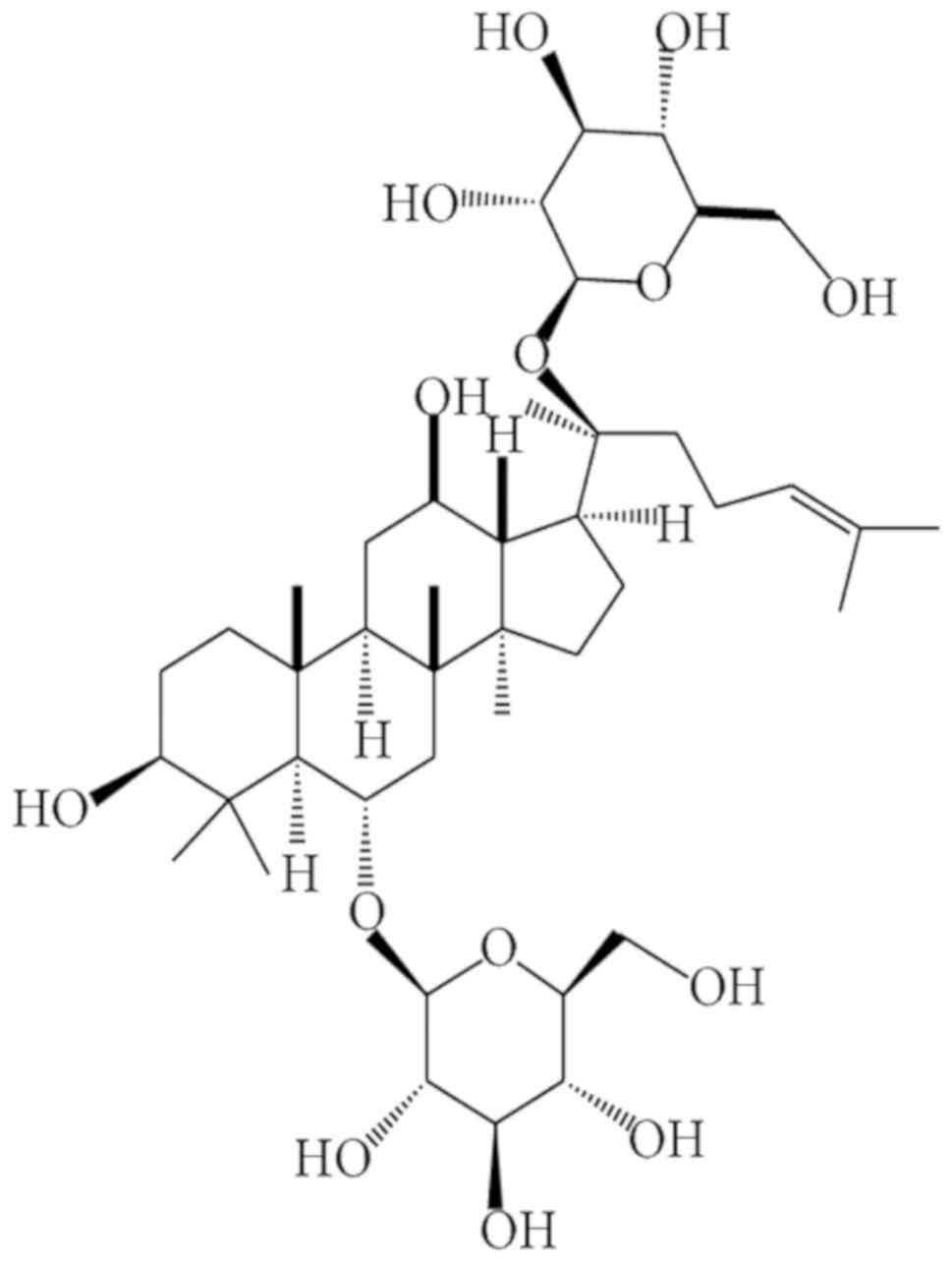
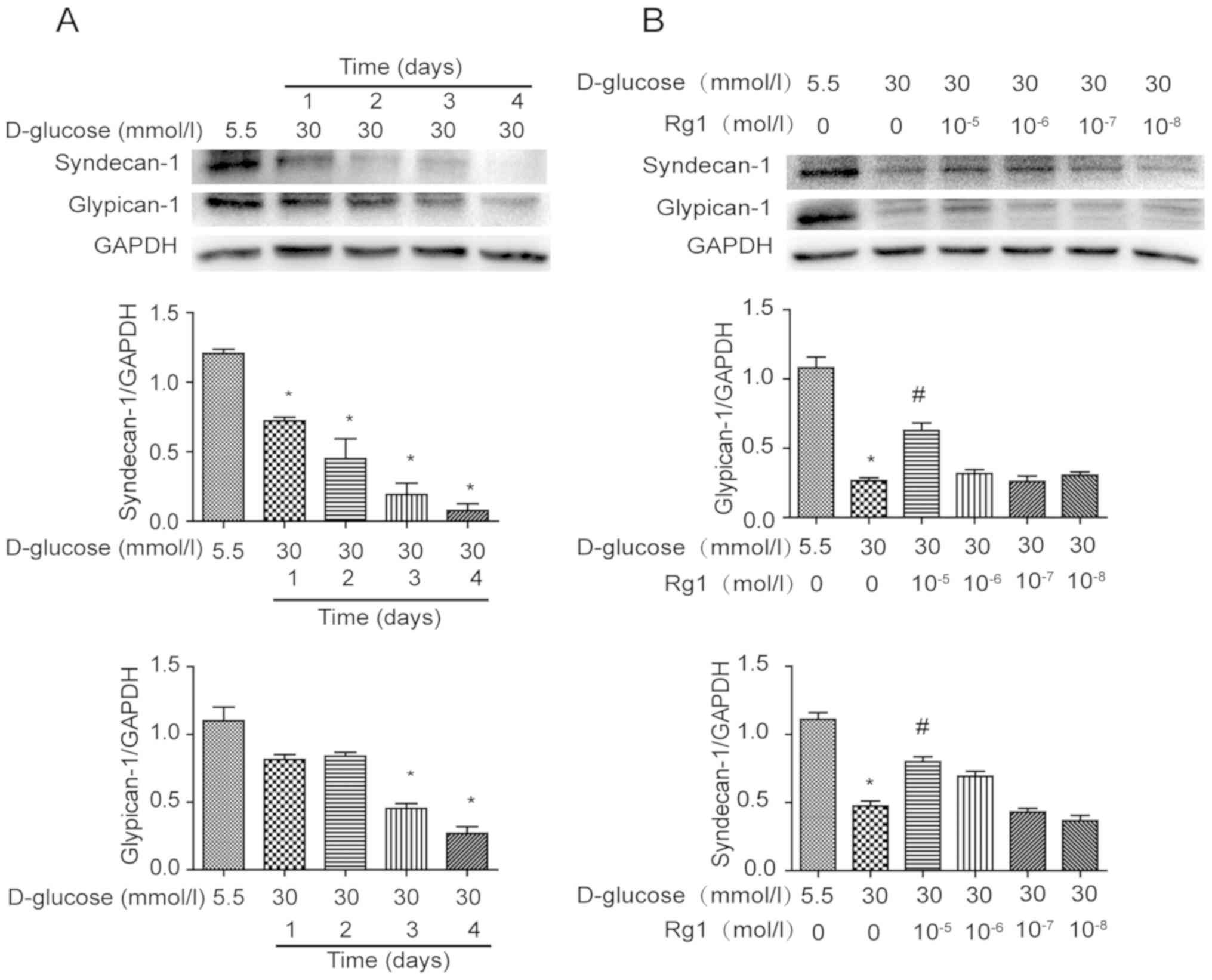
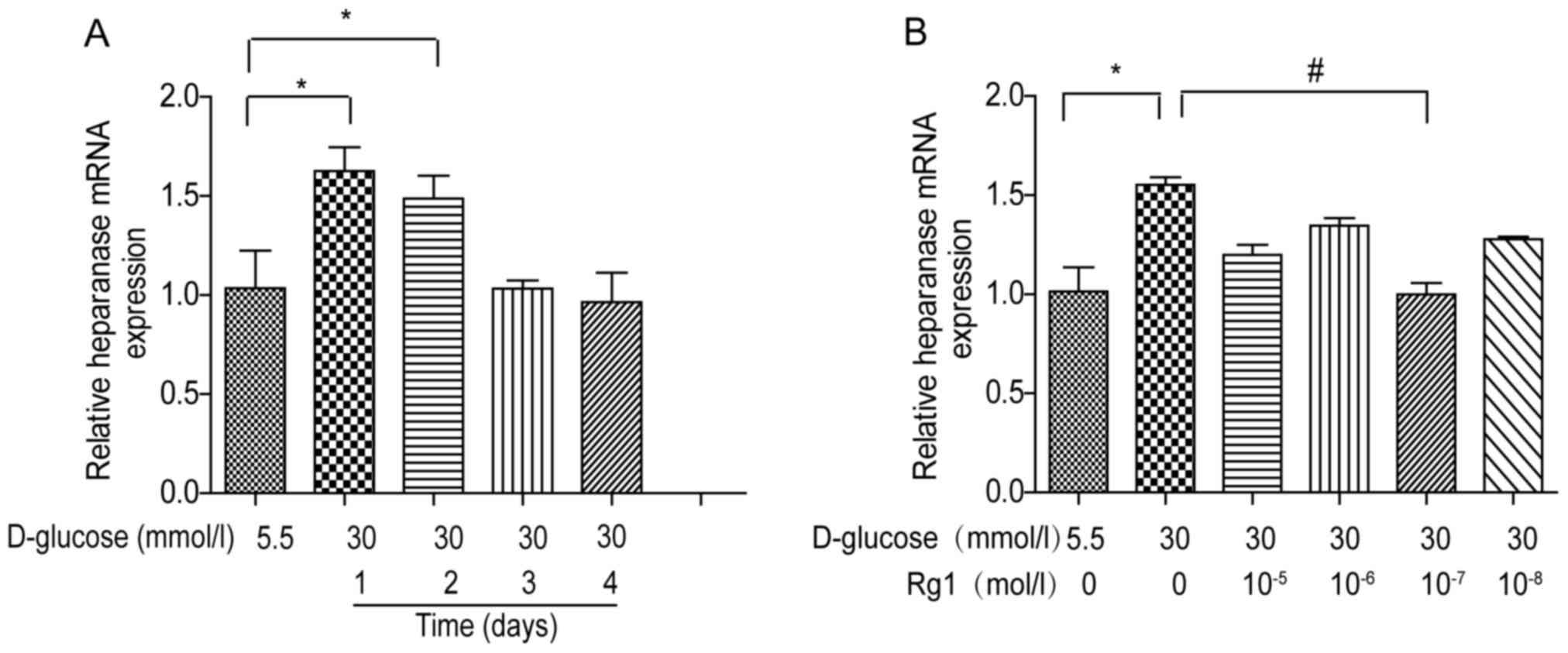
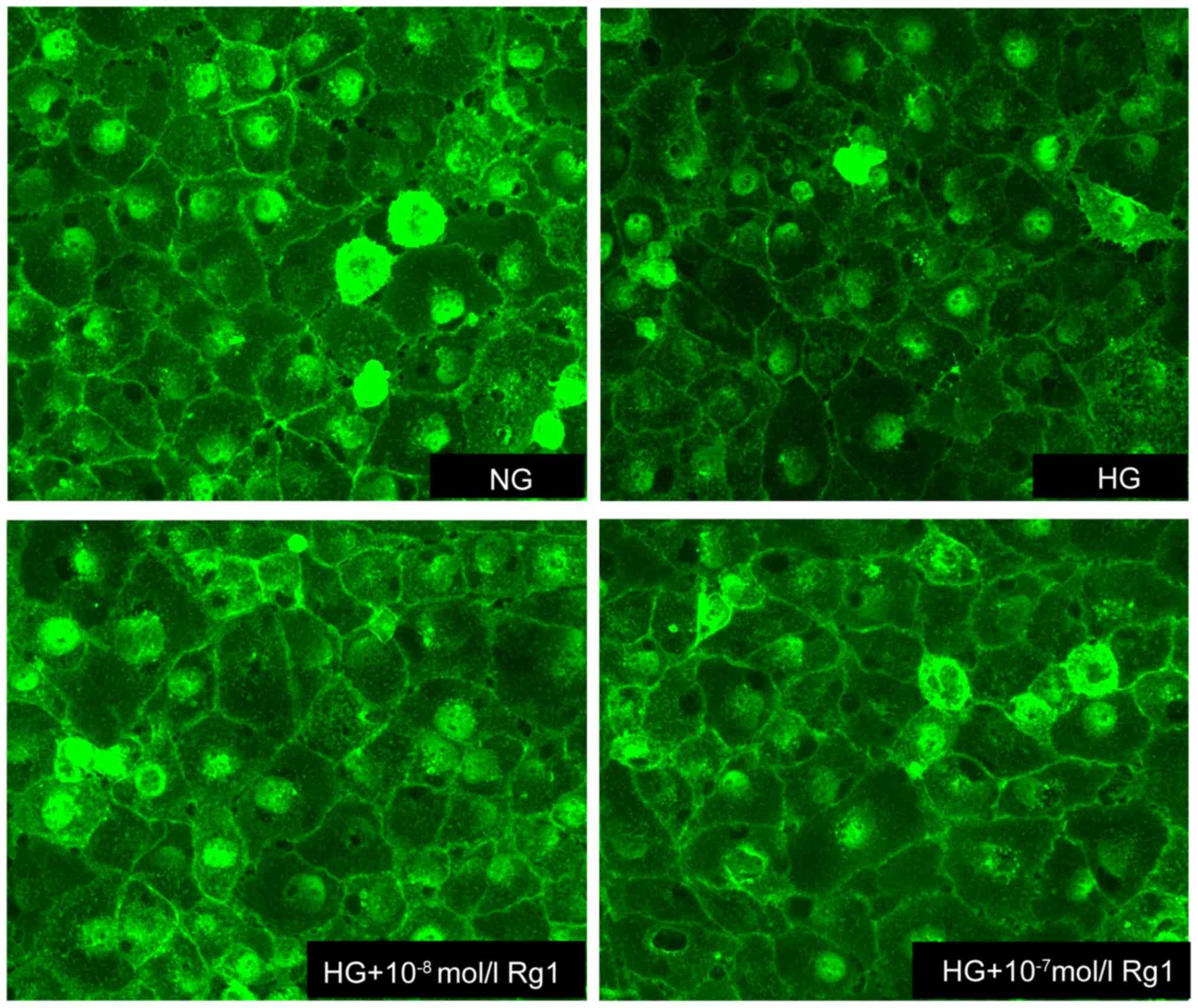
|
1
|
García-Pérez LE, Alvarez M, Dilla T,
Gil-Guillén V and Orozco-Beltrán D: Adherence to therapies in
patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 4:175–194. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shaw JE, Sicree RA and Zimmet PZ: Global
estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes
Res Clin Pract. 87:4–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Potenza MA, Gagliardi S, Nacci C, Carratu'
MR and Montagnani M: Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes: From
mechanisms to therapeutic targets. Curr Med Chem. 16:94–112. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Santi D, Giannetta E, Isidori AM, Vitale
C, Aversa A and Simoni M: Therapy of endocrine disease: Effects of
chronic use of phosphodiesterase inhibitors on endothelial markers
in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Eur J Endocrinol.
172:R103–R114. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bertoluci MC, Cé GV, da Silva AM,
Wainstein MV, Boff W and Punales M: Endothelial dysfunction as a
predictor of cardiovascular disease in type 1 diabetes. World J
Diabetes. 6:679–692. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Widlansky ME, Gokce N, Keaney JF Jr and
Vita JA: The clinical implications of endothelial dysfunction. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 42:1149–1160. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
De Vriese AS, Verbeuren TJ, Van de Voorde
J, Lameire NH and Vanhoutte PM: Endothelial dysfunction in
diabetes. Br J Pharmacol. 130:963–974. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pries AR, Secomb TW and Gaehtgens P: The
endothelial surface layer. Pflugers Arch. 440:653–666. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Reitsma S, Slaaf DW, Vink H, van Zandvoort
MA and oude Egbrink MG: The endothelial glycocalyx: Composition,
functions, and visualization. Pflugers Arch. 454:345–359. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Salmon AH and Satchell SC: Endothelial
glycocalyx dysfunction in disease: Albuminuria and increased
microvascular permeability. J Pathol. 226:562–574. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mulivor AW and Lipowsky HH:
Inflammation-and ischemia-induced shedding of venular glycocalyx.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 286:H1672–H1680. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pearson MJ and Lipowsky HH: Effect of
fibrinogen on leukocyte margination and adhesion in postcapillary
venules. Microcirculation. 11:295–306. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tarbell JM and Pahakis MY:
Mechanotransduction and the glycocalyx. J Intern Med. 259:339–350.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dogné S, Rath G, Jouret F, Caron N, Dessy
C and Flamion B: Hyaluronidase 1 deficiency preserves endothelial
function and glycocalyx integrity in early streptozotocin-induced
diabetes. Diabetes. 65:2742–2753. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nieuwdorp M, Mooij HL, Kroon J, Atasever
B, Spaan JA, Ince C, Holleman F, Diamant M, Heine RJ, Hoekstra JB,
et al: Endothelial glycocalyx damage coincides with
microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 55:1127–1132. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Broekhuizen LN, Lemkes BA, Mooij HL,
Meuwese MC, Verberne H, Holleman F, Schlingemann RO, Nieuwdorp M,
Stroes ES and Vink H: Effect of sulodexide on endothelial
glycocalyx and vascular permeability in patients with type 2
diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 53:2646–2655. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pahwa R, Nallasamy P and Jialal I:
Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 mediate hyperglycemia induced
macrovascular aortic endothelial cell inflammation and perturbation
of the endothelial glycocalyx. J Diabetes Complications.
30:563–572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Singh A, Fridén V, Dasgupta I, Foster RR,
Welsh GI, Tooke JE, Haraldsson B, Mathieson PW and Satchell SC:
High glucose causes dysfunction of the human glomerular endothelial
glycocalyx. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 300:F40–F48. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nassimizadeh M, Ashrafian H, Drury NE,
Howell NJ, Digby J, Pagano D, Frenneaux MP and Born GV: Reduced
negative surface charge on arterial endothelium explains
accelerated atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetic patients. Diab Vasc
Dis Res. 7:213–215. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang X, Xiong X, Wang H and Wang J:
Protective effects of panax notoginseng saponins on
cardiovascular diseases: A comprehensive overview of experimental
studies. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014:2048402014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Uzayisenga R, Ayeka PA and Wang Y:
Anti-diabetic potential of Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS):
A review. Phytother Res. 28:510–516. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ling S, Nheu L, Dai A, Guo Z and
Komesaroff P: Effects of four medicinal herbs on human vascular
endothelial cells in culture. Int J Cardiol. 128:350–358. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lü JM, Yao Q and Chen C: Ginseng
compounds: An update on their molecular mechanisms and medical
applications. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 7:293–302. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu HT, Zhen J, Pang B, Gu JN and Wu SS:
Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates oxidative stress and myocardial
apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Zhejiang Univ
Sci B. 16:344–354. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu H, Zhen J, Yang Y, Gu J, Wu S and Liu
Q: Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy by
inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in a
streptozotocin-induced diabetes rat model. J Cell Mol Med.
20:623–631. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang LN, Xie XS, Zuo C and Fan JM: Effect
of ginsenoside Rgl on the expression of TNF-alpha and MCP-1 in rats
with diabetic nephropathy. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.
40:466–471. 2009.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ma X, Xie X, Zuo C and Fan J: Effects of
ginsenoside Rg1 on streptozocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in
rats. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 27:342–347. 2010.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Singh A, Satchell SC, Neal CR, McKenzie
EA, Tooke JE and Mathieson PW: Glomerular endothelial glycocalyx
constitutes a barrier to protein permeability. J Am Soc Nephrol.
18:2885–2893. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang W, Xu Q, Wu J, Zhou X, Weng J, Xu J,
Wang W, Huang Q and Guo X: Role of src in vascular
hyperpermeability induced by advanced glycation end products. Sci
Rep. 5:140902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Garsen M, Sonneveld R, Rops AL, Huntink S,
van Kuppevelt TH, Rabelink TJ, Hoenderop JG, Berden JH, Nijenhuis T
and van der Vlag J: Vitamin D attenuates proteinuria by inhibition
of heparanase expression in the podocyte. J Pathol. 237:472–481.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xu C, Wu X, Hack BK, Bao L and Cunningham
PN: TNF causes changes in glomerular endothelial permeability and
morphology through a Rho and myosin light chain kinase-dependent
mechanism. Physiol Rep. 3:e126362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Haraldsson B and Nyström J: The glomerular
endothelium: New insights on function and structure. Curr Opin
Nephrol Hypertens. 21:258–263. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fridén V, Oveland E, Tenstad O, Ebefors K,
Nyström J, Nilsson UA and Haraldsson B: The glomerular endothelial
cell coat is essential for glomerular filtration. Kidney Int.
79:1322–1330. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Salmon AH, Ferguson JK, Burford JL,
Gevorgyan H, Nakano D, Harper SJ, Bates DO and Peti-Peterdi J: Loss
of the endothelial glycocalyx links albuminuria and vascular
dysfunction. J Am Soc Nephrol. 23:1339–1350. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rabelink TJ, de Boer HC and van Zonneveld
AJ: Endothelial activation and circulating markers of endothelial
activation in kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 6:404–414. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gil N, Goldberg R, Neuman T, Garsen M,
Zcharia E, Rubinstein AM, van Kuppevelt T, Meirovitz A, Pisano C,
Li JP, et al: Heparanase is essential for the development of
diabetic nephropathy in mice. Diabetes. 61:208–216. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
van den Hoven MJ, Rops AL, Bakker MA, Aten
J, Rutjes N, Roestenberg P, Goldschmeding R, Zcharia E, Vlodavsky
I, van der Vlag J and Berden JH: Increased expression of heparanase
in overt diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 70:2100–2108. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Garsen M, Lenoir O, Rops AL, Dijkman HB,
Willemsen B, van Kuppevelt TH, Rabelink TJ, Berden JH, Tharaux PL
and van der Vlag J: Endothelin-1 induces proteinuria by
heparanase-mediated disruption of the glomerular glycocalyx. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 27:3545–3551. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Goligorsky MS: Vascular endothelium in
diabetes. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 312:F266–F275. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sieve I, Münster-Kühnel AK and
Hilfiker-Kleiner D: Regulation and function of endothelial
glycocalyx layer in vascular diseases. Vascul Pharmacol. 100:26–33.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|