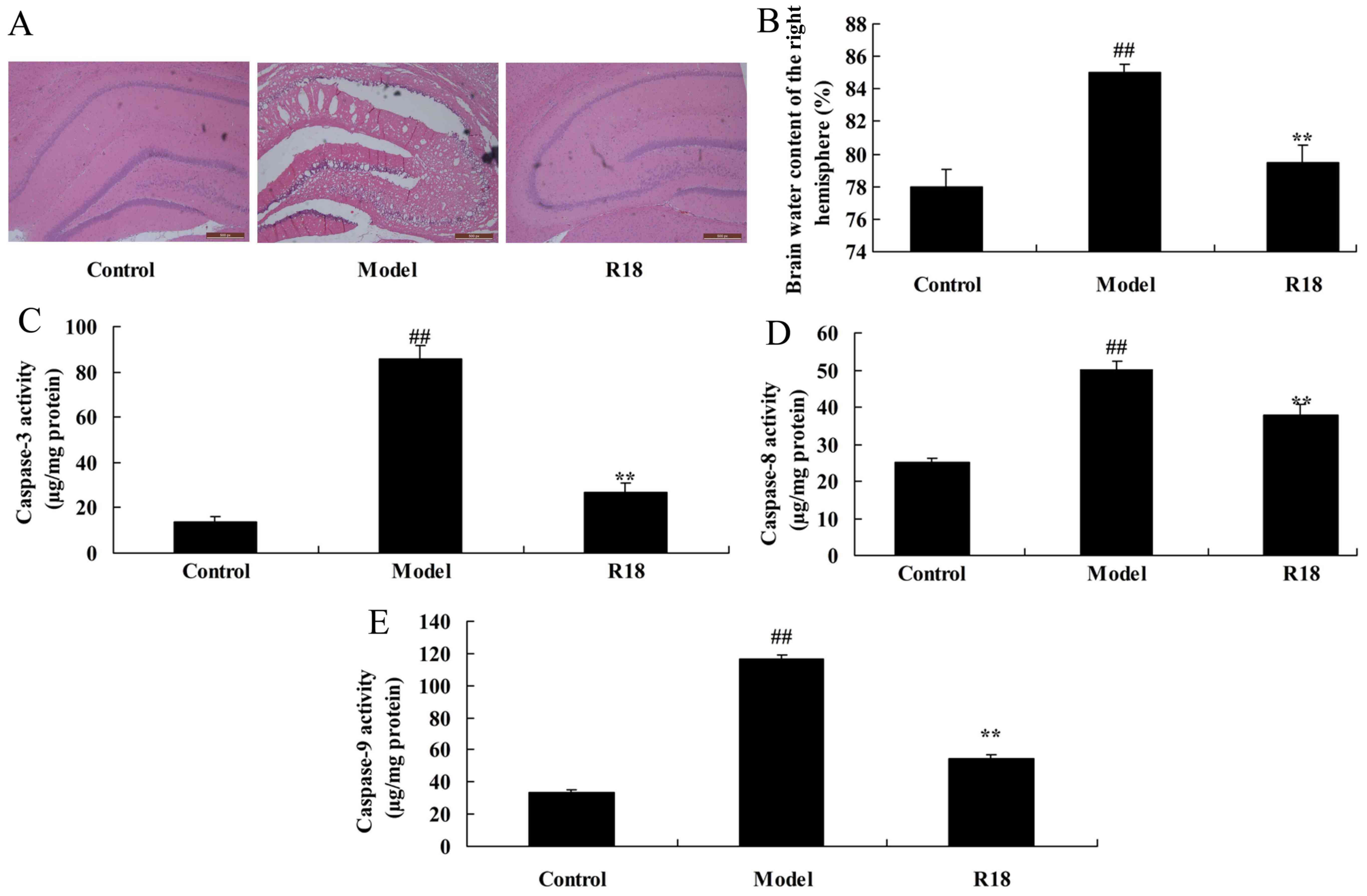
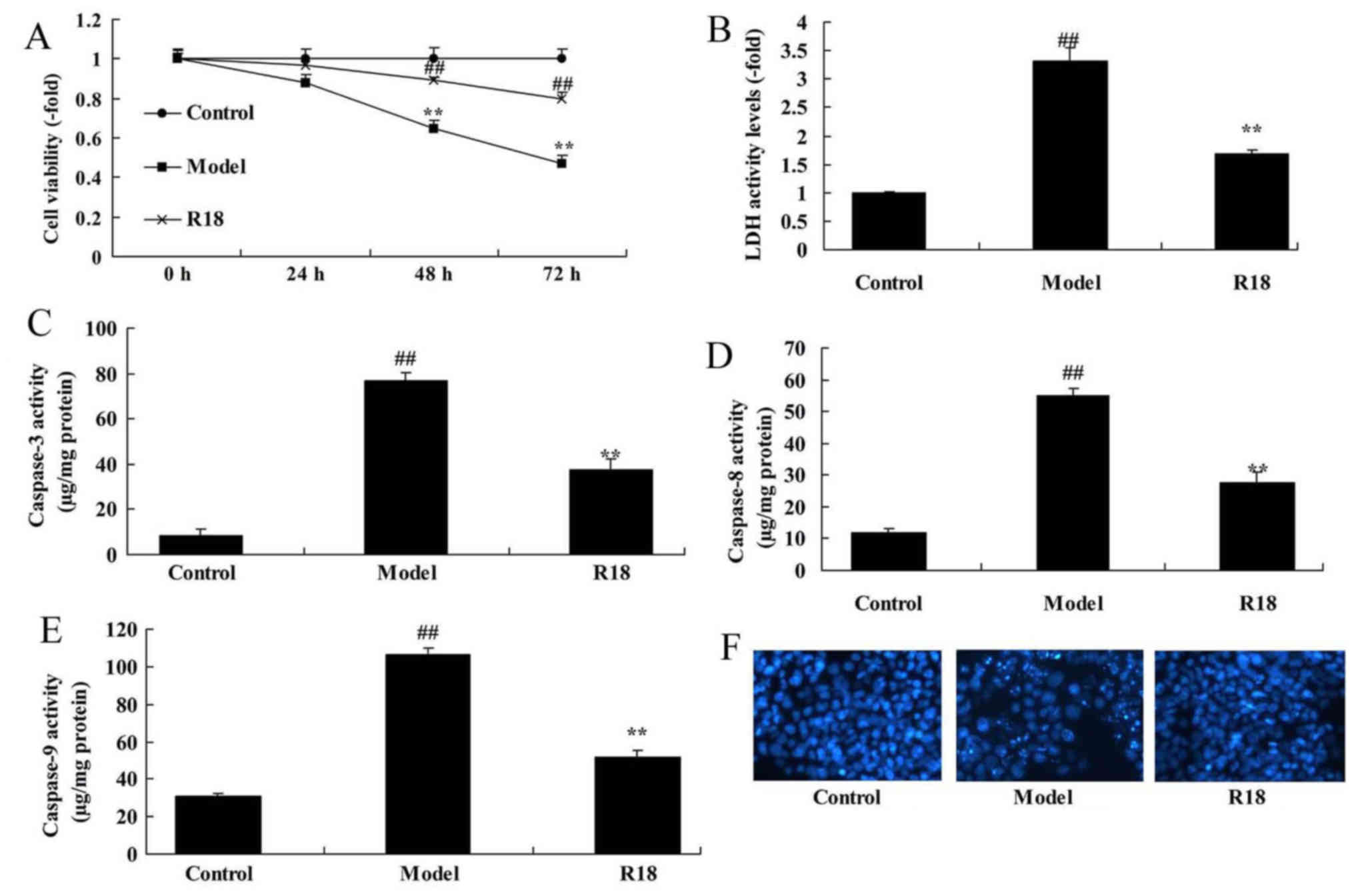
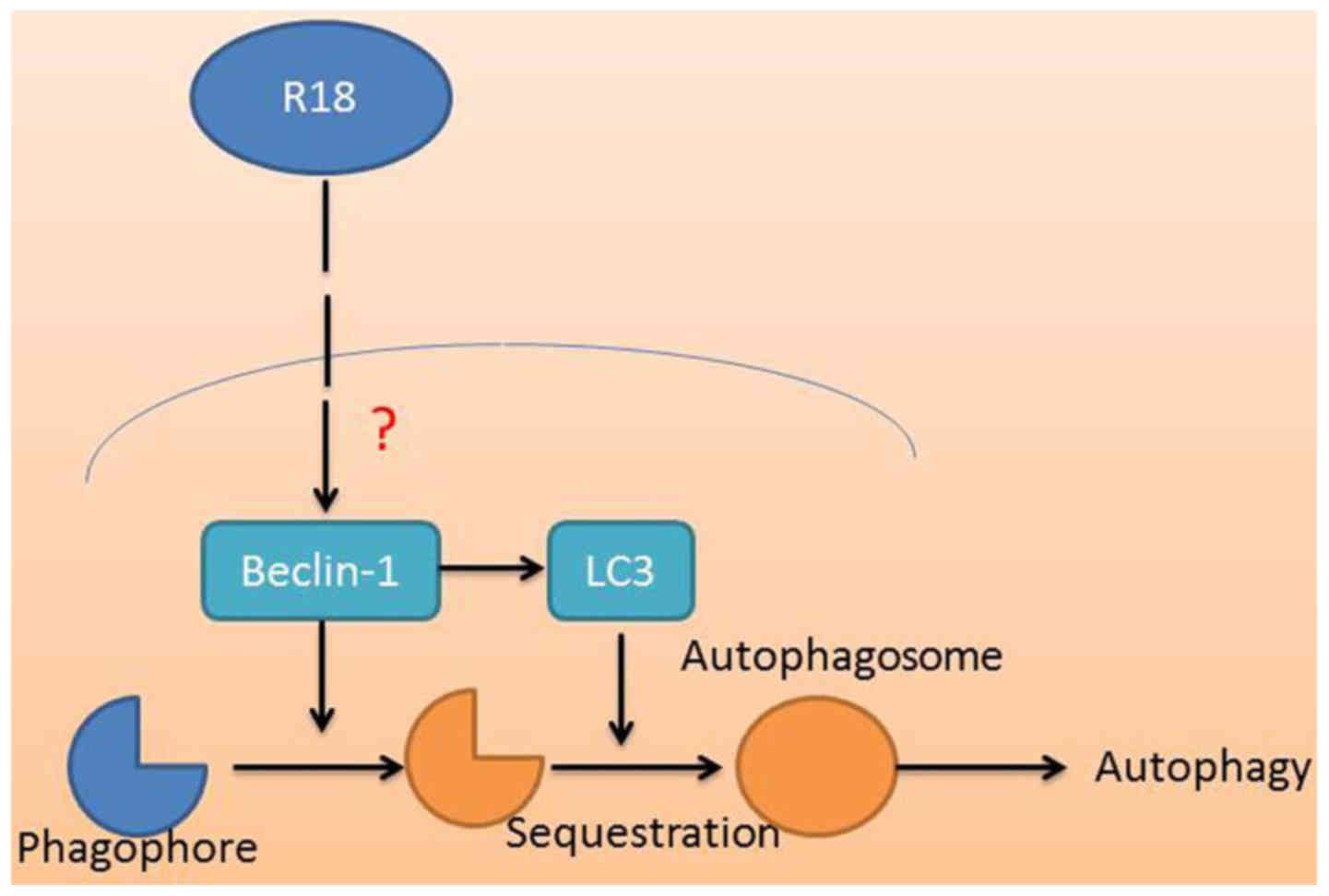
|
1
|
Yang Z, Lin F, Robertson CS and Wang KK:
Dual vulnerability of TDP-43 to calpain and caspase-3 proteolysis
after neurotoxic conditions and traumatic brain injury. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 34:1444–1452. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Okonkwo DO, Shutter LA, Moore C, Temkin
NR, Puccio AM, Madden CJ, Andaluz N, Chesnut RM, Bullock MR, Grant
GA, et al: Brain oxygen optimization in severe traumatic brain
injury Phase-II: A Phase II randomized trial. Crit Care Med.
45:1907–1914. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grima NA, Rajaratnam SMW, Mansfield D,
Sletten TL, Spitz G and Ponsford JL: Efficacy of melatonin for
sleep disturbance following traumatic brain injury: A randomised
controlled trial. BMC Med. 16:82018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun L, Zhao M, Wang Y, Liu A, Lv M, Li Y,
Yang X and Wu Z: Neuroprotective effects of miR-27a against
traumatic brain injury via suppressing FoxO3a-mediated neuronal
autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 482:1141–1147. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zeng XJ, Li P, Ning YL, Zhao Y, Peng Y,
Yang N, Zhao ZA, Chen JF and Zhou YG: Impaired autophagic flux is
associated with the severity of trauma and the role of
A2AR in brain cells after traumatic brain injury. Cell
Death Dis. 9:2522018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen X, Wang H, Zhou M, Li X, Fang Z, Gao
H, Li Y and Hu W: Valproic acid attenuates traumatic brain
injury-induced inflammation in vivo: Involvement of autophagy and
the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Front Mol Neurosci. 11:1172018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Milani D, Knuckey NW, Anderton RS, Cross
JL and Meloni BP: The R18 polyarginine peptide is more effective
than the TAT-NR2B9c (NA-1) peptide when administered 60 minutes
after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Stroke
Res Treat. 2016:23727102016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cui C, Cui J, Jin F, Cui Y, Li R, Jiang X,
Tian Y, Wang K, Jiang P and Gao J: Induction of the Vitamin D
receptor attenuates autophagy dysfunction-mediated cell death
following traumatic brain injury. Cell Physiol Biochem.
42:1888–1896. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Milani D, Bakeberg MC, Cross JL, Clark VW,
Anderton RS, Blacker DJ, Knuckey NW and Meloni BP: Comparison of
neuroprotective efficacy of poly-arginine R18 and R18D
(D-enantiomer) peptides following permanent middle cerebral artery
occlusion in the Wistar rat and in vitro toxicity studies. PLoS
One. 13:e01938842018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Blaha RZ, Arnett AB, Kirkwood MW, Taylor
HG, Stancin T, Brown TM and Wade SL: Factors influencing attrition
in a multisite, randomized, clinical trial following traumatic
brain injury in adolescence. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 30:E33–E40.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hammond FM, Alexander DN, Cutler AJ,
D'Amico S, Doody RS, Sauve W, Zorowitz RD, Davis CS, Shin P, Ledon
F, et al: PRISM II: An open-label study to assess effectiveness of
dextromethorphan/quinidine for pseudobulbar affect in patients with
dementia, stroke or traumatic brain injury. BMC Neurol. 16:892016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Beca J, McSharry B, Erickson S, Yung M,
Schibler A, Slater A, Wilkins B, Singhal A, Williams G, Sherring C,
et al: Hypothermia for traumatic brain injury in children-a phase
II randomized controlled trial. Crit Care Med. 43:1458–1466. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Renaud MI, Lambregts SA, de Kloet AJ,
Catsman-Berrevoets CE, van de Port IG and van Heugten CM:
Activities and participation of children and adolescents after mild
traumatic brain injury and the effectiveness of an early
intervention (Brains Ahead!): Study protocol for a cohort study
with a nested randomised controlled trial. Trials. 17:2362016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chiu LS, Anderton RS, Cross JL, Clark VW,
Edwards AB, Knuckey NW and Meloni BP: Assessment of R18, COG1410,
and APP96-110 in excitotoxicity and traumatic brain injury. Transl
Neurosci. 8:147–157. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wolf MS, Bayir H, Kochanek PM and Clark
RSB: The role of autophagy in acute brain injury: A state of flux?
Neurobiol Dis. 122:9–15. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun LQ, Gao JL, Cui Y, Zhao MM, Jing XB,
Li R, Tian YX, Cui JZ and Wu ZX: Neuronic autophagy contributes to
p-connexin 43 degradation in hippocampal astrocytes following
traumatic brain injury in rats. Mol Med Rep. 11:4419–4423. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jin Y, Lin Y, Feng JF, Jia F, Gao G and
Jiang JY: Attenuation of cell death in injured cortex after
post-traumatic brain injury moderate hypothermia: Possible
involvement of autophagy pathway. World Neurosurg. 84:420–430.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cordaro M, Impellizzeri D, Paterniti I,
Bruschetta G, Siracusa R, De Stefano D, Cuzzocrea S and Esposito E:
Neuroprotective effects of Co-UltraPEALut on secondary inflammatory
process and autophagy involved in traumatic brain injury. J
Neurotrauma. 33:132–146. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|