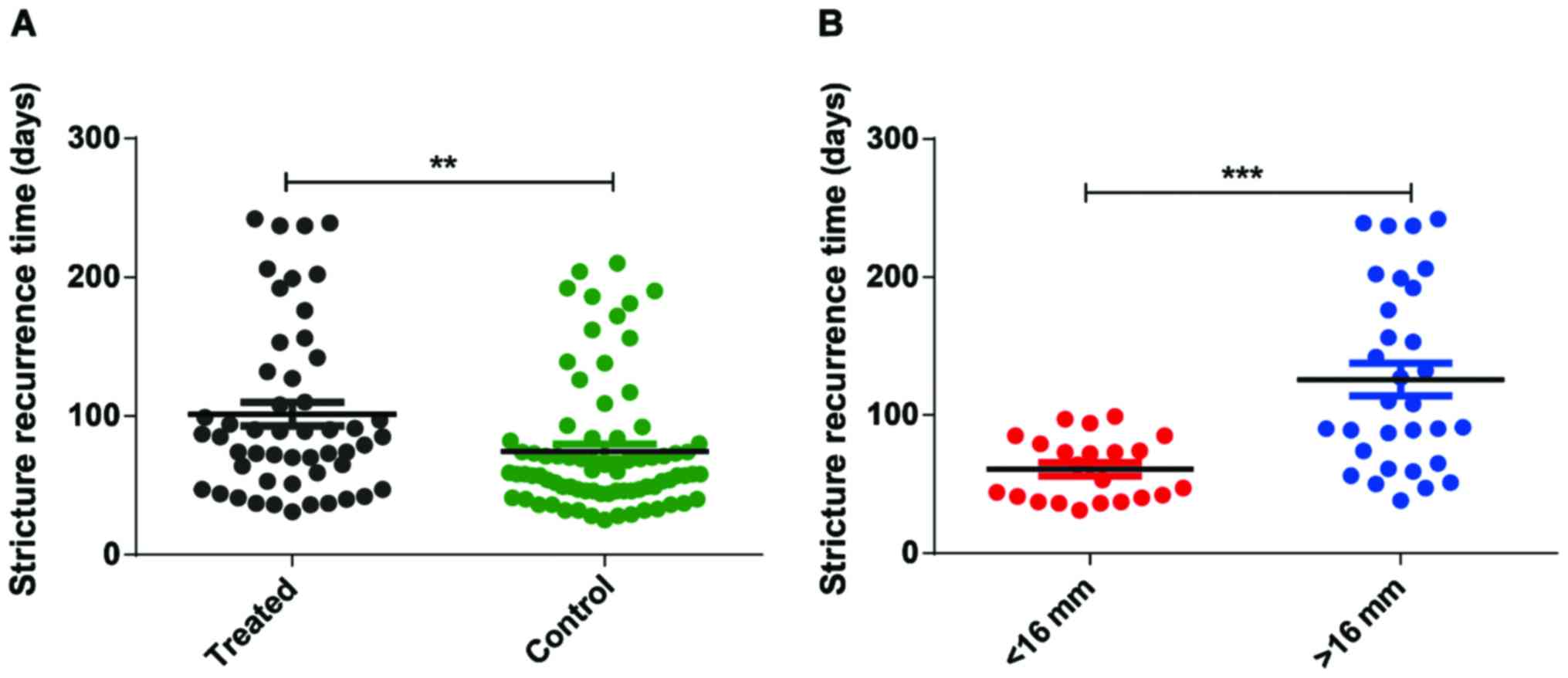
|
1
|
Altintas E, Kacar S, Tunc B, Sezgin O,
Parlak E, Altiparmak E, Saritas U and Sahin B: Intralesional
steroid injection in benign esophageal strictures resistant to
bougie dilation. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 19:1388–1391. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang GM, Liu DF, Xu YP, Meng T and Zhu F:
PET/CT imaging in diagnosing lymph node metastasis of esophageal
carcinoma and its comparison with pathological findings. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:1495–1500. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hirdes MM, Vleggaar FP and Siersema PD:
Stent placement for esophageal strictures: An update. Expert Rev
Med Devices. 8:733–755. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kochman ML, McClave SA and Boyce HW: The
refractory and the recurrent esophageal stricture: A definition.
Gastrointest Endosc. 62:474–475. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miwata T, Oka S, Tanaka S, Kagemoto K,
Sanomura Y, Urabe Y, Hiyama T and Chayama K: Risk factors for
esophageal stenosis after entire circumferential endoscopic
submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Surg Endosc. 30:4049–4056. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mori H, Rafiq K, Kobara H, Fujihara S,
Nishiyama N, Oryuu M, Suzuki Y and Masaki T: Steroid permeation
into the artificial ulcer by combined steroid gel application and
balloon dilatation: Prevention of esophageal stricture. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28:999–1003. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Isomoto H, Yamaguchi N, Nakayama T,
Hayashi T, Nishiyama H, Ohnita K, Takeshima F, Shikuwa S, Kohno S
and Nakao K: Management of esophageal stricture after complete
circular endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol. 11:462011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hanaoka N, Ishihara R, Takeuchi Y, Uedo N,
Higashino K, Ohta T, Kanzaki H, Hanafusa M, Nagai K, Matsui F, et
al: Intralesional steroid injection to prevent stricture after
endoscopic submucosal dissection for esophageal cancer: A
controlled prospective study. Endoscopy. 44:1007–1011. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sato H, Inoue H, Kobayashi Y, Maselli R,
Santi EG, Hayee B, Igarashi K, Yoshida A, Ikeda H, Onimaru M, et
al: Control of severe strictures after circumferential endoscopic
submucosal dissection for esophageal carcinoma: Oral steroid
therapy with balloon dilation or balloon dilation alone.
Gastrointest Endosc. 78:250–257. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kataoka M, Anzai S, Shirasaki T, Ikemiyagi
H, Fujii T, Mabuchi K, Suzuki S, Yoshida M, Kawai T and Kitajima M:
Efficacy of short period, low dose oral prednisolone for the
prevention of stricture after circumferential endoscopic submucosal
dissection (ESD) for esophageal cancer. Endosc Int Open.
3:E113–E117. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamaguchi N, Isomoto H, Nakayama T,
Hayashi T, Nishiyama H, Ohnita K, Takeshima F, Shikuwa S, Kohno S
and Nakao K: Usefulness of oral prednisolone in the treatment of
esophageal stricture after endoscopic submucosal dissection for
superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastrointest
Endosc. 73:1115–1121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Scolapio JS, Pasha TM, Gostout CJ, Mahoney
DW, Zinsmeister AR, Ott BJ and Lindor KD: A randomized prospective
study comparing rigid to balloon dilators for benign esophageal
strictures and rings. Gastrointest Endosc. 50:13–17. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hagel AF, Naegel A, Dauth W, Matzel K,
Kessler HP, Farnbacher MJ, Hohenberger WM, Neurath MF and Raithel
M: Perforation during esophageal dilatation: A 10-year experience.
J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 22:385–389. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kochhar R and Makharia GK: Usefulness of
intralesional triamcinolone in treatment of benign esophageal
strictures. Gastrointest Endosc. 56:829–834. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hamad M: Article conflates academic
standards at UMST with student radicalisation. BMJ. 351:h40322015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ramage JI Jr, Rumalla A, Baron TH, Pochron
NL, Zinsmeister AR, Murray JA, Norton ID, Diehl N and Romero Y: A
prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of
endoscopic steroid injection therapy for recalcitrant esophageal
peptic strictures. Am J Gastroenterol. 100:2419–2425. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Park JY, Song HY, Kim JH, Park JH, Na HK,
Kim YH and Park SI: Benign anastomotic strictures after
esophagectomy: Long-term effectiveness of balloon dilation and
factors affecting recurrence in 155 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol.
198:1208–1213. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim CG, Choi IJ, Lee JY, Cho SJ, Lee JH,
Ryu KW, Park SR, Bae JM and Kim YW: Effective diameter of balloon
dilation for benign esophagojejunal anastomotic stricture after
total gastrectomy. Surg Endosc. 23:1775–1780. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang Q, Zhong J, Yang T, Li J, Luo K,
Zheng Y, Yang H and Fu J: Impacts of anastomotic complications on
the health-related quality of life after esophagectomy. J Surg
Oncol. 111:365–370. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fan Y, Song HY, Kim JH, Park JH,
Ponnuswamy I, Jung HY and Kim YH: Fluoroscopically guided balloon
dilation of benign esophageal strictures: Incidence of esophageal
rupture and its management in 589 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol.
197:1481–1486. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|