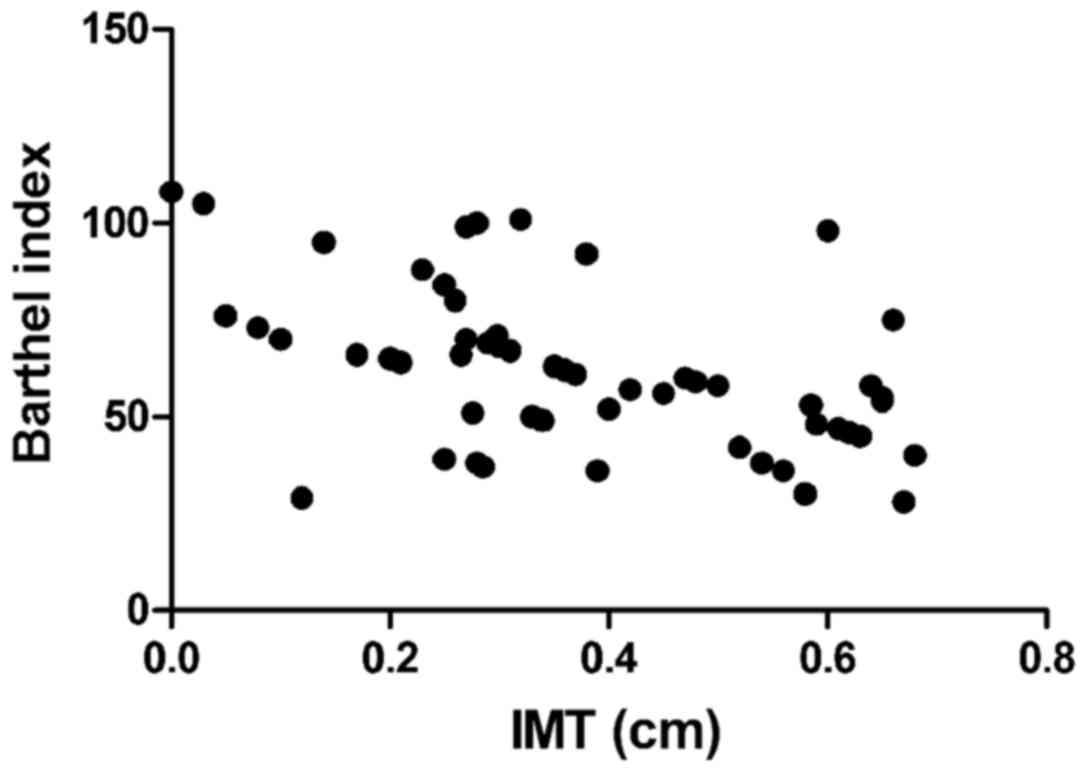
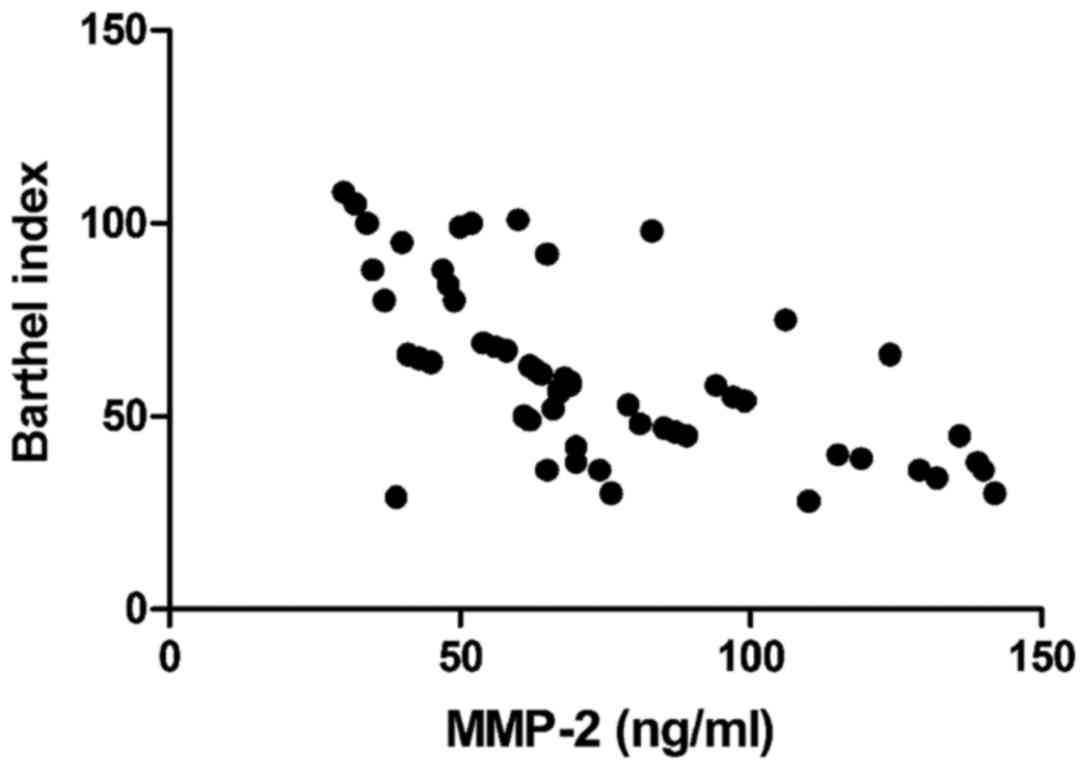
|
1
|
Kim HM, Shin HY, Jeong HJ, An HJ, Kim NS,
Chae HJ, Kim HR, Song HJ, Kim KY, Baek SH, et al: Reduced IL-2 but
elevated IL-4, IL-6, and IgE serum levels in patients with cerebral
infarction during the acute stage. J Mol Neurosci. 14:191–196.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dziedzic T: Clinical significance of acute
phase reaction in stroke patients. Front Biosci. 13:2922–2927.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liapis CD, Kakisis JD and Kostakis AG:
Carotid stenosis: Factors affecting symptomatology. Stroke.
32:2782–2786. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ma LL, Song L, Yu XD, Yu TX, Liang H and
Qiu JX: The clinical study on the treatment for acute cerebral
infarction by intra-arterial thrombolysis combined with mild
hypothermia. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:1999–2006.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Segers D, Helderman F, Cheng C, van Damme
LC, Tempel D, Boersma E, Serruys PW, de Crom R, van der Steen AF,
Holvoet P, et al: Gelatinolytic activity in atherosclerotic plaques
is highly localized and is associated with both macrophages and
smooth muscle cells in vivo. Circulation. 115:609–616. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moreno PR, Purushothaman KR, Fuster V,
Echeverri D, Truszczynska H, Sharma SK, Badimon JJ and O'Connor WN:
Plaque neovascularization is increased in ruptured atherosclerotic
lesions of human aorta: Implications for plaque vulnerability.
Circulation. 110:2032–2038. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Casas JP, Shah T, Hingorani AD, Danesh J
and Pepys MB: C-reactive protein and coronary heart disease: A
critical review. J Intern Med. 264:295–314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Doyle B and Caplice N: Plaque
neovascularization and antiangiogenic therapy for atherosclerosis.
J Am Coll Cardiol. 49:2073–2080. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang N, Lin M, Wang BG, Zeng WY, He YF,
Peng HY, Zeng J, Wu ZY and Zhong Y: Low level of low-density
lipoprotein cholesterol is related with increased hemorrhagic
transformation after acute ischemic cerebral infarction. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:673–678. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bazan HA, Smith TA, Donovan MJ and
Sternbergh WC III: Future management of carotid stenosis: Role of
urgent carotid interventions in the acutely symptomatic carotid
patient and best medical therapy for asymptomatic carotid disease.
Ochsner J. 14:608–615. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bauzá A, Mooibroek TJ and Frontera A:
Corrigendum: The bright future of unconventional σ/π-hole
interactions. Chemphyschem. 16:31302015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hermus L, Tielliu IF, Wallis de Vries BM,
van den Dungen JJ and Zeebregts CJ: Imaging the vulnerable carotid
artery plaque. Acta Chir Belg. 110:159–164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tuttolomondo A, Di Raimondo D, Pecoraro R,
Arnao V, Pinto A and Licata G: Atherosclerosis as an inflammatory
disease. Curr Pharm Des. 18:4266–4288. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Azzurri A, Sow OY, Amedei A, Bah B, Diallo
S, Peri G, Benagiano M, D'Elios MM, Mantovani A and Del Prete G:
IFN-gamma-inducible protein 10 and pentraxin 3 plasma levels are
tools for monitoring inflammation and disease activity in
Mycobacteriumtuberculosis infection. Microbes Infect.
7:1–8. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mairuhu AT, Peri G, Setiati TE, Hack CE,
Koraka P, Soemantri A, Osterhaus AD, Brandjes DP, van der Meer JW,
Mantovani A, et al: Elevated plasma levels of the long pentraxin,
pentraxin 3, in severe dengue virus infections. J Med Virol.
76:547–552. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Muller B, Peri G, Doni A, Torri V,
Landmann R, Bottazzi B and Mantovani A: Circulating levels of the
long pentraxin PTX3 correlate with severity of infection in
critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 29:1404–1407. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sprong T, Peri G, Neeleman C, Mantovani A,
Signorini S, van der Meer JW and van Deuren M: Pentraxin 3 and
C-reactive protein in severe meningococcal disease. Shock.
31:28–32. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bevelacqua V, Libra M, Mazzarino MC,
Gangemi P, Nicotra G, Curatolo S, Massimino D, Plumari A, Merito P,
Valente G, et al: Long pentraxin 3: A marker of inflammation in
untreated psoriatic patients. Int J Mol Med. 18:415–423.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Yang Z, Liu C, Zhao Y and Chen Y:
Activated microglia provide a neuroprotective role by balancing
glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor and tumor necrosis
factor-α secretion after subacute cerebral ischemia. Int J Mol Med.
31:172–178. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yilmaz G, Arumugam TV, Stokes KY and
Granger DN: Role of T lymphocytes and interferon-gamma in ischemic
stroke. Circulation. 113:2105–2112. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|