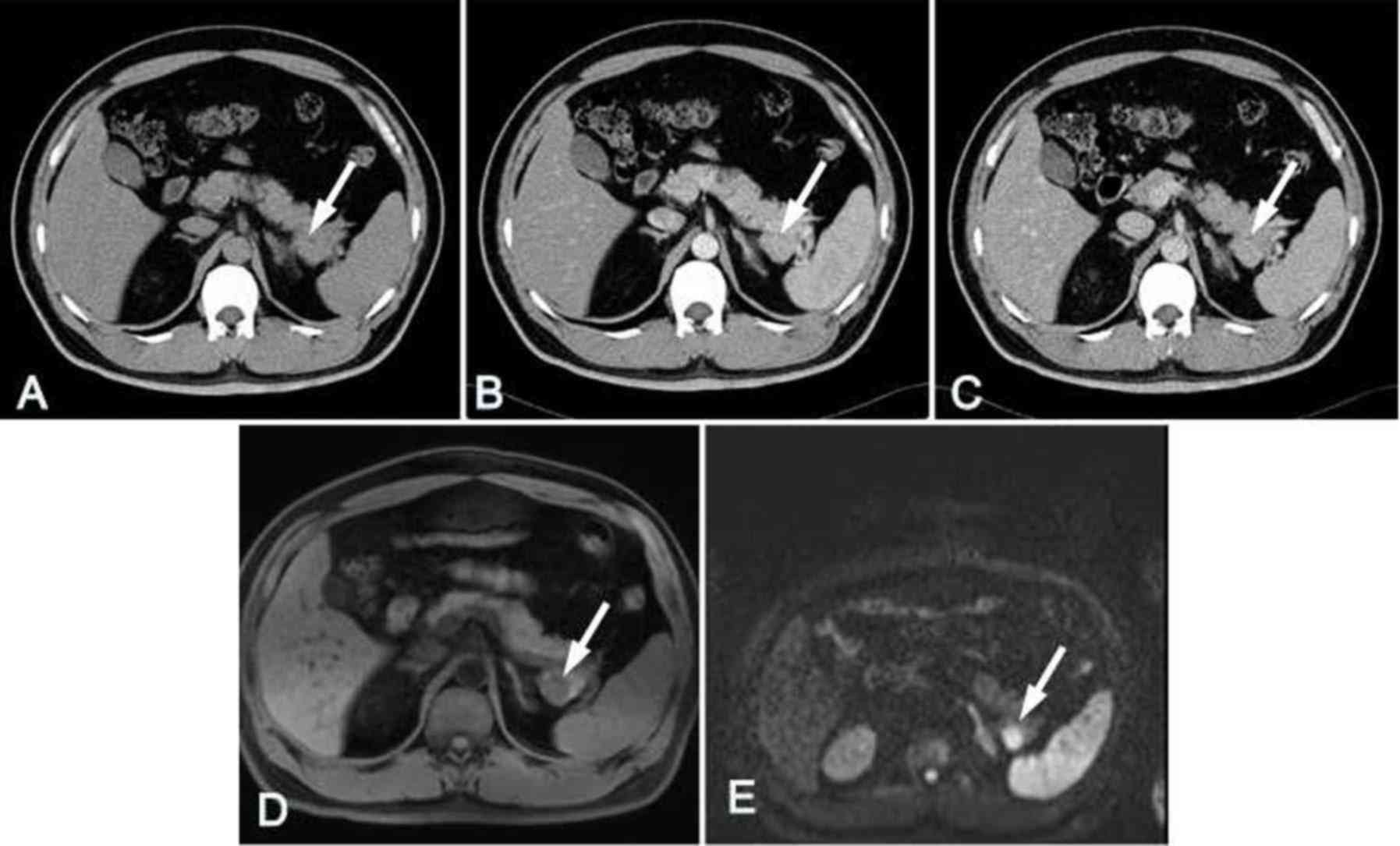
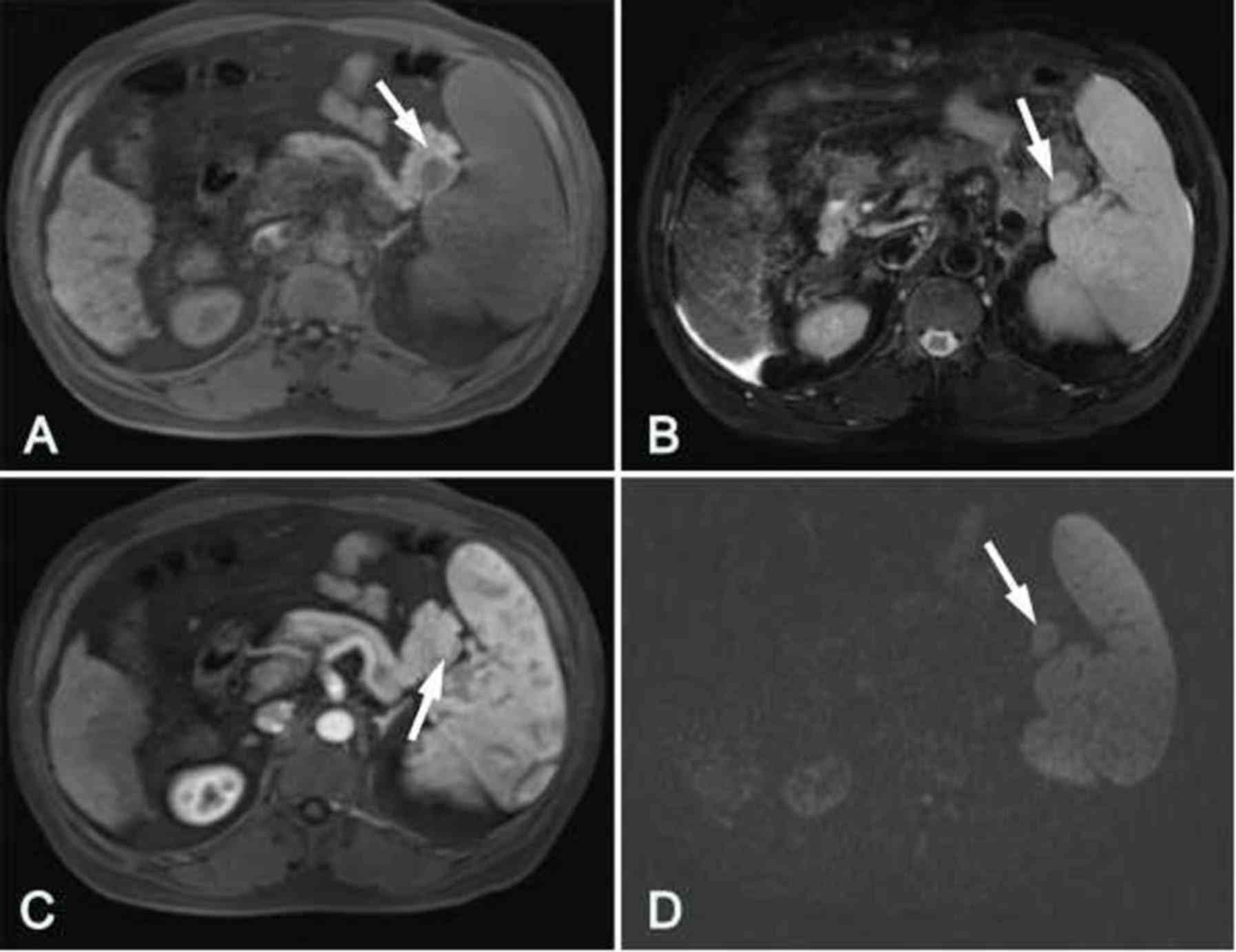
|
1
|
Movitz D: Accessory spleens and
experimental splenosis. Principles of growth. Chic Med Sch Q.
26:183–187. 1967.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim SH, Lee JM, Han JK, Lee JY, Kim KW,
Cho KC and Choi BI: Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: Findings on
MR Imaging, CT, US and scintigraphy, and the pathologic analysis.
Korean J Radiol. 9:162–174. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Halpert B and Alden ZA: Accessory spleens
in or at the tail of the pancreas. A survey of 2700 additoonal
necropsies. Arch Pathol. 77:652–654. 1964.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Halpert B and Gyorkey F: Lesions observed
in accessory spleens of 311 patients. Am J Clin Pathol. 32:165–168.
1959. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Matthaei H, Schmelzle M, Braunstein S,
Bölke E and Peiper M: Pancreatic incidentalomas: A growing clinical
challenge exemplified by an intrapancreatic accessory spleen. Wien
Klin Wochenschr. 123:186–188. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Churei H, Inoue H and Nakajo M:
Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: Case report. Abdom Imaging.
23:191–193. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sica GT and Reed MF: Case 27:
Intrapancreatic accessory spleen. Radiology. 217:134–137. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tozbikian G, Bloomston M, Stevens R,
Ellison EC and Frankel WL: Accessory spleen presenting as a mass in
the tail of the pancreas. Ann Diagn Pathol. 11:277–281. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Uchiyama S, Chijiiwa K, Hiyoshi M,
Ohuchida J, Imamura N, Nagano M, Hidaka H, Yorita K, Akiyama Y and
Nishiura M: Intrapancreatic accessory spleen mimicking endocrine
tumor of the pancreas: Case report and review of the literature. J
Gastrointest Surg. 12:1471–1473. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Spencer LA, Spizarny DL and Williams TR:
Imaging features of intrapancreatic accessory spleen. Br J Radiol.
83:668–673. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Low G, Panu A, Millo N and Leen E:
Multimodality imaging of neoplastic and nonneoplastic solid lesions
of the pancreas. Radiographics. 31:993–1015. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kawamoto S, Johnson PT, Hall H, Cameron
JL, Hruban RH and Fishman EK: Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: CT
appearance and differential diagnosis. Abdom Imaging. 37:812–827.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dodds WJ, Taylor AJ, Erickson SJ, Stewart
ET and Lawson TL: Radiologic imaging of splenic anomalies. American
Journal of Roentgenology. 155:805–810. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ota T, Tei M, Yoshioka A, Mizuno M,
Watanabe S, Seki M, Nakata H, Yamamoto I and Morita R:
Intrapancreatic accessory spleen diagnosed by technetium-99m
heat-damaged red blood cell SPECT. J Nucl Med. 38:494–495.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brasca LE, Zanello A, De Gaspari A, De
Cobelli F, Zerbi A, Fazio F and Del Maschio A: Intrapancreatic
accessory spleen mimicking a neuroendocrine tumor: Magnetic
resonance findings and possible diagnostic role of different
nuclear medicine tests. Eur Radiol. 14:1322–1323. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Belkhir SM, Archambaud F, Prigent A and
Chaumet-Riffaud P: Intrapancreatic accessory spleen diagnosed on
radionuclide imaging. Clin Nucl Med. 34:642–644. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim KA, Park CM, Kim CH, Choi SY, Park SW,
Kang EY, Seol HY and Cha IH: An interesting hepatic mass: Splenosis
mimicking a hepatocellular carcinoma (2003:9b). Eur Radiol.
13:2713–2715. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hilal Abu M, Harb A, Zeidan B, Steadman B,
Primrose JN and Pearce NW: Hepatic splenosis mimicking HCC in a
patient with hepatitis C liver cirrhosis and mildly raised alpha
feto protein; the important role of explorative laparoscopy. World
J Surg Oncol. 7:12009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fiamingo P, Veroux M, Da Rold A, Guerriero
S, Pariset S, Buffone A and Tedeschi U: A rare diagnosis for a
pancreatic mass: Splenosis. J Gastrointest Surg. 8:915–916. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Varga I, Galfiova P, Adamkov M, Danisovic
L, Polak S, Kubikova E and Galbavy S: Congenital anomalies of the
spleen from an embryological point of view. Med Sci Monit.
15:RA269–RA276. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mortelé KJ, Mortelé B and Silverman SG: CT
features of the accessory spleen. AJR Am J Roentgenol.
183:1653–1657. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hwang HS, Lee SS, Kim SC, Seo DW and Kim
J: Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: Clinicopathologic analysis of
12 cases. Pancreas. 40:956–965. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim SH, Lee JM, Han JK, Lee JY, Kang WJ,
Jang JY, Shin KS, Cho KC and Choi BI: MDCT and superparamagnetic
iron oxide (SPIO)-enhanced MR findings of intrapancreatic accessory
spleen in seven patients. Eur Radiol. 16:1887–1897. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Paterson A, Frush DP, Donnelly LF, Foss
JN, O'Hara SM and Bisset GS 3rd: A pattern-oriented approach to
splenic imaging in infants and children. Radiographics.
19:1465–1485. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Park JS, Kim WJ, Jeong YG, Park YS, Koo
HC, Lee TI, Choi GC and Kim S: A case of intrapancreatic accessory
spleen mistaken as a pancreatic mass due to different enhancing
pattern from normal spleen. Korean J Gastroenterol. 58:357–360.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Blomley MJ, Kormano M, Coulden R,
Lim-Dunham J, Dawson P and Lipton MJ: Splenic blood flow:
Evaluation with computed tomography. Acad Radiol. 4:13–20. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Davidson ED, Campbell WG and Hersh T:
Epidermoid splenic cyst occurring in an intrapancreatic accessory
spleen. Dig Dis Sci. 25:964–917. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hu S, Zhu L, Song Q and Chen K: Epidermoid
cyst in intrapancreatic accessory spleen: Computed tomography
findings and clinical manifestation. Abdom Imaging. 37:828–833.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Okura N, Mori K, Morishita Y, Oda T, Tanoi
T and Minami M: Inflammatory pseudotumor of the intrapancreatic
accessory spleen: Computed tomography and magnetic resonance
imaging findings. Jpn J Radiol. 30:171–175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sukaiti R, Robinson K and Menias C:
Retrospective review of cross sectional imaging findings of
pancreatic non-functional islet cell tumor (NFICT) and its hepatic
metastases. Oman Med J. 26:39–42. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kurata Y, Kido A, Moribata Y, Kameyama K,
Himoto Y, Minamiguchi S, Konishi I and Togashi K: Diagnostic
performance of MR imaging findings and quantitative values in the
differentiation of seromucinous borderline tumour from
endometriosis-related malignant ovarian tumour. Eur Radiol.
27:1695–1703. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ma XL, Wang JH, Jiang H, Lu JP and Liu Q:
Solid-pseudopapillary tumor of pancreas: Different types of imaging
features and their correlation with pathological findings. Zhonghua
Yi Xue Za Zhi. 92:170–174. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ng CS, Loyer EM, Iyer RB, David CL, DuBrow
RA and Charnsangavej C: Metastases to the pancreas from renal cell
carcinoma: Findings on three-phase contrast-enhanced helical CT.
AJR Am J Roentgenol. 172:1555–1559. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|