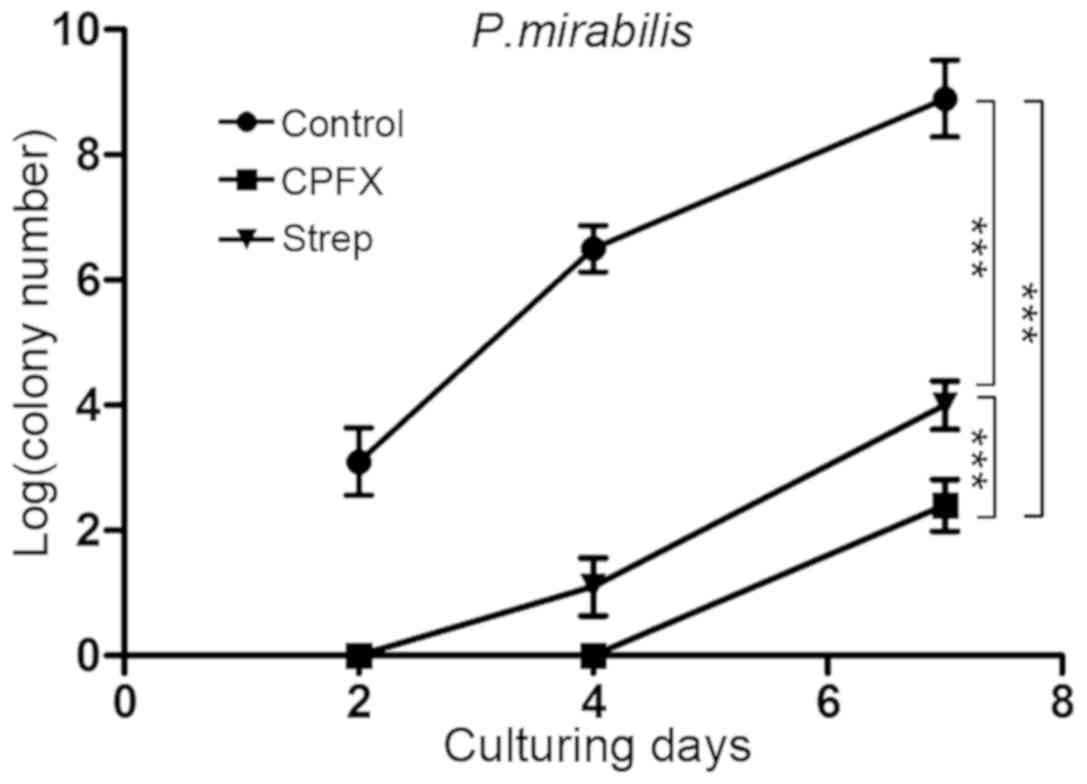
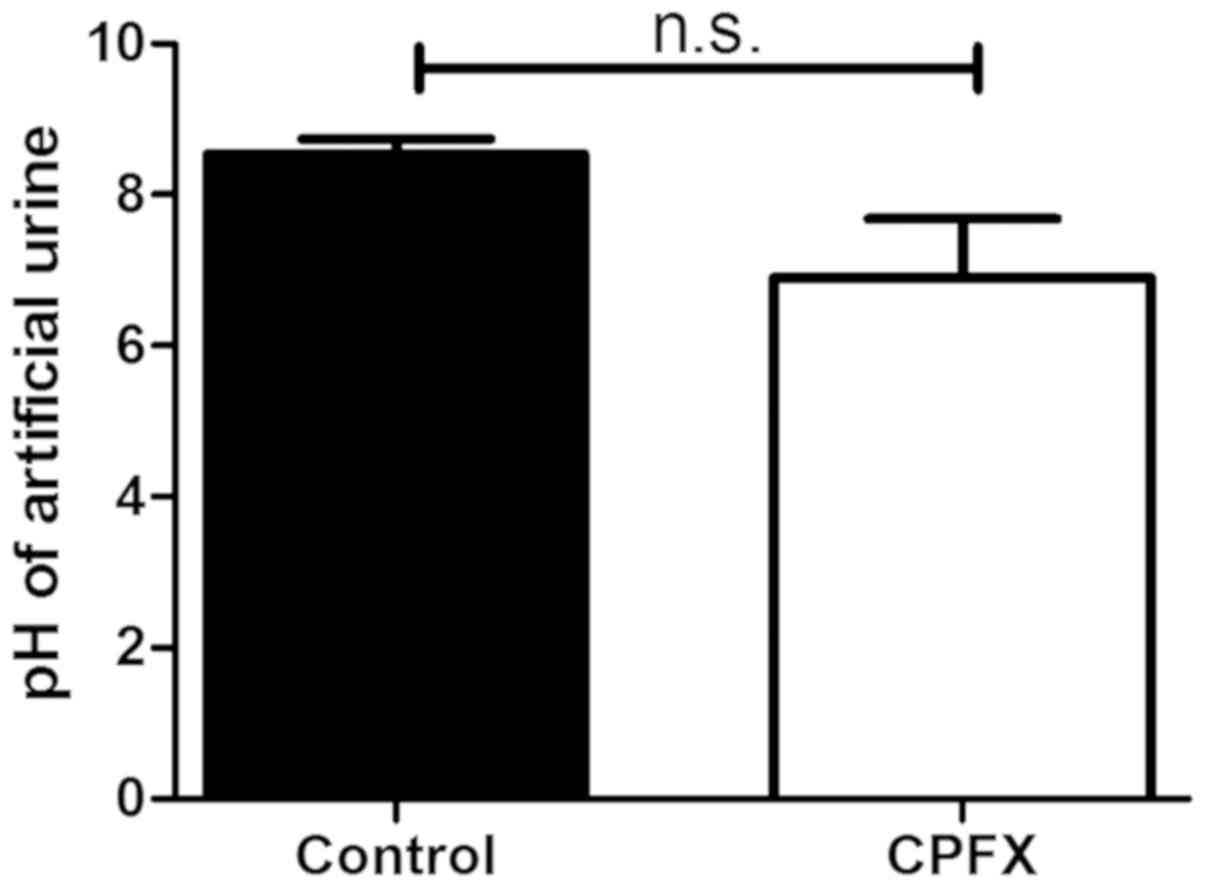
|
1
|
Orthopedic implants-a global market
overview. Indus Exp. 2011.
|
|
2
|
Koseoglu H, Aslan G, Esen N, Sen BH and
Coban H: Ultrastructural stages of biofilm development of
Escherichia coli on urethral catheters and effects of antibiotics
on biofilm formation. Urology. 68:942–946. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Veerachamy S, Yarlagadda T, Manivasagam G
and Yarlagadda PK: Bacterial adherence and biofilm formation on
medical implants: A review. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 228:1083–1099.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheng G, Zhang Z, Chen S, Bryers JD and
Jiang S: Inhibition of bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation on
zwitterionic surfaces. Biomaterials. 28:4192–4199. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Magana M, Sereti C, Ioannidis A, Mitchell
CA, Ball AR, Magiorkinis E, Chatzipanagiotou S, Hamblin MR,
Hadjifrangiskou M and Tegos GP: Options and limitations in clinical
investigation of bacterial biofilms. Clin Microbiol Rev. 31(pii):
e00084–16. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tai Z, Ma H, Liu B, Yan X and Xue Q:
Facile synthesis of Ag/GNS-g-PAA nanohybrids for antimicrobial
applications. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 89:147–151. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sivakumar PM, Iyer G, Natesan L and Doble
M: 3′-Hydroxy-4-methoxychalcone as a potential antibacterial
coating on polymeric biomaterials. Appl Surf Sci. 256:6018–6024.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kowalczuk D, Ginalska G and Golus J:
Characterization of the developed antimicrobial urological
catheters. Int J Pharm. 402:175–183. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kara F, Aksoy EA, Yuksekdag Z, Hasirci N
and Aksoy S: Synthesis and surface modification of polyurethanes
with chitosan for antibacterial properties. Carbohydr Polym.
112:39–47. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Z, Yu L, Ding M, Tan H, Li J and Fu
Q: Preparation and rapid degradation of nontoxic biodegradable
polyurethanes based on poly(lactic acid)-poly(ethylene
glycol)-poly(lactic acid) and l -lysine diisocyanate. Polym Chem.
2-3:6012011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jiang X, Yu F, Wang Z, Li J, Tan H, Ding M
and Fu Q: Fabrication and characterization of waterborne
biodegradable polyurethanes 3-dimensional porous scaffolds for
vascular tissue engineering. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 21:1637–1652.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kang SY, Ji Z, Tseng LF, Turner SA,
Villanueva DA, Johnson R, Albano A and Langer R: Design and
synthesis of waterborne polyurethanes. Adv Mater. 30:e17062372018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sivak WN: Synthesis and characterization
of novel polyurethane drug delivery systems. Dissertations &
Theses-Gradworks. 2007.
|
|
14
|
Sivak WN, Zhang J, Petoud S and Beckman
EJ: Simultaneous drug release at different rates from biodegradable
polyurethane foams. Acta Biomater. 5:2398–2408. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang X, Li J, Ding M, Tan H, Ling Q,
Zhong Y and Fu Q: Synthesis and degradation of nontoxic
biodegradable waterborne polyurethanes elastomer with
poly(ε-caprolactone) and poly(ethylene glycol) as soft segment. Eur
Polym J. 43:1838–1846. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Liu Q, Tian Y, Jian Z, Li H and
Wang K: Biodegradable hydrophilic polyurethane PEGU25 loading
antimicrobial peptide Bmap-28: A sustained-release membrane able to
inhibit bacterial biofilm formation in vitro. Sci Rep. 5:86342015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ye T, Jian Z, Wang J, He W, Liu Q, Wang K,
Li H and Tan H: Antimicrobial activity study of triclosan-loaded
WBPU on Proteus mirabilis in vitro. Int Urol Nephrol. 49:563–571.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Griffith DP, Musher DM and Itin C: Urease.
The primary cause of infection-induced urinary stones. Invest Urol.
13:346–350. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Morris NS, Stickler DJ and Winters C:
Which indwelling urethral catheters resist encrustation by Proteus
mirabilis biofilms? Br J Urol. 80:58–63. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Römling U and Balsalobre C: Biofilm
infections, their resilience to therapy and innovative treatment
strategies. J Intern Med. 272:541–561. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Costerton JW, Stewart PS and Greenberg EP:
Bacterial biofilms: A common cause of persistent infections.
Science. 284:1318–1322. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lebeaux D, Ghigo JM and Beloin C:
Biofilm-related infections: Bridging the gap between clinical
management and fundamental aspects of recalcitrance toward
antibiotics. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 78:510–543. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Darouiche RO, Raad II, Heard SO, Thornby
JI, Wenker OC, Gabrielli A, Berg J, Khardori N, Hanna H, Hachem R,
et al: A comparison of two antimicrobial-impregnated central venous
catheters. Catheter Study Group. N Engl J Med. 340:1–8. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ruggeri V, Francolini I, Donelli G and
Piozzi A: Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro activity of
antibiotic releasing polyurethanes to prevent bacterial resistance.
J Biomed Mater Res A. 81:287–298. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou L, Yu L, Ding M, Li J, Tan H, Wang Z
and Fu Q: Synthesis and characterization of pH-sensitive
biodegradable polyurethane for potential drug delivery
applications. Macromolecules. 44:857–864. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cakić SM, Ristić IS, Krakovský I,
Stojiljković DT, Bělský P and Kollová L: Crystallization and
thermal properties in waterborne polyurethane elastomers: Influence
of mixed soft segment block. Mater Chem Phys. 144:31–40. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Williams GJ and Stickler DJ: Some
observations on the diffusion of antimicrobial agents through the
retention balloons of foley catheters. J Urol. 178:697–701. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stickler DJ, Lear JC, Morris NS, Macleod
SM, Downer A, Cadd DH and Feast WJ: Observations on the adherence
of Proteus mirabilis onto polymer surfaces. J Appl Microbiol.
100:1028–1033. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Morris NS, Stickler DJ and McLean RJ: The
development of bacterial biofilms on indwelling urethral catheters.
World J Urol. 17:345–350. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stickler D, Ganderton L, King J, Nettleton
J and Winters C: Proteus mirabilis biofilms and the encrustation of
urethral catheters. Urol Res. 21:407–411. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Suller MT, Anthony VJ, Mathur S, Feneley
RC, Greenman J and Stickler DJ: Factors modulating the pH at which
calcium and magnesium phosphates precipitate from human urine. Urol
Res. 33:254–260. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|