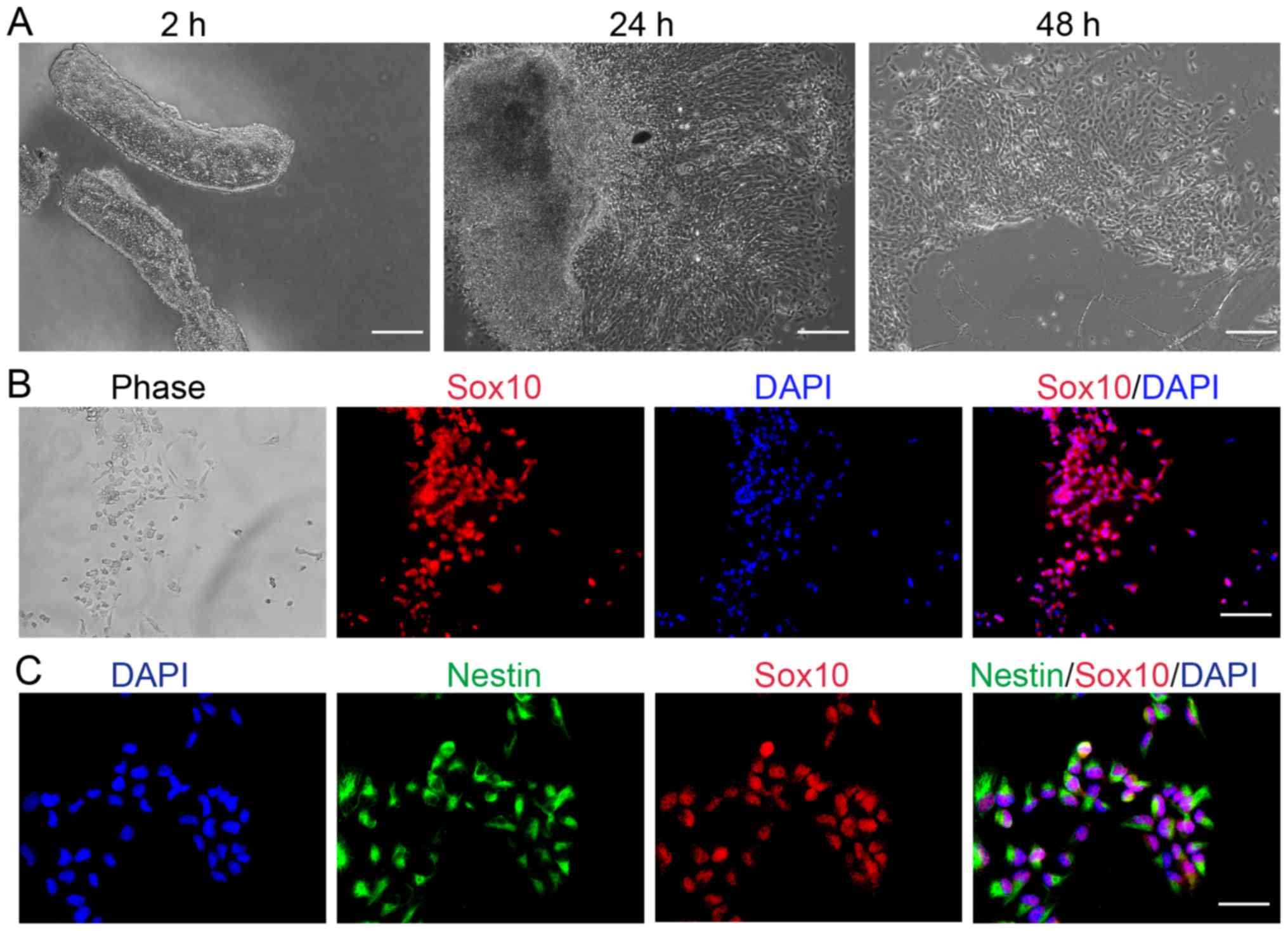
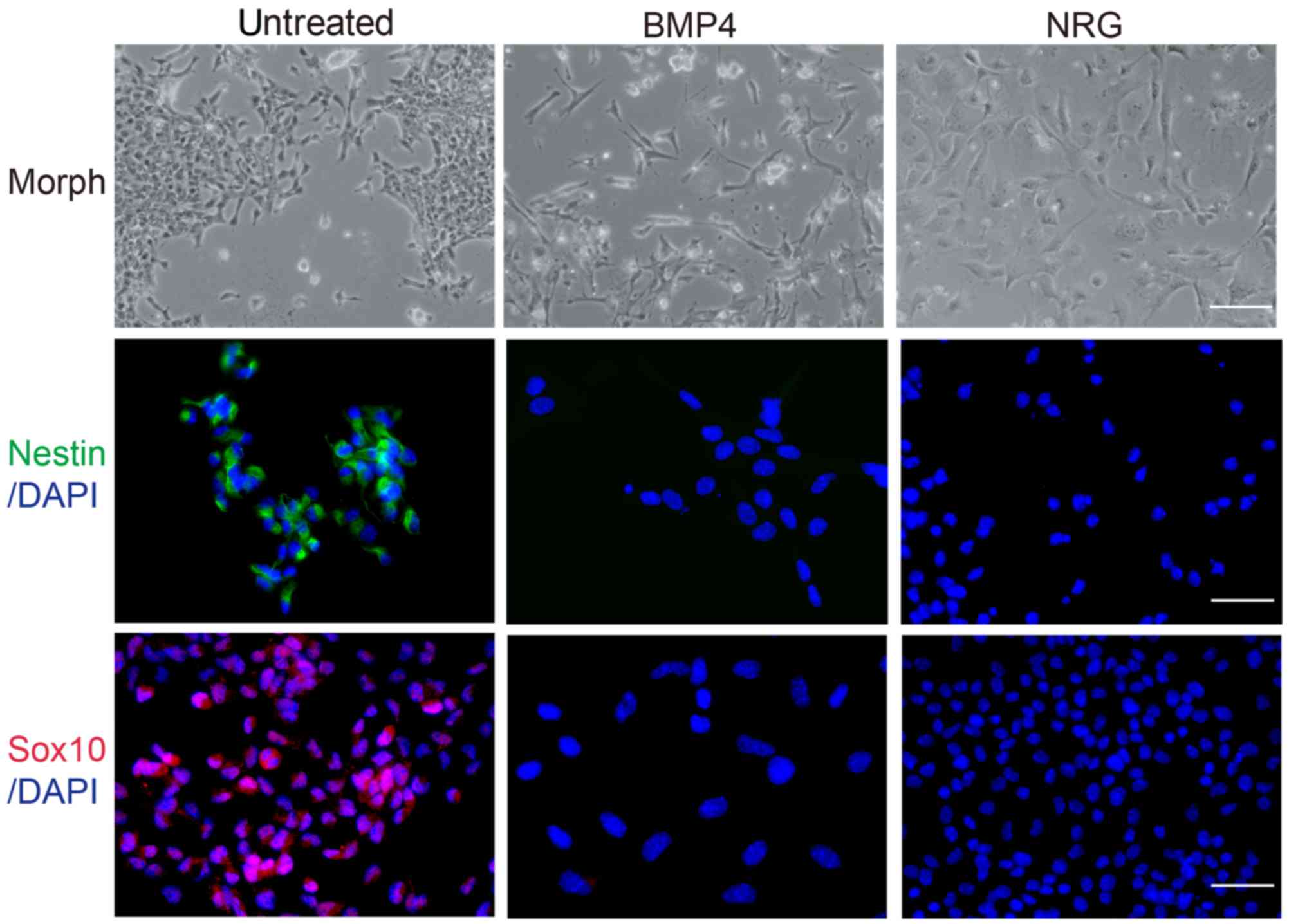
|
1
|
Gonzalez Malagon SG, Lopez Munoz AM, Doro
D, Bolger TG, Poon E, Tucker ER, Adel Al-Lami H, Krause M, Phiel
CJ, Chesler L and Liu KJ: Glycogen synthase kinase 3 controls
migration of the neural crest lineage in mouse and Xenopus. Nat
Commun. 9:11262018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang T, Moore M and He F: Pten regulates
neural crest proliferation and differentiation during mouse
craniofacial development. Dev Dyn. 247:304–314. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang J, Duan X, Zhang H, Deng Z, Zhou Z,
Wen N, Smith AJ, Zhao W and Jin Y: Isolation of neural
crest-derived stem cells from rat embryonic mandibular processes.
Biol Cell. 98:567–575. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yoshida S, Shimmura S, Nagoshi N, Fukuda
K, Matsuzaki Y, Okano H and Tsubota K: Isolation of multipotent
neural crest-derived stem cells from the adult mouse cornea. Stem
Cells. 24:2714–2722. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Morrison SJ, White PM, Zock C and Anderson
DJ: Prospective identification, isolation by flow cytometry, and in
vivo self-renewal of multipotent mammalian neural crest stem cells.
Cell. 96:737–749. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang X, Gwye Y, McKeown SJ,
Bronner-Fraser M, Lutzko C and Lawlor ER: Isolation and
characterization of neural crest stem cells derived from in
vitro-differentiated human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev.
18:1059–1070. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chung KF, Sicard F, Vukicevic V, Hermann
A, Storch A, Huttner WB, Bornstein SR and Ehrhart-Bornstein M:
Isolation of neural crest derived chromaffin progenitors from adult
adrenal medulla. Stem Cells. 27:2602–2613. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lumb R and Schwarz Q: Sympathoadrenal
neural crest cells: The known, unknown and forgotten? Dev Growth
Differ. 57:146–157. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sauka-Spengler T and Bronner-Fraser M: A
gene regulatory network orchestrates neural crest formation. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:557–568. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Joseph NM, Mukouyama YS, Mosher JT, Jaegle
M, Crone SA, Dormand EL, Lee KF, Meijer D, Anderson DJ and Morrison
SJ: Neural crest stem cells undergo multilineage differentiation in
developing peripheral nerves to generate endoneurial fibroblasts in
addition to Schwann cells. Development. 131:5599–5612. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wakamatsu Y, Maynard TM and Weston JA:
Fate determination of neural crest cells by NOTCH-mediated lateral
inhibition and asymmetrical cell division during gangliogenesis.
Development. 127:2811–2821. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Steventon B, Araya C, Linker C, Kuriyama S
and Mayor R: Differential requirements of BMP and Wnt signalling
during gastrulation and neurulation define two steps in neural
crest induction. Development. 136:771–779. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sykaras N and Opperman LA: Bone
morphogenetic proteins (BMPs): How do they function and what can
they offer the clinician. J Oral Sci. 45:57–73. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sykaras N and Opperman LA: Bone
morphogenetic proteins (BMPs): How do they function and what can
they offer the clinician? J Oral Sci. 45:57–73. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ripamonti U and Reddi AH: Tissue
engineering, morphogenesis, and regeneration of the periodontal
tissues by bone morphogenetic proteins. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med.
8:154–163. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Paralkar VM, Weeks BS, Yu YM, Kleinman HK
and Reddi AH: Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2B
stimulates PC12 cell differentiation: Potentiation and binding to
type IV collagen. J Cell Biol. 119:1721–1728. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shah NM, Groves AK and Anderson DJ:
Alternative neural crest cell fates are instructively promoted by
TGFbeta superfamily members. Cell. 85:331–343. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stottmann RW and Klingensmith J: Bone
morphogenetic protein signaling is required in the dorsal neural
folds before neurulation for the induction of spinal neural crest
cells and dorsal neurons. Dev Dyn. 240:755–765. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Raabe TD, Francis A and DeVries GH:
Neuregulins in glial cells. Neurochem Res. 23:311–318. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wen D, Peles E, Cupples R, Suggs SV, Bacus
SS, Luo Y, Trail G, Hu S, Silbiger SM, Levy RB, et al: Neu
differentiation factor: A transmembrane glycoprotein containing an
EGF domain and an immunoglobulin homology unit. Cell. 69:559–572.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Marchionni MA, Goodearl AD, Chen MS,
Bermingham-McDonogh O, Kirk C, Hendricks M, Danehy F, Misumi D,
Sudhalter J, Kobayashi K, et al: Glial growth factors are
alternatively spliced erbB2 ligands expressed in the nervous
system. Nature. 362:312–318. 1993. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Carraway KL III and Cantley LC: A neu
acquaintance for erbB3 and erbB4: A role for receptor
heterodimerization in growth signaling. Cell. 78:5–8. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Meyer D and Birchmeier C: Multiple
essential functions of neuregulin in development. Nature.
378:386–390. 1995. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Garratt AN, Britsch S and Birchmeier C:
Neuregulin, a factor with many functions in the life of a schwann
cell. Bioessays. 22:987–996. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jessen KR and Mirsky R: Origin and early
development of Schwann cells. Microsc Res Tech. 41:393–402. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jessen KR and Mirsky R: Schwann cells and
their precursors emerge as major regulators of nerve development.
Trends Neurosci. 22:402–410. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Freeman MR: Sculpting the nervous system:
Glial control of neuronal development. Curr Opin Neurobiol.
16:119–125. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mirsky R, Jessen KR, Brennan A, Parkinson
D, Dong Z, Meier C, Parmantier E and Lawson D: Schwann cells as
regulators of nerve development. J Physiol Paris. 96:17–24. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Falls DL: Neuregulins: Functions, forms,
and signaling strategies. Exp Cell Res. 284:14–30. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li L, Habbes HW, Eiberger J, Willecke K,
Dermietzel R and Meier C: Analysis of connexin expression during
mouse Schwann cell development: Connexin29 as a novel marker for
the transition of neural crest to precursor cells. Glia. 55:93–103.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Aquino JB, Hjerling-Leffler J, Koltzenburg
M, Edlund T, Villar MJ and Ernfors P: In vitro and in vivo
differentiation of boundary cap neural crest stem cells into mature
Schwann cells. Exp Neurol. 198:438–449. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Buchstaller J, Sommer L, Bodmer M,
Hoffmann R, Suter U and Mantei N: Efficient isolation and gene
expression profiling of small numbers of neural crest stem cells
and developing Schwann cells. J Neurosci. 24:2357–2365. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Laurenti E, Varnum-Finney B, Wilson A,
Ferrero I, Blanco-Bose WE, Ehninger A, Knoepfler PS, Cheng PF,
MacDonald HR, Eisenman RN, et al: Hematopoietic stem cell function
and survival depend on c-Myc and N-Myc activity. Cell Stem Cell.
3:611–624. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Crane JF and Trainor PA: Neural crest stem
and progenitor cells. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 22:267–286. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang M and Weiss WA: Neuroblastoma and
MYCN. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 3:a0144152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Alam G, Cui H, Shi H, Yang L, Ding J, Mao
L, Maltese WA and Ding HF: MYCN promotes the expansion of
Phox2B-positive neuronal progenitors to drive neuroblastoma
development. Am J Pathol. 175:856–866. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mao L, Ding J, Perdue A, Yang L, Zha Y,
Ren M, Huang S, Cui H and Ding HF: Cyclin E1 is a common target of
BMI1 and MYCN and a prognostic marker for neuroblastoma
progression. Oncogene. 31:3785–3795. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brodeur GM: Neuroblastoma: Biological
insights into a clinical enigma. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:203–216. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Martinewski A, Correia CS, de Souza NL and
Merusse JL: Mouse housing system using pressurized cages
intraventilated by direct-current microfans. J Am Assoc Lab Anim
Sci. 51:177–180. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Itahana K, Zou Y, Itahana Y, Martinez JL,
Beausejour C, Jacobs JJ, Van Lohuizen M, Band V, Campisi J and
Dimri GP: Control of the replicative life span of human fibroblasts
by p16 and the polycomb protein Bmi-1. Mol Cell Biol. 23:389–401.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cui H, Schroering A and Ding HF: p53
mediates DNA damaging drug-induced apoptosis through a
caspase-9-dependent pathway in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 1:679–686. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lo L, Dormand E, Greenwood A and Anderson
DJ: Comparison of the generic neuronal differentiation and neuron
subtype specification functions of mammalian achaete-scute and
atonal homologs in cultured neural progenitor cells. Development.
129:1553–1567. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Greenwood AL, Turner EE and Anderson DJ:
Identification of dividing, determined sensory neuron precursors in
the mammalian neural crest. Development. 126:3545–3559.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kelsh RN: Sorting out Sox10 functions in
neural crest development. Bioessays. 28:788–798. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kawaguchi J, Nichols J, Gierl MS, Faial T
and Smith A: Isolation and propagation of enteric neural crest
progenitor cells from mouse embryonic stem cells and embryos.
Development. 137:693–704. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Selander L and Edlund H: Nestin is
expressed in mesenchymal and not epithelial cells of the developing
mouse pancreas. Mech Dev. 113:189–212. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lendahl U, Zimmerman LB and McKay RD: CNS
stem cells express a new class of intermediate filament protein.
Cell. 60:585–595. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lee H, Mok KH, Muhandiram R, Park KH, Suk
JE, Kim DH, Chang J, Sung YC, Choi KY and Han KH: Local structural
elements in the mostly unstructured transcriptional activation
domain of human p53. J Biol Chem. 275:29426–29432. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Trainor PA: Specification of neural crest
cell formation and migration in mouse embryos. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
16:683–693. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sugimoto T, Kato T, Sawada T, Horii Y,
Kemshead JT, Hino T, Morioka H and Hosoi H: Schwannian cell
differentiation of human neuroblastoma cell lines in vitro induced
by bromodeoxyuridine. Cancer Res. 48:2531–2537. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ross RA, Spengler BA, Domenech C, Porubcin
M, Rettig WJ and Biedler JL: Human neuroblastoma I-type cells are
malignant neural crest stem cells. Cell Growth Differ. 6:449–456.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lee S, Lee B, Lee JW and Lee SK: Retinoid
signaling and neurogenin2 function are coupled for the
specification of spinal motor neurons through a chromatin modifier
CBP. Neuron. 62:641–654. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jessen KR and Mirsky R: The origin and
development of glial cells in peripheral nerves. Nat Rev Neurosci.
6:671–682. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bhatt S, Diaz R and Trainor PA: Signals
and switches in Mammalian neural crest cell differentiation. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5(pii): a0083262013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Blasky AJ, Pan L, Moens CB and Appel B:
Pard3 regulates contact between neural crest cells and the timing
of Schwann cell differentiation but is not essential for neural
crest migration or myelination. Dev Dyn. 243:1511–1523. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ren YJ, Zhang S, Mi R, Liu Q, Zeng X, Rao
M, Hoke A and Mao HQ: Enhanced differentiation of human neural
crest stem cells towards the Schwann cell lineage by aligned
electrospun fiber matrix. Acta Biomater. 9:7727–7736. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Xi J, Wu Y, Li G, Ma L, Feng K, Guo X, Jia
W, Wang G, Yang G, Li P and Kang J: Mir-29b mediates the neural
tube versus neural crest fate decision during embryonic stem cell
neural differentiation. Stem Cell Reports. 9:571–586. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Makoolati Z, Movahedin M and
Forouzandeh-Moghadam M: In vitro germ cell differentiation from
embryonic stem cells of mice: Induction control by BMP4 signaling.
Biosci Rep. 36:e004072016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yang S, Yuan Q, Niu M, Hou J, Zhu Z, Sun
M, Li Z and He Z: BMP4 promotes mouse iPS cell differentiation to
male germ cells via Smad1/5, Gata4, Id1 and Id2. Reproduction.
153:211–220. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mamo TM, Wittern AB, Kleppa MJ, Bohnenpoll
T, Weiss AC and Kispert A: BMP4 uses several different effector
pathways to regulate proliferation and differentiation in the
epithelial and mesenchymal tissue compartments of the developing
mouse ureter. Hum Mol Genet. 26:3553–3563. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Peng T, Zhu G, Dong Y, Zeng J, Li W, Guo
W, Chen Y, Duan M, Hocher B and Xie D: BMP4: A possible key factor
in differentiation of auditory neuron-like cells from bone-derived
mesenchymal stromal cells. Clin Lab. 61:1171–1178. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Britsch S, Li L, Kirchhoff S, Theuring F,
Brinkmann V, Birchmeier C and Riethmacher D: The ErbB2 and ErbB3
receptors and their ligand, neuregulin-1, are essential for
development of the sympathetic nervous system. Genes Dev.
12:1825–1836. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Milet C and Monsoro-Burq AH: Neural crest
induction at the neural plate border in vertebrates. Dev Biol.
366:22–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Borowicz S, Van Scoyk M, Avasarala S,
Karuppusamy Rathinam MK, Tauler J, Bikkavilli RK and Winn RA: The
soft agar colony formation assay. J Vis Exp. 92:e519982014.
|
|
65
|
Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman
J and van Bree C: Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc.
1:2315–2319. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Hamburger AW and Salmon SE: Primary
bioassay of human tumor stem cells. Science. 197:461–463. 1977.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Cui H, Ma J, Ding J, Li T, Alam G and Ding
HF: Bmi-1 regulates the differentiation and clonogenic self-renewal
of I-type neuroblastoma cells in a concentration-dependent manner.
J Biol Chem. 281:34696–34704. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Reynolds BA and Weiss S: Generation of
neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian
central nervous system. Science. 255:1707–1710. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhang JT, Weng ZH, Tsang KS, Tsang LL,
Chan HC and Jiang XH: MycN is critical for the maintenance of human
embryonic stem cell-derived neural crest stem cells. PLoS One.
11:e01480622016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ke XX, Zhang D, Zhao H, Hu R, Dong Z, Yang
R, Zhu S, Xia Q, Ding HF and Cui H: Phox2B correlates with MYCN and
is a prognostic marker for neuroblastoma development. Oncol Lett.
9:2507–2514. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Newman EA, Chukkapalli S, Bashllari D,
Thomas TT, Van Noord RA, Lawlor ER, Hoenerhoff MJ, Opipari AW and
Opipari VP: Alternative NHEJ pathway proteins as components of MYCN
oncogenic activity in human neural crest stem cell differentiation:
Implications for neuroblastoma initiation. Cell Death Dis.
8:32082017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Althoff K, Beckers A, Bell E, Nortmeyer M,
Thor T, Sprüssel A, Lindner S, De Preter K, Florin A, Heukamp LC,
et al: A Cre-conditional MYCN-driven neuroblastoma mouse model as
an improved tool for preclinical studies. Oncogene. 34:3357–3368.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ferlemann FC, Menon V, Condurat AL, Rößler
J and Pruszak J: Surface marker profiling of SH-SY5Y cells enables
small molecule screens identifying BMP4 as a modulator of
neuroblastoma differentiation. Sci Rep. 7:136122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Schlitter AM, Dorneburg C, Barth TF, Wahl
J, Schulte JH, Brüderlein S, Debatin KM and Beltinger C: CD57(high)
neuroblastoma cells have aggressive attributes ex situ and an
undifferentiated phenotype in Patients. PLoS One. 7:e420252012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|