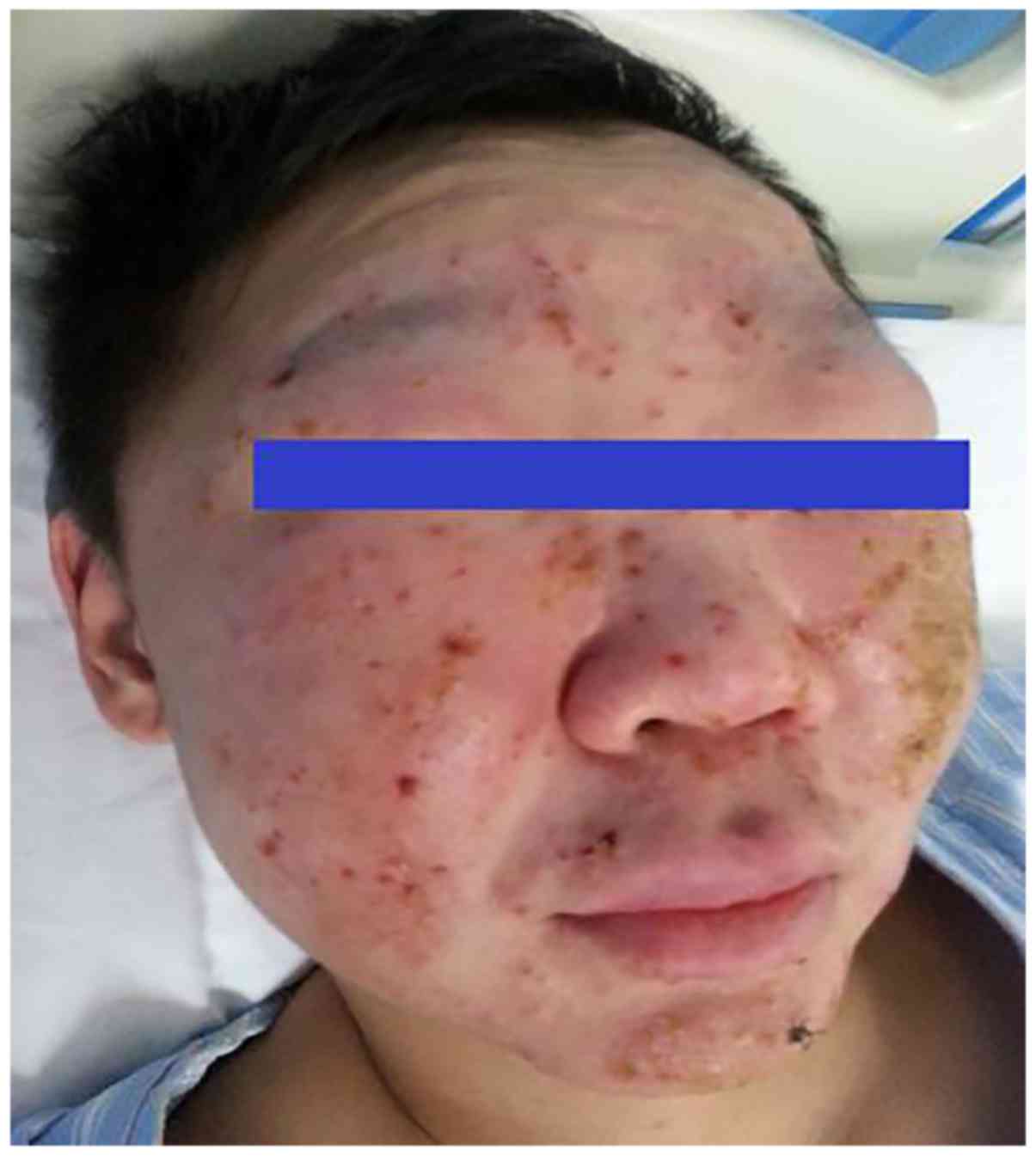
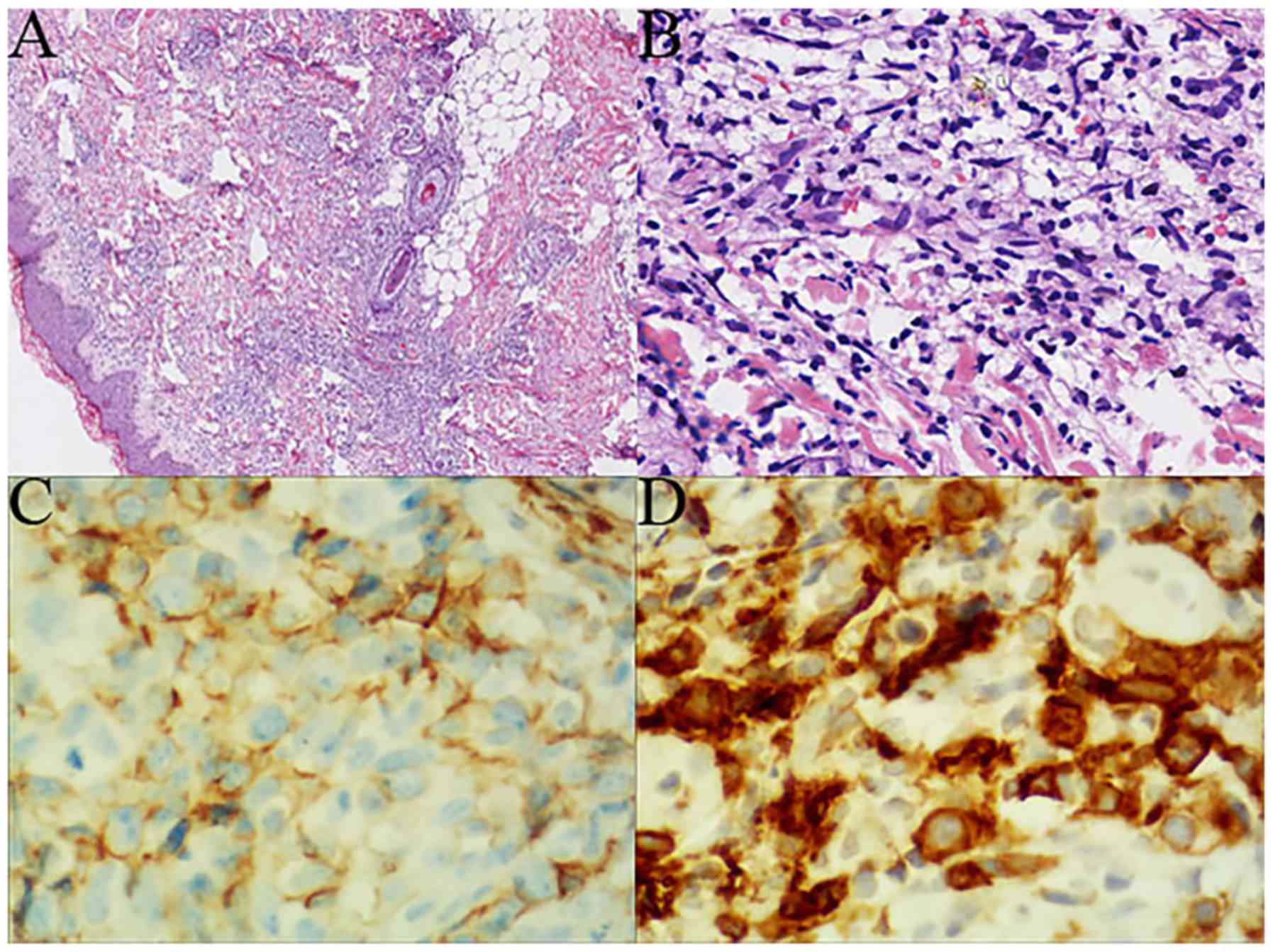
|
1
|
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES,
Pileri SA, Thiele Jurgen HS and Vardiman JW: World Health
Organization Classification of Tumors of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid
Tissues. 4th. IARC Press; Lyon: 2008
|
|
2
|
Cho KH, Kim CW, Heo DS, Lee DS, Choi WW,
Rim JH and Han WS: Epstein-Barr virus-associated peripheral T-cell
lymphoma in adults with hydroa vacciniforme-like lesions. Clin Exp
Dermatol. 26:242–247. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Feng S, Jin P and Zeng X: Hydroa
vacciniforme-like primary cutaneous CD8-positive T-cell lymphoma.
Eur J Dermatol. 18:364–365. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Magaña M, Sangüeza P, Gil-Beristain J,
Sánchez-Sosa S, Salgado A, Ramón G and Sangüeza OP: Angiocentric
cutaneous T-cell lymphoma of childhood (hydroa-like lymphoma): A
distinctive type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Am Acad Dermatol.
38:574–579. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Barrionuevo C, Anderson VM,
Zevallos-Giampietri E, Zaharia M, Misad O, Bravo F, Cáceres H, Taxa
L, Martínez MT, Wachtel A and Piris MA: Hydroa-like cutaneous
T-cell lymphoma: A clinicopathologic and molecular genetic study of
16 pediatric cases from Peru. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol.
10:7–14. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu Z and Lian S: Epstein-Barr
virus-associated hydroa vacciniforme-like cutaneous lymphoma in
seven Chinese children. Pediatr Dermatol. 27:463–469. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, Harris
NL, Stein H, Siebert R, Advani R, Ghielmini M, Salles GA, Zelenetz
AD and Jaffe ES: The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization
(WHO) classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood. 127:2375–2390.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Iwatsuki K, Ohtsuka M, Akiba H and Kaneko
F: Atypical hydroa vacciniforme in childhood: From a smoldering
stage to Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoid malignancy. J Am
Acad Dermatol. 40:283–284. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Iwatsuki K, Satoh M, Yamamoto T, Oono T,
Morizane S, Ohtsuka M, Xu ZG, Suzuki D and Tsuji K: Pathogenic link
between hydroa vacciniforme and Epstein-Barr virus-associated
hematologic disorders. Arch Dermatol. 142:587–595. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Doeden K, Molina-Kirsch H, Perez E, Warnke
R and Sundram U: Hydroa-like lymphoma with CD56 expression. J Cutan
Pathol. 35:488–494. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rodriguez-pinilla SM, Barrionuevo C,
Garcia J, Martínez MT, Pajares R, Montes-Moreno S, Casavilca S,
Montes J, Bravo F, Zaharia M, et al: EBV-associated cutaneous
NK/T-cell lymphoma: Review of a series of 14 cases from Peru in
children and young adults. Am J Surg Pathol. 34:1773–1782. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Quintanilla-Martínez L, Ridaura C, Nagl F,
Sáez-de-Ocariz M, Durán-McKinster C, Ruiz-Maldonado R, Alderete G,
Grube P, Lome-Maldonado C, Bonzheim I and Fend F: Hydroa
vacciniforme like lymphoma: A chronic EBV+ lymphoproliferative
disorder with risk to develop a systemic lymphoma. Blood.
122:3101–3110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Santos M, Nogueira L, Talahri C, Massone
C, Cerroni L, Mira MT and Talhari S: Hydroavacciniforme-like
lymphoma in a patient from the Brazilian Amazon. Int J Dermatol.
52:641–643. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Magaña M, Massone C, Magaña P and Cerroni
L: Clinicopathologic features of hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoma:
A series of 9 patients. Am J Dermato pathol. 38:20–25. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Patel KP, Pan Q, Wang Y, Maitta RW, Du J,
Xue X, Lin J and Ratech H: Comparison of BIOMED-2 versus
laboratory-developed polymerase chain reaction assays for detecting
T-cell receptor-gamma gene rearrangements. J Mol Diagn. 12:226–237.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mraz-Gernhard S, Natkunam Y, Hoppe RT,
LeBoit P, Kohler S and Kim YH: Natural killer/natural killer-like
T-cell lymphoma, CD56+, presenting in the skin: An increasingly
recognized entity with an aggressive course. J Clin Oncol.
19:2179–2188. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Child FJ, Mitchell TJ, Whittaker SJ,
Calonje E, Spittle M, Crocker J and Russell-Jones R: Blastic
natural killer cell and extranodal natural killer cell-like T-cell
lymphoma presenting in the skin: Report of six cases from the UK.
Br J Dermatol. 148:507–515. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu JB, Zuo Z, Tang Y, Zhao S, Zhang YC, Bi
CF, Wang WY, Zhang WY, Wang L and Liu WP: Extranodal nasal-type
natural killer/T-cell lymphoma of the skin: A clinicopathologic
study of 16 cases in China. Hum Pathol. 40:807–816. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Takata K, Hong ME, Sitthinamsuwan P, Loong
F, Tan SY, Liau JY, Hsieh PP, Ng SB, Yang SF, Pongpruttipan T, et
al: Primary cutaneous NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type and
CD56-positive peripheral T-cell lymphoma: A cellular lineage and
clinicopathologic study of 60 patients from Asia. Am J Surg Pathol.
39:1–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hsi AC1 and Rosman IS: Histopathology of
cutaneous inflammatory disorders in children. Pediatr Dev Pathol.
21:115–149. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sangueza M and Plaza JA: Hydroa
vacciniforme-like cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: Clinicopathologic and
immunohistochemical study of 12 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol.
69:112–119. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang YQ, Fan L, Wang L, Xu J, Zhang R, Ge
Z, Li JY and Xu W: Systemic lymphoma arising from hydroa
vacciniforme-like lymphoma: Report of two cases with review of
literature. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:6403–6408. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|