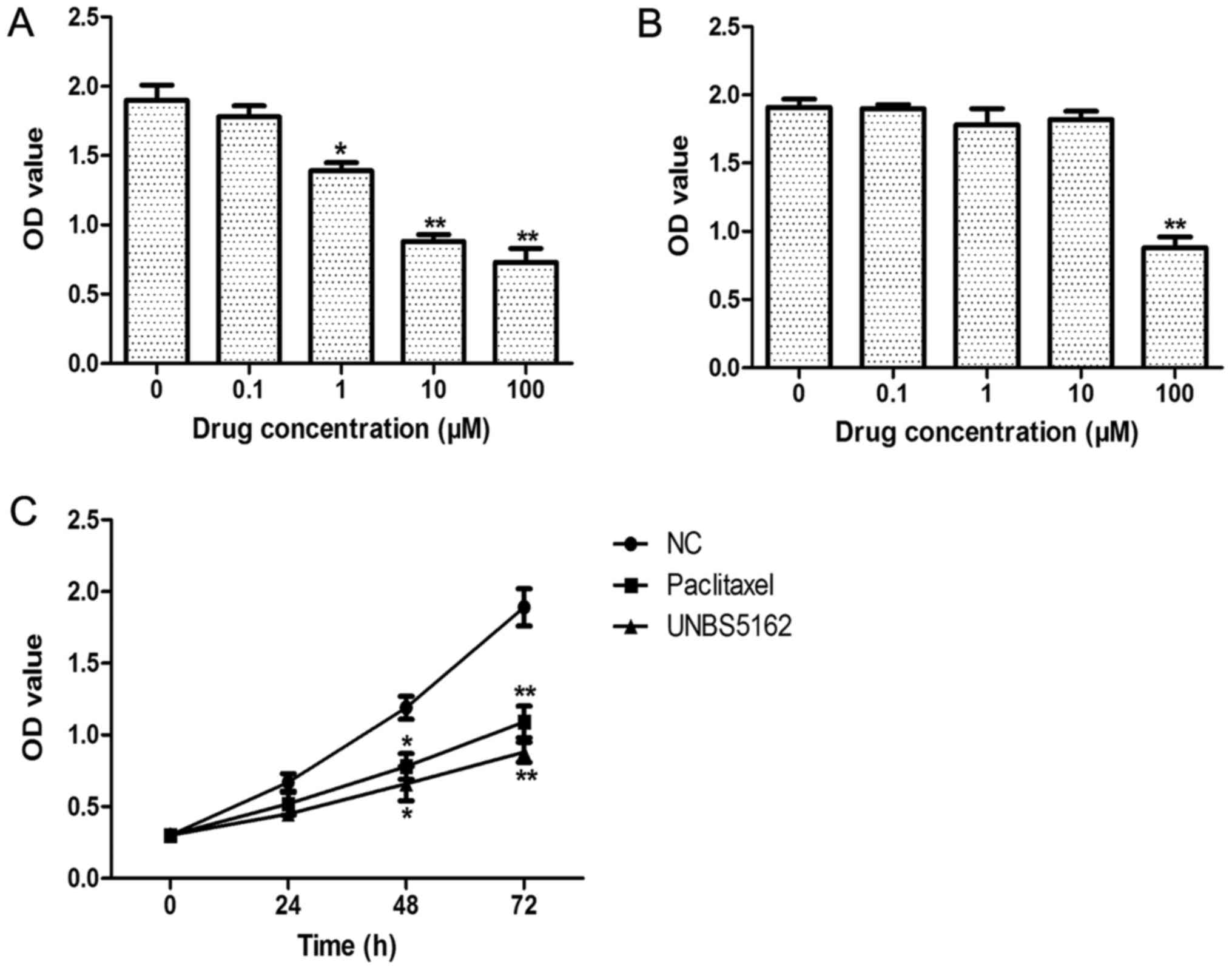
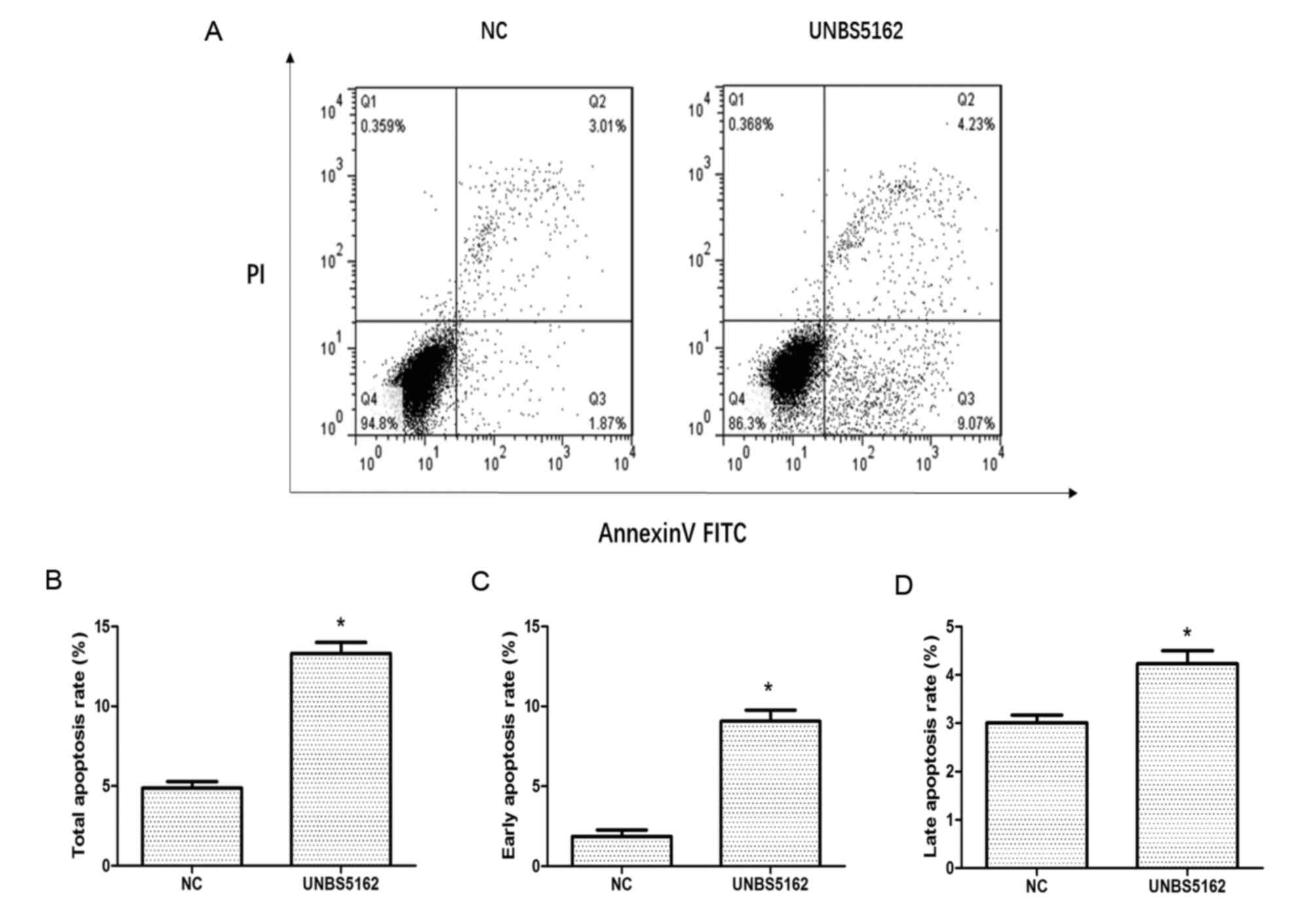
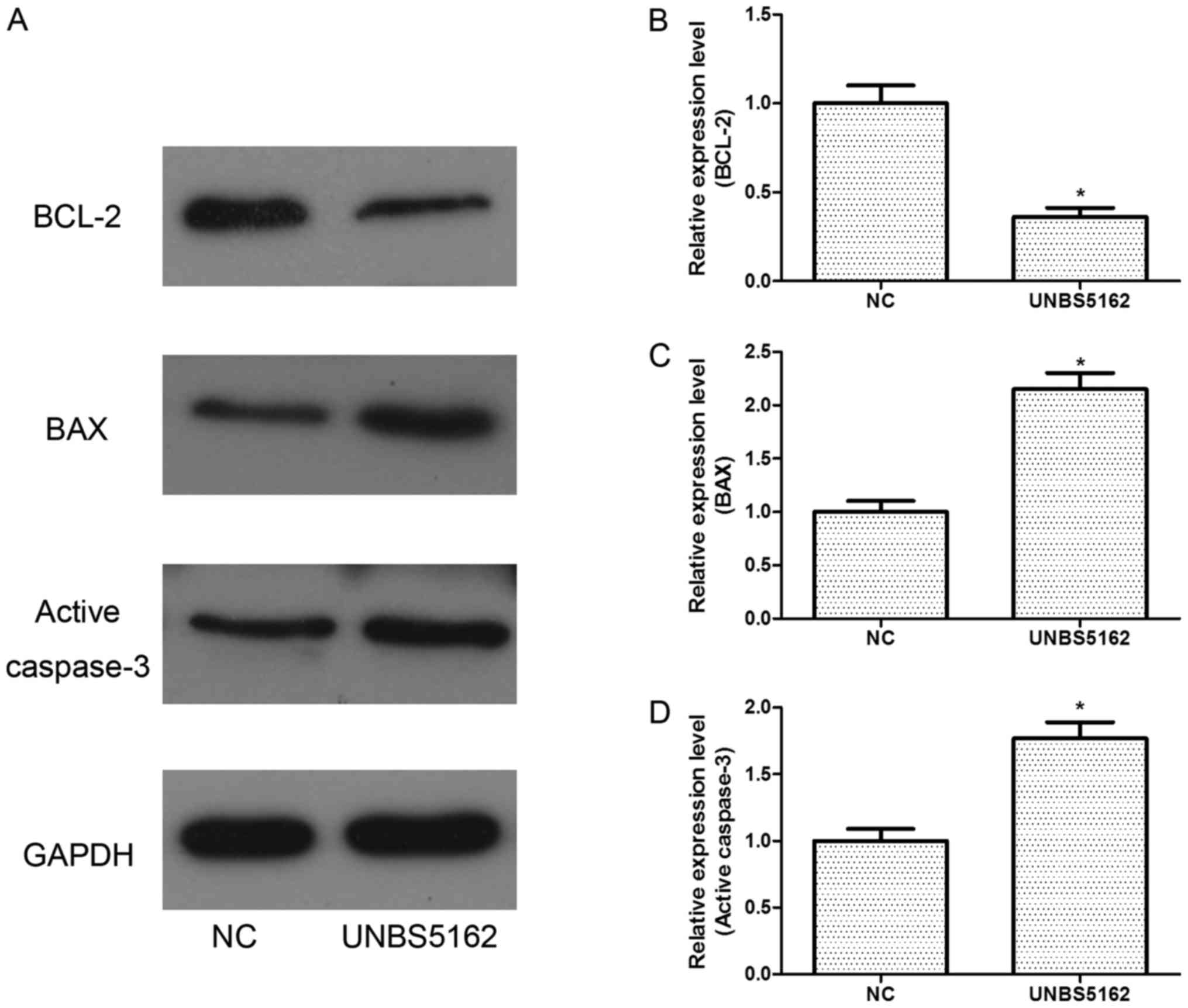
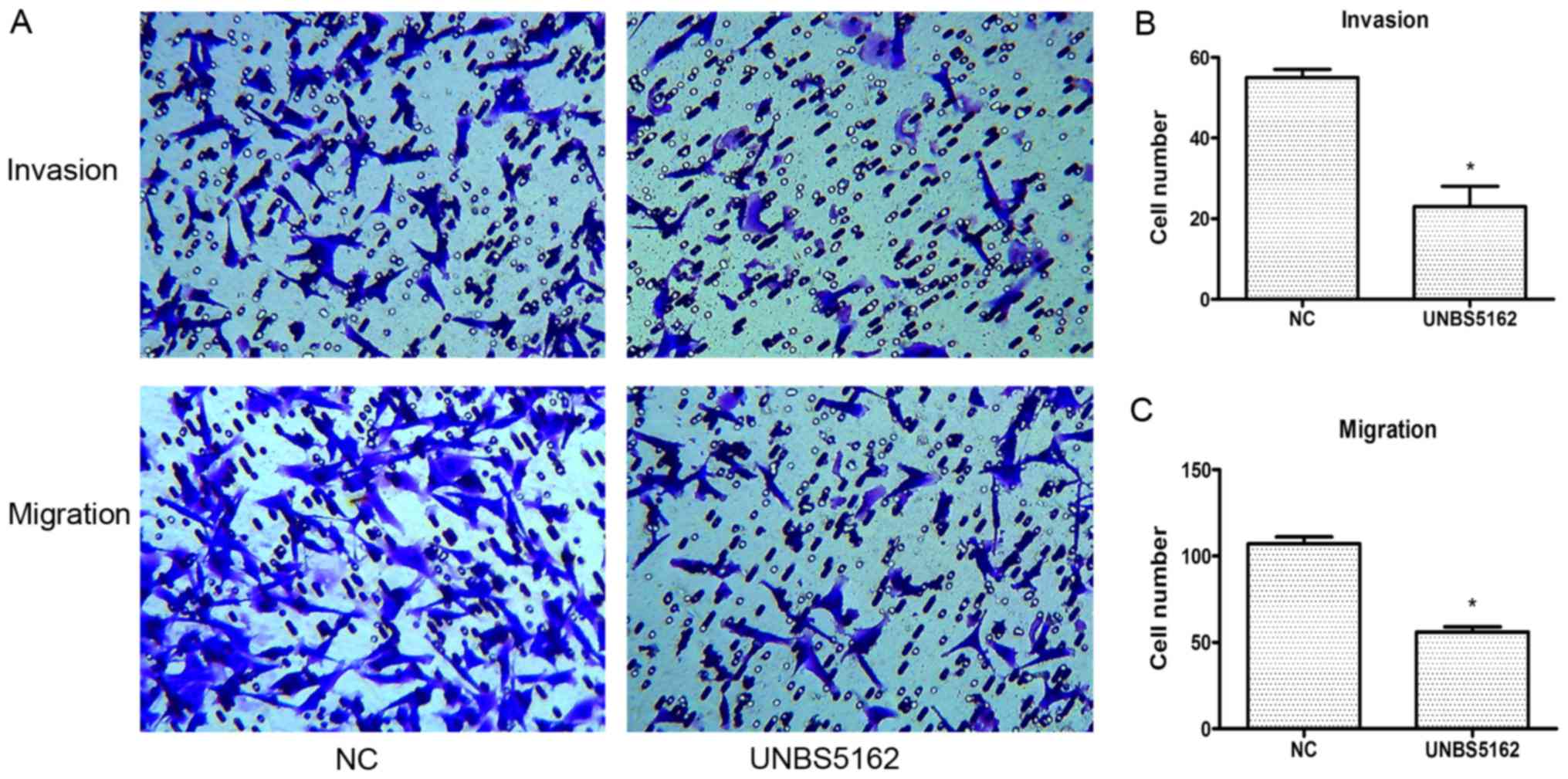
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL, Ward EM and Jemal A:
Global cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends-an update.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 25:16–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network: Comprehensive
molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 490:61–70.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn
M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA,
et al: Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
406:747–752. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T,
Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey
SS, et al: Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas
distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:10869–10874. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, Hastie
T, Marron JS, Nobel A, Deng S, Johnsen H, Pesich R, Geisler S, et
al: Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent
gene expression data sets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:8418–8423.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Foulkes WD, Smith IE and Reis-Filho JS:
Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1938–1948. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Loi S, Pommey S, Haibe-Kains B, Beavis PA,
Darcy PK, Smyth MJ and Stagg J: CD73 promotes anthracycline
resistance and poor prognosis in triple negative breast cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:11091–11096. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Coates AS, Winer EP, Goldhirsch A, Gelber
RD, Gnant M, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thürlimann B and Senn HJ: Panel
Members: Tailoring therapies-improving the management of early
breast cancer: St gallen international expert consensus on the
primary therapy of early breast cancer 2015. Ann Oncol.
26:1533–1546. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Gelber RD, Coates
AS, Thürlimann B and Senn HJ: 10th St. Gallen conference: Progress
and promise: Highlights of the international expert consensus on
the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2007. Ann Oncol.
18:1133–1144. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Banda M, Speyer CL, Semma SN, Osual KO,
Kounalakis N, Torres Torres KE, Barnard NJ, Kim HJ, Sloane BF,
Miller FR, et al: Metabotropic glutamate receptor-1 contributes to
progression in triple negative breast cancer. PLoS One.
9:e811262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pal SK, Childs BH and Pegram M: Triple
negative breast cancer: Unmet medical needs. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 125:627–636. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lehmann BD and Pietenpol JA: Clinical
implications of molecular heterogeneity in triple negative breast
cancer. Breast. 24 Suppl 2:S36–S40. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Perou CM: Molecular stratification of
triple-negative breast cancers. Oncologist. 16 Suppl 1:S61–S70.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Juvekar A, Burga LN, Hu H, Lunsford EP,
Ibrahim YH, Balmañà J, Rajendran A, Papa A, Spencer K, Lyssiotis
CA, et al: Combining a PI3K inhibitor with a PARP inhibitor
provides an effective therapy for BRCA1-related breast cancer.
Cancer Discov. 2:1048–1063. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Braña MF and Ramos A: Naphthalimides as
anti-cancer agents: Synthesis and biological activity. Curr Med
Chem Anticancer Agents. 1:237–255. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Costanza ME, Berry D, Henderson IC, Ratain
MJ, Wu K, Shapiro C, Duggan D, Kalra J, Berkowitz I and Lyss AP:
Amonafide: An active agent in the treatment of previously untreated
advanced breast cancer-a cancer and leukemia group B study (CALGB
8642). Clin Cancer Res. 1:699–704. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Scheithauer W, Dittrich C, Kornek G,
Haider K, Linkesch W, Gisslinger H and Depisch D: Phase II study of
amonafide in advanced breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
20:63–67. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kuhn JG, Burris HA III, Jones SF, Hein DE,
Willcutt NT, Greco FA, Thompson DS, Meluch AA, Schwartz RS and
Brown DM: Phase I/II dose-escalation trial of amonafide for
treatment of advanced solid tumors: Genotyping to optimize dose
based on polymorphic metabolism. J Clin Oncol. 25:25032007.
|
|
20
|
Ratain MJ, Mick R, Berezin F, Janisch L,
Schilsky RL, Williams SF and Smiddy J: Paradoxical relationship
between acetylator phenotype and amonafide toxicity. Clin Pharmacol
Ther. 50:573–579. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ingrassia L, Lefranc F, Kiss R and
Mijatovic T: Naphthalimides and azonafides as promising anti-cancer
agents. Curr Med Chem. 16:1192–1213. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lv M and Xu H: Overview of naphthalimide
analogs as anticancer agents. Curr Med Chem. 16:4797–4813. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mijatovic T, Mahieu T, Bruyère C, De Nève
N, Dewelle J, Simon G, Dehoux MJ, van der Aar E, Haibe-Kains B,
Bontempi G, et al: UNBS5162, a novel naphthalimide that decreases
CXCL chemokine expression in experimental prostate cancers.
Neoplasia. 10:573–586. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mahadevan D, Northfelt DW, Chalasani P,
Rensvold D, Kurtin S, Von Hoff DD, Borad MJ and Tibes R: Phase I
trial of UNBS5162, a novel naphthalimide in patients with advanced
solid tumors or lymphoma. Int J Clin Oncol. 18:934–941. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Balkwill F: Cancer and the chemokine
network. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:540–550. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fernandez EJ and Lolis E: Structure,
function, and inhibition of chemokines. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
42:469–499. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu P, Cheng H, Roberts TM and Zhao JJ:
Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 8:627–644. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Massihnia D, Galvano A, Fanale D, Perez A,
Castiglia M, Incorvaia L, Listì A, Rizzo S, Cicero G, Bazan V, et
al: Triple negative breast cancer: shedding light onto the role of
pi3k/akt/mtor pathway. Oncotarget. 7:60712–60722. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Blanchard Z, Paul BT, Craft B and Elshamy
WM: BRCA1-IRIS inactivation overcomes paclitaxel resistance in
triple negative breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. 17:52015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Krammer PH: CD95's deadly mission in the
immune system. Nature. 407:789–795. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lo AC, Woo TT, Wong RL and Wong D:
Apoptosis and other cell death mechanisms after retinal detachment:
Implications for photoreceptor rescue. Ophthalmologica. 226 Suppl
1:S10–S17. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Krammer PH, Arnold R and Lavrik IN: Life
and death in peripheral T cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:532–542. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
King D, Yeomanson D and Bryant HE: PI3King
the lock: Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as a novel
therapeutic strategy in neuroblastoma. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol.
37:245–251. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Man HY, Wang Q, Lu WY, Ju W, Ahmadian G,
Liu L, D'Souza S, Wong TP, Taghibiglou C, Lu J, et al: Activation
of PI3-kinase is required for AMPA receptor insertion during LTP of
mEPSCs in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 38:611–624. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rafalski VA and Brunet A: Energy
metabolism in adult neural stem cell fate. Prog Neurobiol.
93:182–203. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rozengurt E, Soares HP and Sinnet-Smith J:
Suppression of feedback loops mediated by PI3K/mTOR induces
multiple overactivation of compensatory pathways: An unintended
consequence leading to drug resistance. Mol Cancer Ther.
13:2477–2488. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Courtney KD, Corcoran RB and Engelman JA:
The PI3K pathway as drug target in human cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:1075–1083. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ayub A, Yip WK and Seow HF: Dual
treatments targeting IGF-1R, PI3K, mTORC or MEK synergize to
inhibit cell growth, induce apoptosis, and arrest cell cycle at G1
phase in MDA-MB-231 cell line. Biomed Pharmacother. 75:40–50. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|