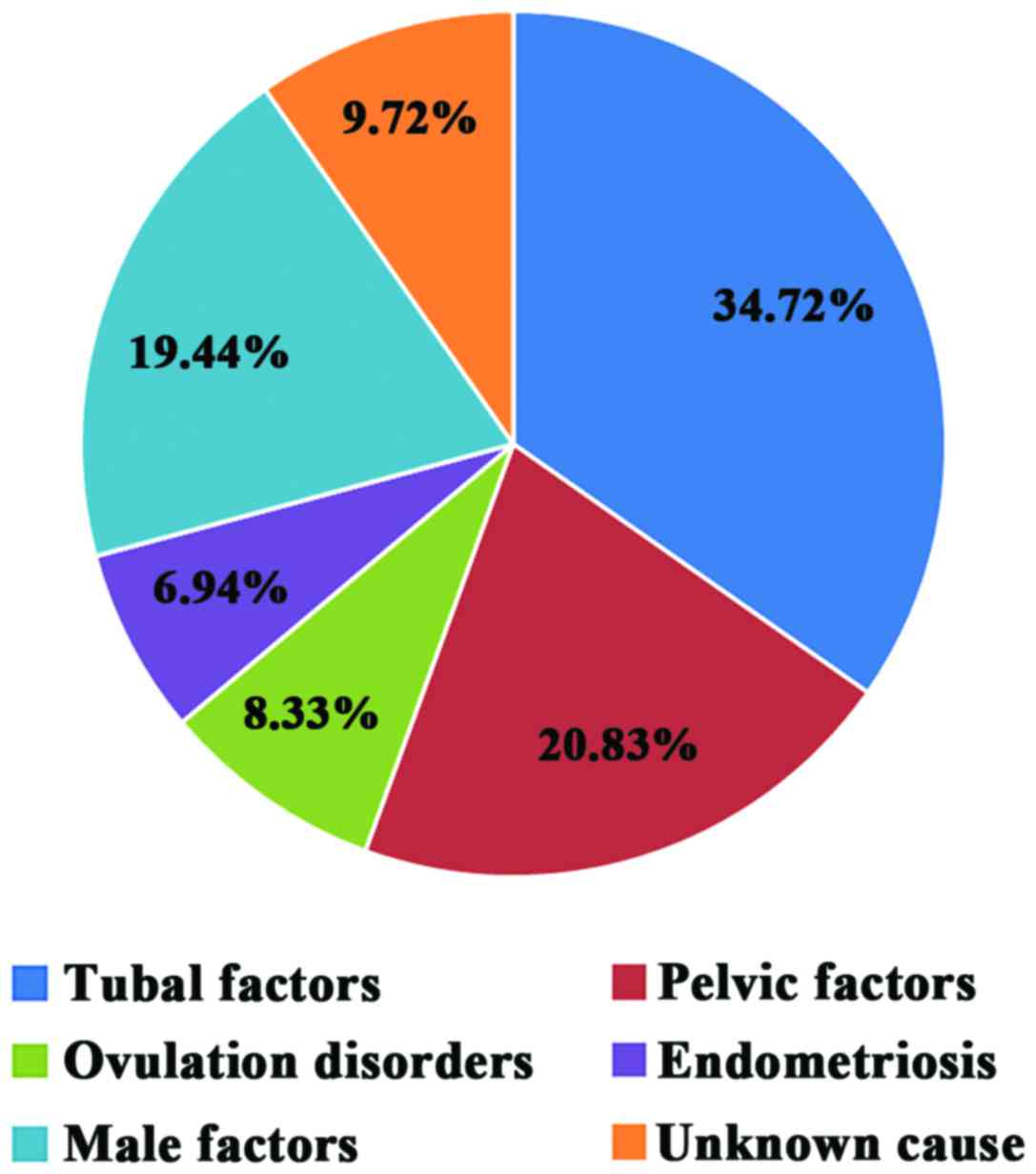
|
1
|
Norwitz ER, Schust DJ and Fisher SJ:
Implantation and the survival of early pregnancy. N Engl J Med.
345:1400–1408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lim HJ and Dey SK: HB-EGF: A unique
mediator of embryo-uterine interactions during implantation. Exp
Cell Res. 315:619–626. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Valdez-Morales FJ, Gamboa-Domínguez A,
Vital-Reyes VS, Cruz JC, Chimal-Monroy J, Franco-Murillo Y and
Cerbón M: Changes in receptivity epithelial cell markers of
endometrium after ovarian stimulation treatments: Its role during
implantation window. Reprod Health. 12:452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lédée-Bataille N, Laprée-Delage G, Taupin
JL, Dubanchet S, Frydman R and Chaouat G: Concentration of
leukaemia inhibitory factor (LIF) in uterine flushing fluid is
highly predictive of embryo implantation. Hum Reprod. 17:213–218.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Scalici J, Laughlin BB, Finan MA, Wang B
and Rocconi RP: The trend towards minimally invasive surgery (MIS)
for endometrial cancer: An ACS-NSQIP evaluation of surgical
outcomes. Gynecol Oncol. 136:512–515. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang HY, Wen Y, Kruessel JS, Raga F,
Soong YK and Polan ML: Interleukin (IL)-1beta regulation of
IL-1beta and IL-1 receptor antagonist expression in cultured human
endometrial stromal cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 86:1387–1393.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stavreus-Evers A, Aghajanova L, Brismar H,
Eriksson H, Landgren BM and Hovatta O: Co-existence of
heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor and
pinopodes in human endometrium at the time of implantation. Mol Hum
Reprod. 8:765–769. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kintiraki E, Papakatsika S, Kotronis G,
Goulis DG and Kotsis V: Pregnancy-induced hypertension. Hormones
(Athens). 14:211–223. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen ZJ, Shi Y, Sun Y, Zhang B, Liang X,
Cao Y, Yang J, Liu J, Wei D, Weng N, et al: Fresh versus frozen
embryos for infertility in the polycystic ovary syndrome. N Engl J
Med. 375:523–533. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grey ST, Csizmadia V and Hancock WW:
Differential effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on
thrombomodulin gene expression by human monocytoid (THP-1) cell
versus endothelial cells. Int J Hematol. 67:53–62. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lédée N, Dubanchet S, Oger P, Meynant C,
Lombroso R, Ville Y and Chaouat G: Uterine receptivity and
cytokines: New concepts and new applications. Gynecol Obstet
Invest. 64:138–143. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tobai H and Nishiya I: Nitric oxide
mediates inhibitory effect of interleukin-1beta on estrogen
production in human granulosa-luteal cells. J Obstet Gynaecol Res.
27:53–59. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qinglei L, Jiang N, Shuling B and Lan Y:
Effect of interleukin-1 β on progesterone production and
sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase activity by rat luteal
cell in vitro. J Reprod Med. 9:88–91. 2000.
|
|
15
|
Austgulen R, Arntzen KJ, Vatten LJ, Kahn J
and Sunde A: Detection of cytokines (interleukin-1, interleukin-6,
transforming growth factor-beta) and soluble tumour necrosis factor
receptors in embryo culture fluids during in-vitro fertilization.
Hum Reprod. 10:171–176. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Takacs P and Kauma S: The expression of
interleukin-1 alpha, interleukin-1 beta, and interleukin-1 receptor
type I mRNA during preimplantation mouse development. J Reprod
Immunol. 32:27–35. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gonzalez RR and Leavis P: Leptin
upregulates beta 3-integrin expression and interleukin-1beta,
upregulates leptin and leptin receptor expression in human
endometrial epithelial cell cultures. Endocrine. 16:21–28. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Machelon V, Nome F, Durand-Gasselin I and
Emilie D: Macrophage and granulosa interleukin-1 beta mRNA in human
ovulatory follicles. Hum Reprod. 10:2198–2203. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Díaz Flores M, Ortega-Camarillo C,
Rosales-Torres AM, Baiza-Gutman LA and Hicks JJ: Nitric oxide as
main effector in the interleukin-1 system in ovulation. Gac Med
Mex. 137:291–302. 2001.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Simón C, Piquette GN, Frances A and Polan
ML: Localization of interleukin-1 type I receptor and interleukin-1
beta in human endometrium throughout the menstrual cycle. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 77:549–555. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bourdiec A and Akoum A: Embryo
implantation: Role of interleukin 1 family members. Med Sci
(Paris). 30:644–650. 2014.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Geisert R, Fazleabas A, Lucy M and Mathew
D: Interaction of the conceptus and endometrium to establish
pregnancy in mammals: Role of interleukin 1β. Cell Tissue Res.
349:825–838. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bourdiec A, Shao R, Rao CV and Akoum A:
Human chorionic gonadotropin triggers angiogenesis via the
modulation of endometrial stromal cell responsiveness to
interleukin 1: A new possible mechanism underlying embryo
implantation. Biol Reprod. 87:662012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jessmon P, Leach RE and Armant DR: Diverse
functions of HBEGF during pregnancy. Mol Reprod Dev. 76:1116–1127.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Umata T: Mechanism for activation of
heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor induced by stimuli. J UOEH.
26:85–97. 2004.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Birdsall MA, Hopkisson JF, Grant KE,
Barlow DH and Mardon HJ: Expression of heparin-binding epidermal
growth factor messenger RNA in the human endometrium. Mol Hum
Reprod. 2:31–34. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Leach RE, Khalifa R, Ramirez ND, Das SK,
Wang J, Dey SK, Romero R and Armant DR: Multiple roles for
heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor are
suggested by its cell-specific expression during the human
endometrial cycle and early placentation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
84:3355–3363. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stavreus-Evers A, Koraen L, Scott JE,
Zhang P and Westlund P: Distribution of cyclooxygenase-1,
cyclooxygenase-2, and cytosolic phospholipase A2 in the luteal
phase human endometrium and ovary. Fertil Steril. 83:156–162. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Armant DR, Wang J and Liu Z: Intracellular
signaling in the developing blastocyst as a consequence of the
maternal-embryonic dialogue. Semin Reprod Med. 18:273–287. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sher G and Fisch JD: Effect of vaginal
sildenafil on the outcome of in vitro fertilization (IVF) after
multiple IVF failures attributed to poor endometrial development.
Fertil Steril. 78:1073–1076. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|