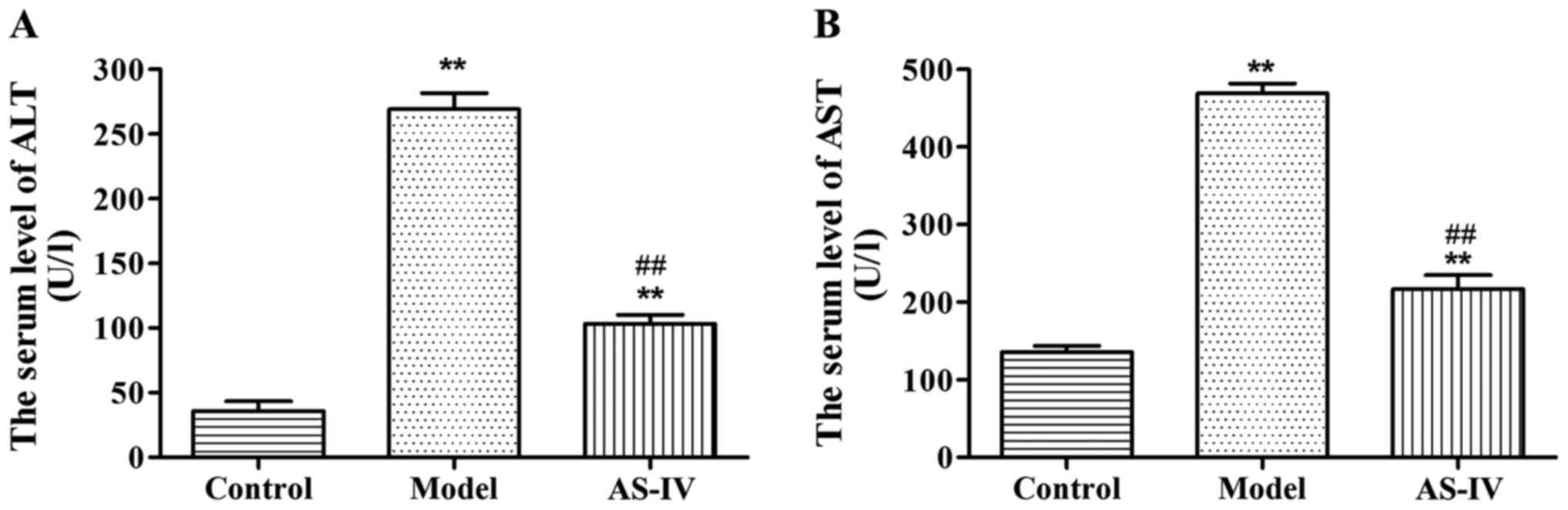
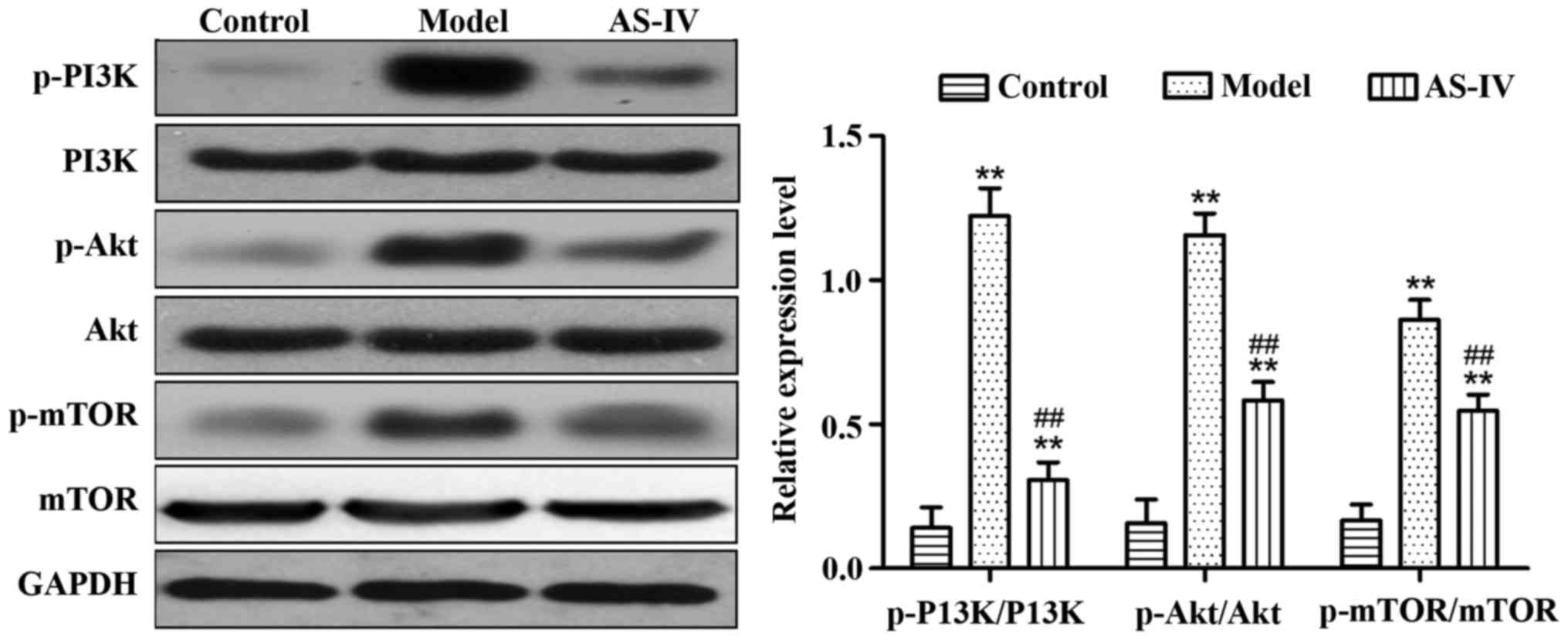
|
1
|
Liaw YF, Lin DY, Chen TJ and Chu CM:
Natural course after the development of cirrhosis in patients with
chronic type B hepatitis: A prospective study. Liver. 9:235–241.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hsu YS, Chien RN, Yeh CT, Sheen IS, Chiou
HY, Chu CM and Liaw YF: Long-term outcome after spontaneous HBeAg
seroconversion in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology.
35:1522–1527. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang Y and Liu YP: Research advances in
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and tumor multidrug resistance. Zhonghua
Linchuang Yishi Zazhi. 5:446–449. 2011.
|
|
4
|
Pettinelli P, Obregón AM and Videla LA:
Molecular mechanisms of steatosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease. Nutr Hosp. 26:441–450. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Weichhart T and Säemann MD: The
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in innate immune cells: Emerging therapeutic
applications. Ann Rheum Dis. 67 Suppl 3:iii70–iii74. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang SG, Xu Y, Chen JD, Yang CH and Chen
XH: Astragaloside IV stimulates angiogenesis and increases nitric
oxide accumulation via JAK2/STAT3 and ERK1/2 pathway. Molecules.
18:12809–12819. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cheng MX, Chen ZZ, Cai YL, Liu CA and Tu
B: Astragaloside IV protects against ischemia reperfusion in a
murine model of orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplant Proc.
43:1456–1461. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li M, Qu YZ, Zhao ZW, Wu SX, Liu YY, Wei
XY, Gao L and Gao GD: Astragaloside IV protects against focal
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury correlating to suppression of
neutrophils adhesion-related molecules. Neurochem Int. 60:458–465.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xin Y, Li G, Liu H and Ai D: AS-IV
protects against kidney IRI through inhibition of NF-κB activity
and PUMA upregulation. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:18293–18301.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pinzani M, Rosselli M and Zuckermann M:
Liver cirrhosis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 25:281–290.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee UE and Friedman SL: Mechanisms of
hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.
25:195–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hernandez-Gea V and Friedman SL:
Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:425–456. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chang TT, Liaw YF, Wu SS, Schiff E, Han
KH, Lai CL, Safadi R, Lee SS, Halota W, Goodman Z, et al: Long-term
entecavir therapy results in the reversal of fibrosis/cirrhosis and
continued histological improvement in patients with chronic
hepatitis B. Hepatology. 52:886–893. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Serpaggi J, Carnot F, Nalpas B, Canioni D,
Guéchot J, Lebray P, Vallet-Pichard A, Fontaine H, Bedossa P and
Pol S: Direct and indirect evidence for the reversibility of
cirrhosis. Hum Pathol. 37:1519–1526. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bortolotti F and Guido M: Reversal of
liver cirrhosis: A desirable clinical outcome and its pathogenic
background. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 44:401–406. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Desmet VJ: Comments on cirrhosis reversal.
Dig Liver Dis. 37:909–916. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Reif S, Lang A, Lindquist JN, Yata Y,
Gabele E, Scanga A, Brenner DA and Rippe RA: The role of focal
adhesion kinase-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-akt signaling in
hepatic stellate cell proliferation and type I collagen expression.
J Biol Chem. 278:8083–8090. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang J, Chu ES, Chen HY, Man K, Go MY,
Huang XR, Lan HY, Sung JJ and Yu J: microRNA-29b prevents liver
fibrosis by attenuating hepatic stellate cell activation and
inducing apoptosis through targeting PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget.
6:7325–7338. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hua H, Zhu Y and Song YH: Ruscogenin
suppressed the hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 101:115–122.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gäbele E, Reif S, Tsukada S, Bataller R,
Yata Y, Morris T, Schrum LW, Brenner DA and Rippe RA: The role of
p70S6K in hepatic stellate cell collagen gene expression and cell
proliferation. J Biol Chem. 280:13374–13382. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Coffey JC, Wang JH, Smith MJ, Laing A,
Bouchier-Hayes D, Cotter TG and Redmond HP: Phosphoinositide
3-kinase accelerates postoperative tumor growth by inhibiting
apoptosis and enhancing resistance to chemotherapy-induced
apoptosis. Novel role for an old enemy. J Biol Chem.
280:20968–20977. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cai CX, Buddha H, Castelino-Prabhu S,
Zhang Z, Britton RS, Bacon BR and Neuschwander-Tetri BA: Activation
of insulin- PI3K/Akt-p70S6K pathway in hepatic stellate cells
contributes to fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig Dis
Sci. 62:968–978. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Patsenker E, Schneider V, Ledermann M,
Saegesser H, Dorn C, Hellerbrand C and Stickel F: Potent
antifibrotic activity of mTOR inhibitors sirolimus and everolimus
but not of cyclosporine A and tacrolimus in experimental liver
fibrosis. J Hepatol. 55:388–398. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|