|
1
|
Raghu G, Weycker D, Edelsberg J, Bradford
WZ and Oster G: Incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 174:810–816. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tzouvelekis A, Bonella F and Spagnolo P:
Update on therapeutic management of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Ther Clin Risk Manag. 11:359–370. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ahluwalia N, Shea BS and Tager AM: New
therapeutic targets in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Aiming to
rein in runaway wound-healing responses. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
190:867–878. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ryu JH, Moua T, Daniels CE, Hartman TE, Yi
ES, Utz JP and Limper AH: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Evolving
concepts. Mayo Clin Proc. 89:1130–1142. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tzouvelekis A and Kaminski N: Epigenetics
in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Biochem Cell Biol. 93:159–170.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Degryse AL and Lawson WE: Progress toward
improving animal models for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Med
Sci. 341:444–449. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mouratis MA and Aidinis V: Modeling
pulmonary fibrosis with bleomycin. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 17:355–361.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moore BB and Hogaboam CM: Murine models of
pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
294:L152–L160. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dong LH, Jiang YY, Liu YJ, Cui S, Xia CC,
Qu C, Jiang X, Qu YQ, Chang PY and Liu F: The anti-fibrotic effects
of mesenchymal stem cells on irradiated lungs via stimulating
endogenous secretion of HGF and PGE2. Sci Rep. 5:87132015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fireman E: A silica-induced pulmonary
fibrosis model: Are we closer to ‘real life’ ? Int Arch Allergy
Immunol. 158:211–212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tashiro J, Rubio GA, Limper AH, Williams
K, Elliot SJ, Ninou I, Aidinis V, Tzouvelekis A and Glassberg MK:
Exploring animal models that resemble idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Front Med (Lausanne). 4:1182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jenkins RG, Moore BB, Chambers RC,
Eickelberg O, Königshoff M, Kolb M, Laurent GJ, Nanthakumar CB,
Olman MA, Pardo A, et al: An official American thoracic society
workshop report: Use of animal models for the preclinical
assessment of potential therapies for pulmonary fibrosis. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 56:667–679. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
King TE Jr, Bradford WZ, Castro-Bernardini
S, Fagan EA, Glaspole I, Glassberg MK, Gorina E, Hopkins PM,
Kardatzke D, Lancaster L, et al: A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in
patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med.
370:2083–2092. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Richeldi L, du Bois RM, Raghu G, Azuma A,
Brown KK, Costabel U, Cottin V, Flaherty KR, Hansell DM, Inoue Y,
et al: Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 370:2071–2082. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li X, Wang Y, An G, Liang D, Zhu Z, Lian
X, Niu P, Guo C and Tian L: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
attenuate silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis via paracrine
mechanisms. Toxicol Lett. 270:96–107. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ni S, Wang D, Qiu X, Pang L, Song Z and
Guo K: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect against
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rat by activating Nrf2
signaling. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:7752–7761. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao MM, Cui JZ, Cui Y, Li R, Tian YX,
Song SX, Zhang J and Gao JL: Therapeutic effect of exogenous bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on silicosis
via paracrine mechanisms in rats. Mol Med Rep. 8:741–746. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou MI, Chen DL, Jiang T, Feng YM and Han
XL: Effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells
transfected with survivin on pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Exp Ther
Med. 10:1857–1864. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Abumaree M, Al Jumah M, Pace RA and
Kalionis B: Immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stem cells.
Stem Cell Rev. 8:375–392. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu SH, Liu LJ, Lv B, Che CL, Fan DP, Wang
LF and Zhang YM: Inhibition of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis
by bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells might be mediated by
decreasing MMP9, TIMP-1, INF-γ and TGF-β. Cell Biochem Funct.
33:356–366. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rubio GA, Elliot SJ, Wikramanayake TC, Xia
X, Pereira-Simon S, Thaller SR, Glinos GD, Jozic I, Hirt P, Pastar
I, et al: Mesenchymal stromal cells prevent bleomycin-induced lung
and skin fibrosis in aged mice and restore wound healing. J Cell
Physiol. 233:5503–5512. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ortiz LA, Dutreil M, Fattman C, Pandey AC,
Torres G, Go K and Phinney DG: Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist
mediates the antiinflammatory and antifibrotic effect of
mesenchymal stem cells during lung injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:11002–11007. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ortiz LA, Gambelli F, McBride C, Gaupp D,
Baddoo M, Kaminski N and Phinney DG: Mesenchymal stem cell
engraftment in lung is enhanced in response to bleomycin exposure
and ameliorates its fibrotic effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:8407–8411. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rojas M, Xu J, Woods CR, Mora AL, Spears
W, Roman J and Brigham KL: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells in repair of the injured lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
33:145–152. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hutton B, Salanti G, Caldwell DM, Chaimani
A, Schmid CH, Cameron C, Ioannidis JP, Straus S, Thorlund K, Jansen
JP, et al: The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of
systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health
care interventions: Checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med.
162:777–784. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Higgins JP and Sally G: Cochrane Jandbook
for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. A John Wiley & Sons,
Ltd.; West Sussex: 2009
|
|
27
|
Hooijmans CR, Rovers MM, de Vries RB,
Leenaars M, Ritskes-Hoitinga M and Langendam MW: SYRCLE's risk of
bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 14:432014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
DerSimonian R and Kacker R: Random-effects
model for meta-analysis of clinical trials: An update. Contemp Clin
Trials. 28:105–114. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
DerSimonian R and Laird N: Meta-analysis
in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 7:177–188. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lau J, Ioannidis JP and Schmid CH:
Quantitative synthesis in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med.
127:820–826. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
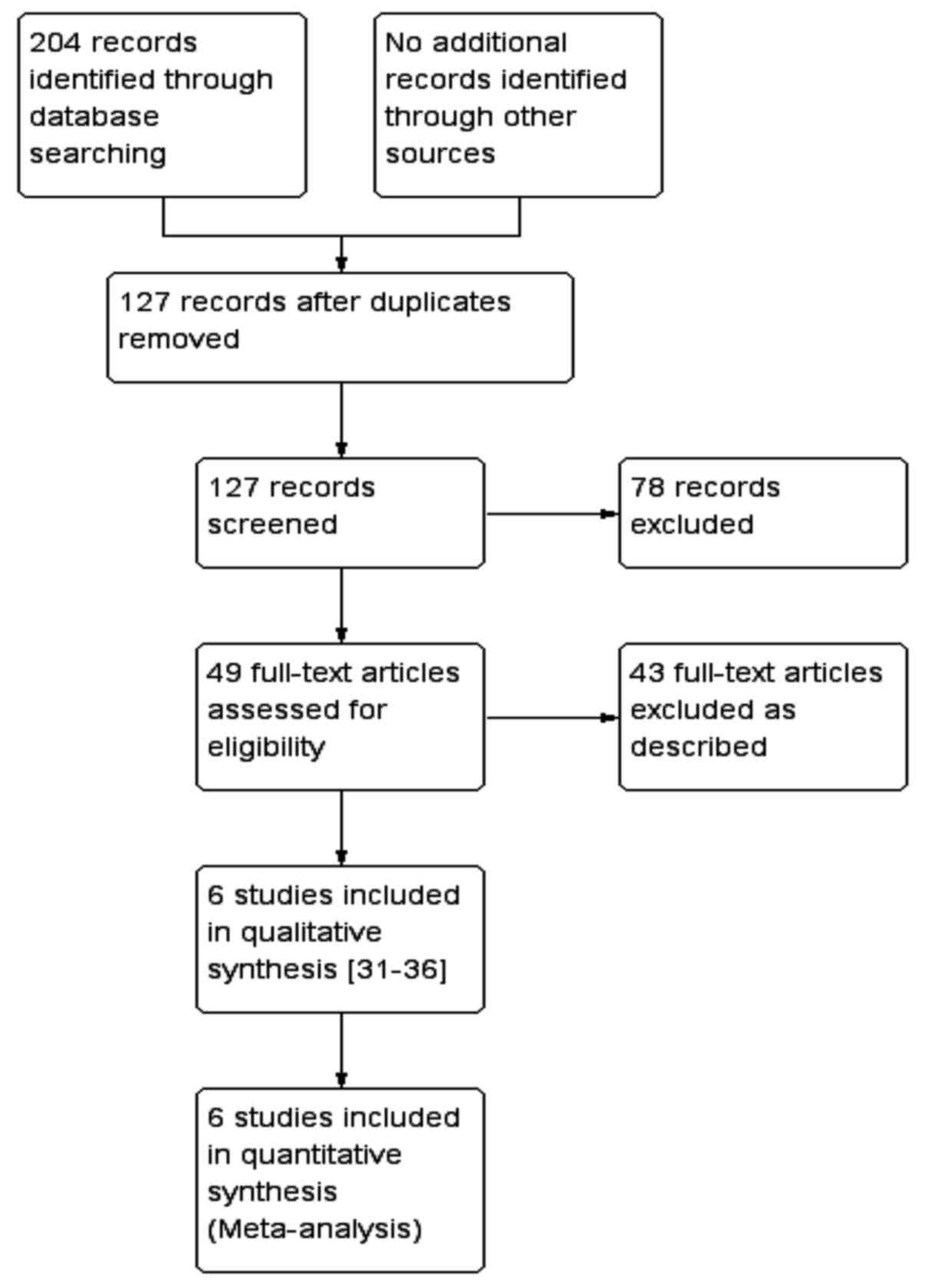
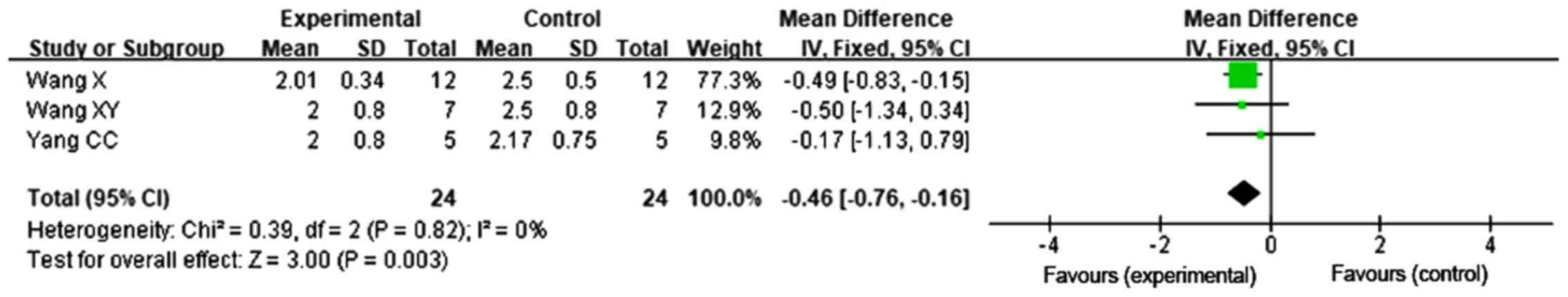
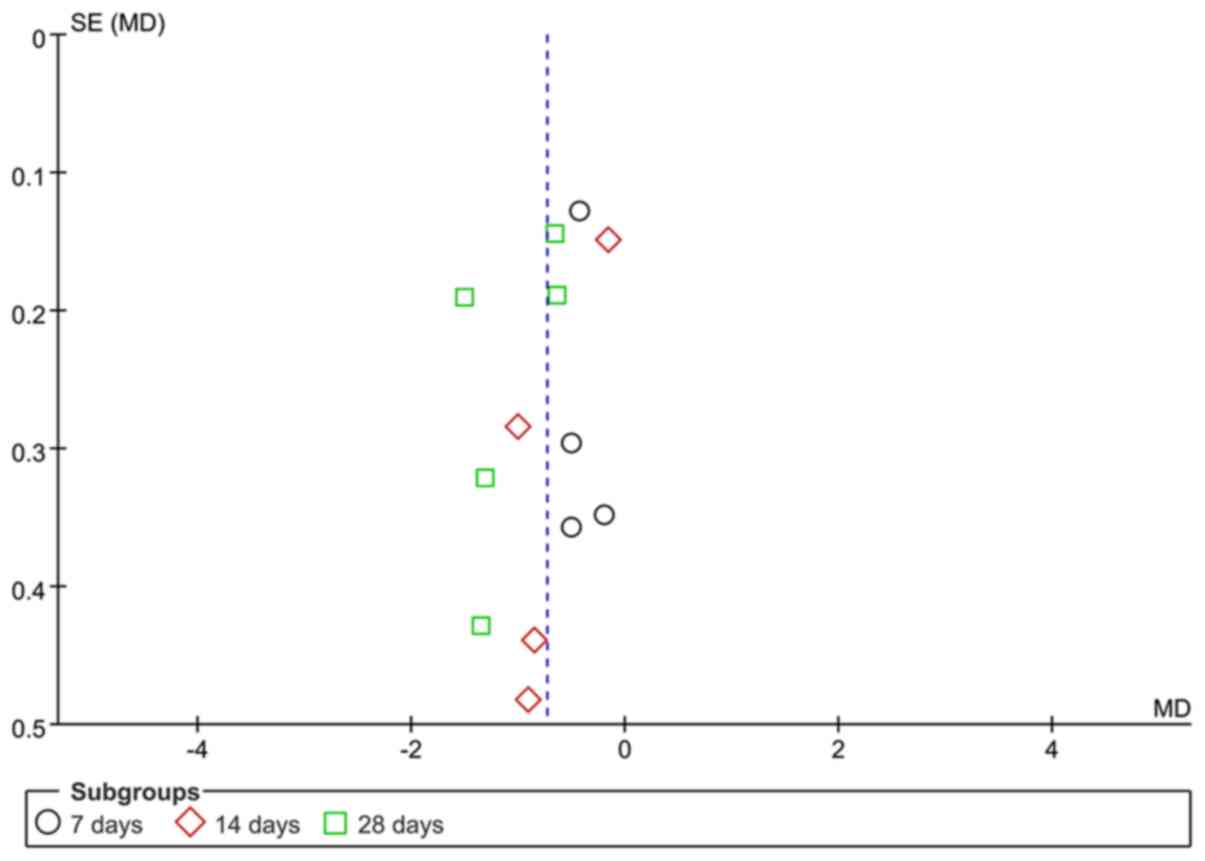
31
|
Yang CC and Wu XM: Inhibitory effect of
bone mesenchymal stem cells on pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Chin J
Int Med. 14:1091–1094. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
32
|
Cui A, Dai HP, Dai JW, Pang BS, Niu SJ, Lü
YP and Wang C: Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on
bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu
Xi Za Zhi. 30:677–682. 2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huang K, Wu XM, Wang XY, Kang XW, Xiao JL,
Li ZG and Lu P: The effect of marrow mesenchymal stem cell
transplantation on pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Zhonghua Jie He He
Hu Xi Za Zhi. 35:659–664. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang X, Zeng Y and Peng H: Inhibitory
effect of mesenchymal stem cells on pulmonary fibrosis in rats.
Acta Med Univ Sci Technol Huazhong. 3:300–303. 2014.
|
|
35
|
Wang XY, Wu XM, Huang K, Kang XW, Li B,
Chen FH and Bai L: The treatment of experimental pulmonary fibrosis
with bone mesenchymal stem cells transplantation. Chin J Rehab.
3:149–152. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
36
|
Zeng XD, Zhang W and Kang XH: Experimental
study of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. J Gannan Med Uni.
1:20–23. 2016.
|
|
37
|
Szapiel SV, Elson NA, Fulmer JD,
Hunninghake GW and Crystal RG: Bleomycin-induced interstitial
pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis.
120:893–899. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Briggs BA, Bradley TM, Vernon P, Cooke NT,
Drinkwater C, Gillett MK and Snashall PD: Measurement of lung
tissue mass, thoracic blood and interstitial volumes by
transmission/emission scanning using [99mTc]pertechnetate. Clin Sci
(Lond). 73:319–327. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schrier DJ, Kunkel RG and Phan SH: The
role of strain variation in murine bleomycin-induced pulmonary
fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 127:63–66. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Janick-Buckner D, Ranges GE and Hacker MP:
Alteration of bronchoalveolar lavage cell populations following
bleomycin treatment in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 100:465–473.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhu HX, Gao JL, Zhao MM, Li R, Tian YX,
Wang X, Zhang J and Cui JZ: Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cell transplantation on silicosis fibrosis in different time
windows in rats. Chin J Immun. 193–196. 209:2015.
|
|
42
|
Epperly MW, Guo H, Gretton JE and
Greenberger JS: Bone marrow origin of myofibroblasts in irradiation
pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 29:213–224. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hoyt DG and Lazo JS: Alterations in
pulmonary mRNA encoding procollagens, fibronectin and transforming
growth factor-beta precede bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in
mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 246:765–771. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Stefanov AN, Fox J, Depault F and Haston
CK: Positional cloning reveals strain-dependent expression of
Trim16 to alter susceptibility to bleomycin-induced pulmonary
fibrosis in mice. PLoS Genet. 9:e10032032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|