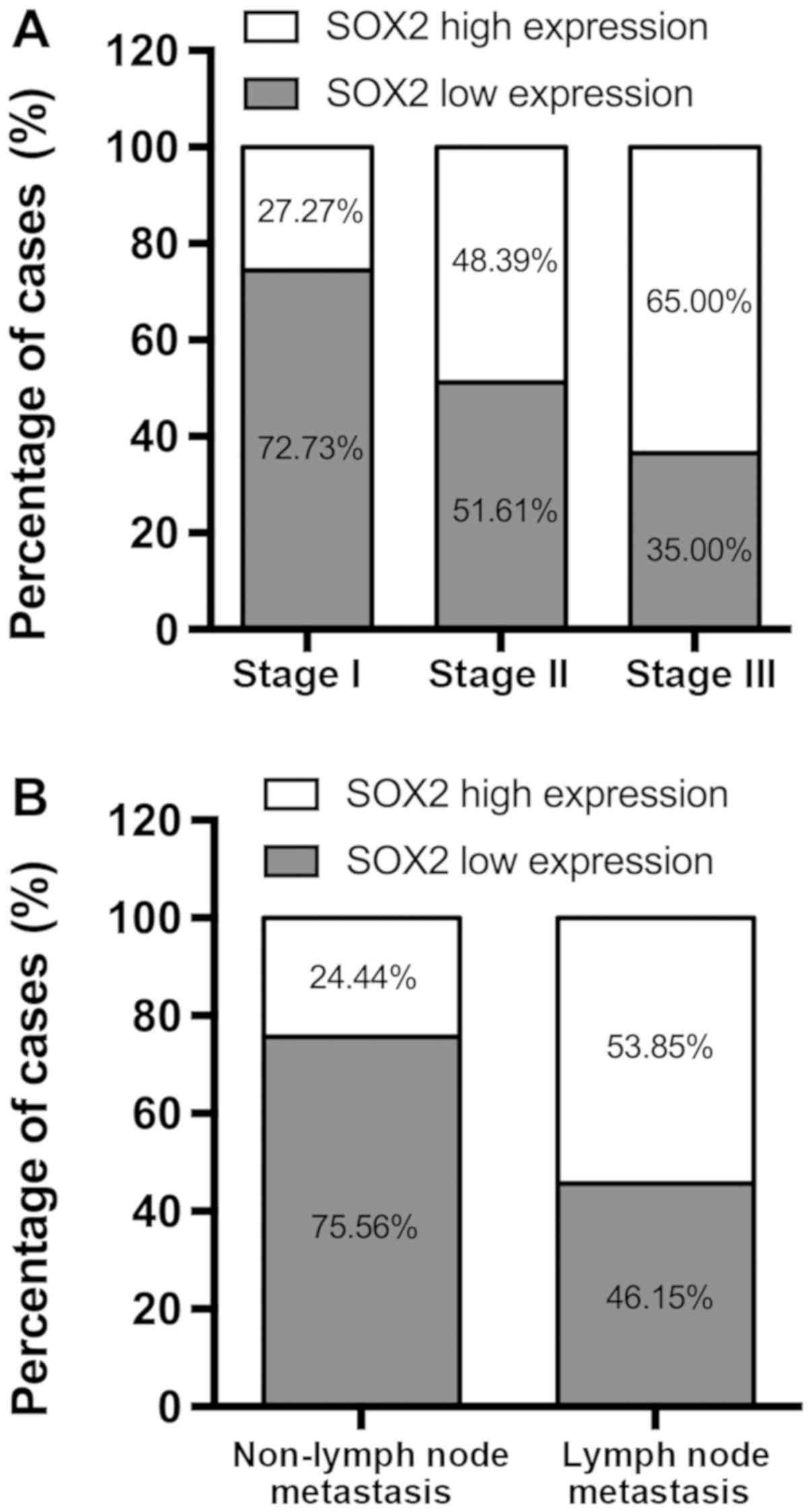
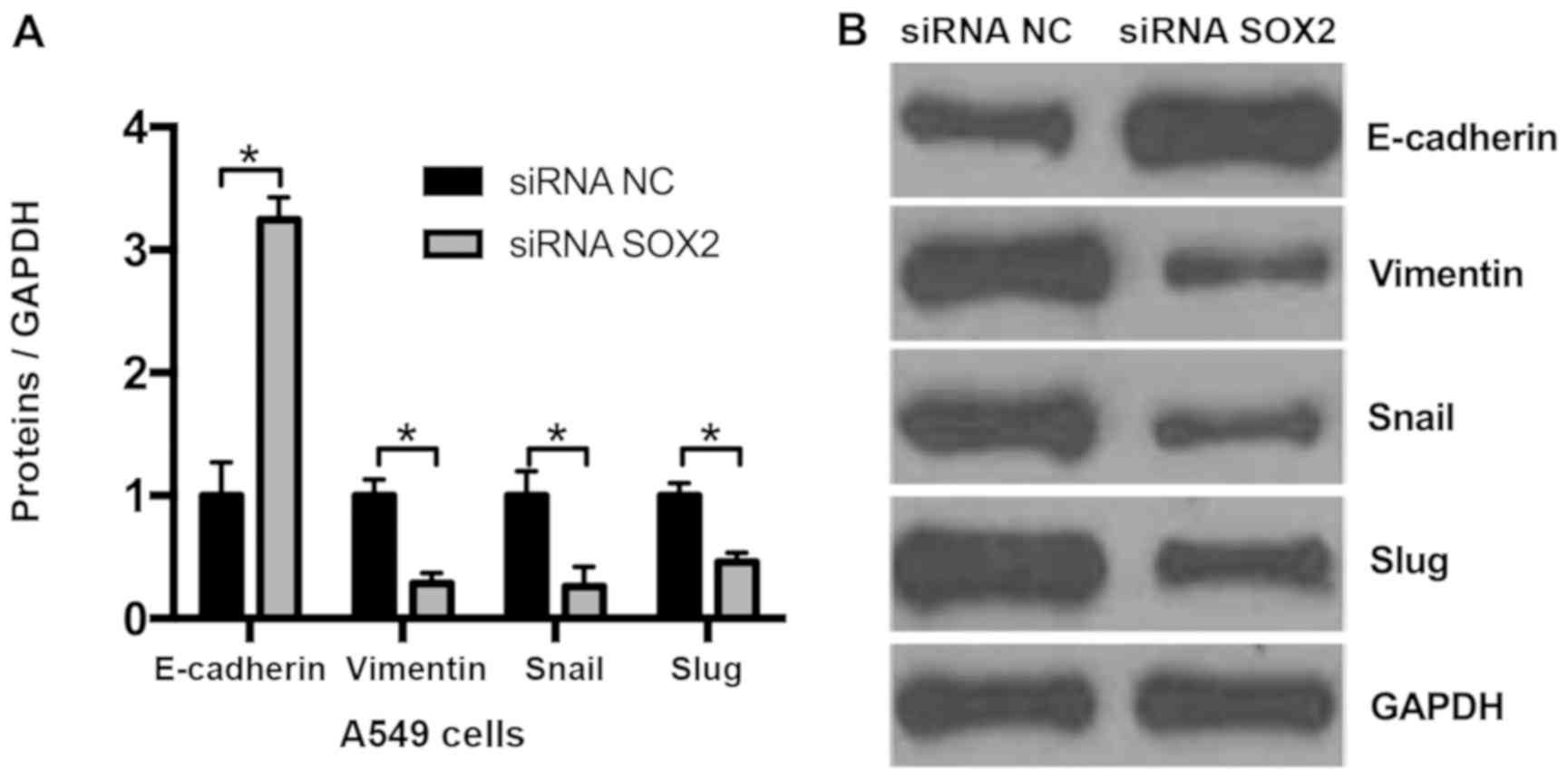
|
1
|
Sarkar A and Hochedlinger K: The sox
family of transcription factors: Versatile regulators of stem and
progenitor cell fate. Cell Stem Cell. 12:15–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schepers GE, Teasdale RD and Koopman P:
Twenty pairs of sox: Extent, homology, and nomenclature of the
mouse and human sox transcription factor gene families. Dev Cell.
3:167–170. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stevanovic M, Zuffardi O, Collignon J,
Lovell-Badge R and Goodfellow P: The cDNA sequence and chromosomal
location of the human SOX2 gene. Mamm Genome. 5:640–642. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Collignon J, Sockanathan S, Hacker A,
Cohen-Tannoudji M, Norris D, Rastan S, Stevanovic M, Goodfellow PN
and Lovell-Badge R: A comparison of the properties of Sox-3 with
Sry and two related genes, Sox-1 and Sox-2. Development.
122:509–520. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lengerke C, Fehm T, Kurth R, Neubauer H,
Scheble V, Müller F, Schneider F, Petersen K, Wallwiener D, Kanz L,
et al: Expression of the embryonic stem cell marker SOX2 in
early-stage breast carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 11:422011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Boumahdi S, Driessens G, Lapouge G, Rorive
S, Nassar D, Le Mercier M, Delatte B, Caauwe A, Lenglez S, Nkusi E,
et al: SOX2 controls tumour initiation and cancer stem-cell
functions in squamous-cell carcinoma. Nature. 511:246–250. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xie C, Han Y, Liu Y, Han L and Liu J:
miRNA-124 down-regulates SOX8 expression and suppresses cell
proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:6534–6542. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Toschi L, Finocchiaro G, Nguyen TT, Skokan
MC, Giordano L, Gianoncelli L, Perrino M, Siracusano L, Di Tommaso
L, Infante M, et al: Increased SOX2 gene copy number is associated
with FGFR1 and PIK3CA gene gain in non-small cell lung cancer and
predicts improved survival in early stage disease. PLoS One.
9:e953032014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang FF, Wang S, Xue WH and Cheng JL:
microRNA-590 suppresses the tumorigenesis and invasiveness of
non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting ADAM9. Mol Cell
Biochem. 423:29–37. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou L, Zhao LC, Jiang N, Wang XL, Zhou
XN, Luo XL and Ren J: MicroRNA miR-590-5p inhibits breast cancer
cell stemness and metastasis by targeting SOX2. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 21:87–94. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American Joint
Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gen Y, Yasui K, Nishikawa T and Yoshikawa
T: SOX2 promotes tumor growth of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
through the AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 signaling
pathway. Cancer Sci. 104:810–816. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun C, Sun L, Li Y, Kang X, Zhang S and
Liu Y: Sox2 expression predicts poor survival of hepatocellular
carcinoma patients and it promotes liver cancer cell invasion by
activating Slug. Med Oncol. 30:5032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen S, Li X, Lu D, Xu Y, Mou W, Wang L,
Chen Y, Liu Y, Li X, Li LY, et al: SOX2 regulates apoptosis through
MAP4K4-survivin signaling pathway in human lung cancer cells.
Carcinogenesis. 35:613–623. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chou YT, Lee CC, Hsiao SH, Lin SE, Lin SC,
Chung CH, Chung CH, Kao YR, Wang YH, Chen CT, et al: The emerging
role of SOX2 in cell proliferation and survival and its crosstalk
with oncogenic signaling in lung cancer. Stem Cells. 31:2607–2619.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stewart DJ: Wnt signaling pathway in
non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 106:djt3562014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li X, Xu Y, Chen Y, Chen S, Jia X, Sun T,
Liu Y, Li X, Xiang R and Li N: SOX2 promotes tumor metastasis by
stimulating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via regulation of
WNT/β-catenin signal network. Cancer Lett. 336:379–389. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yuan XW, Wang DM, Hu Y, Tang YN, Shi WW,
Guo XJ and Song JG: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 suppresses the
migration and invasive growth of lung cancer cells through p53 and
the inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem.
288:31206–31216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kitamura K, Seike M, Okano T, Matsuda K,
Miyanaga A, Mizutani H, Noro R, Minegishi Y, Kubota K and Gemma A:
MiR-134/487b/655 cluster regulates TGF-β-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and drug resistance to gefitinib
by targeting MAGI2 in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
13:444–453. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chu Y, Ouyang Y, Wang F, Zheng A, Bai L,
Han L, Chen Y and Wang H: MicroRNA-590 promotes cervical cancer
cell growth and invasion by targeting CHL1. J Cell Biochem.
115:847–853. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pang H, Zheng Y, Zhao Y, Xiu X and Wang J:
miR-590-3p suppresses cancer cell migration, invasion and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma multiforme by
targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 468:739–745.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|