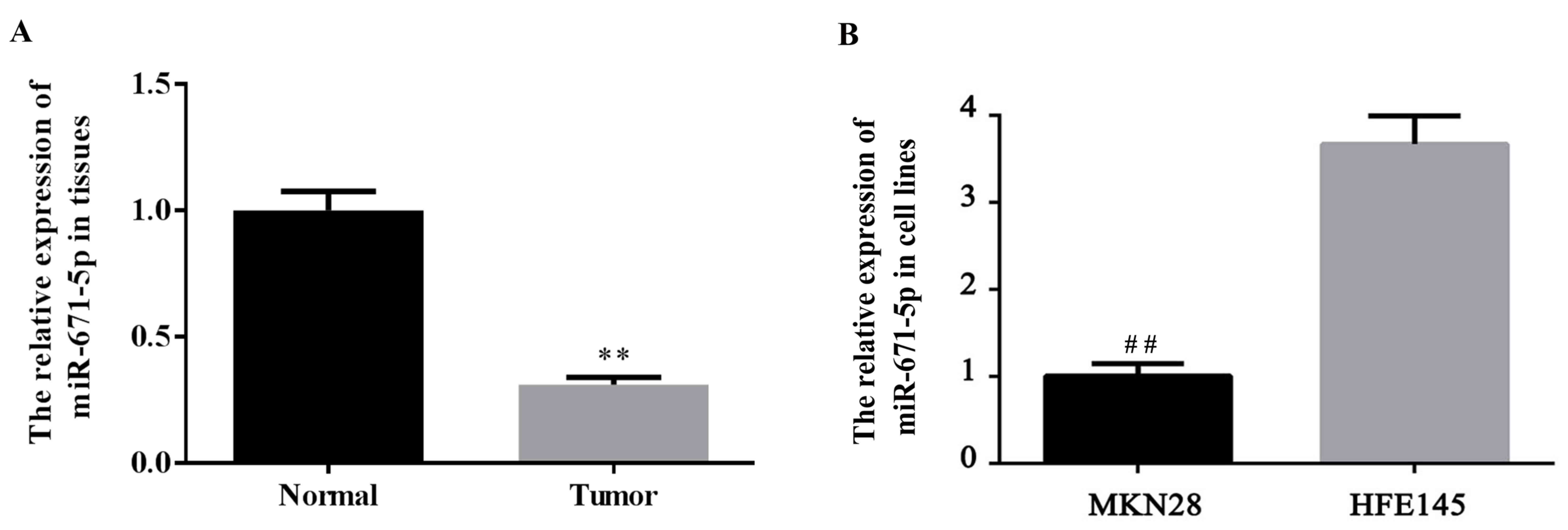
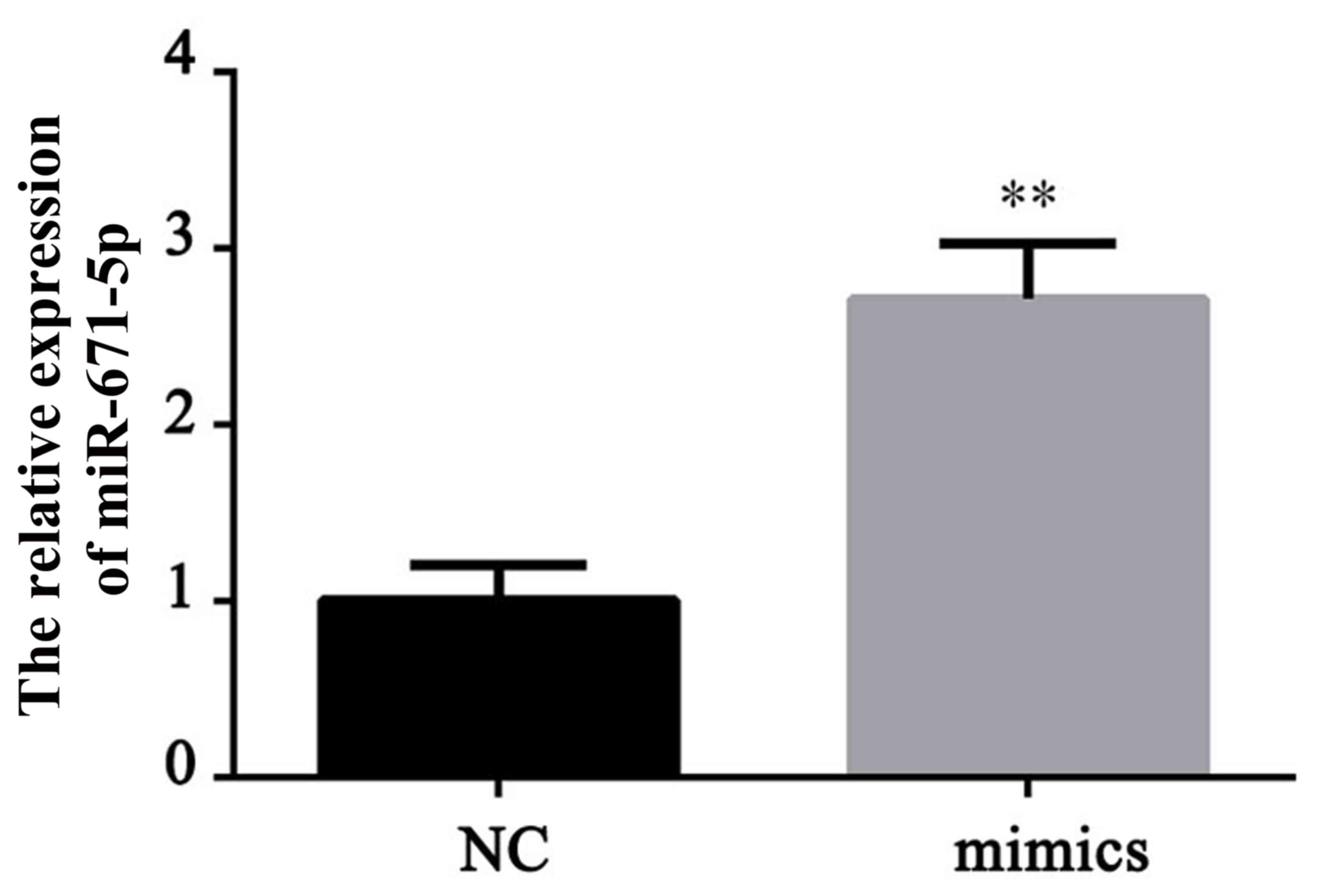
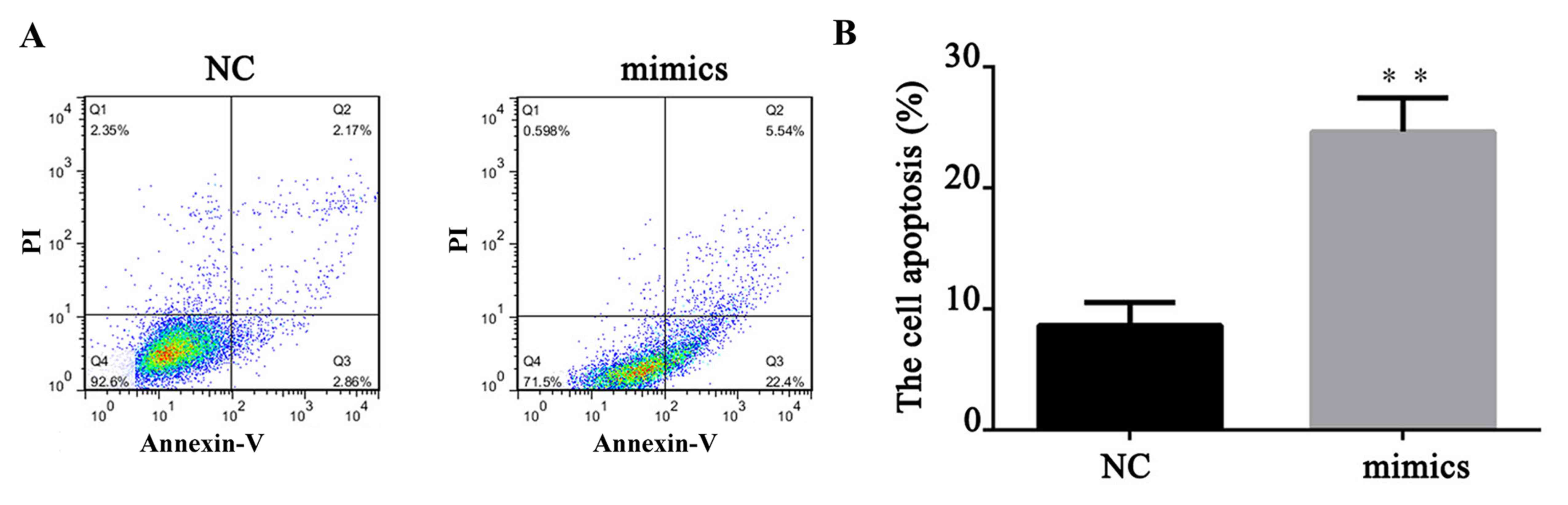
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferro A, Peleteiro B, Malvezzi M, Bosetti
C, Bertuccio P, Levi F, Negri E, La Vecchia C and Lunet N:
Worldwide trends in gastric cancer mortality (1980–2011), with
predictions to 2015, and incidence by subtype. Eur J Cancer.
50:1330–1344. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guggenheim DE and Shah MA: Gastric cancer
epidemiology and risk factors. J Surg Oncol. 107:230–236. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Coburn NG: Lymph nodes and gastric cancer.
J Surg Oncol. 99:199–206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shi Y and Zhou Y: The role of surgery in
the treatment of gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 101:687–692. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Orditura M, Galizia G, Sforza V,
Gambardella V, Fabozzi A, Laterza MM, Andreozzi F, Ventriglia J,
Savastano B, Mabilia A, et al: Treatment of gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:1635–1649. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kelley JR and Duggan JM: Gastric cancer
epidemiology and risk factors. J Clin Epidemiol. 56:1–9. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu Q, Sun W, Wang C and Gu Z: Recent
advances of cocktail chemotherapy by combination drug delivery
systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 98:19–34. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang H: Apatinib for molecular targeted
therapy in tumor. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:6075–6081. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mendell JT: MicroRNAs: Critical regulators
of development, cellular physiology and malignancy. Cell Cycle.
4:1179–1184. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jansson MD and Lund AH: MicroRNA and
cancer. Mol Oncol. 6:590–610. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chang S, He S, Qiu G, Lu J, Wang J, Liu J,
Fan L, Zhao W and Che X: MicroRNA-125b promotes invasion and
metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting STARD13 and NEU1. Tumour
Biol. 37:12141–12151. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu B, Lv X, Su L, Li J, Yu Y, Gu Q, Yan M,
Zhu Z and Liu B: MiR-148a functions as a tumor suppressor by
targeting CCK-BR via inactivating STAT3 and Akt in human gastric
cancer. PLoS One. 11:e01589612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yin G, Zhou H, Xue Y, Yao B and Zhao W:
MicroRNA-340 promotes the tumor growth of human gastric cancer by
inhibiting cyclin G2. Oncol Rep. 36:1111–1118. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cai J, Li R, Xu X, Zhang L, Wu S, Yang T,
Fang L, Wu J, Zhu X, Li M and Huang Y: URGCP promotes non-small
cell lung cancer invasiveness by activating the NF-κB-MMP-9
pathway. Oncotarget. 6:36489–36504. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Papp G, Krausz T, Stricker TP, Szendrői M
and Sápi Z: SMARCB1 expression in epithelioid sarcoma is regulated
by miR-206, miR-381, and miR-671-5p on both mRNA and protein
levels. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 53:168–176. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xie C, Song LB, Wu JH, Li J, Yun JP, Lai
JM, Xie DY, Lin BL, Yuan YF, Li M and Gao ZL: Upregulator of cell
proliferation predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma
and contributes to hepatocarcinogenesis by downregulating FOXO3a.
PLoS One. 7:e406072012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li WP and Zhou N: URG4 upregulation is
associated with tumor growth and poor survival in epithelial
ovarian cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 286:209–215. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang J, Zhu B, Lu L, Lian Z, Wang Y, Yang
X, Satiroglu-Tufan NL, Liu J and Luo Z: The expression of novel
gene URG4 in osteosarcoma: Correlation with patients' prognosis.
Pathology. 41:149–154. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bossel Ben-Moshe N, Avraham R, Kedmi M,
Zeisel A, Yitzhaky A, Yarden Y and Domany E: Context-specific
microRNA analysis: Identification of functional microRNAs and their
mRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:10614–10627. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang X, Peng Y, Jin Z, Huang W, Cheng Y,
Liu Y, Feng X, Yang M, Huang Y, Zhao Z, et al: Integrated miRNA
profiling and bioinformatics analyses reveal potential causative
miRNAs in gastric adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:32878–32889. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Song J, Xie H, Lian Z, Yang G, Du R, Du Y,
Zou X, Jin H, Gao J, Liu J and Fan D: Enhanced cell survival of
gastric cancer cells by a novel gene URG4. Neoplasia. 8:995–1002.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Marano L, Boccardi V, Braccio B, Esposito
G, Grassia M, Petrillo M, Pezzella M, Porfidia R, Reda G, Romano A,
et al: Comparison of the 6th and 7th editions of the AJCC/UICC TNM
staging system for gastric cancer focusing on the ‘N’
parameter-related survival: The monoinstitutional NodUs Italian
study. World J Surg Oncol. 13:2152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Capes-Davis A, Theodosopoulos G, Atkin I,
Drexler HG, Kohara A, MacLeod RA, Masters JR, Nakamura Y, Reid YA,
Reddel RR and Freshney RI: Check your cultures A list of
cross-contaminated or misidentified cell lines. Int J Cancer.
127:1–8. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Petrocca F, Pilozzi E, Rapazzotti M,
Aurello P, Mercantini P, Volinia S, Ruco L, Croce CM and Vecchione
A: MicroRNAs deregulation in gastric cancer. Cancer Res.
66:13382006.
|
|
31
|
Barbagallo D, Condorelli A, Ragusa M,
Salito L, Sammito M, Banelli B, Caltabiano R, Barbagallo G, Zappalà
A, Battaglia R, et al: Dysregulated miR-671-5p/CDR1-AS/CDR1/VSNL1
axis is involved in glioblastoma multiforme. Oncotarget.
7:4746–4759. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tan X, Fu Y, Chen L, Lee W, Lai Y, Rezaei
K, Tabbara S, Latham P, Teal CB, Man YG, et al: miR-671-5p inhibits
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by downregulating FOXM1
expression in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 7:293–307. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Song J, Xie H, Lian Z, Yang G, Du R, Du Y,
Zou X, Jin H, Gao J, Liu J and Fan D: Enhanced cell survival of
gastric cancer cells by a novel gene URG4. Neoplasia. 8:995–1002.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|