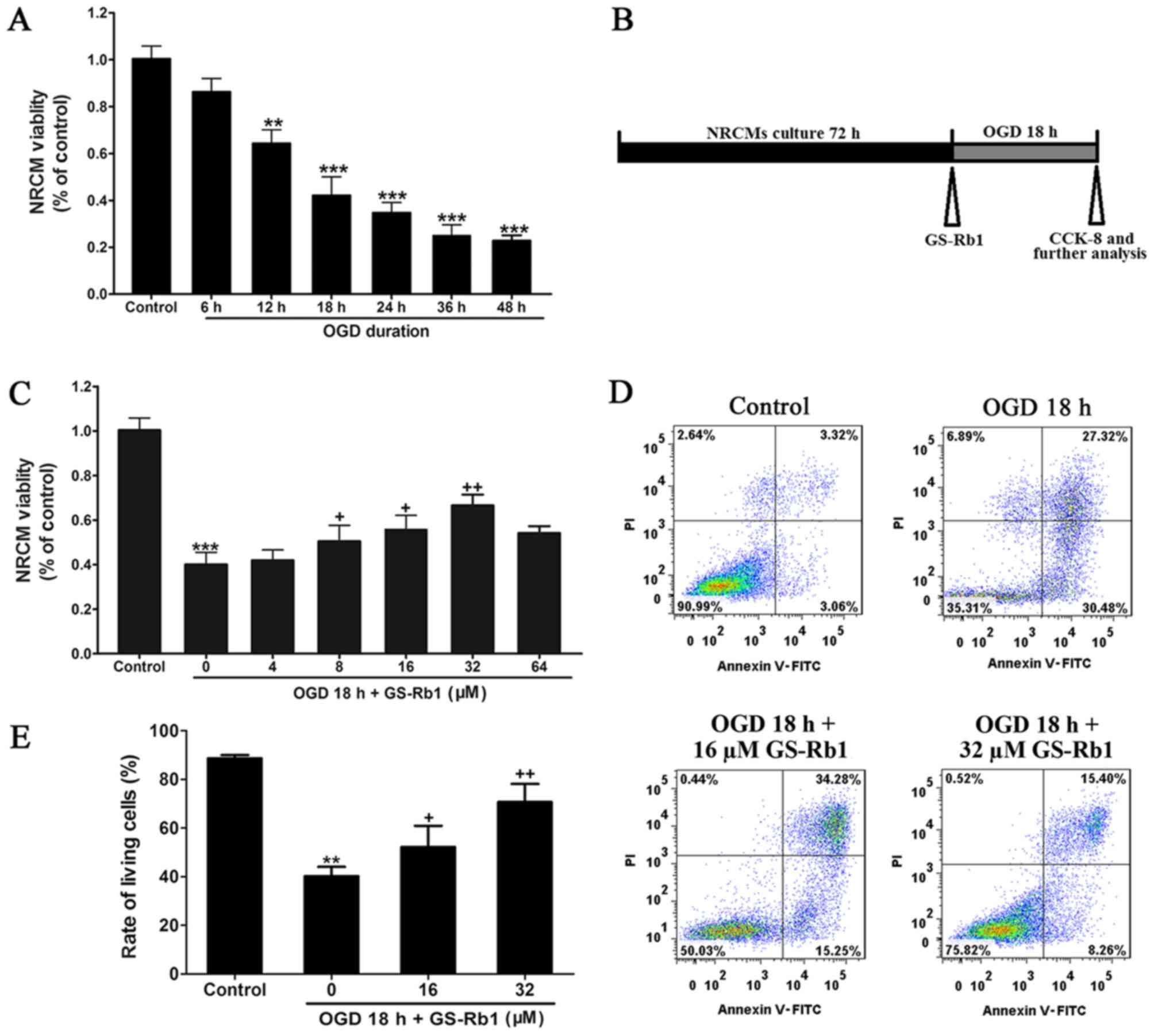
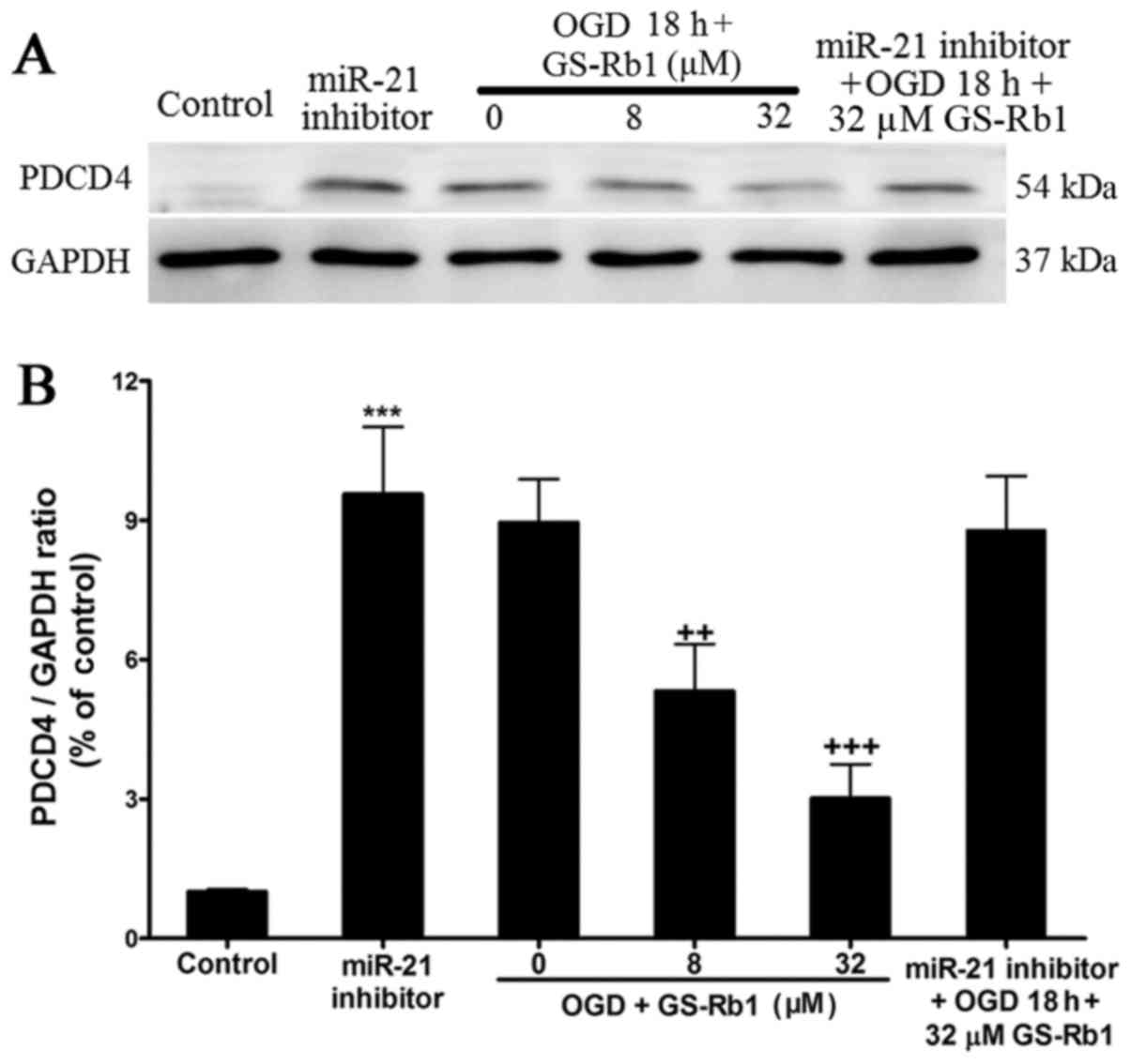
|
1
|
Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman
M, Das SR, Deo R, de Ferranti SD, Floyd J, Fornage M, Gillespie C,
et al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2017 update: A report
from the american heart association. Circulation. 135:e146–e603.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Andersson C and Vasan RS: Epidemiology of
cardiovascular disease in young individuals. Nat Rev Cardiol.
15:230–240. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fordyce CB, Gersh BJ, Stone GW and Granger
CB: Novel therapeutics in myocardial infarction: Targeting
microvascular dysfunction and reperfusion injury. Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 36:605–616. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yao L, Zhou QS, Wang L and Hou G:
MicroRNA-182-5p protects H9c2 cardiomyocytes from hypoxia-induced
apoptosis by down-regulation of PTEN. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
10:5220–5226. 2017.
|
|
5
|
van Rooij E, Sutherland LB, Liu N,
Williams AH, McAnally J, Gerard RD, Richardson JA and Olson EN: A
signature pattern of stress-responsive microRNAs that can evoke
cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:18255–18260. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang K, Jiang Z, Webster KA, Chen J, Hu H,
Zhou Y, Zhao J, Wang L, Wang Y, Zhong Z, et al: Enhanced
cardioprotection by human endometrium mesenchymal stem cells driven
by exosomal MicroRNA-21. Stem Cells Transl Med. 6:209–222. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cheng Y and Zhang C: MicroRNA-21 in
cardiovascular disease. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 3:251–255. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Krichevsky AM and Gabriely G: miR-21: A
small multi-faceted RNA. J Cell Mol Med. 13:39–53. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu XN, Chen Y, Xu Z, Liang X, Wang XH,
Zhang Y, Yuan M, Ni YP, Liu HM and Li GP: MiR-21 suppresses
ox-LDL-induced HUVECs apoptosis by targeting PDCD4. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 10:10075–10084. 2017.
|
|
10
|
Suzuki C, Garces RG, Edmonds KA, Hiller S,
Hyberts SG, Marintchev A and Wagner G: PDCD4 inhibits translation
initiation by binding to eIF4A using both its MA3 domains. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:3274–3279. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee CH and Kim JH: A review on the
medicinal potentials of ginseng and ginsenosides on cardiovascular
diseases. J Ginseng Res. 38:161–166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yan X, Xue J, Wu H, Wang S, Liu Y, Zheng
S, Zhang C and Yang C: Ginsenoside-Rb1 protects Hypoxic- and
ischemic-damaged cardiomyocytes by regulating expression of miRNAs.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015:1713062015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yan X, Liu J, Wu H, Liu Y, Zheng S, Zhang
C and Yang C: Impact of miR-208 and its target gene Nemo-like
kinase on the protective effect of ginsenoside Rb1 in
Hypoxia/Ischemia injuried cardiomyocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem.
39:1187–1195. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yan X, Tian J, Wu H, Liu Y, Ren J, Zheng
S, Zhang C, Yang C, Li Y and Wang S: Ginsenoside rb1 protects
neonatal rat cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/ischemia induced apoptosis
and inhibits activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014:1491952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brown DI and Griendling KK: Regulation of
signal transduction by reactive oxygen species in the
cardiovascular system. Circ Res. 116:531–549. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Duygu B and Da Costa Martins PA: miR-21: A
star player in cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Res. 105:235–237.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tong Z, Jiang B, Wu Y, Liu Y, Li Y, Gao M,
Jiang Y, Lv Q and Xiao X: MiR-21 Protected cardiomyocytes against
doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by targeting BTG2. Int J Mol Sc.
16:14511–14525. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mukhopadhyay P, Mukherjee S, Ahsan K,
Bagchi A, Pacher P and Das DK: Restoration of altered microRNA
expression in the ischemic heart with resveratrol. PLoS One.
5:e157052010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fasanaro P, D'Alessandra Y, Magenta A,
Pompilio G and Capogrossi MC: microRNAs: Promising biomarkers and
therapeutic targets of acute myocardial ischemia. Curr Vasc
Pharmacol. 13:305–315. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dong SM, Cheng Y, Yang J, Li J, Liu X,
Wang X, Wang D, Krall TJ, Delphin ES and Zhang C: MicroRNA
expression signature and the role of MicroRNA-21 in the early phase
of acute myocardial infarction. J Biol Chem. 284:29514–29525. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qin Y, Yu Y, Dong H, Bian X, Guo X and
Dong S: MicroRNA 21 inhibits left ventricular remodeling in the
early phase of rat model with ischemia-reperfusion injury by
suppressing cell apoptosis. Int J Med Sci. 9:413–423. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:2015.doi: 10.7554/eLife.05005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tu YF, Wan L, Fan YH, Wang K, Bu L, Huang
T, Cheng Z and Shen BZ: Ischemic Postconditioning-mediated miRNA-21
protects against cardiac ischemia/reperfusion Injury via PTEN/Akt
pathway. PLoS One. 8:e758722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Han L, Yue X, Zhou X, Lan FM, You G, Zhang
W, Zhang KL, Zhang CZ, Cheng JQ, Yu SZ, et al: MicroRNA-21
expression is regulated by β-catenin/STAT3 pathway and promotes
glioma cell invasion by direct targeting RECK. CNS Neurosci Ther.
18:573–583. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cheng Y, Zhu P, Yang J, Liu X, Dong S,
Wang X, Chun B, Zhuang J and Zhang C: Ischaemic
preconditioning-regulated miR-21 protects heart against
ischaemia/reperfusion injury via anti-apoptosis through its target
PDCD4. Cardiovasc Res. 87:431–439. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xiao J, Pan Y, Li XH, Yang XY, Feng YL,
Tan HH, Jiang L, Feng J and Yu XY: Cardiac progenitor cell-derived
exosomes prevent cardiomyocytes apoptosis through exosomal miR-21
by targeting PDCD4. Cell Death Dis. 7:e22772016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wei C, Li L, Kim IK, Sun P and Gupta S:
NF-κB mediated miR-21 regulation in cardiomyocytes apoptosis under
oxidative stress. Free Radic Res. 48:282–291. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Q and Yang HS: The role of Pdcd4 in
tumour suppression and protein translation. Biol Cell. May
28–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang LH, Ge MH, Hou XX, Cao J, Hu SS, Lu
XX, Han J, Wu YC, Liu X, Zhu X, et al: miR-21 regulates tumor
progression through the miR-21-PDCD4-Stat3 pathway in human
salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Lab Invest. 95:1398–1408. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rodrigues PM, Afonso MB, Simão AL,
Borralho PM, Rodrigues CMP and Castro RE: Inhibition of NF-κB by
deoxycholic acid induces miR-21/PDCD4-dependent hepatocellular
apoptosis. Sci Rep. 5:175282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Uriel N, Sayer G, Annamalai S, Kapur NK
and Burkhoff D: Mechanical Unloading in heart failure. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 72:569–580. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|