|
1
|
Irinyi B, Széles G, Gyimesi E, Tumpek J,
Herédi E, Dimitrios G, Adány R, Hunyadi J and Szegedi A: Clinical
and laboratory examinations in the subgroups of chronic urticaria.
Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 144:217–225. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fraser K and Robertson L: Chronic
urticaria and autoimmunity. Skin Therapy Lett. 18:5–9.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Al-Hamamy HR, Hameed AF and Abdulhadi AS:
Autologous serum skin test as a diagnostic aid in chronic
idiopathic urticaria. ISRN Dermatol. 2013:2915242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sabroe RA, Grattan CE, Francis DM, Barr
RM, Kobza Black A and Greaves MW: The autologous serum skin test: A
screening test for autoantibodies in chronic idiopathic urticaria.
Br J Dermatol. 140:446–452. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Feng L, Song ZQ and Hao F: Application of
autologous serum skin test in chronic urticaria: Current advances.
J Clin Dermatol. 08:508–510. 2011.
|
|
6
|
Song Z, Zhai Z, Zhong H, Zhou Z, Chen W
and Hao F: Evaluation of autologous serum skin test and skin prick
test reactivity to house dust mite in patients with chronic
spontaneous urticaria. PLoS One. 8:e641422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhong H, Song Z, Chen W, Li H, He L, Gao
T, Fang H, Guo Z, Xu J, Yu B, et al: Chronic urticaria in Chinese
population: A hospital-based multicenter epidemiological study.
Allergy. 69:359–364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Konstantinou GN, Asero R, Maurer M, Sabroe
RA, Schmid-Grendelmeier P and Grattan CE: EAACI/GA(2)LEN task force
consensus report: The autologous serum skin test in urticaria.
Allergy. 64:1256–1268. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Auyeung P, Mittag D, Hodgkin PD and
Harrison LC: Autoreactive T cells in chronic spontaneous urticaria
target the IgE Fc receptor Iα subunit. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
138:761–768.e4. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kulthanan K, Nuchkull P, Ungaksornpairote
C, Chularojanamontri L and Tuchinda P: Prevalence and clinical
correlation of serum immunoglobulin E in patients with chronic
spontaneous urticaria. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 116:258–259. e2.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Navines-Ferrer A, Serrano-Candelas E,
Molina-Molina GJ and Martin M: IgE-related chronic diseases and
Anti-IgE-based treatments. J Immunol Res. 2016:81638032016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Confino-Cohen R, Chodick G, Shalev V,
Leshno M, Kimhi O and Goldberg A: Chronic urticaria and
autoimmunity: Associations found in a large population study. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 129:1307–1313. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sugiyama A, Nishie H, Takeuchi S,
Yoshinari M and Furue M: Hashimoto's disease is a frequent
comorbidity and an exacerbating factor of chronic spontaneous
urticaria. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 43:249–253. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Boonpiyathad T and Sangasapaviliya A:
Autologous serum and plasma skin test to predict 2-year outcome in
chronic spontaneous urticaria. Asia Pac Allergy. 6:226–235. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
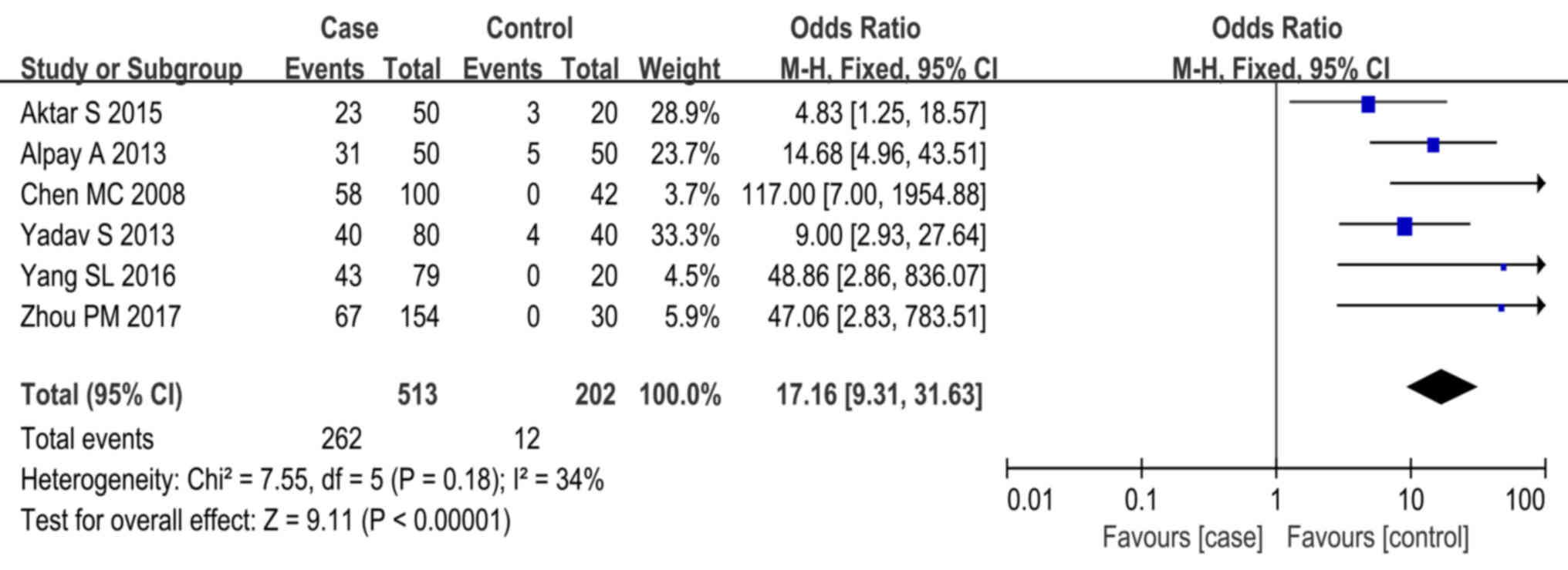
Aktar S, Akdeniz N, Ozkol HU, Calka O and
Karadag AS: The relation of autologous serum and plasma skin test
results with urticarial activity score, sex and age in patients
with chronic urticaria. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 32:173–178. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
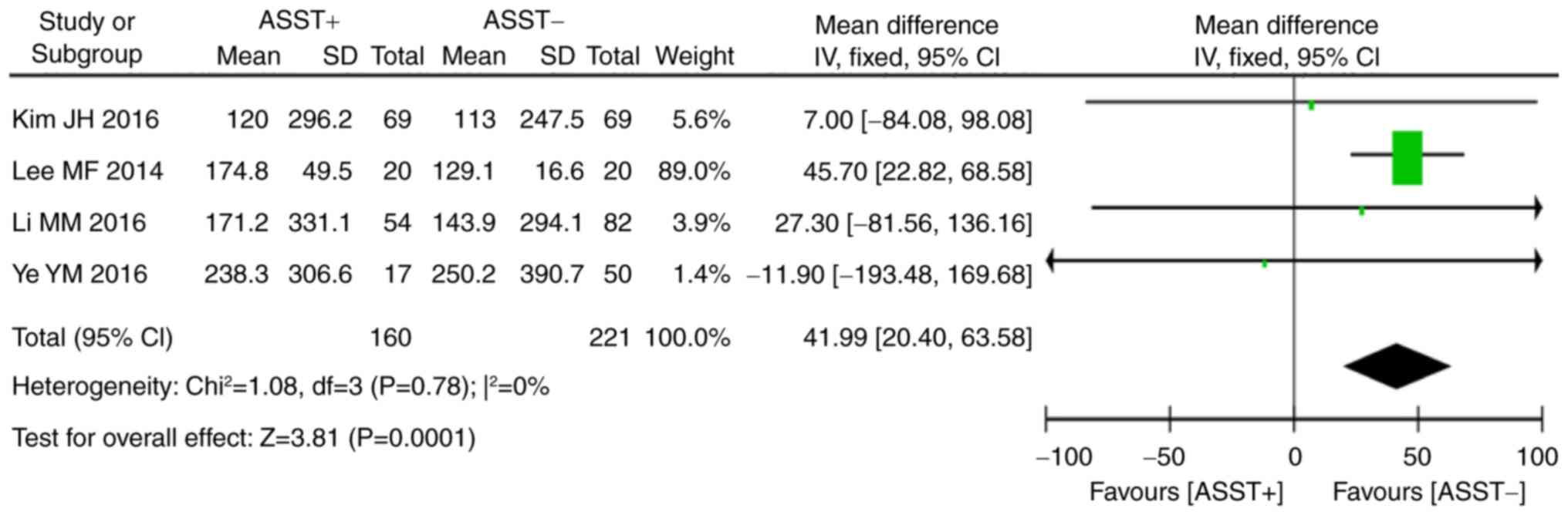
Ye YM, Park JW, Kim SH, Ban GY, Kim JH,
Shin YS, Lee HY and Park HS;: PRANA Group: Prognostic factors for
chronic spontaneous urticaria: A 6-month prospective observational
study. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 8:115–123. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim JH, Lee HY, Ban GY, Shin YS, Park HS
and Ye YM: Serum clusterin as a prognostic marker of chronic
spontaneous urticaria. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e36882016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee MF, Lin TM, Liu SW and Chen YH: A
rapid method of detecting autoantibody against FcεRIα for chronic
spontaneous urticaria. PLoS One. 9:e1095652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Alpay A, Solak Tekin N, Tekin IÖ,
Altinyazar HC, Koca R and Cinar S: Autologous serum skin test
versus autologous plasma skin test in patients with chronic
spontaneous urticaria. Dermatol Res Pract. 2013:2672782013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kumar YH, Bhaskar S and Shankar K:
Comparative study of positive versus negative autologous serum skin
test in chronic spontaneous urticaria and its treatment outcome. N
Am J Med Sci. 8:25–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yadav S, Kanwar A, Parsad D and Minz R:
Chronic idiopathic urticaria and thyroid autoimmunity: Perplexing
association. Indian J Dermatol. 58:3252013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Krupashankar DS, Shashikala K and Madala
R: Clinical and investigative assessment of patients with positive
versus negative autologous serum skin test: A study of 80 South
Indian patients. Indian J Dermatol. 57:434–438. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou PM, Lu YH, Chen T, Huang J, Fang J,
Liu P and Liu H: Analysis of autologous serum skin test results in
154 cases of patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria. Chin J
Dermatov Integr Tradit and West Med. 02:135–137. 2017.
|
|
24
|
Yang SL, Xie SX, Yin SC, Ou FX, Zhang YQ
and Lai W: Analysis of the clinical value of autologous serum skin
test in chronic urticaria. Chin J Health Lab Technol. 21:3158–3160.
2016.
|
|
25
|
Chen MC, Li D, Guo Q and Zhai FQ:
Investigation into the correlation of clinical features and
autologous serum skin test of chronic urticaria. China Tropical
Med. 05:736–738. 2008.
|
|
26
|
Li MM, Guo ZP, Li JY, Xie XQ, Song Q, Ye
YY and Chen SY: Autologous serum skin test and some laboratory test
analysis in 136 patients with chronic urticaria. Chin J Leprosy and
Skin Dis. 10:595–597. 2016.
|
|
27
|
Sun WL and Bi ZG: Clinical features of
chronic urticaria in patients with positive and negative autologous
serum skin test. Chin J Dermatol. 06:342–344. 2005.
|
|
28
|
Zuberbier T, Bindslev-Jensen C, Canonica
W, Grattan CE, Greaves MW, Henz BM, Kapp A, Kozel MM, Maurer M,
Merk HF, et al: EAACI/GA2LEN/EDF guideline: Definition,
classification and diagnosis of urticaria. Allergy. 61:316–320.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ye YM, Park JW, Kim SH, Choi JH, Hur GY,
Lee HY, Lee EH and Park HS: Clinical evaluation of the computerized
chronic urticaria-specific quality of life questionnaire in Korean
patients with chronic urticaria. Clin Exp Dermatol. 37:722–728.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hou XW, Shi JP and Chen X: How to estimate
the mean and standard deviation based on the median, range and
sample size when conducting meta-analysis. Chin J Evid-based Med.
15:484–487. 2015.
|
|
31
|
Bork K: Angioedema. Immunol Allergy Clin
North Am. 34:23–31. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Boccon-Gibod I and Bouillet L: Angioedema
and urticaria. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 141 (Suppl 3):S586–S595.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hacard F, Nosbaum A, Bensaid B, Nicolas
JF, Augey F, Goujon C and Bérard F: Histaminergic angioedema and
chronic urticaria. Presse Med. 44:37–42. 2015.(In French).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Petra AI, Panagiotidou S, Stewart JM,
Conti P and Theoharides TC: Spectrum of mast cell activation
disorders. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 10:729–739. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chang KL, Yang YH, Yu HH, Lee JH, Wang LC
and Chiang BL: Analysis of serum total IgE, specific IgE and
eosinophils in children with acute and chronic urticaria. J
Microbiol Immunol Infect. 46:53–58. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kessel A, Helou W, Bamberger E, Sabo E,
Nusem D, Panassof J and Toubi E: Elevated serum total IgE-a
potential marker for severe chronic urticaria. Int Arch Allergy
Immunol. 153:288–293. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Toubi E, Kessel A, Avshovich N, Bamberger
E, Sabo E, Nusem D and Panasoff J: Clinical and laboratory
parameters in predicting chronic urticaria duration: A prospective
study of 139 patients. Allergy. 59:869–873. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kasperska-Zajac A, Brzoza Z and Rogala B:
Sex hormones and urticaria. J Dermatol Sci. 52:79–86. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kasperska-Zajac A, Brzoza Z and Rogala B:
Lower serum concentration of dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate in
patients suffering from chronic idiopathic urticaria. Allergy.
61:1489–1490. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hizal M, Tüzün B, Wolf R and Tüzün Y: The
relationship between Helicobacter pylori IgG antibody and
autologous serum test in chronic urticaria. Int J Dermatol.
39:443–445. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|