|
1
|
Cui LH, Xu HR, Yang W and Yu LJ: lncRNA
PCAT6 promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation,
migration and invasion through regulating miR-330-5p. Onco Targets
Ther. 11:7715–7724. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li J and Wei L: Increased expression of
LINC01510 predicts poor prognosis and promotes malignant
progression in human non-small cell lung cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 109:519–529. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
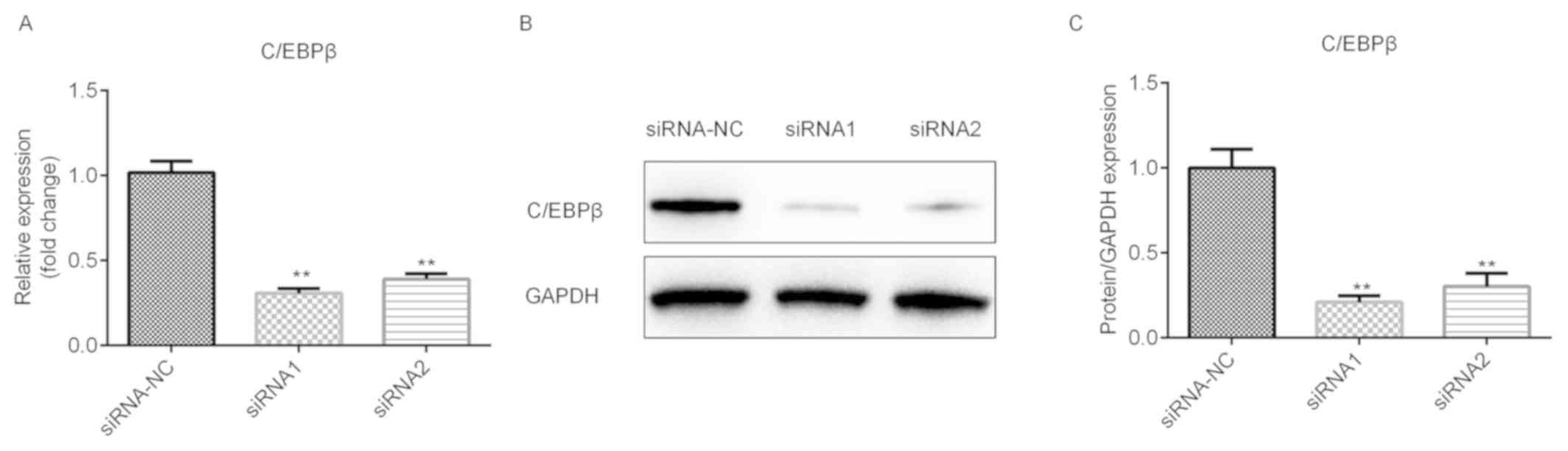
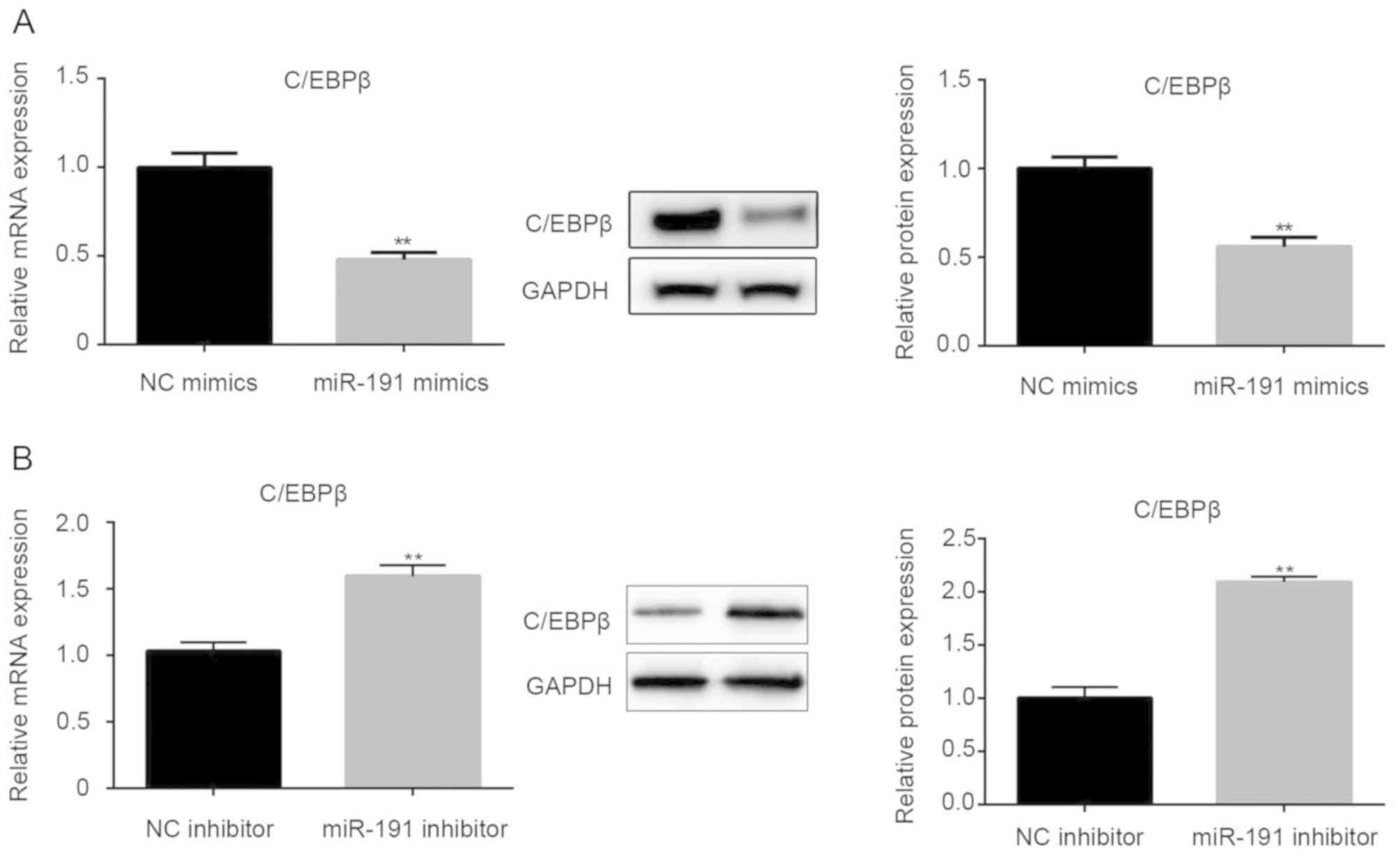
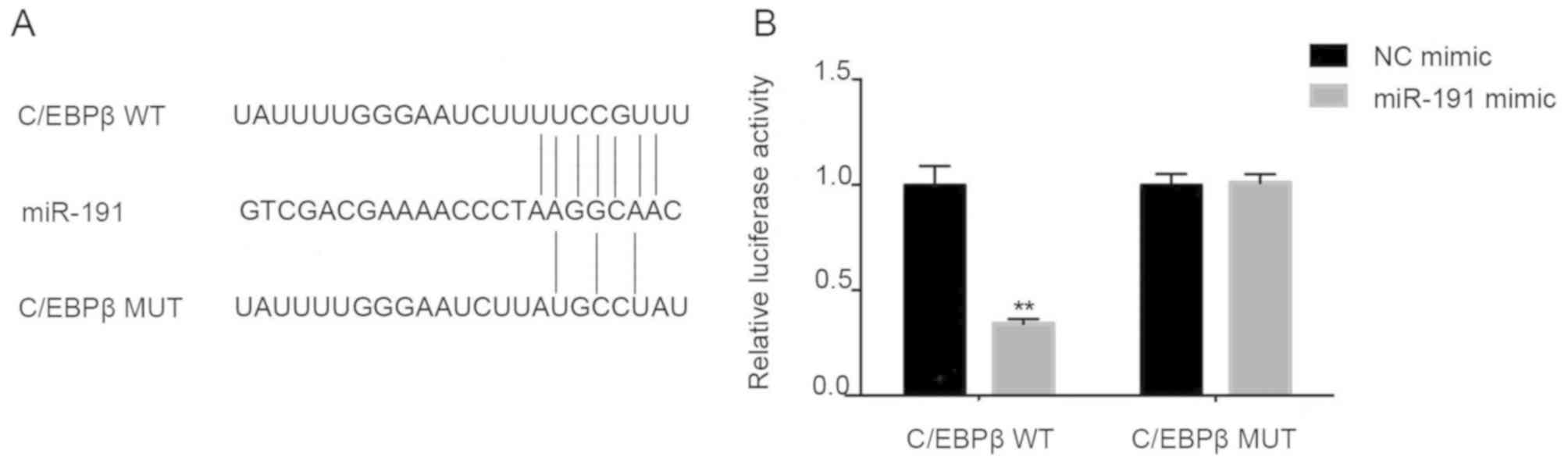
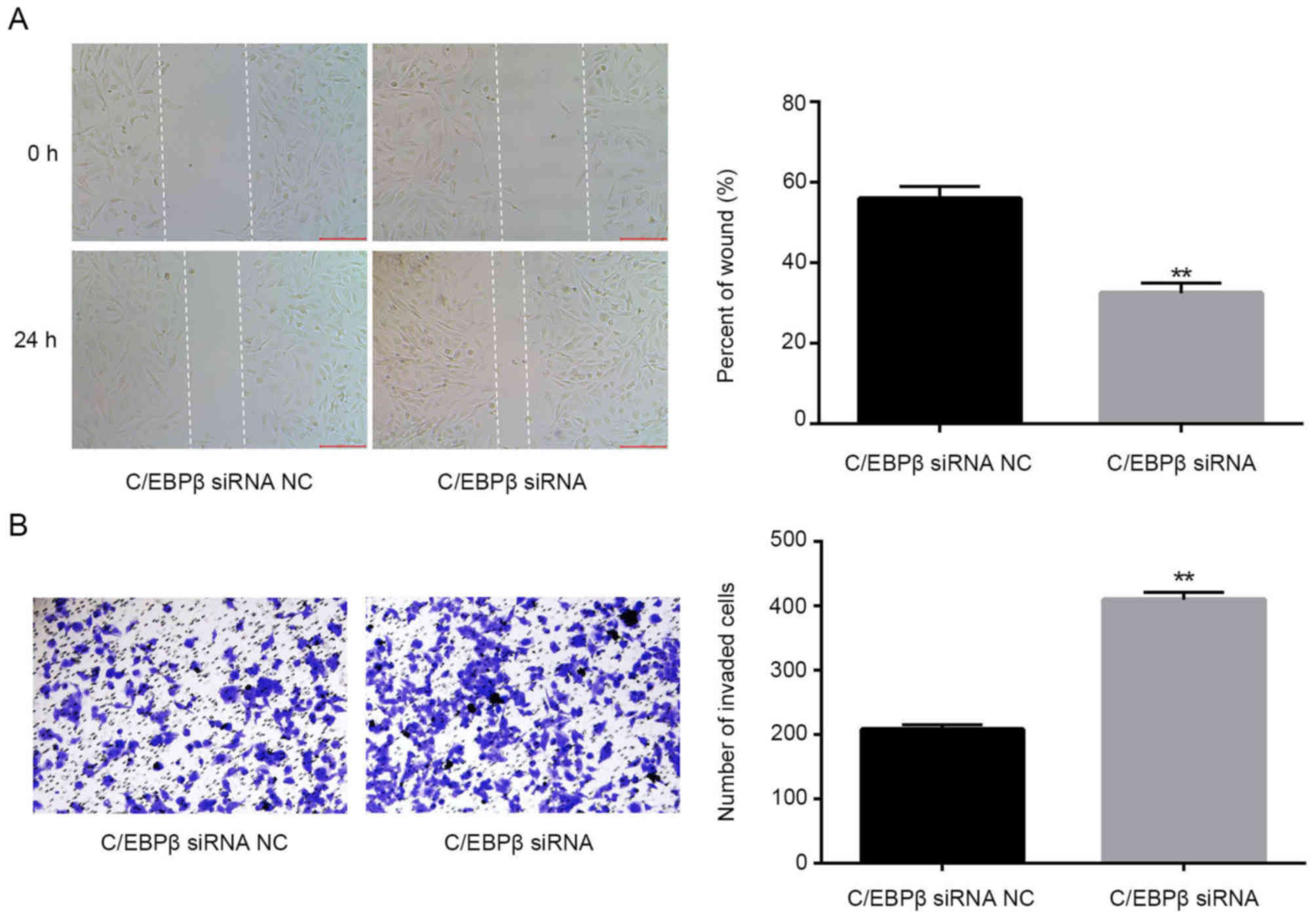
Wang B, Lv K, Chen W, Zhao J, Luo J, Wu J,
Li Z, Qin H, Wong TS, Yang W, et al: miR-375 and miR-205 regulate
the invasion and migration of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
synergistically via AKT-mediated EMT. Biomed Res Int.
2016:96527892016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lages E, Ipas H, Guttin A, Nesr H, Berger
F and Issartel JP: MicroRNAs: Molecular features and role in
cancer. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 17:2508–2540. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nagpal N, Ahmad HM, Molparia B and
Kulshreshtha R: MicroRNA-191, an estrogen-responsive microRNA,
functions as an oncogenic regulator in human breast cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 34:1889–1899. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shi X, Su S, Long J, Mei B and Chen Y:
MicroRNA-191 targets N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 1 and
promotes cell growth in human gastric carcinoma cell line MGC803.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 43:849–856. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu H, Xu XF, Zhao Y, Tang MC, Zhou YQ, Lu
J and Gao FH: MicroRNA-191 promotes pancreatic cancer progression
by targeting USP10. Tumour Biol. 35:12157–12163. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Elyakim E, Sitbon E, Faerman A, Tabak S,
Montia E, Belanis L, Dov A, Marcusson EG, Bennett CF, Chajut A, et
al: hsa-miR-191 is a candidate oncogene target for hepatocellular
carcinoma therapy. Cancer Res. 70:8077–8087. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qin S, Zhu Y, Ai F, Li Y, Bai B, Yao W and
Dong L: MicroRNA-191 correlates with poor prognosis of colorectal
carcinoma and plays multiple roles by targeting tissue inhibitor of
metalloprotease 3. Neoplasma. 61:27–34. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li H, Zhou ZQ, Yang ZR, Tong DN, Guan J,
Shi BJ, Nie J, Ding XT, Li B, Zhou GW and Zhang ZY: MicroRNA-191
acts as a tumor promoter by modulating the TET1-p53 pathway in
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 66:136–151. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cruz-Munoz W and Khokha R: The role of
tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in tumorigenesis and
metastasis. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 45:291–338. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Robinson GW, Johnson PF, Hennighausen L
and Sterneck E: The C/EBPbeta transcription factor regulates
epithelial cell proliferation and differentiation in the mammary
gland. Genes Dev. 12:1907–1916. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Seagroves TN, Krnacik S, Raught B, Gay J,
Burgess-Beusse B, Darlington GJ and Rosen JM: C/EBPbeta, but not
C/EBPalpha, is essential for ductal morphogenesis, lobuloalveolar
proliferation, and functional differentiation in the mouse mammary
gland. Genes Dev. 12:1917–1928. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Smink JJ, Bégay V, Schoenmaker T, Sterneck
E, de Vries TJ and Leutz A: Transcription factor C/EBPbeta isoform
ratio regulates osteoclastogenesis through MafB. EMBO J.
28:1769–1781. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wethmar K, Bégay V, Smink JJ, Zaragoza K,
Wiesenthal V, Dörken B, Calkhoven CF and Leutz A:
C/EBPbetaDeltauORF mice-a genetic model for uORF-mediated
translational control in mammals. Genes Dev. 24:15–20. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang XF, Li KK, Gao L, Li SZ, Chen K,
Zhang JB, Wang D, Tu RF, Zhang JX, Tao KX, et al: miR-191 promotes
tumorigenesis of human colorectal cancer through targeting C/EBPβ.
Oncotarget. 6:4144–4158. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sundfeldt K, Ivarsson K, Carlsson M,
Enerbäck S, Janson PO, Brännström M and Hedin L: The expression of
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) in the human ovary in vivo:
Specific increase in C/EBPbeta during epithelial tumour
progression. Br J Cancer. 79:1240–1248. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Barakat DJ, Zhang J, Barberi T, Denmeade
SR, Friedman AD and Paz-Priel I: CCAAT/Enhancer binding protein β
controls androgen-deprivation-induced senescence in prostate cancer
cells. Oncogene. 34:5912–5922. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Aguilar-Morante D, Morales-Garcia JA,
Santos A and Perez-Castillo A: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β
induces motility and invasion of glioblastoma cells through
transcriptional regulation of the calcium binding protein S100A4.
Oncotarget. 6:4369–4384. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gomis RR, Alarcón C, Nadal C, Van Poznak C
and Massagué J: C/EBPbeta at the core of the TGFbeta cytostatic
response and its evasion in metastatic breast cancer cells. Cancer
Cell. 10:203–214. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park BH, Kook S, Lee S, Jeong JH, Brufsky
A and Lee BC: An isoform of C/EBPβ, LIP, regulates expression of
the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and modulates breast cancer cell
migration. J Biol Chem. 288:28656–28667. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fang T, Cui M, Sun J, Ge C, Zhao F, Zhang
L, Tian H, Zhang L, Chen T, Jiang G, et al: Orosomucoid 2 inhibits
tumor metastasis and is upregulated by CCAAT/enhancer binding
protein β in hepatocellular carcinomas. Oncotarget. 6:16106–16119.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin SS, Peng CY, Liao YW, Chou MY, Hsieh
PL and Yu CC: miR-1246 targets CCNG2 to enhance cancer stemness and
chemoresistance in oral carcinomas. Cancers (Basel). 10(pii):
E2722018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen M, Wu L, Tu J, Zhao Z, Fan X, Mao J,
Weng Q, Wu X, Huang L, Xu M and Ji J: miR-590-5p suppresses
hepatocellular carcinoma chemoresistance by targeting YAP1
expression. EBioMedicine. 35:142–154. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Anand S, Ebner J, Warren CB, Raam MS,
Piliang M, Billings SD and Maytin EV: C/EBP transcription factors
in human squamous cell carcinoma: Selective changes in expression
of isoforms correlate with the neoplastic state. PLoS One.
9:e1120732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang X, Du T, Wang X, Zhang Y, Hu W, Du X,
Miao L and Han C: IDH1, a CHOP and C/EBPβ-responsive gene under ER
stress, sensitizes human melanoma cells to hypoxia-induced
apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 365:201–210. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yan Y, Hanse EA, Stedman K, Benson JM,
Lowman XH, Subramanian S and Kelekar A: Transcription factor
C/EBP-β induces tumor-suppressor phosphatase PHLPP2 through
repression of the miR-17-92 cluster in differentiating AML cells.
Cell Death Differ. 23:1232–1242. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|